2005 SUZUKI JIMNY inflation pressure
[x] Cancel search: inflation pressurePage 44 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION 0B-13
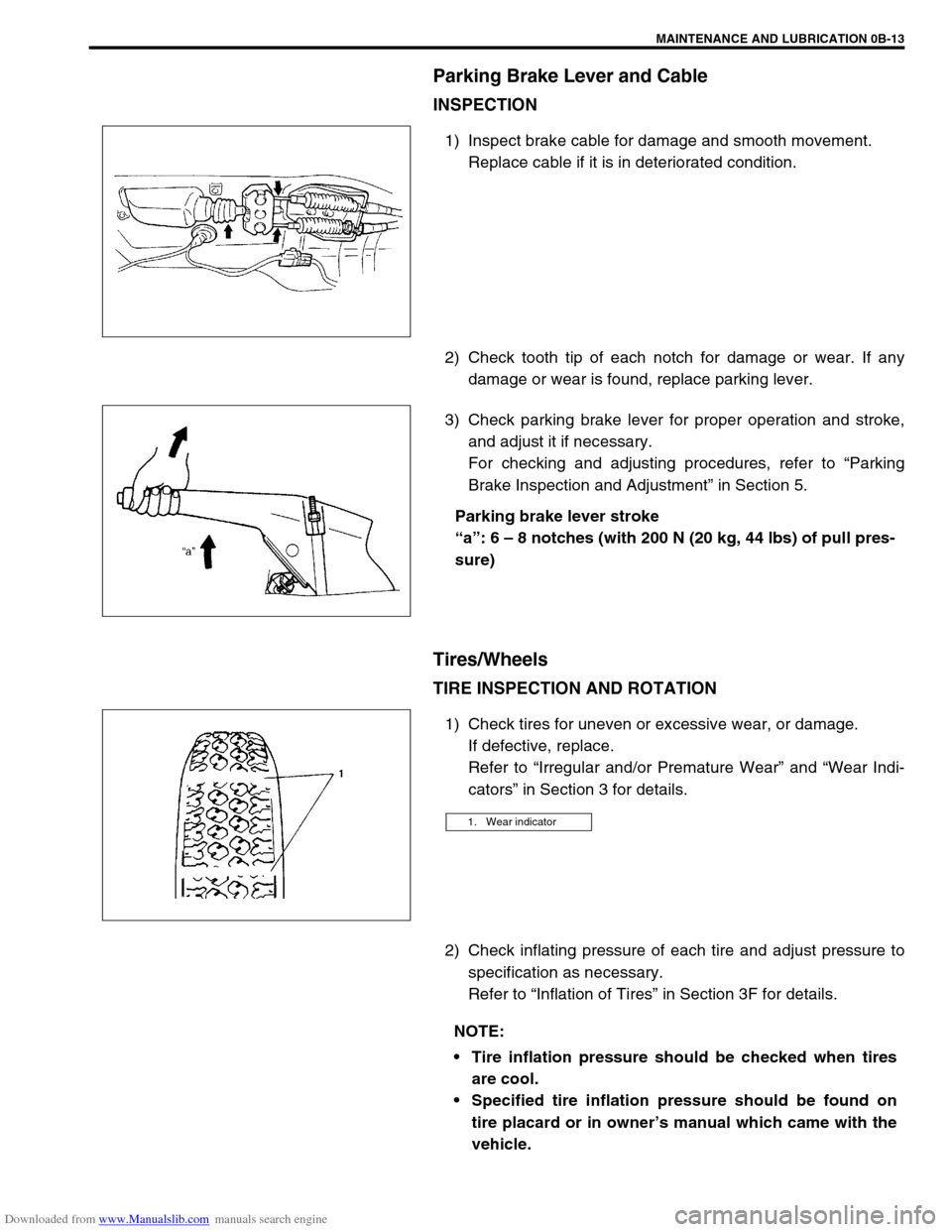
Parking Brake Lever and Cable
INSPECTION
1) Inspect brake cable for damage and smooth movement.
Replace cable if it is in deteriorated condition.
2) Check tooth tip of each notch for damage or wear. If any
damage or wear is found, replace parking lever.
3) Check parking brake lever for proper operation and stroke,
and adjust it if necessary.
For checking and adjusting procedures, refer to “Parking
Brake Inspection and Adjustment” in Section 5.
Parking brake lever stroke
“a”: 6 – 8 notches (with 200 N (20 kg, 44 lbs) of pull pres-
sure)
Tires/Wheels
TIRE INSPECTION AND ROTATION
1) Check tires for uneven or excessive wear, or damage.
If defective, replace.
Refer to “Irregular and/or Premature Wear” and “Wear Indi-
cators” in Section 3 for details.
2) Check inflating pressure of each tire and adjust pressure to
specification as necessary.
Refer to “Inflation of Tires” in Section 3F for details.
1. Wear indicator
NOTE:
Tire inflation pressure should be checked when tires
are cool.
Specified tire inflation pressure should be found on
tire placard or in owner’s manual which came with the
vehicle.
Page 114 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine STEERING, SUSPENSION, WHEELS AND TIRES 3-5
Tire Diagnosis
Irregular and/or Premature Wear
Irregular and premature wear has many possible causes. Some
of them are: incorrect inflation pressures lack of tire rotation, driv-
ing habits, improper alignment.
If the following conditions are noted rotation is in order:
Front tire wear is different from rear.
Uneven wear exists across the tread of any tire.
Left front and right front tire wear is unequal.
Left rear and right rear tire wear is unequal.
There is cupping, flat spotting, etc.
A wheel alignment check is in order if the following conditions are
noted:
Left front and right front tire wear is unequal.
Wear is uneven across the tread of any front tire.
Front tire treads have scuffed appearance with “feather”
edges on one side of tread ribs or blocks.
Wear Indicators
The original equipment tires have built-in tread wear indicators to
show when tires need replacement. These indicators will appear
as 12 mm (0.47 inch) wide bands when the tire tread depth
becomes 1.6 mm (0.063 inch). When the indicators appear in 3 or
more grooves at 6 locations, tire replacement is recommended.
Radial Tire Waddle
Waddle is side to side movement at the front and/or rear of the
vehicle. It is caused by the steel belt not being straight within the
tire. It is most noticeable at low speed, 5 to 30 mph. It is possible
to road test a vehicle and tell on which end of the vehicle the
faulty tire is located. If the waddle tire is on the rear, the rear end
of the vehicle will shake from side to side or “waddle”. From the
driver’s seat it feels as though someone is pushing on the side of
the vehicle. If the faulty tire is on the front, the waddle is more
visual. The front sheet metal appears to be moving back and forth
and the driver feels as though he is at the pivot point in the vehi-
cle. Waddle can be quickly diagnosed by using a Tire Problem
Detector (TPD) and following the equipment manufacturer’s rec-
ommendations.
If a TPD is not available, the more time consuming method of sub-
stituting known good tire / wheel assemblies on the problem vehi-
cle can be used as follows:
[A] : Hard cornering, under inflation or lack of tire rotation
[B] : Incorrect wheel alignment, tire construction not uniform or wheel heavy acceleration
Page 120 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT 3A-3
Diagnosis
Diagnosis Table
For the details, refer to “Diagnosis Table” in Section 3.
Preliminary Checks Prior To Adjusting Front Wheel Alignment
Steering and vibration complaints are not always the result of improper alignment. An additional item to be
checked is the possibility of tire lead due to worn or improperly manufactured tires. “Lead” is the deviation of the
vehicle from a straight path on a level road without hand pressure on the steering wheel. Section 3 of this man-
ual contains a procedure for determining the presence of a tire lead problem. Before making any adjustment
affecting toe setting, the following checks and inspections should be made to ensure correctness of alignment
readings and alignment adjustments:
1) Check all tires for proper inflation pressures and approximately the same tread wear.
2) Check for loose of king pin bearings. Check tie rod ends; if excessive looseness is noted, it must be cor-
rected before adjusting.
3) Check for run-out of wheels and tires.
4) Check vehicle trim heights; if out of limits and a correction is to be made, it must be made before adjusting
toe.
5) Check for loose of suspension arms.
6) Check for loose or missing stabilizer bar attachments.
7) Consideration must be given to excess loads, such as tool boxes. If this excess load is normally carried in
vehicle, it should remain in vehicle during alignment checks.
8) Consider condition of equipment being used to check alignment and follow manufacturer's instructions.
9) Regardless of equipment used to check alignment, vehicle must be on a level surface both fore and aft and
transversely.
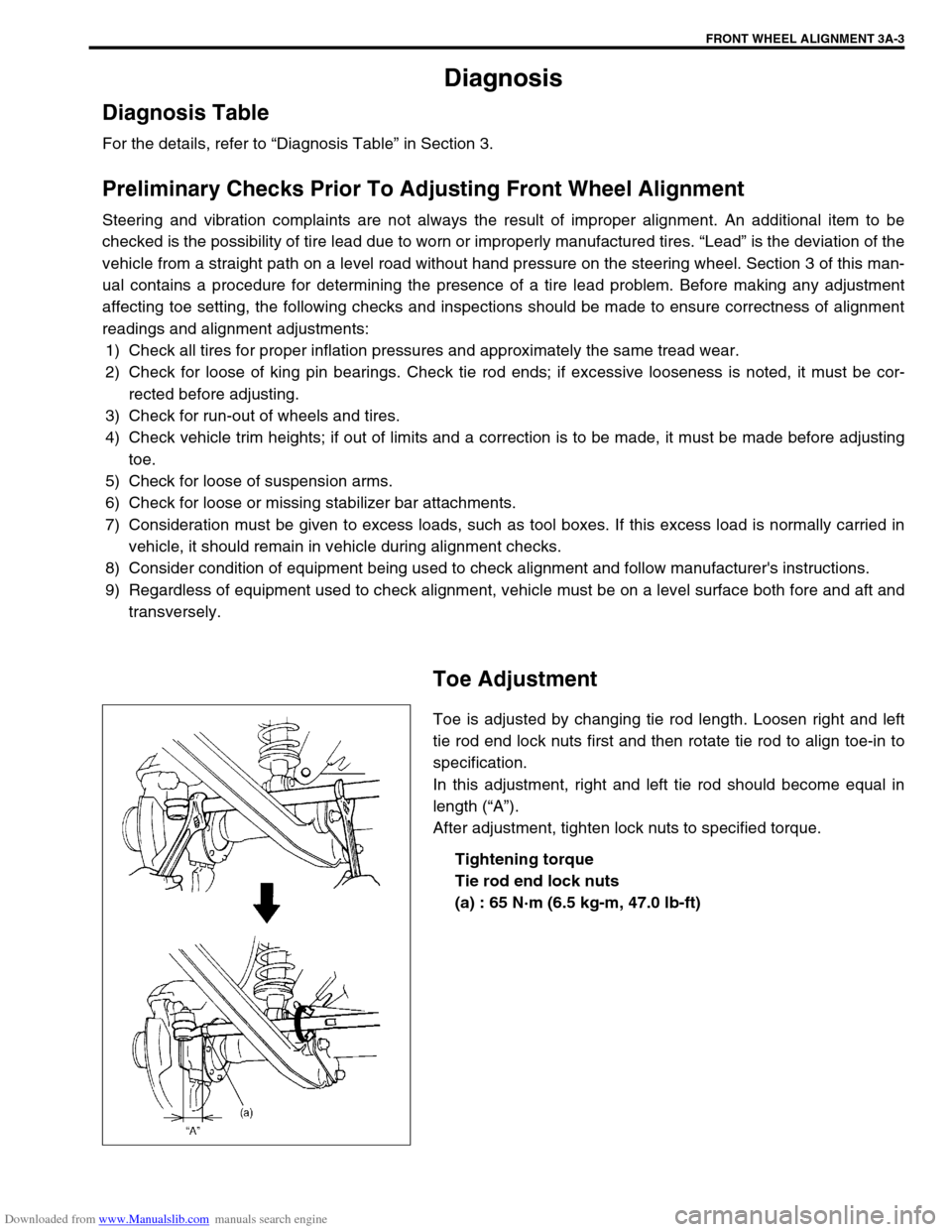
Toe Adjustment
Toe is adjusted by changing tie rod length. Loosen right and left
tie rod end lock nuts first and then rotate tie rod to align toe-in to
specification.
In this adjustment, right and left tie rod should become equal in
length (“A”).
After adjustment, tighten lock nuts to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Tie rod end lock nuts
(a) : 65 N·m (6.5 kg-m, 47.0 lb-ft)
Page 134 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine POWER STEERING (P/S) SYSTEM (If equipped) 3B1-3
Diagnosis
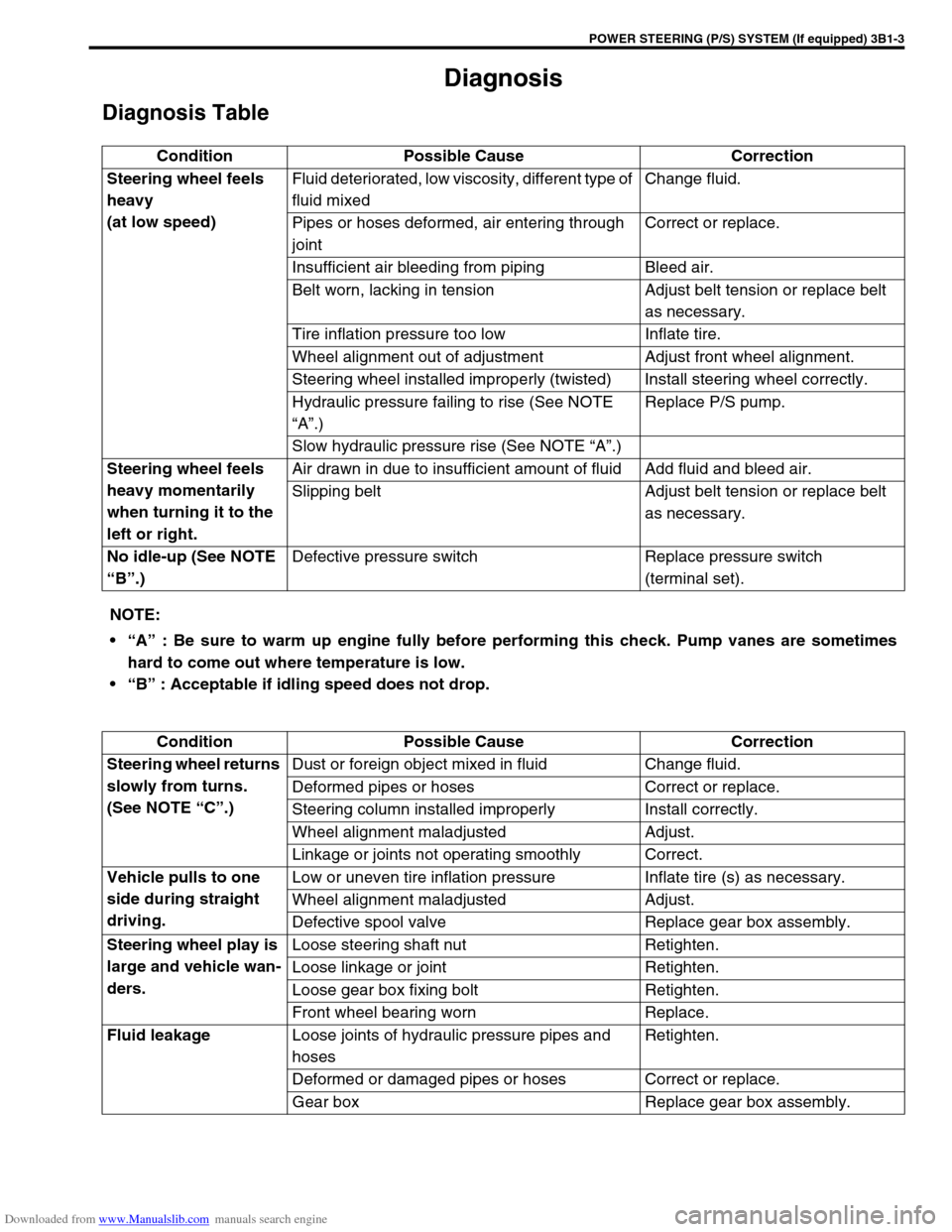
Diagnosis Table
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Steering wheel feels
heavy
(at low speed)Fluid deteriorated, low viscosity, different type of
fluid mixedChange fluid.
Pipes or hoses deformed, air entering through
jointCorrect or replace.
Insufficient air bleeding from piping Bleed air.
Belt worn, lacking in tension Adjust belt tension or replace belt
as necessary.
Tire inflation pressure too low Inflate tire.
Wheel alignment out of adjustment Adjust front wheel alignment.
Steering wheel installed improperly (twisted) Install steering wheel correctly.
Hydraulic pressure failing to rise (See NOTE
“A”.)Replace P/S pump.
Slow hydraulic pressure rise (See NOTE “A”.)
Steering wheel feels
heavy momentarily
when turning it to the
left or right.Air drawn in due to insufficient amount of fluid Add fluid and bleed air.
Slipping belt Adjust belt tension or replace belt
as necessary.
No idle-up (See NOTE
“B”.)Defective pressure switch Replace pressure switch
(terminal set).
NOTE:
“A” : Be sure to warm up engine fully before performing this check. Pump vanes are sometimes
hard to come out where temperature is low.
“B” : Acceptable if idling speed does not drop.
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Steering wheel returns
slowly from turns.
(See NOTE “C”.)Dust or foreign object mixed in fluid Change fluid.
Deformed pipes or hoses Correct or replace.
Steering column installed improperly Install correctly.
Wheel alignment maladjusted Adjust.
Linkage or joints not operating smoothly Correct.
Vehicle pulls to one
side during straight
driving.Low or uneven tire inflation pressure Inflate tire (s) as necessary.
Wheel alignment maladjusted Adjust.
Defective spool valve Replace gear box assembly.
Steering wheel play is
large and vehicle wan-
ders.Loose steering shaft nut Retighten.
Loose linkage or joint Retighten.
Loose gear box fixing bolt Retighten.
Front wheel bearing worn Replace.
Fluid leakage
Loose joints of hydraulic pressure pipes and
hosesRetighten.
Deformed or damaged pipes or hoses Correct or replace.
Gear box Replace gear box assembly.
Page 136 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine POWER STEERING (P/S) SYSTEM (If equipped) 3B1-5
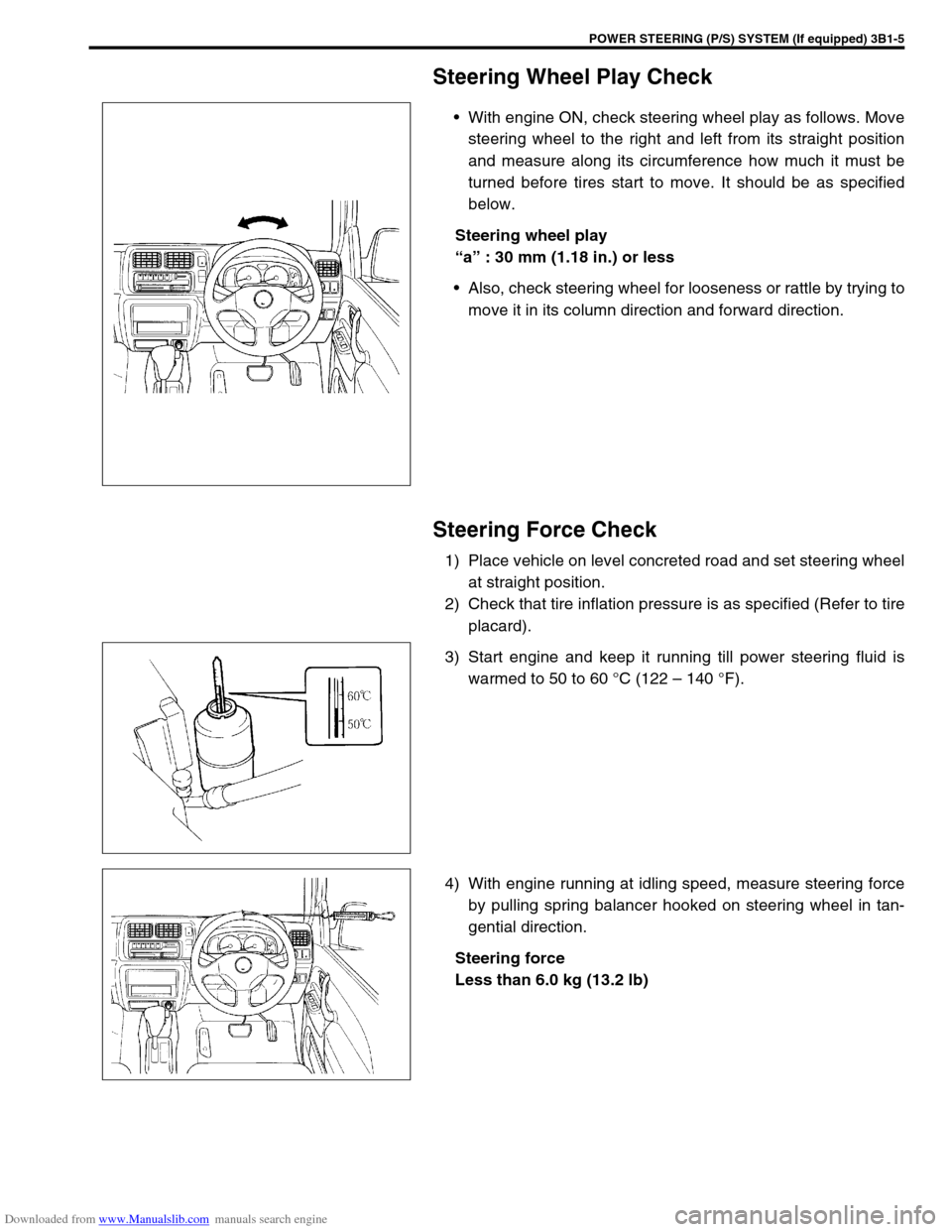
Steering Wheel Play Check
With engine ON, check steering wheel play as follows. Move
steering wheel to the right and left from its straight position
and measure along its circumference how much it must be
turned before tires start to move. It should be as specified
below.
Steering wheel play
“a” : 30 mm (1.18 in.) or less
Also, check steering wheel for looseness or rattle by trying to
move it in its column direction and forward direction.
Steering Force Check
1) Place vehicle on level concreted road and set steering wheel
at straight position.
2) Check that tire inflation pressure is as specified (Refer to tire
placard).
3) Start engine and keep it running till power steering fluid is
warmed to 50 to 60 °C (122 – 140 °F).
4) With engine running at idling speed, measure steering force
by pulling spring balancer hooked on steering wheel in tan-
gential direction.
Steering force
Less than 6.0 kg (13.2 lb)
Page 245 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3F-2 WHEELS AND TIRES
General Description
Tires
This vehicle is equipped with following tire.
Tire size
: 205/70 R15 or 175/80 R15
The tires are of tubeless type. The tires are designed to operate satisfactorily with loads up to the full rated load
capacity when inflated to the recommended inflation pressure.
Correct tire pressures and driving habits have an important influence on tire life Heavy cornering, excessively
rapid acceleration, and unnecessary sharp braking increase tire wear.
Wheels
Standard equipment wheels are following steel wheels.
15 x 5 1/2 JJ
Replacement Tires
When replacement is necessary, the original equipment type tire should be used. Refer to the Tire Placard.
Replacement tires should be of the same size, load range and construction as those originally on the vehicle.
Use of any other size or type tire may affect ride, handling, speedometer / odometer calibration, vehicle ground
clearance and tire or snow chain clearance to the body and chassis.
It is recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on the same axle. If necessary to replace only one tire, it
should be paired with the tire having the most tread, to equalize braking traction.
The metric term for tire inflation pressure is the kilopascal (kPa).
Tire pressures will usually be printed in both kPa and psi on the
Tire Placard. Metric tire gauges are available from tool suppliers.
The following chart, converts commonly used inflation pressures
from kPa to psi. WARNING:
Do not mix different types of tires on the same vehicle such as radial, bias and bias-belted tires except
in emergencies, because vehicle handling may be seriously affected and may result in loss of control.
kPa
kgf/cm2psi
160
180
200
220
240
260
280
300
320
3401.6
1.8
2.0
2.2
2.4
2.6
2.8
3.0
3.2
3.423
26
29
32
35
38
41
44
47
50
Page 249 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3F-6 WHEELS AND TIRES
Maintenance and Minor Adjustments
Wheel and Tire
Wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or peening are not approved. All damaged wheels should be replaced.
Studs
If a broken stud is found, see Section 3E (rear) or Section 3D (front) for Note and Replacement procedure.
Matched tires and wheels
(For vehicle equipped with steel wheels)
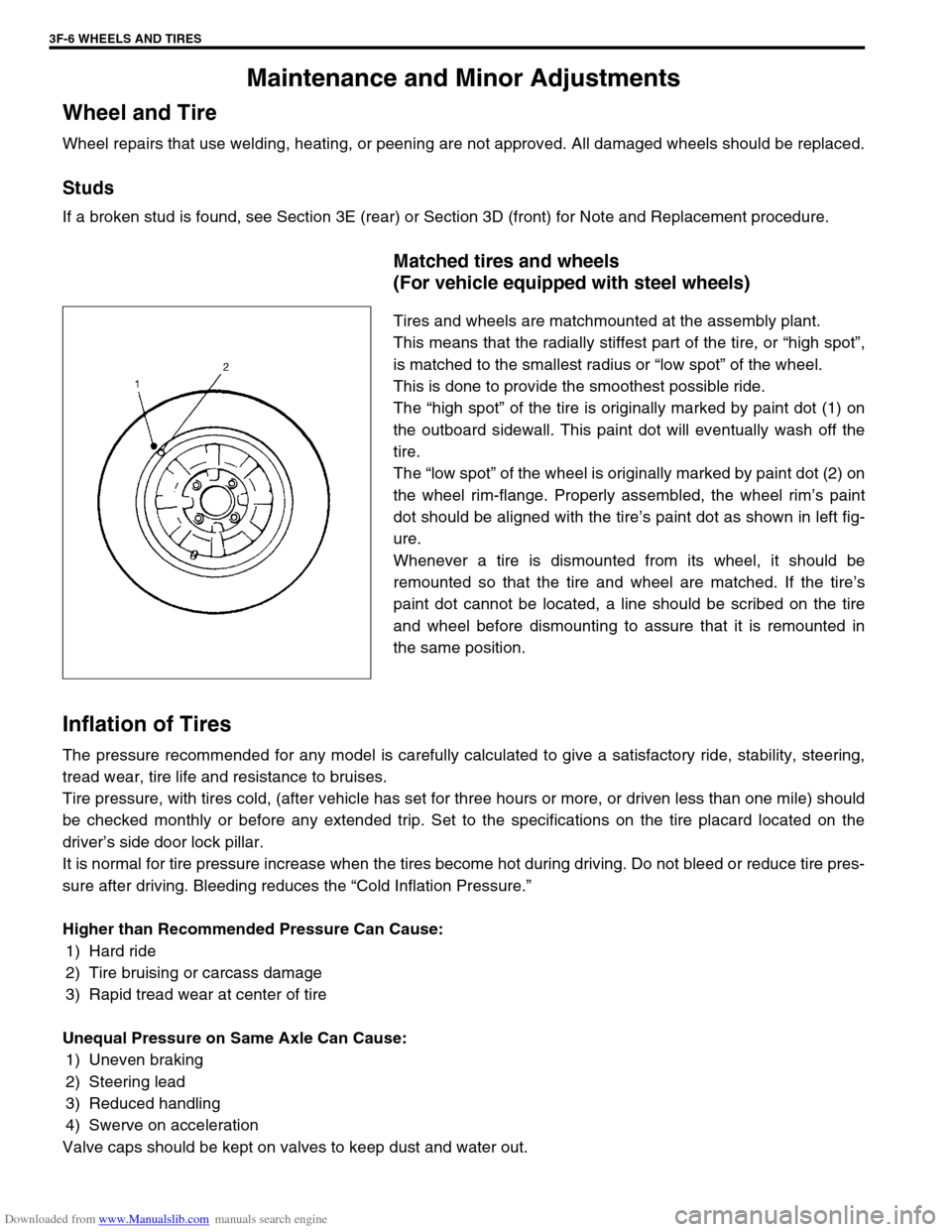
Tires and wheels are matchmounted at the assembly plant.
This means that the radially stiffest part of the tire, or “high spot”,
is matched to the smallest radius or “low spot” of the wheel.
This is done to provide the smoothest possible ride.
The “high spot” of the tire is originally marked by paint dot (1) on
the outboard sidewall. This paint dot will eventually wash off the
tire.
The “low spot” of the wheel is originally marked by paint dot (2) on
the wheel rim-flange. Properly assembled, the wheel rim’s paint
dot should be aligned with the tire’s paint dot as shown in left fig-
ure.
Whenever a tire is dismounted from its wheel, it should be
remounted so that the tire and wheel are matched. If the tire’s
paint dot cannot be located, a line should be scribed on the tire
and wheel before dismounting to assure that it is remounted in
the same position.
Inflation of Tires
The pressure recommended for any model is carefully calculated to give a satisfactory ride, stability, steering,
tread wear, tire life and resistance to bruises.
Tire pressure, with tires cold, (after vehicle has set for three hours or more, or driven less than one mile) should
be checked monthly or before any extended trip. Set to the specifications on the tire placard located on the
driver’s side door lock pillar.
It is normal for tire pressure increase when the tires become hot during driving. Do not bleed or reduce tire pres-
sure after driving. Bleeding reduces the “Cold Inflation Pressure.”
Higher than Recommended Pressure Can Cause:
1) Hard ride
2) Tire bruising or carcass damage
3) Rapid tread wear at center of tire
Unequal Pressure on Same Axle Can Cause:
1) Uneven braking
2) Steering lead
3) Reduced handling
4) Swerve on acceleration
Valve caps should be kept on valves to keep dust and water out.
Page 252 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine WHEELS AND TIRES 3F-9
Tire
Mounting and demounting
Use tire changing machine to mount or demount tires. Follow equipment manufacturer’s instructions. Do not use
hand tools or tire irons alone to change tires as they may damage tire beads or wheel rim.
Rim bead seats should be cleaned with wire brush or coarse steel wool to remove lubricants, old rubber and
light rust. Before mounting or demounting tire, bead area should be well lubricated with approved tire lubricant.
After mounting, inflate to 240 kPa (35 psi) so that beads are completely seated. Then adjust pressure to speci-
fied shown on tire placard.
Install valve core and inflate to proper pressure.
Repair
There are many different materials and techniques on the market to repair tires. As not all of these work on all
types of tires, tire manufacturers have published detailed instructions on how and when to repair tires. These
instructions can be obtained from the tire manufacturer.WARNING:
Do not stand over tire when inflating. Bead may break when bead snaps over rim’s safety hump and
cause serious personal injury.
Do not exceed 240 kPa (35 psi) pressure when inflating. If 240 kPa (35 psi) pressure will not seat
beads, deflate, re-lubricate and reinflate. Over inflation may cause bead to break and cause serious
personal injury.