2005 SUZUKI JIMNY king
[x] Cancel search: kingPage 20 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION 0A-15
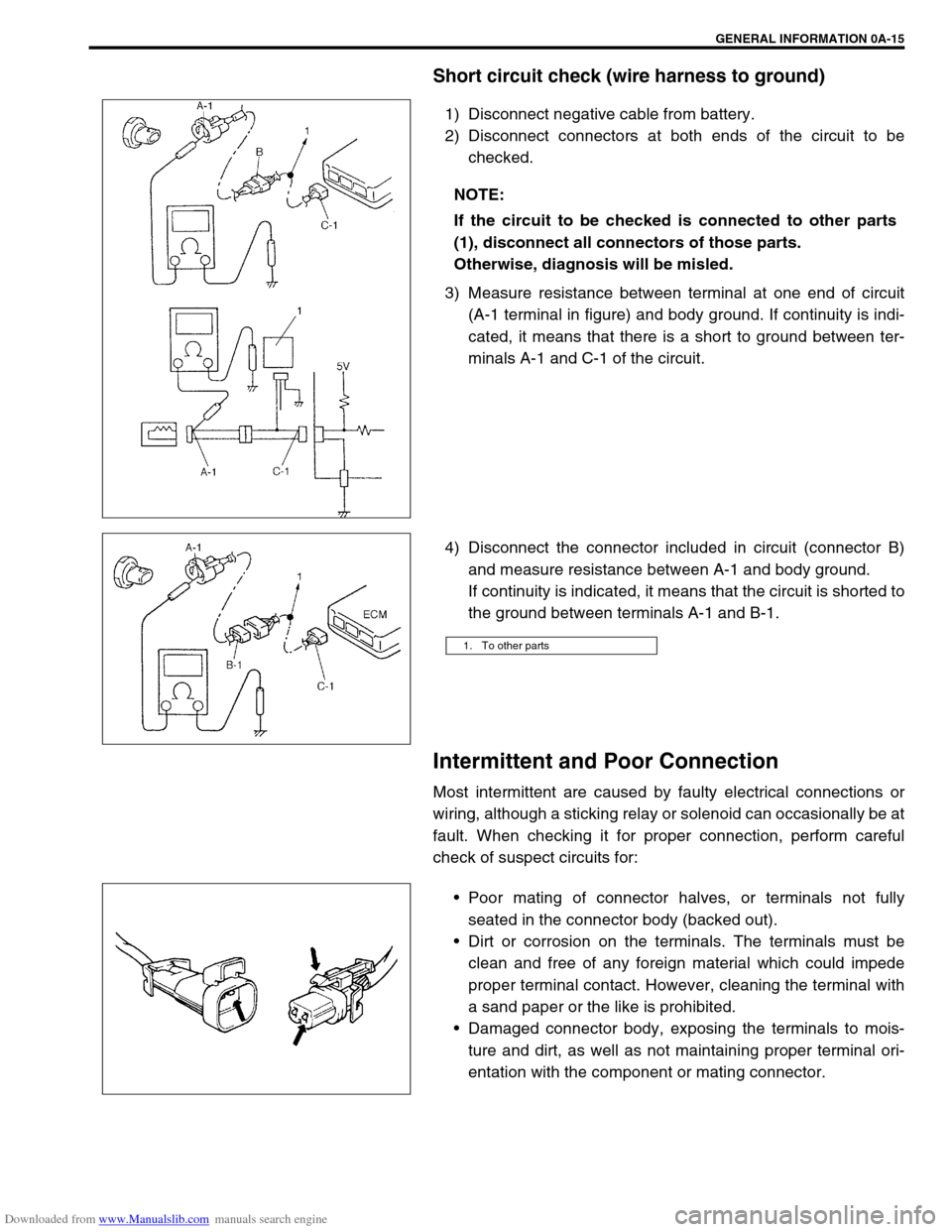
Short circuit check (wire harness to ground)
1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
2) Disconnect connectors at both ends of the circuit to be
checked.
3) Measure resistance between terminal at one end of circuit
(A-1 terminal in figure) and body ground. If continuity is indi-
cated, it means that there is a short to ground between ter-
minals A-1 and C-1 of the circuit.
4) Disconnect the connector included in circuit (connector B)
and measure resistance between A-1 and body ground.
If continuity is indicated, it means that the circuit is shorted to
the ground between terminals A-1 and B-1.
Intermittent and Poor Connection
Most intermittent are caused by faulty electrical connections or
wiring, although a sticking relay or solenoid can occasionally be at
fault. When checking it for proper connection, perform careful
check of suspect circuits for:
Poor mating of connector halves, or terminals not fully
seated in the connector body (backed out).
Dirt or corrosion on the terminals. The terminals must be
clean and free of any foreign material which could impede
proper terminal contact. However, cleaning the terminal with
a sand paper or the like is prohibited.
Damaged connector body, exposing the terminals to mois-
ture and dirt, as well as not maintaining proper terminal ori-
entation with the component or mating connector. NOTE:
If the circuit to be checked is connected to other parts
(1), disconnect all connectors of those parts.
Otherwise, diagnosis will be misled.
1. To other parts
Page 21 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-16 GENERAL INFORMATION
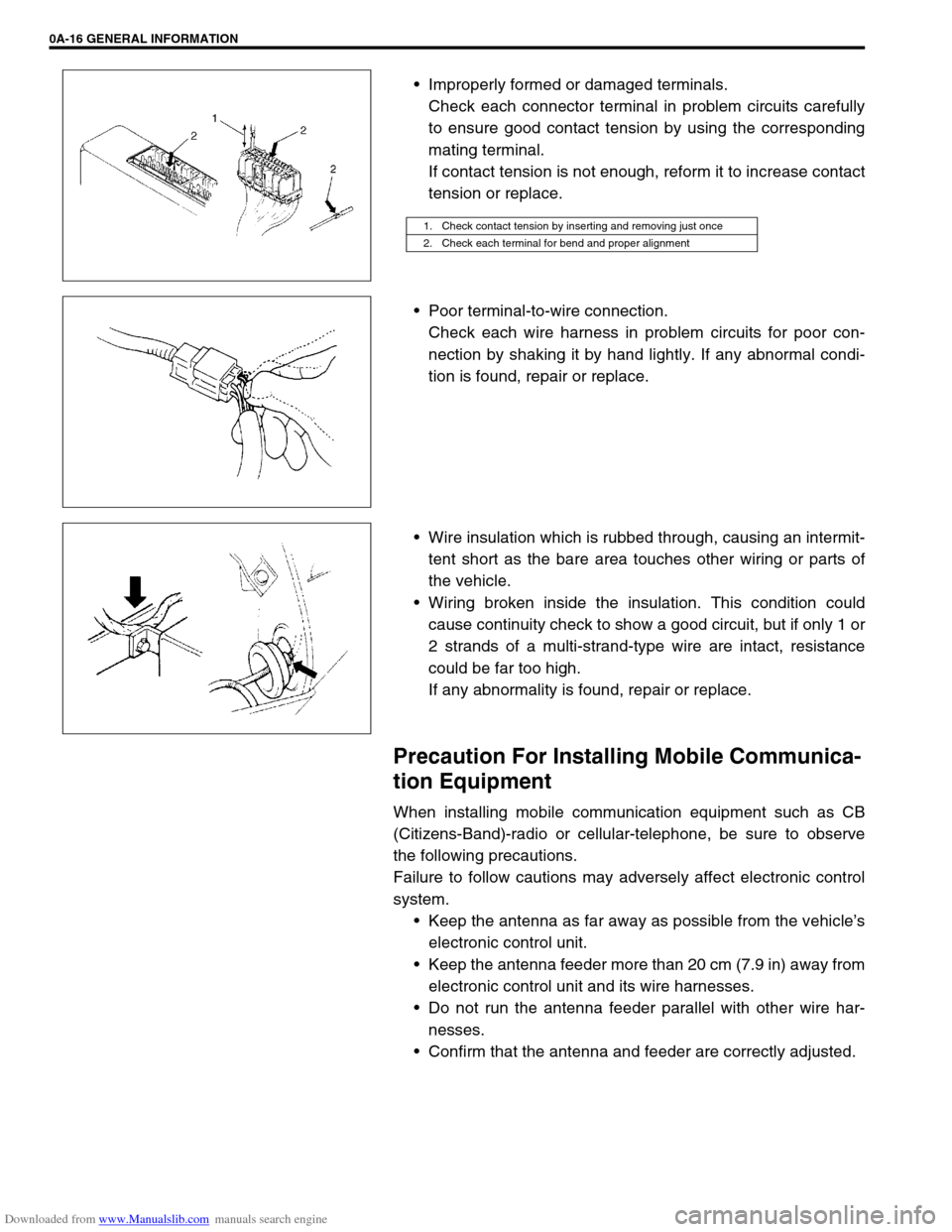
Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Check each connector terminal in problem circuits carefully
to ensure good contact tension by using the corresponding
mating terminal.
If contact tension is not enough, reform it to increase contact
tension or replace.
Poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Check each wire harness in problem circuits for poor con-
nection by shaking it by hand lightly. If any abnormal condi-
tion is found, repair or replace.
Wire insulation which is rubbed through, causing an intermit-
tent short as the bare area touches other wiring or parts of
the vehicle.
Wiring broken inside the insulation. This condition could
cause continuity check to show a good circuit, but if only 1 or
2 strands of a multi-strand-type wire are intact, resistance
could be far too high.
If any abnormality is found, repair or replace.
Precaution For Installing Mobile Communica-
tion Equipment
When installing mobile communication equipment such as CB
(Citizens-Band)-radio or cellular-telephone, be sure to observe
the following precautions.
Failure to follow cautions may adversely affect electronic control
system.
Keep the antenna as far away as possible from the vehicle’s
electronic control unit.
Keep the antenna feeder more than 20 cm (7.9 in) away from
electronic control unit and its wire harnesses.
Do not run the antenna feeder parallel with other wire har-
nesses.
Confirm that the antenna and feeder are correctly adjusted.
1. Check contact tension by inserting and removing just once
2. Check each terminal for bend and proper alignment
Page 25 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-20 GENERAL INFORMATION
When Using Floor Jack
In raising front or rear vehicle end off the floor by jacking, be sure
to put the jack against the center portion of the front axle housing
(1) or rear axle housing (2).
To perform service with either front or rear vehicle end jacked up,
be sure to place safety stands (1) under chassis frame so that
body is securely supported. And then check to ensure that chas-
sis frame does not slide on safety stands (1) and the vehicle is
held stable for safety’s sake. WARNING:
If the vehicle to be jacked up only at the front or rear end,
be sure to block the wheels on ground in order to ensure
safety.
After the vehicle is jacked up, be sure to support it on
stands. It is extremely dangerous to do any work on the
vehicle raised on jack alone.
CAUTION:
Never apply jack against suspension parts (i.e., stabi-
lizer, etc.) or vehicle floor, or it may get deformed.
[A]: Front
[B]: Rear
Page 26 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION 0A-21
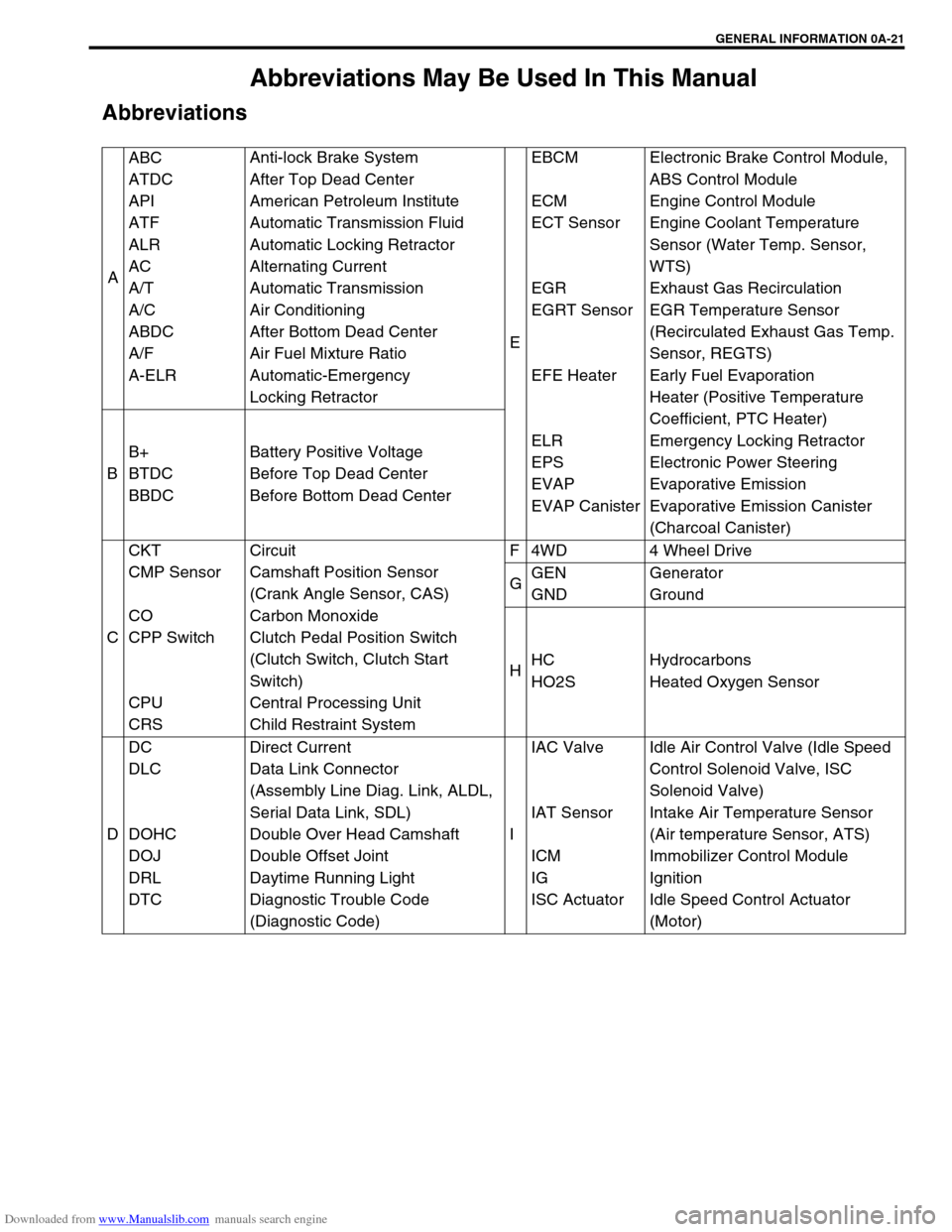
Abbreviations May Be Used In This Manual
Abbreviations
AABC
ATDC
API
ATF
ALR
AC
A/T
A/C
ABDC
A/F
A-ELRAnti-lock Brake System
After Top Dead Center
American Petroleum Institute
Automatic Transmission Fluid
Automatic Locking Retractor
Alternating Current
Automatic Transmission
Air Conditioning
After Bottom Dead Center
Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
Automatic-Emergency
Locking RetractorEEBCM
ECM
ECT Sensor
EGR
EGRT Sensor
EFE Heater
ELR
EPS
EVAP
EVAP CanisterElectronic Brake Control Module,
ABS Control Module
Engine Control Module
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor (Water Temp. Sensor,
WTS)
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGR Temperature Sensor
(Recirculated Exhaust Gas Temp.
Sensor, REGTS)
Early Fuel Evaporation
Heater (Positive Temperature
Coefficient, PTC Heater)
Emergency Locking Retractor
Electronic Power Steering
Evaporative Emission
Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister) BB+
BTDC
BBDCBattery Positive Voltage
Before Top Dead Center
Before Bottom Dead Center
CCKT
CMP Sensor
CO
CPP Switch
CPU
CRSCircuit
Camshaft Position Sensor
(Crank Angle Sensor, CAS)
Carbon Monoxide
Clutch Pedal Position Switch
(Clutch Switch, Clutch Start
Switch)
Central Processing Unit
Child Restraint SystemF 4WD 4 Wheel Drive
GGEN
GNDGenerator
Ground
HHC
HO2SHydrocarbons
Heated Oxygen Sensor
DDC
DLC
DOHC
DOJ
DRL
DTCDirect Current
Data Link Connector
(Assembly Line Diag. Link, ALDL,
Serial Data Link, SDL)
Double Over Head Camshaft
Double Offset Joint
Daytime Running Light
Diagnostic Trouble Code
(Diagnostic Code)IIAC Valve
IAT Sensor
ICM
IG
ISC ActuatorIdle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed
Control Solenoid Valve, ISC
Solenoid Valve)
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
(Air temperature Sensor, ATS)
Immobilizer Control Module
Ignition
Idle Speed Control Actuator
(Motor)
Page 29 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-24 GENERAL INFORMATION
Fasteners Information
Metric Fasteners
Most of the fasteners used for this vehicle are metric fasteners. When replacing any fasteners, it is most impor-
tant that replacement fasteners be the correct diameter, thread pitch and strength.
Fastener Strength Identification
Most commonly used metric fastener strength property classes are 4T, 6.8, 7T, 8.8 and radial line with the class
identification embossed on the head of each bolt. Some metric nuts will be marked with punch, 6 or 8 mark
strength identification on the nut face. Figure shows the different strength markings.
When replacing metric fasteners, be careful to use bolts and nuts of the same strength or greater than the origi-
nal fasteners (the same number marking or higher). It is likewise important to select replacement fasteners of
the correct diameter and thread pitch. Correct replacement bolts and nuts are available through the parts divi-
sion.
Metric bolts: Identification class numbers or marks correspond to bolt strength (increasing numbers represent
increasing strength).
Standard Tightening Torque
Each fastener should be tightened to the torque specified in each section of this manual. If no description or
specification is provided, refer to the following tightening torque chart for the applicable torque for each fastener.
When a fastener of greater strength than the original one is used, however, use the torque specified for the orig-
inal fastener.
1. Nuts strength identification
NOTE:
For the flanged bolt, flanged nut and self-lock nut of 4T and 7T strength, add 10% to the tightening
torque given in the chart below.
The chart below is applicable only where the fastened parts are made of steel light alloy.
Page 32 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION 0B-1
0A 6F1
0B
0B
6G
1A 6H
1B 6K
37A
3A 7A1
3B1 7B1
3C1 7C1
3D 7D
3E 7E
3F 7F
4A2 8A
4B 8B
8C
58D
5A 8E
5B
5C 9
5E
5E1 10
10A
610B
6-1
6A1
6A2
6A4
6B
6C
6E1
6E2
SECTION 0B
MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
CONTENTS
Maintenance Schedule .................................. 0B-2
Maintenance Schedule Under Normal
Driving Conditions ........................................ 0B-2
Maintenance Recommended Under Severe
Driving Conditions ........................................ 0B-4
Maintenance Service...................................... 0B-5
Engine .......................................................... 0B-5
Drive Belt .................................................. 0B-5
Valve Lash................................................ 0B-6
Engine Oil and Filter ................................. 0B-6
Engine Coolant ......................................... 0B-8
Exhaust System ....................................... 0B-8
Ignition System ............................................. 0B-9
Spark Plugs .............................................. 0B-9
Fuel System ................................................. 0B-9
Air Cleaner Filter ...................................... 0B-9
Fuel Lines and Connections ................... 0B-10
Fuel Filter ............................................... 0B-10
Fuel Tank ............................................... 0B-10
Emission Control System ........................... 0B-10
Crankcase Ventilation Hoses and
Connections ........................................... 0B-10
PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation)
Valve ..................................................... 0B-11Fuel Evaporative Emission Control
System ................................................... 0B-11
Chassis and Body ...................................... 0B-11
Clutch ..................................................... 0B-11
Brake Discs and Pads ............................ 0B-11
Brake Drums and Shoes ........................ 0B-12
Brake Hoses and Pipes.......................... 0B-12
Brake Fluid ............................................. 0B-12
Parking Brake Lever and Cable ............. 0B-13
Tires/Wheels .......................................... 0B-13
Suspension System ............................... 0B-14
Propeller Shafts...................................... 0B-15
Manual Transmission Oil........................ 0B-16
Automatic Transmission Fluid ................ 0B-16
Transfer and Differential Oil ................... 0B-17
Steering System ..................................... 0B-18
Steering Knuckle Seal ............................ 0B-18
Power Steering (P/S) System
(if equipped) ........................................... 0B-19
All Hinges, Latches and Locks ............... 0B-19
Final Inspection............................................ 0B-20
Recommended Fluids and Lubricants ....... 0B-22
WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System:
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
Page 39 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-8 MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
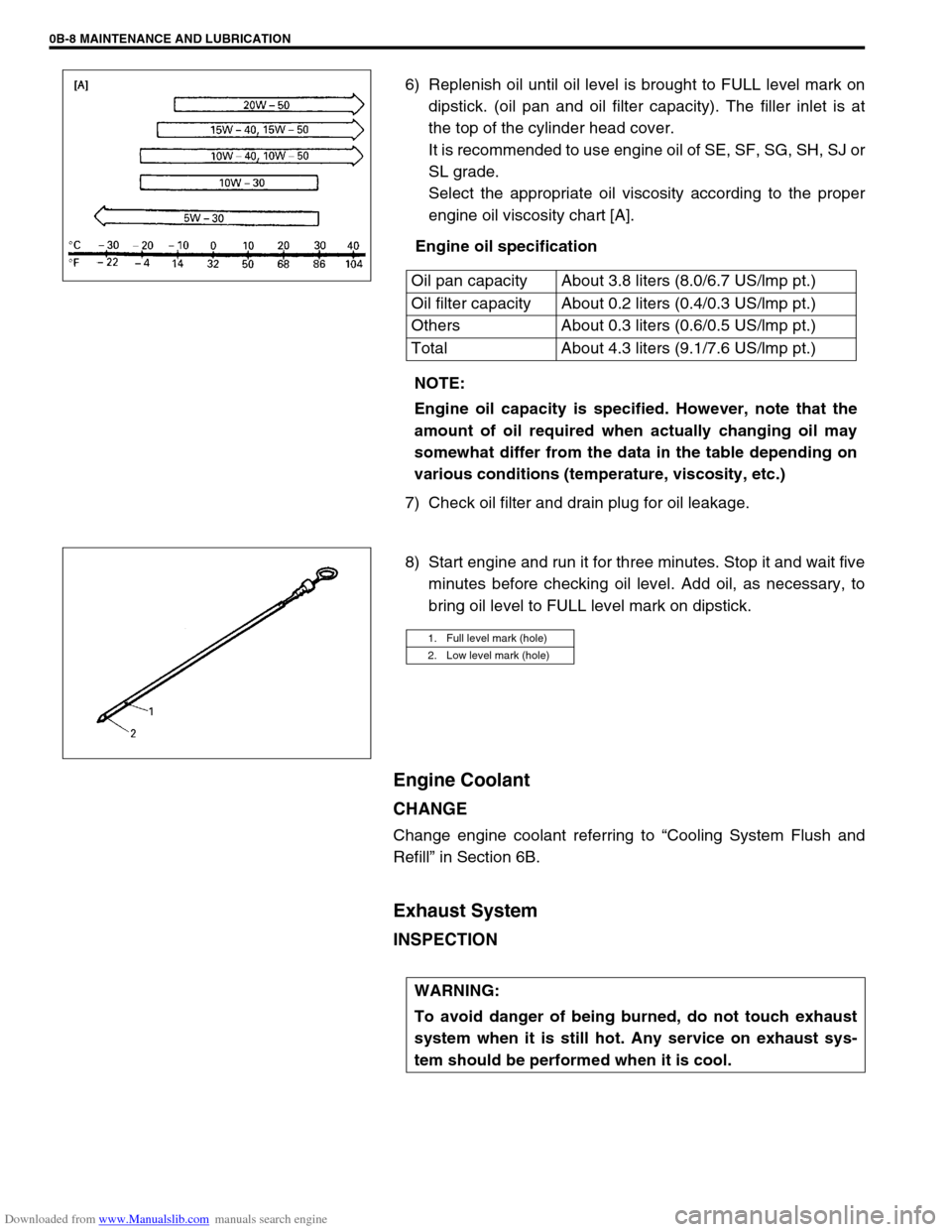
6) Replenish oil until oil level is brought to FULL level mark on
dipstick. (oil pan and oil filter capacity). The filler inlet is at
the top of the cylinder head cover.
It is recommended to use engine oil of SE, SF, SG, SH, SJ or
SL grade.
Select the appropriate oil viscosity according to the proper
engine oil viscosity chart [A].
Engine oil specification
7) Check oil filter and drain plug for oil leakage.
8) Start engine and run it for three minutes. Stop it and wait five
minutes before checking oil level. Add oil, as necessary, to
bring oil level to FULL level mark on dipstick.
Engine Coolant
CHANGE
Change engine coolant referring to “Cooling System Flush and
Refill” in Section 6B.
Exhaust System
INSPECTION
Oil pan capacity About 3.8 liters (8.0/6.7 US/lmp pt.)
Oil filter capacity About 0.2 liters (0.4/0.3 US/lmp pt.)
Others About 0.3 liters (0.6/0.5 US/lmp pt.)
Total About 4.3 liters (9.1/7.6 US/lmp pt.)
NOTE:
Engine oil capacity is specified. However, note that the
amount of oil required when actually changing oil may
somewhat differ from the data in the table depending on
various conditions (temperature, viscosity, etc.)
1. Full level mark (hole)
2. Low level mark (hole)
WARNING:
To avoid danger of being burned, do not touch exhaust
system when it is still hot. Any service on exhaust sys-
tem should be performed when it is cool.
Page 41 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-10 MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
REPLACEMENT
Replace air cleaner filter with new one according to steps 1), 2)
and 5), 6) of inspection procedure.
Fuel Lines and Connections
INSPECTION
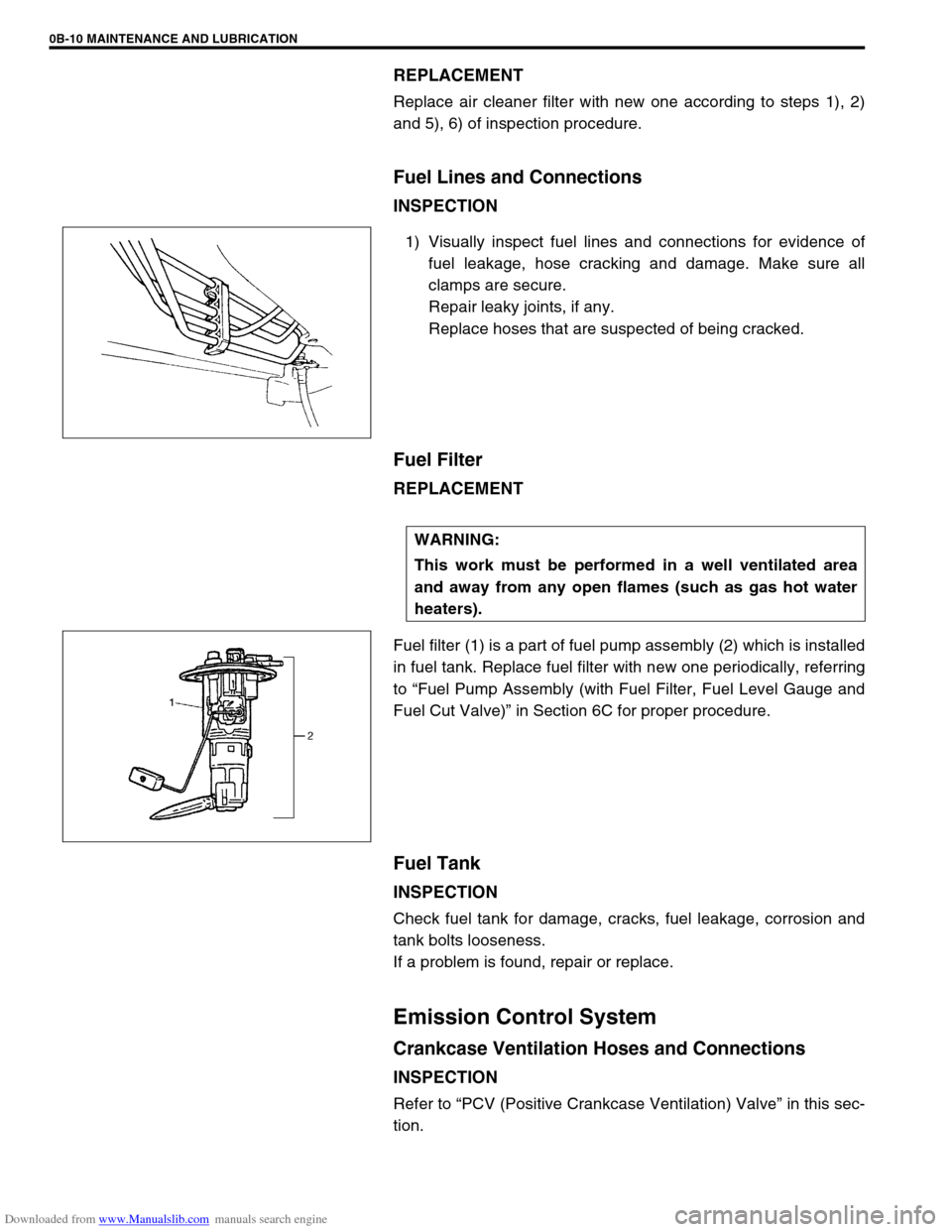
1) Visually inspect fuel lines and connections for evidence of
fuel leakage, hose cracking and damage. Make sure all
clamps are secure.
Repair leaky joints, if any.
Replace hoses that are suspected of being cracked.
Fuel Filter
REPLACEMENT
Fuel filter (1) is a part of fuel pump assembly (2) which is installed
in fuel tank. Replace fuel filter with new one periodically, referring
to “Fuel Pump Assembly (with Fuel Filter, Fuel Level Gauge and
Fuel Cut Valve)” in Section 6C for proper procedure.
Fuel Tank
INSPECTION
Check fuel tank for damage, cracks, fuel leakage, corrosion and
tank bolts looseness.
If a problem is found, repair or replace.
Emission Control System
Crankcase Ventilation Hoses and Connections
INSPECTION
Refer to “PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) Valve” in this sec-
tion.
WARNING:
This work must be performed in a well ventilated area
and away from any open flames (such as gas hot water
heaters).