2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN body
[x] Cancel search: bodyPage 1729 of 2339
(3) Install steering column lower shroud.
(4) Install knee bolster (Fig. 302).
(5) Install instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
303).
(6) Connect battery negative cable.
(7) Verify proper shift interlock system operation.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID -
OPERATION)
SOLENOID/PRESSURE
SWITCH ASSY
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly (Fig. 304)
is external to the transaxle and mounted to thetransaxle case. The assembly consists of four sole-
noids that control hydraulic pressure to the LR/CC,
2/4, OD, and UD friction elements. The reverse
clutch is controlled by line pressure from the manual
valve in the valve body. The solenoids are contained
within the Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly, and
can only be serviced by replacing the assembly.
The solenoid assembly also contains pressure
switches that monitor and send hydraulic circuit
information to the PCM/TCM. Likewise, the pressure
switches can only be service by replacing the assem-
bly.
OPERATION
SOLENOIDS
The solenoids receive electrical power from the
Transmission Control Relay through a single wire.
The PCM/TCM energizes or operates the solenoids
individually by grounding the return wire of the sole-
noid needed. When a solenoid is energized, the sole-
noid valve shifts, and a fluid passage is opened or
closed (vented or applied), depending on its default
operating state. The result is an apply or release of a
frictional element.
The 2/4 and UD solenoids are normally applied,
which by design allow fluid to pass through in their
relaxed or ªoffº state. This allows transaxle limp-in
(P,R,N,2) in the event of an electrical failure.
The continuity of the solenoids and circuits are
periodically tested. Each solenoid is turned on or off
depending on its current state. An inductive spike
Fig. 302 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
Fig. 303 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 304 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly
1 - SOLENOID AND PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
21 - 268 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 1741 of 2339
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The engagement and disengagement of the TCC
are automatic and controlled by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The engagement cannot be acti-
vated in the lower gears because it eliminates the
torque multiplication effect of the torque converter
necessary for acceleration. Inputs that determine
clutch engagement are: coolant temperature, vehicle
speed and throttle position. The torque converter
clutch is engaged by the clutch solenoid on the valve
body. The clutch will engage at approximately 56
km/h (35 mph) with light throttle, after the shift to
third gear.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE - REMOVAL)
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate converter hub and oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
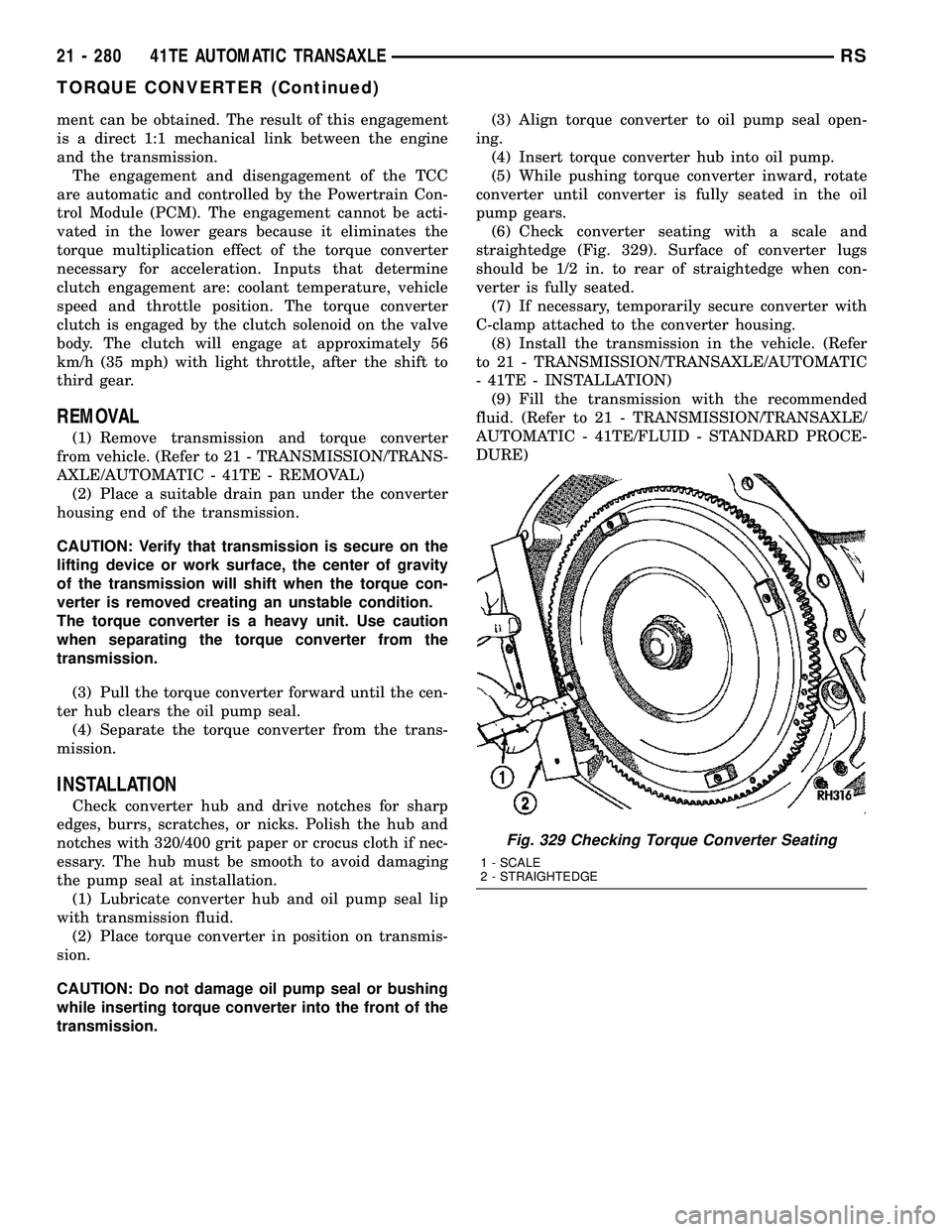
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 329). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE - INSTALLATION)
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
Fig. 329 Checking Torque Converter Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 280 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1742 of 2339
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
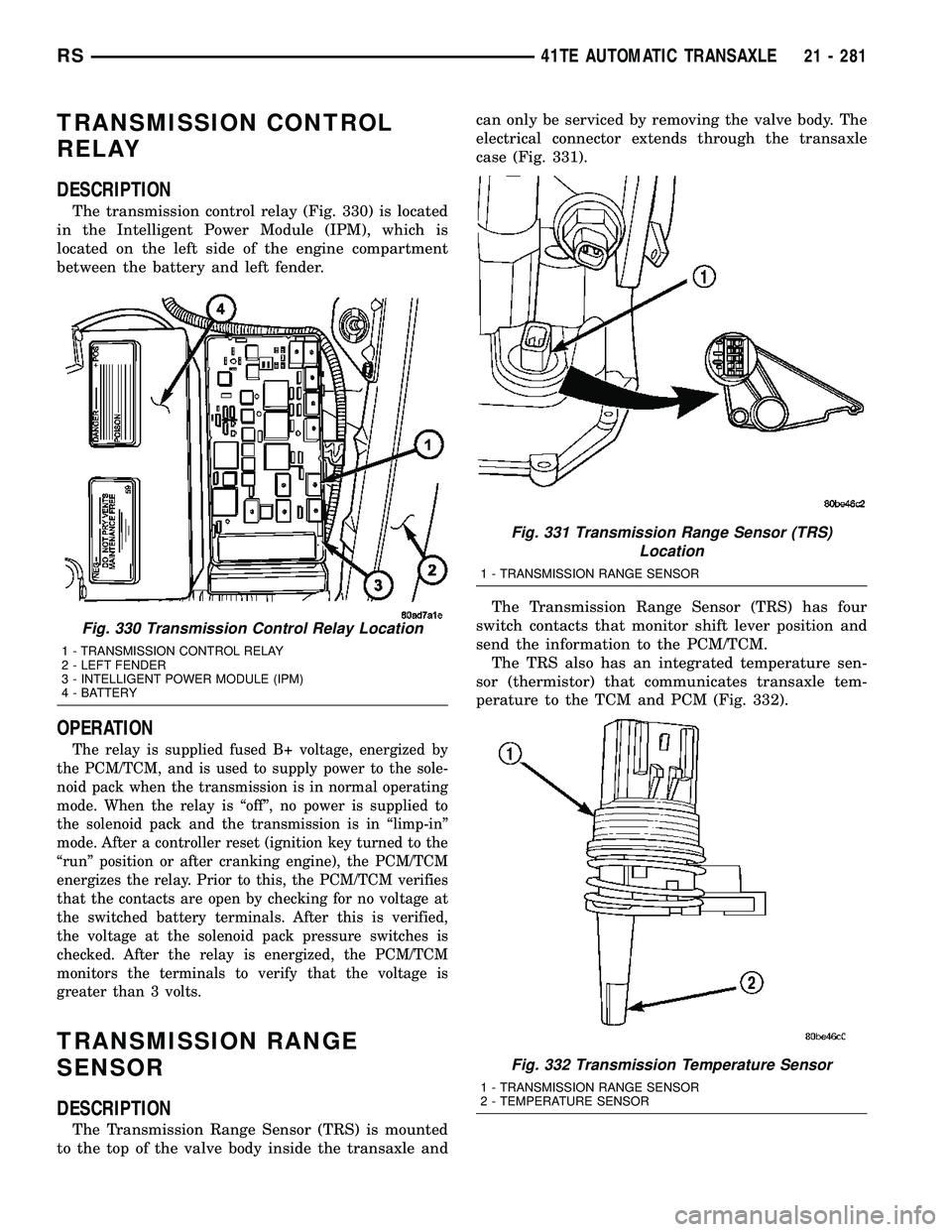
The transmission control relay (Fig. 330) is located
in the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is
located on the left side of the engine compartment
between the battery and left fender.
OPERATION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized by
the PCM/TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal operating
mode. When the relay is ªoffº, no power is supplied to
the solenoid pack and the transmission is in ªlimp-inº
mode. After a controller reset (ignition key turned to the
ªrunº position or after cranking engine), the PCM/TCM
energizes the relay. Prior to this, the PCM/TCM verifies
that the contacts are open by checking for no voltage at
the switched battery terminals. After this is verified,
the voltage at the solenoid pack pressure switches is
checked. After the relay is energized, the PCM/TCM
monitors the terminals to verify that the voltage is
greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
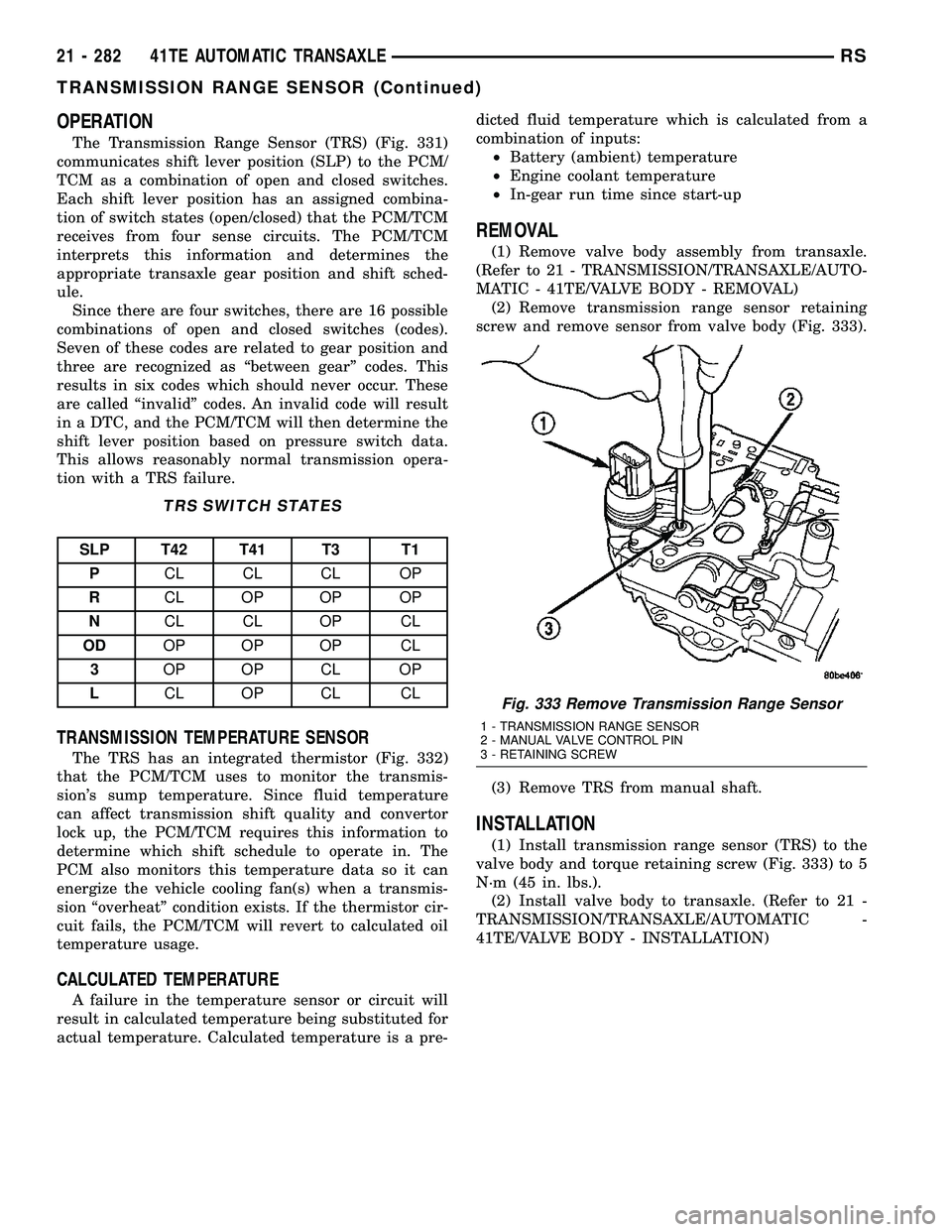
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is mounted
to the top of the valve body inside the transaxle andcan only be serviced by removing the valve body. The
electrical connector extends through the transaxle
case (Fig. 331).
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has four
switch contacts that monitor shift lever position and
send the information to the PCM/TCM.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transaxle tem-
perature to the TCM and PCM (Fig. 332).
Fig. 330 Transmission Control Relay Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
2 - LEFT FENDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE (IPM)
4 - BATTERY
Fig. 331 Transmission Range Sensor (TRS)
Location
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 332 Transmission Temperature Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - TEMPERATURE SENSOR
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 281
Page 1743 of 2339
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) (Fig. 331)
communicates shift lever position (SLP) to the PCM/
TCM as a combination of open and closed switches.
Each shift lever position has an assigned combina-
tion of switch states (open/closed) that the PCM/TCM
receives from four sense circuits. The PCM/TCM
interprets this information and determines the
appropriate transaxle gear position and shift sched-
ule.
Since there are four switches, there are 16 possible
combinations of open and closed switches (codes).
Seven of these codes are related to gear position and
three are recognized as ªbetween gearº codes. This
results in six codes which should never occur. These
are called ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result
in a DTC, and the PCM/TCM will then determine the
shift lever position based on pressure switch data.
This allows reasonably normal transmission opera-
tion with a TRS failure.
TRS SWITCH STATES
SLP T42 T41 T3 T1
PCL CL CL OP
RCL OP OP OP
NCL CL OP CL
ODOP OP OP CL
3OP OP CL OP
LCL OP CL CL
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The TRS has an integrated thermistor (Fig. 332)
that the PCM/TCM uses to monitor the transmis-
sion's sump temperature. Since fluid temperature
can affect transmission shift quality and convertor
lock up, the PCM/TCM requires this information to
determine which shift schedule to operate in. The
PCM also monitors this temperature data so it can
energize the vehicle cooling fan(s) when a transmis-
sion ªoverheatº condition exists. If the thermistor cir-
cuit fails, the PCM/TCM will revert to calculated oil
temperature usage.
CALCULATED TEMPERATURE
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
REMOVAL
(1) Remove valve body assembly from transaxle.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/VALVE BODY - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove transmission range sensor retaining
screw and remove sensor from valve body (Fig. 333).
(3) Remove TRS from manual shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install transmission range sensor (TRS) to the
valve body and torque retaining screw (Fig. 333) to 5
N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(2) Install valve body to transaxle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
41TE/VALVE BODY - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 333 Remove Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
21 - 282 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1744 of 2339
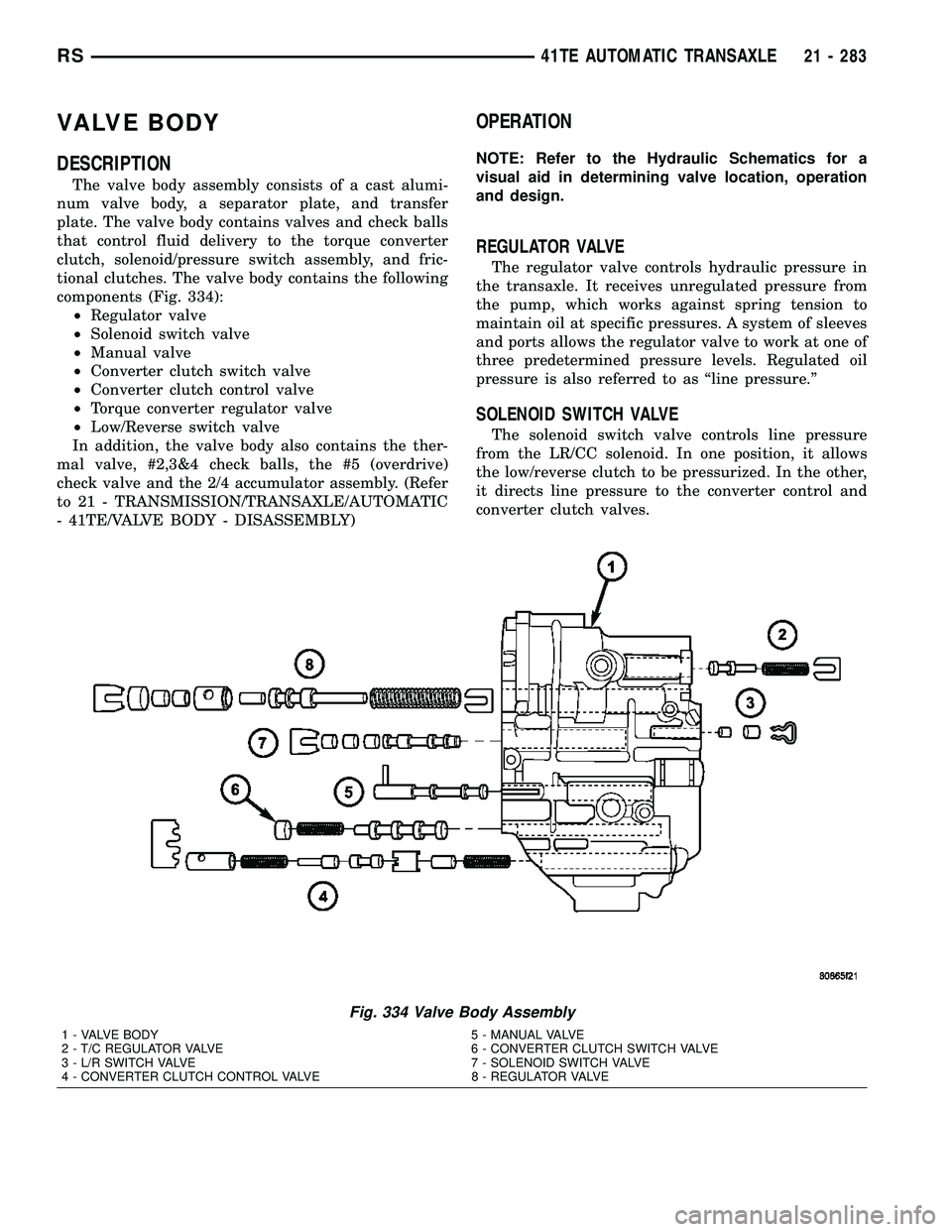
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body assembly consists of a cast alumi-
num valve body, a separator plate, and transfer
plate. The valve body contains valves and check balls
that control fluid delivery to the torque converter
clutch, solenoid/pressure switch assembly, and fric-
tional clutches. The valve body contains the following
components (Fig. 334):
²Regulator valve
²Solenoid switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch switch valve
²Converter clutch control valve
²Torque converter regulator valve
²Low/Reverse switch valve
In addition, the valve body also contains the ther-
mal valve, #2,3&4 check balls, the #5 (overdrive)
check valve and the 2/4 accumulator assembly. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE/VALVE BODY - DISASSEMBLY)
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
REGULATOR VALVE
The regulator valve controls hydraulic pressure in
the transaxle. It receives unregulated pressure from
the pump, which works against spring tension to
maintain oil at specific pressures. A system of sleeves
and ports allows the regulator valve to work at one of
three predetermined pressure levels. Regulated oil
pressure is also referred to as ªline pressure.º
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
The solenoid switch valve controls line pressure
from the LR/CC solenoid. In one position, it allows
the low/reverse clutch to be pressurized. In the other,
it directs line pressure to the converter control and
converter clutch valves.
Fig. 334 Valve Body Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY 5 - MANUAL VALVE
2 - T/C REGULATOR VALVE 6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
3 - L/R SWITCH VALVE 7 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
4 - CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE 8 - REGULATOR VALVE
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 283
Page 1745 of 2339
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve is operated by the mechanical
shift linkage. Its primary responsibility is to send
line pressure to the appropriate hydraulic circuits
and solenoids. The valve has three operating ranges
or positions.
CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
The main responsibility of the converter clutch
switch valve is to control hydraulic pressure applied
to the front (off) side of the converter clutch piston.
Line pressure from the regulator valve is fed to the
torque converter regulator valve, where it passes
through the valve, and is slightly regulated. The
pressure is then directed to the converter clutch
switch valve and to the front side of the converter
clutch piston. This pressure pushes the piston back
and disengages the converter clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE
The converter clutch control valve controls the
back (on) side of the torque converter clutch. When
the PCM/TCM energizes or modulates the LR/CC
solenoid to apply the converter clutch piston, both
the converter clutch control valve and the converter
control valve move, allowing pressure to be applied to
the back side of the clutch.
T/C REGULATOR VALVE
The torque converter regulator valve slightly regu-
lates the flow of fluid to the torque converter.
LOW/REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
The low/reverse clutch is applied from different
sources, depending on whether low (1st) gear or
reverse is selected. The low/reverse switch valve
alternates positions depending on from which direc-
tion fluid pressure is applied. By design, when the
valve is shifted by fluid pressure from one channel,
the opposing channel is blocked. The switch valve
alienates the possibility of a sticking ball check, thus
providing consistent application of the low/reverse
clutch under all operating conditions.
REMOVAL
NOTE: If valve body is replaced or reconditioned,
the ªQuick-Learnº Procedure must be performed.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROLMODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect gearshift cable from manual valve
lever.
(3) Remove manual valve lever from manual shaft.
(4) Raise vehicle on hoist.
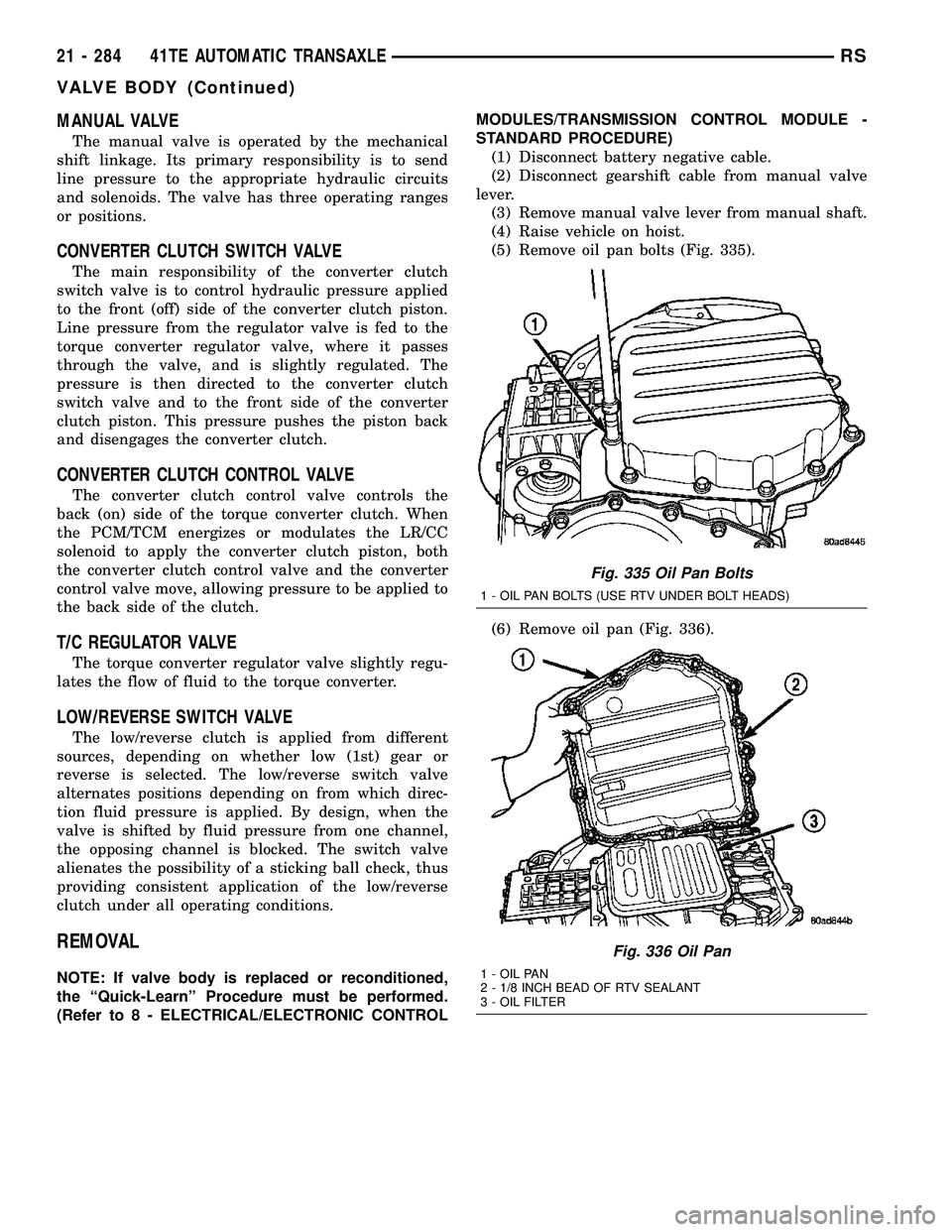
(5) Remove oil pan bolts (Fig. 335).
(6) Remove oil pan (Fig. 336).
Fig. 335 Oil Pan Bolts
1 - OIL PAN BOLTS (USE RTV UNDER BOLT HEADS)
Fig. 336 Oil Pan
1 - OIL PAN
2 - 1/8 INCH BEAD OF RTV SEALANT
3 - OIL FILTER
21 - 284 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1746 of 2339
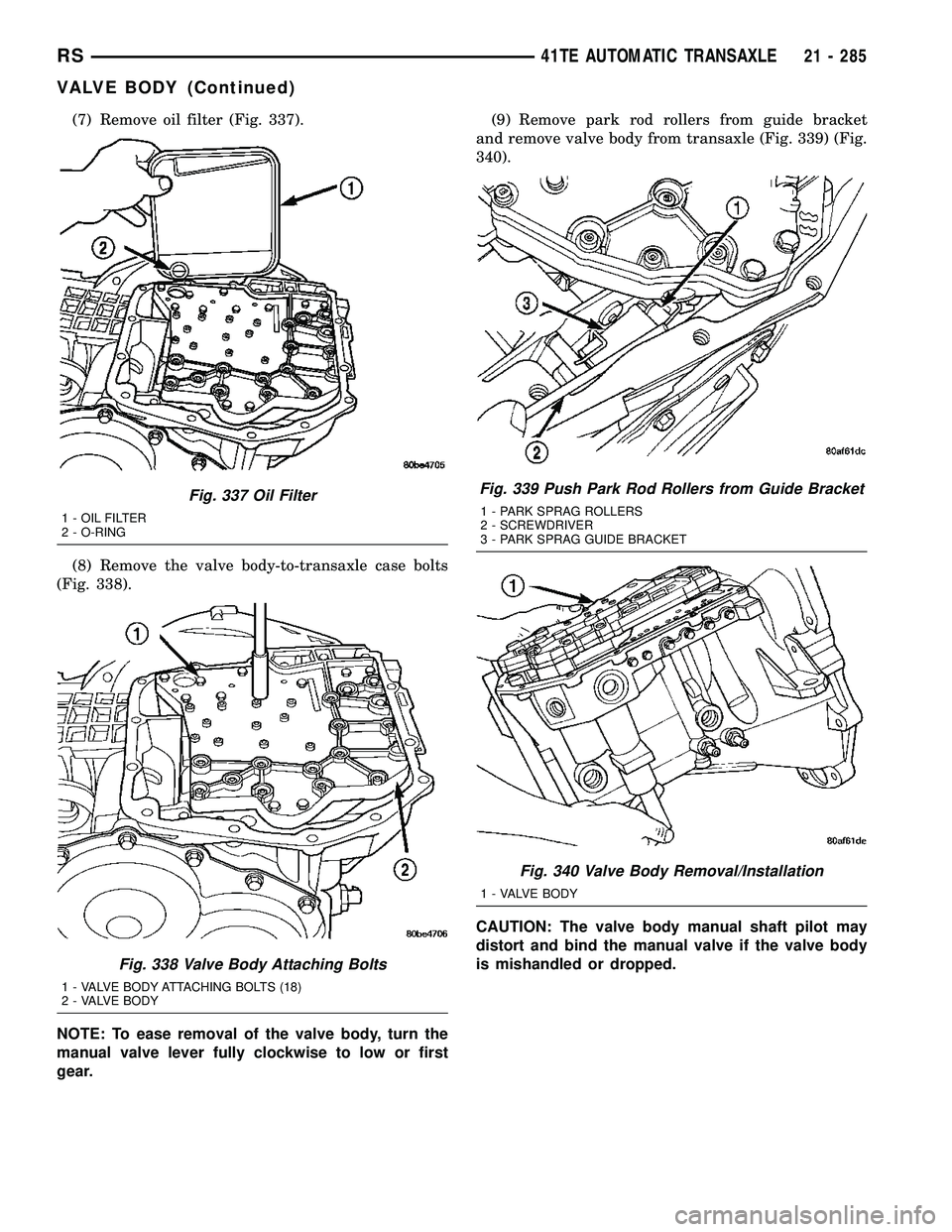
(7) Remove oil filter (Fig. 337).
(8) Remove the valve body-to-transaxle case bolts
(Fig. 338).
NOTE: To ease removal of the valve body, turn the
manual valve lever fully clockwise to low or first
gear.(9) Remove park rod rollers from guide bracket
and remove valve body from transaxle (Fig. 339) (Fig.
340).
CAUTION: The valve body manual shaft pilot may
distort and bind the manual valve if the valve body
is mishandled or dropped.
Fig. 337 Oil Filter
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
Fig. 338 Valve Body Attaching Bolts
1 - VALVE BODY ATTACHING BOLTS (18)
2 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 339 Push Park Rod Rollers from Guide Bracket
1 - PARK SPRAG ROLLERS
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - PARK SPRAG GUIDE BRACKET
Fig. 340 Valve Body Removal/Installation
1 - VALVE BODY
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 285
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1747 of 2339
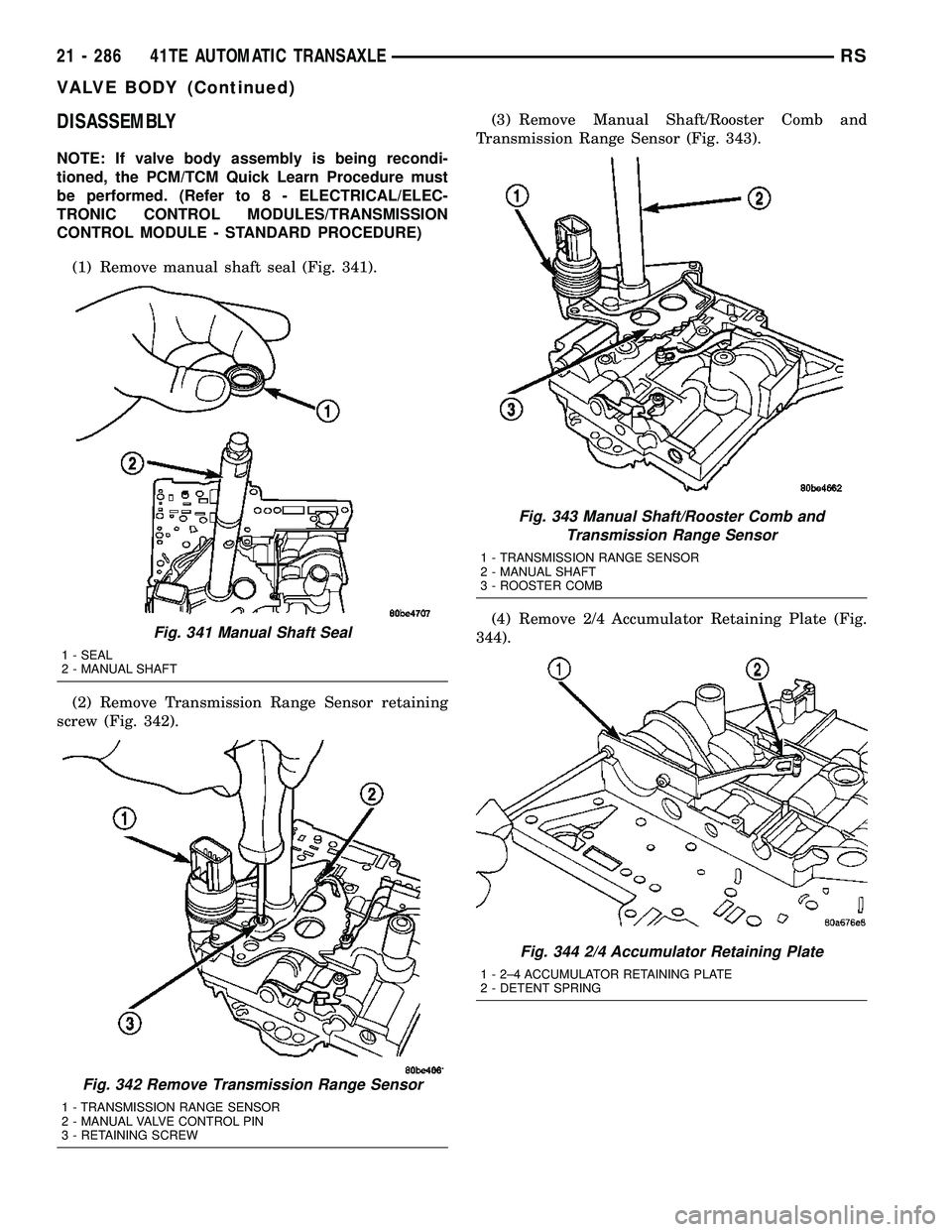
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: If valve body assembly is being recondi-
tioned, the PCM/TCM Quick Learn Procedure must
be performed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELEC-
TRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Remove manual shaft seal (Fig. 341).
(2) Remove Transmission Range Sensor retaining
screw (Fig. 342).(3) Remove Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor (Fig. 343).
(4) Remove 2/4 Accumulator Retaining Plate (Fig.
344).
Fig. 341 Manual Shaft Seal
1 - SEAL
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
Fig. 342 Remove Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
Fig. 343 Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
3 - ROOSTER COMB
Fig. 344 2/4 Accumulator Retaining Plate
1 - 2±4 ACCUMULATOR RETAINING PLATE
2 - DETENT SPRING
21 - 286 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)