2005 SUZUKI JIMNY All
[x] Cancel search: AllPage 313 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5-52 BRAKES
Parking Brake Lever/Cable
Parking brake lever
REMOVAL
1) Hoist vehicle and release parking brake lever.
2) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
3) Remove parking brake lever cover.
4) Disconnect lead wire of parking brake switch at coupler.
5) Remove adjusting nut.
6) Loosen bracket nut (3) and disconnect parking brake cables
(2) from equalizer (4).
7) Remove parking brake lever bolts and then remove parking
brake lever assembly (1).
INSTALLATION
1) Install in reverse order of REMOVAL procedure.
Equalizer angle “a” : within 15 degrees
Tightening torque
Parking brake lever bolts
(a) : 23 N·m (2.3 kg-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
2) After all parts are installed, parking brake lever needs to be
adjusted. Refer to “Parking Brake Inspection and Adjust-
ment” in this section.
3) Check brake drum for dragging and brake system for proper
performance. NOTE:
Don’t disassemble parking brake lever switch. It must be
removed and installed as a complete switch assembly.
1. Parking brake lever
2. Parking brake cable
3. Adjusting nut
4. Equalizer
Page 314 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine BRAKES 5-53
Parking Brake Cable
REMOVAL
1) Raise, suitably support vehicle and remove wheel if necessary.
2) Remove parking brake cable.
INSTALLATION
1) Install it by reversing removal procedure, noting the following points.
Install clamps properly referring to figure below.
Tighten bolts and nuts to specified torque.
2) Upon completion of installation, adjust cable. (Refer to “Parking Brake Inspection and Adjustment” in this
section.) Then check brake drum for dragging and brake system for proper performance. After removing
vehicle from hoist, brake test should be performed.
E : View E J : View J 2. Floor Tightening torque
G : View G K : View K 3. Cross member
H : View H 1. Bracket 4. Clamp
Page 318 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-1
6F1
6F2
6G
6H
6K
7A
7A1
7B1
7C1
7D
7E
7F
8E
5E
9
10
10A
10B
10
10A
10B
SECTION 5E
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
CONTENTS
General Description ....................................... 5E-2
System Schematic ....................................... 5E-3
ABS Component Parts Location .................. 5E-4
ABS Control Module ..................................... 5E-5
Self-diagnosis function ............................. 5E-5
Fail-safe function ...................................... 5E-5
Diagnosis ........................................................ 5E-6
Precaution in Diagnosing Troubles .............. 5E-6
ABS Diagnostic Flow Table .......................... 5E-6
“ABS” Warning Lamp Check ........................ 5E-9
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check ........ 5E-9
DTC Check (Using SUZUKI Scan Tool) ..... 5E-10
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
Clearance ................................................... 5E-10
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Table ....... 5E-11
System Circuit ............................................ 5E-12
Table – A “ABS” Warning Lamp Circuit
Check – Lamp Does Not Come “ON”
at Ignition Switch ON .................................. 5E-14
Table – B “ABS” Warning Lamp Circuit
Check – Lamp Comes “ON” Steady ........... 5E-15
Table – C “ABS” Warning Lamp Circuit
Check – Lamp Flashes Continuously
While Ignition Switch is ON ........................ 5E-16
Table – D Code (DTC) is Not Outputted
Even With Diag. Switch Terminal
Connected to Ground. ................................ 5E-17
DTC C1015 (DTC 15) – G Sensor
Circuit ......................................................... 5E-18
DTC C1016 (DTC 16) – Stop Lamp
Circuit ......................................................... 5E-20
DTC C1021 (DTC 21), DTC C1022
(DTC 22) – Right Front Wheel Speed
Sensor Circuit ............................................. 5E-21
DTC C1025 (DTC 25), DTC C1026
(DTC 26) – Left Front Wheel Speed
Sensor Circuit ............................................. 5E-21DTC C1031 (DTC 31), DTC C1032
(DTC 32) – Right Rear Wheel Speed
Sensor Circuit ............................................ 5E-21
DTC C1035 (DTC 35), DTC C1036
(DTC 36) – Left Rear Wheel Speed
Sensor Circuit ............................................ 5E-21
DTC C1041 (DTC 41), DTC C1042
(DTC 42) – Right Front Solenoid Circuit .... 5E-24
DTC C1045 (DTC 45), DTC C1046
(DTC 46) – Left Front Solenoid Circuit....... 5E-24
DTC C1055 (DTC 55), DTC C1056
(DTC 56) – Rear Solenoid Circuit .............. 5E-24
DTC C1057 (DTC 57) – Power Source
Circuit ......................................................... 5E-25
DTC C1061 (DTC 61) – ABS Pump
Motor Circuit............................................... 5E-26
DTC C1063 (DTC 63) – ABS Fail Safe
Circuit ......................................................... 5E-27
DTC C1071 (DTC 71) – ABS Control
Module ....................................................... 5E-28
On-Vehicle Service ...................................... 5E-29
Precaution .................................................. 5E-29
ABS Hydraulic Unit Operation Check ........ 5E-29
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly ................................................... 5E-30
Front Wheel Speed Sensor........................ 5E-32
Front Wheel Sensor Ring........................... 5E-35
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor ........................ 5E-36
Rear Wheel Sensor Ring ........................... 5E-38
G Sensor .................................................... 5E-39
Tightening Torque Specification ................ 5E-40
Special Tool .................................................. 5E-40 NOTE:
All brake fasteners are important attaching parts in that they could affect the performance of vital
parts and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with one of
same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design.
Torque values must be used as specified during reassembly to assure proper retention of all parts.
There is to be no welding as it may result in extensive damage and weakening of the metal.
Page 319 of 687
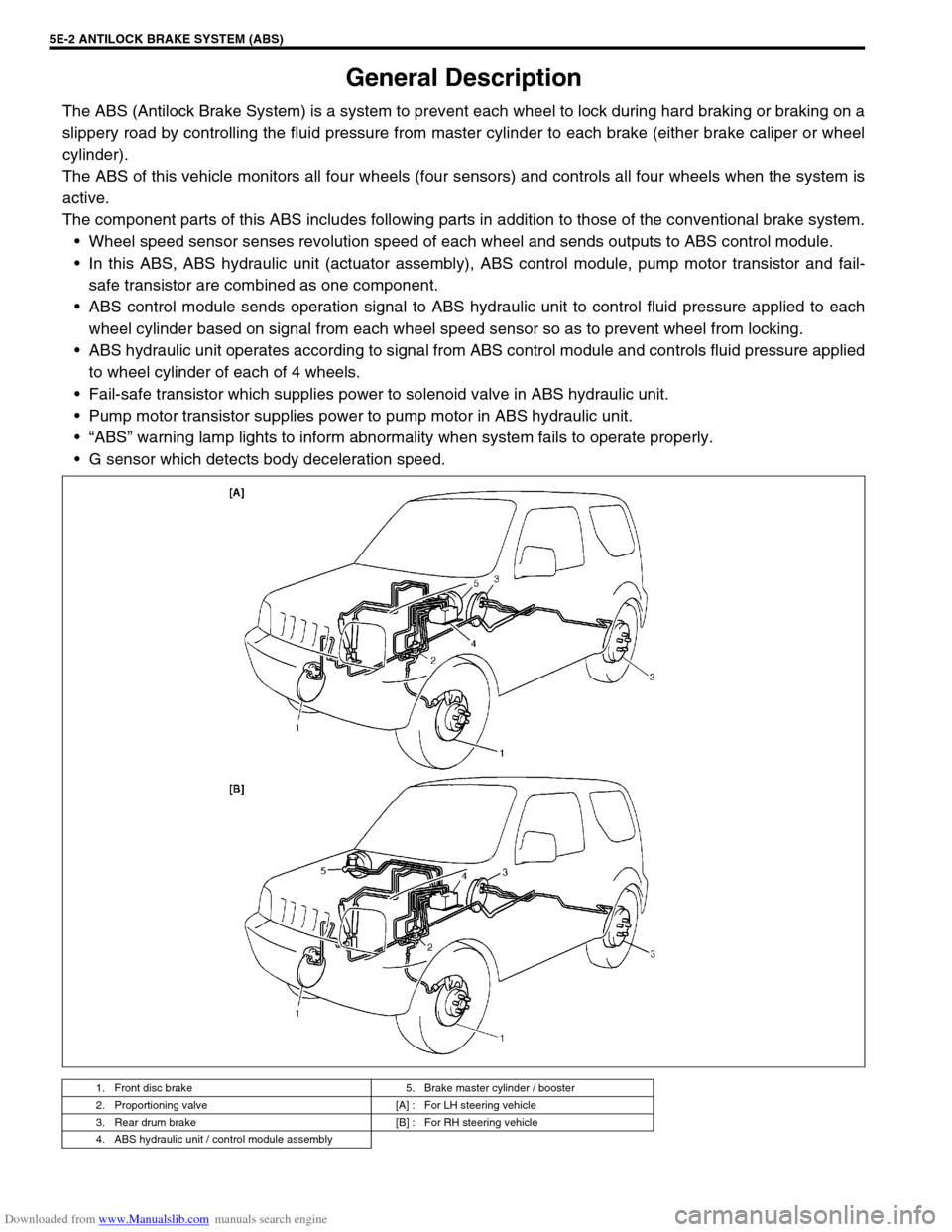
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5E-2 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
General Description
The ABS (Antilock Brake System) is a system to prevent each wheel to lock during hard braking or braking on a
slippery road by controlling the fluid pressure from master cylinder to each brake (either brake caliper or wheel
cylinder).
The ABS of this vehicle monitors all four wheels (four sensors) and controls all four wheels when the system is
active.
The component parts of this ABS includes following parts in addition to those of the conventional brake system.
Wheel speed sensor senses revolution speed of each wheel and sends outputs to ABS control module.
In this ABS, ABS hydraulic unit (actuator assembly), ABS control module, pump motor transistor and fail-
safe transistor are combined as one component.
ABS control module sends operation signal to ABS hydraulic unit to control fluid pressure applied to each
wheel cylinder based on signal from each wheel speed sensor so as to prevent wheel from locking.
ABS hydraulic unit operates according to signal from ABS control module and controls fluid pressure applied
to wheel cylinder of each of 4 wheels.
Fail-safe transistor which supplies power to solenoid valve in ABS hydraulic unit.
Pump motor transistor supplies power to pump motor in ABS hydraulic unit.
“ABS” warning lamp lights to inform abnormality when system fails to operate properly.
G sensor which detects body deceleration speed.
1. Front disc brake 5. Brake master cylinder / booster
2. Proportioning valve [A] : For LH steering vehicle
3. Rear drum brake [B] : For RH steering vehicle
4. ABS hydraulic unit / control module assembly
Page 322 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-5
ABS Control Module
Self-diagnosis function
ABS control module diagnoses conditions of the system compo-
nent parts (whether or not there is any abnormality) all the time
and indicates the results (warning of abnormality occurrence and
DTC) through the “ABS” warning lamp as described below.
1) When ignition switch is turned ON, “ABS” warning lights for 2
seconds to check its bulb and circuit.
2) When no abnormality has been detected (the system is in
good condition), “ABS” warning lamp turns OFF after 2 sec-
onds.
3) When an abnormality in the system is detected, “ABS” warn-
ing lamp lights and the area where that abnormality lies is
stored in the memory in ABS control module.
4) When Diag. switch terminal of monitor connector is
grounded, the abnormal area is output as DTC.
For procedure to clear all DTC’s, refer to the item “Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) Clearance” in this section.
Fail-safe function
When an abnormality occurs (an abnormal DTC is detected),
ABS control module turns OFF the fail-safe transistor which sup-
plies power to ABS hydraulic unit. Thus, with ABS not operating,
brakes function just like the brake system of the vehicle without
ABS.SYSTEM CONDITIONDIAGNOSIS
SWITCH
TERMINAL“ABS”
WARNING
LAMP
In good
condition
at presentNo trouble in the past Open OFF
Grounded DTC 12
Trouble occurred in
the pastOpen OFF
Grounded History DTC
Abnormal-
ity exists
at presentNo trouble in the past Open ON
Grounded Current DTC
Trouble occurred in
the pastOpen ON
GroundedCurrent and
history DTC
NOTE:
The current code and the history code are displayed
without any classification.
1. Ignition switch 4. ABS control module
2.“ABS” warning lamp 5. Sensed information
3. Monitor connector 6. Output
3-1. Diag. switch terminal 7. Lamp driver module
3-2. Ground terminal
Page 324 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-7
1) MALFUNCTION ANALYSIS
a) Customer Complaint Analysis
Record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer.
For this purpose, use of such a questionnaire form as shown below will facilitate collecting information to
the point required for proper analysis and diagnosis.
CUSTOMER QUESTIONNAIRE (EXAMPLE)
b) Problem Symptom Confirmation
Check if what the customer claimed in “Customer Questionnaire” is actually found in the vehicle and if the
symptom is found, determine whether it is identified as a failure. (This step should be shared with the cus-
tomer if possible.) When “ABS” warning lamp is not operating correctly, proceed to “Diagnostic Flow Table-
A, B or C” in this section.
c) Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check, Record and Clearance
Perform “Diagnostic Trouble Code Check” procedure in this section, record it and then clear it referring to
“Diagnostic Trouble Code Clearance” in this section.
If the malfunction DTC which was once displayed and then cleared cannot be detected (indicated) again
when the ignition switch is turned ON, attempt to diagnose the trouble based on the DTC recorded in this
step may mislead the diagnosis or make diagnosing difficult. Proceed to Step 2 to check ABS control mod-
ule for proper self-diagnosis function.
If the malfunction DTC which was once displayed and then cleared can be detected (indicated) again when
ignition switch is turned ON, proceed to Step 3.
Page 326 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-9
“ABS” Warning Lamp Check
Turn ignition switch ON and check that “ABS” warning lamp
comes ON for about 2 seconds and then goes OFF. If any faulty
condition is found, advance to Diagnostic Flow Table-A, B or C.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check
1) Test drive vehicle at 40 km/h for more than a minute.
2) Stop vehicle and while IG switch OFF, connect diagnosis
switch terminal (3) and ground terminal (2) of monitor con-
nector (1) with service wire (4).
3) Turn IG switch ON, read the flashing “ABS” warning lamp
which represents DTC as shown in example below and write
it down. When more than 2 DTC’s are stored in memory,
flashing for each DTC is repeated three times starting with
the smallest DTC number in increasing order.
For details of DTC, refer to “DTC Table”.
Example : When right front wheel speed sensor circuit opens (DTC 21)
4) After completing the check, turn ignition switch off, discon-
nect service wire from monitor connector.
NOTE:
“ABS” warning lamp indicates only following DTCs, DTC
12 which means that no malfunction DTC is stored and
history DTC which indicates history trouble area. When
there is current trouble, “ABS” warning lamp remains ON
and therefore DTC is not indicated.
Page 327 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5E-10 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
DTC Check (Using SUZUKI Scan Tool)
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector after set-
ting cartridge for ABS to it.
Special tool
(A) : SUZUKI scan tool
2) Turn ignition switch ON.
3) Read DTC according to instructions displayed on SUZUKI
scan tool and print it or write it down. Refer to SUZUKI scan
tool operator's manual for further details.
4) After completing the check, turn ignition switch off and dis-
connect SUZUKI scan tool from DLC.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Clearance
After repair or replace malfunction part(s), clear all DTC’s by pre-
forming the following procedure.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Using service wire (4), connect diag. switch terminal (3) of
monitor connector (1) to ground terminal (2).
3) With connection described in above step 2) maintained, turn
ignition switch ON.
4) Repeat ON/OFF operation of service wire (4) at ground ter-
minal (2) at least 5 times within 10 seconds.
5) Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect service wire (4)
from monitor connector (1).
6) Perform “DRIVING TEST” (Step 2 of “ABS Diagnostic Flow
Table”) and “DTC CHECK” and confirm that normal DTC
(DTC 12) is displayed.
WARNING:
When preforming a driving test, select a safe place where
there is neither any traffic nor any traffic accident possi-
bility and be very careful during testing to avoid occur-
rence of an accident.
NOTE:
Service wire ON time must be for 0.1 second and more.
NOTE:
It is also possible to clear DTC by using SUZUKI scan
tool. Refer to Cartridge Manual for procedure to clear
DTC.