2005 SUZUKI JIMNY AIR CON
[x] Cancel search: AIR CONPage 365 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-8 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
In the 2nd through the 4th frames, the freeze frame data of each
malfunction is stored in the order as the malfunction is detected.
These data are not updated.
Shown in the table below are examples of how freeze frame data
are stored when two or more malfunctions are detected.
Freeze Frame Data Clearance :
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as clearance of
diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
DATA LINK CONNECTOR (DLC)
DLC (1) is in compliance with SAEJ1962 in its installation posi-
tion, the shape of connector and pin assignment.
Serial data line (K line of ISO 9141) (3) is used for SUZUKI scan
tool or generic scan tool to communicate with ECM, TCM, Air Bag
SDM and ABS control module.
SUZUKI serial data line (6) is used for SUZUKI scan tool to com-
municate with immobilizer control module.FRAME
FRAME 1 FRAME 2 FRAME 3 FRAME4
FREEZE FRAME
DATA to be updated1st FREEZE
FRAME DATA2nd FREEZE
FRAME DATA3rd FREEZE
FRAME DATA
MALFUNCTION
DETECTED
ORDERNo malfunction No freeze frame data
1 P0400 (EGR)
detectedData at P0400
detectionData at P0400
detection––
2 P0171 (Fuel sys-
tem) detectedData at P0171
detectionData at P0400
detectionData at P0171
detection–
3 P0300 (Misfire)
detectedData at P0171
detectionData at P0400
detectionData at P0171
detectionData at P0300
detection
4 P0301 (Misfire)
detectedData at P0171
detectionData at P0400
detectionData at P0171
detectionData at P0300
detection
2. B+
4. ECM ground
5. Body ground
Page 368 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-11
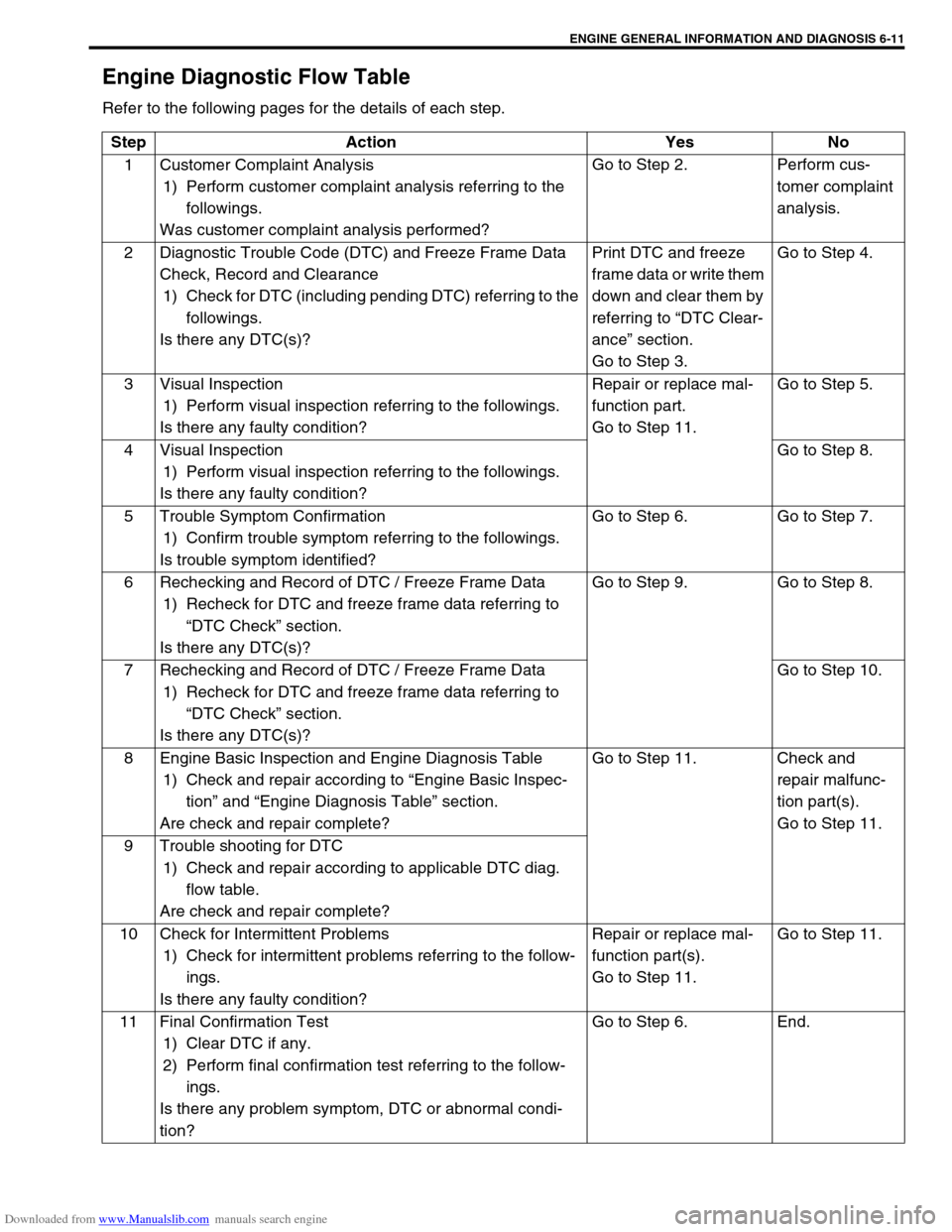
Engine Diagnostic Flow Table
Refer to the following pages for the details of each step.
Step Action Yes No
1 Customer Complaint Analysis
1) Perform customer complaint analysis referring to the
followings.
Was customer complaint analysis performed?Go to Step 2. Perform cus-
tomer complaint
analysis.
2 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and Freeze Frame Data
Check, Record and Clearance
1) Check for DTC (including pending DTC) referring to the
followings.
Is there any DTC(s)?Print DTC and freeze
frame data or write them
down and clear them by
referring to “DTC Clear-
ance” section.
Go to Step 3.Go to Step 4.
3 Visual Inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to the followings.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace mal-
function part.
Go to Step 11.Go to Step 5.
4 Visual Inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to the followings.
Is there any faulty condition?Go to Step 8.
5 Trouble Symptom Confirmation
1) Confirm trouble symptom referring to the followings.
Is trouble symptom identified?Go to Step 6. Go to Step 7.
6 Rechecking and Record of DTC / Freeze Frame Data
1) Recheck for DTC and freeze frame data referring to
“DTC Check” section.
Is there any DTC(s)?Go to Step 9. Go to Step 8.
7 Rechecking and Record of DTC / Freeze Frame Data
1) Recheck for DTC and freeze frame data referring to
“DTC Check” section.
Is there any DTC(s)?Go to Step 10.
8 Engine Basic Inspection and Engine Diagnosis Table
1) Check and repair according to “Engine Basic Inspec-
tion” and “Engine Diagnosis Table” section.
Are check and repair complete?Go to Step 11. Check and
repair malfunc-
tion part(s).
Go to Step 11.
9 Trouble shooting for DTC
1) Check and repair according to applicable DTC diag.
flow table.
Are check and repair complete?
10 Check for Intermittent Problems
1) Check for intermittent problems referring to the follow-
ings.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace mal-
function part(s).
Go to Step 11.Go to Step 11.
11 Final Confirmation Test
1) Clear DTC if any.
2) Perform final confirmation test referring to the follow-
ings.
Is there any problem symptom, DTC or abnormal condi-
tion?Go to Step 6. End.
Page 369 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-12 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
1. CUSTOMER COMPLAINT ANALYSIS
Record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer. For this
purpose, use of such an inspection form will facilitate collecting information to the point required for proper anal-
ysis and diagnosis.
2. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) / FREEZE FRAME DATA CHECK, RECORD AND CLEAR-
ANCE
First, check DTC (including pending DTC), referring to “DTC check” section. If DTC is indicated, print it and
freeze frame data or write them down and then clear them by referring to “DTC clearance” section. DTC indi-
cates malfunction that occurred in the system but does not indicate whether it exists now or it occurred in the
past and the normal condition has been restored now. To check which case applies, check the symptom in ques-
tion according to Step 4 and recheck DTC according to Step 5.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step only or failure to clear the DTC in this step will lead to
incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit or difficulty in troubleshooting.
3. AND 4. VISUAL INSPECTION
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of the items that support proper function of the engine
referring to “Visual Inspection” section.
5. TROUBLE SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION
Based on information obtained in Step 1 Customer complaint analysis and Step 2 DTC / freeze frame data
check, confirm trouble symptoms. Also, reconfirm DTC according to “DTC Confirmation Procedure” described in
each DTC Diagnosis section.
6. AND 7. RECHECKING AND RECORD OF DTC / FREEZE FRAME DATA
Refer to “DTC Check” section for checking procedure.
8. ENGINE BASIC INSPECTION AND ENGINE DIAGNOSIS TABLE
Perform basic engine check according to the “Engine Basic Inspection” first. When the end of the flow table has
been reached, check the parts of the system suspected as a possible cause referring to “Engine Diagnosis
Table” and based on symptoms appearing on the vehicle (symptoms obtained through steps of customer com-
plaint analysis, trouble symptom confirmation and / or basic engine check) and repair or replace faulty parts, if
any.
9. TROUBLESHOOTING FOR DTC (SEE EACH DTC DIAG. FLOW TABLE)
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 5 and referring to the applicable DTC diag. flow table in this section, locate
the cause of the trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness, connector, actuator, ECM or other part and
repair or replace faulty parts.
10. CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEM
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connection” in Section 0A and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2.
11. FINAL CONFIRMATION TEST
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the engine is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has
been repaired is related to the DTC, clear the DTC once, perform DTC confirmation procedure and confirm that
no DTC is indicated.NOTE:
If only Automatic transmission DTCs (P0702-P1717) or Immobilizer DTCs (P1620-P1623) are indicated
in this step, perform trouble diagnosis according to “Diagnosis” in Section 7B or Section 8G.
Page 373 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-16 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) table
DTC
NO.DETECTING ITEM DETECTING CONDITION
(DTC will set when detecting :)MIL
(vehicle
with immo-
bilizer indi-
cator lamp)MIL
(vehicle
without
immobi-
lizer indica-
tor lamp)
P0105
(No.11)Manifold absolute pressure
circuit malfunctionLow pressure-high vacuum-low voltage
(or MAP sensor circuit shorted to ground)
High pressure-low vacuum-high voltage
(or MAP sensor circuit open)1 driving
cycle1 driving
cycle
P0110
(No.18)Intake air temp. circuit mal-
functionIntake air temp. circuit low input
Intake air temp. circuit high input1 driving
cycle1 driving
cycle
P0115
(No.19)Engine coolant temp. cir-
cuit malfunctionEngine coolant temp. circuit low input
Engine coolant temp. circuit high input1 driving
cycle1 driving
cycle
P0120
(No.13)Throttle position circuit mal-
functionThrottle position circuit low input
Throttle position circuit high input1 driving
cycle1 driving
cycle
P0121Throttle position circuit per-
formance problemPoor performance of TP sensor 2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0130
(No.14)HO2S circuit malfunction
(Sensor-1)Min. output voltage of HO2S-higher than
specification
Max. output voltage of HO2S-lower than
specification2 driving
cycles1 driving
cycle
P0133HO2S circuit slow response
(Sensor-1)Response time of HO2S-1 output voltage
between rich and lean is longer than spec-
ification.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0135
(No.14)HO2S heater circuit mal-
function (Sensor-1)Terminal voltage is lower than specification
at heater OFF or it is higher at heater ON.2 driving
cycles1 driving
cycle
P0136HO2S circuit malfunction
(Sensor-2)HO2S-2 voltage is higher than specifica-
tion2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0141HO2S heater circuit mal-
function (Sensor-2)Terminal voltage is lower than specification
at heater OFF or it is higher at heater ON.
(or heater circuit or short)2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0171 Fuel system too leanShort term fuel trim or total fuel trim (short
and long terms added) is larger than spec-
ification for specified time or longer.
(fuel trim toward rich side is large.)2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0172 Fuel system too richShort term fuel trim or total fuel trim (short
and long term added) is smaller than spec-
ification for specified time or longer.
(fuel trim toward lean side is large.)2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0300
P0301
P0302
P0303
P0304Random misfire detected
Cylinder 1 misfire detected
Cylinder 2 misfire detected
Cylinder 3 misfire detected
Cylinder 4 misfire detectedMisfire of such level as to cause damage
to three way catalystMIL flashing
during mis-
fire detec-
tionNot
applicable
Misfire of such level as to deteriorate emis-
sion but not to cause damage to three way
catalyst2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0325
(No.17)Knock sensor circuit mal-
functionKnock sensor circuit low input
Knock sensor circuit high input1 driving
cycle1 driving
cycle
Page 376 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-19
Fail-safe table
When any of the following DTCs is detected, ECM enters fail-safe mode as long as malfunction continues to
exist but that mode is canceled when ECM detects normal condition after that.
DTC NO. DETECTED ITEM FAIL-SAFE OPERATION (SYMPTOM)
P0105
(No.11)Manifold absolute pressure sensor circuit
malfunctionECM uses value determined by throttle opening and
engine speed.
P0110
(No.18)Intake air temp. sensor circuit malfunctionECM controls actuators assuming that intake air tem-
perature is 20 °C (68 °F).
P0115
(No.19)Engine coolant temp. sensor circuit mal-
functionECM controls actuators assuming that engine coolant
temperature is 80 °C (176 °F).
P0120
(No.13)Throttle position sensor circuit malfunc-
tionECM controls actuators assuming that throttle opening
is 20°. (High idle speed)
P0335
(No.23)Crankshaft position sensor circuit mal-
functionECM controls injection system sequential injection to
synchronous injection. (Cranking for a few seconds to
start engine)
P0340
(No.15)Camshaft position sensor circuit malfunc-
tionECM controls injection system sequential injection to
synchronous injection. (Cranking for a few seconds to
start engine)
P0500
(No.16)Vehicle speed sensor malfunction ECM stops idle air control.
P1450Barometric pressure sensor low / high
inputECM controls actuators assuming that barometric
pressure is 100 kPa (760 mmHg).
P1570
(No.21)ABS signal circuit malfunctionECM controls actuators assuming that ABS signal is
OFF.
Page 377 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-20 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Visual inspection
Visually check following parts and systems.
INSPECTION ITEM REFERRING SECTION
Engine oil – level, leakage Section 0B
Engine coolant – level, leakage Section 0B
Fuel – level, leakage Section 0B
A/T fluid – level, leakage Section 0B
Air cleaner element – dirt, clogging Section 0B
Battery – fluid level, corrosion of terminal
Water pump belt – tension, damage Section 0B
Throttle cable – play, installation
Section 6E Vacuum hoses of air intake system – disconnection, looseness,
deterioration, bend
Connectors of electric wire harness – disconnection, friction
Fuses – burning Section 8
Parts – installation, bolt – looseness
Parts – deformation
Other parts that can be checked visually
Also check following items at engine start, if possible
Malfunction indicator lamp – operation Section 6
Charge warning lamp – operation Section 6H
Engine oil pressure warning lamp – operation Section 8 (Section 6 for pressure check)
Engine coolant temp. meter – operation Section 8
Fuel level meter – operation Section 8
Tachometer, if equipped – operation
Abnormal air being inhaled from air intake system
Exhaust system – leakage of exhaust gas, noise
Other parts that can be checked visually
Page 378 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-21
Engine basic inspection
This check is very important for troubleshooting when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been
found in visual inspection.
Follow the flow table carefully.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine Diag. Flow Table” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine Diag. Flow
Table”.
2 Check battery voltage.
Is it 11 V or more?Go to Step 3. Charge or replace battery.
3 Is engine cranked? Go to Step 4. Go to “Diagnosis” in Sec-
tion 6G.
4 Does engine start? Go to Step 5. Go to Step 9.
5 Check idle speed as follows :
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temp.
2) Shift transmission to neutral position for M/T
(“P” position for A/T).
3) All of electrical loads are switched off.
4) Check engine idle speed with scan tool.
See Fig. 1.
Is it 650 – 750 r/min (700 – 800 r/min. for A/T
vehicle)?Go to Step 6. Go to “Engine Diagnosis
Table”.
6 Is SUZUKI scan tool available? Go to Step 8. Go to Step 7.
7 Check ignition timing as follows :
1) Connect test switch terminal (2) of monitor
coupler (1) to ground. See Fig. 2.
2) Remove air cleaner bolt and crips and shift
air cleaner position to observe ignition tim-
ing.
3) Using timing light (1), check initial ignition
timing.
See Fig. 4.
Is it 5° ± 3° BTDC at specified idle speed?Go to “Engine Diagnosis
Table”.Check ignition control
related parts referring to
Section 6F.
8 Check ignition timing as follows :
1) Select “MISC” mode on SUZUKI scan tool
and fix ignition timing to initial one. See Fig.
3.
2) Remove air cleaner bolt and crips and shift
air cleaner position to observe ignition tim-
ing.
3) Using timing light (1), check initial ignition
timing. See Fig. 4.
Is it 5° ± 3° BTDC at specified idle speed?Go to “Engine Diagnosis
Table”.Check ignition control
related parts referring to
Section 6F.
9 Check immobilizer system malfunction as fol-
lows (if equipped) :
1) Check immobilizer indicator lamp or MIL
(malfunction indicator lamp) for flashing.
Is it flashing when ignition switch is turned to
ON position?Go to “Diagnosis” in Sec-
tion 8G.Go to Step 10.
Page 380 of 687
![SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.G Service Workshop Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-23
[D] Fig. 4 for Step 7 or 8 / [E] Fig. 5 for Step 10 / [F] Fig. 6 for Step 13
Engine diagnosis tab SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.G Service Workshop Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-23
[D] Fig. 4 for Step 7 or 8 / [E] Fig. 5 for Step 10 / [F] Fig. 6 for Step 13
Engine diagnosis tab](/manual-img/20/7588/w960_7588-379.png)
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-23
[D] Fig. 4 for Step 7 or 8 / [E] Fig. 5 for Step 10 / [F] Fig. 6 for Step 13
Engine diagnosis table
Perform troubleshooting referring to following table when ECM has no DTC and no abnormality found in visual
inspection and engine basic inspection previously.
Condition Possible Cause Reference Item
Hard Starting
(Engine cranks OK)Faulty ignition coil Ignition coil assembly in Section 6F.
Faulty CMP sensing rotor or CKP sensing
rotorCMP sensing rotor or CKP sensing
rotor inspection in Section 6E.
Faulty idle air control system Diagnostic Flow Table B-4
Faulty ECT sensor, TP sensor, CKP sen-
sor, CMP sensor or MAP sensorECT sensor, TP sensor, CKP sensor,
CMP sensor or MAP sensor in Sec-
tion 6E.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Faulty fuel injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Malfunctioning PCV system PCV system in Section 6E.
Low compression Compression check in Section 6A1.
Improper valve lash Valve lash in Section 6A1.
Improper valve timing Timing chain and chain tensioner in
Section 6A1.
Compression leak from valve seat Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Sticky valve stem Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Weak or damaged valve springs Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Compression leak at cylinder head gasket Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Sticking or damaged piston ring Pistons, piston rings, connecting rods
and cylinders in Section 6A1.
Worn piston, ring or cylinder Pistons, piston rings, connecting rods
and cylinders in Section 6A1.