Page 1603 of 2339
(8) Install the overdrive clutch (#5) check valve to
separator plate (Fig. 339)
(9) Install oil screen to separator plate (Fig. 340).(10) Install transfer plate to valve body and sepa-
rator plate. Make sure oil screen and #5 check valve
do not bind (Fig. 341).
(11) Install twenty-four transfer plate to valve
body screws (Fig. 342) and torque to 5 N´m (45 in.
lbs.).
Fig. 339 Install Overdrive Clutch (#5) Check Valve
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH (#5) CHECK VALVE
Fig. 340 Install Oil Screen
1 - OIL SCREEN
Fig. 341 Install Transfer Plate
1 - TRANSFER PLATE
Fig. 342 Install Valve Body to Transfer Plate Screws
1 - SCREW (24)
2 - TRANSFER PLATE
3 - VALVE BODY
21 - 142 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1604 of 2339
(12) Install 2/4 Accumulator components as shown
in (Fig. 343).
(13) Torque 2/4 Accumulator retainer to 5 N´m (45
in. lbs.) (Fig. 344).
(14) Install Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor (Fig. 345).
(15) Make sure Manual Valve control pin is con-
tained within the rooster comb slot (Fig. 346). Install
Transmission Range Sensor retaining screw (Fig.
346) and torque to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.).
Fig. 343 2/4 Accumulator Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - RETAINER PLATE
3 - DETENT SPRING
4 - RETURN SPRINGS
5 - PISTON
Fig. 344 2/4 Accumulator Retaining Plate
1 - 2±4 ACCUMULATOR RETAINING PLATE
2 - DETENT SPRING
Fig. 345 Install Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
3 - ROOSTER COMB
Fig. 346 Install Transmission Range Sensor
Retaining Screw
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 143
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1605 of 2339
(16) Install manual shaft seal (Fig. 347).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If valve body assembly is being replaced or
reconditioned, the ªQuick-Learnº procedure must
be performed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELEC-
TRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Install valve body assembly to transaxle (Fig.
348). Install and torque valve body-to-transaxle case
bolts (Fig. 349) to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).(2) Install transaxle oil filter (Fig. 350). Inspect
the o-ring and replace if necessary.
Fig. 347 Manual Shaft Seal
1 - SEAL
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
Fig. 348 Valve Body Removal/Installation
1 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 349 Valve Body Attaching Bolts
1 - VALVE BODY ATTACHING BOLTS (18)
2 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 350 Oil Filter
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
21 - 144 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1606 of 2339
(3) Ensure the transaxle oil pan and transaxle
case sealing surfaces are clean and dry. Install an
1/8º bead of MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant to the oil pan and install (Fig. 351). Torque oil
pan-to-transaxle case bolts (Fig. 352) to 19 N´m (165
in. lbs.).
(4) Lower vehicle.(5) Connect transmission range sensor connector.
(6) Install manual valve lever to manual shaft.
(7) Install gearshift cable to manual valve lever.
(8) Connect battery negative cable.
(9) Fill transaxle with MopartATF +4 Transmis-
sion fluid. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
Fig. 351 Oil Pan
1 - OIL PAN
2 - 1/8 INCH BEAD OF RTV SEALANT
3 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 352 Oil Pan Bolts
1 - OIL PAN BOLTS (USE RTV UNDER BOLT HEADS)
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 145
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1608 of 2339

VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................283
OPERATION..........................283
REMOVAL............................284DISASSEMBLY........................286
ASSEMBLY...........................291
INSTALLATION........................295
41TE AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
DESCRIPTION
The 41TE (Fig. 1) is a four-speed transaxle that is
a conventional hydraulic/mechanical assembly with
an integral differential, and is controlled with adap-
tive electronic controls and monitors. The hydraulic
system of the transaxle consists of the transaxle
fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic valves, and various
line pressure control components. An input clutch
assembly which houses the underdrive, overdrive,
and reverse clutches is used. It also utilizes separate
holding clutches: 2nd/4th gear and Low/Reverse. The
primary mechanical components of the transaxle con-
sist of the following:
²Three multiple disc input clutches
²Two multiple disc holding clutches
²Four hydraulic accumulators
²Two planetary gear sets
²Hydraulic oil pump
²Valve body²Solenoid/Pressure switch assembly
²Integral differential assembly
Control of the transaxle is accomplished by fully
adaptive electronics. Optimum shift scheduling is
accomplished through continuous real-time sensor
feedback information provided to the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) or Transmission Control Mod-
ule (TCM).
The PCM/TCM is the heart of the electronic control
system and relies on information from various direct
and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.) to deter-
mine driver demand and vehicle operating condi-
tions. With this information, the PCM/TCM can
calculate and perform timely and quality shifts
through various output or control devices (solenoid
pack, transmission control relay, etc.).
The PCM/TCM also performs certain self-diagnos-
tic functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 147
Page 1614 of 2339

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR
PRESSURE TESTS
Inoperative clutches can be located using a series
of tests by substituting air pressure for fluid pressure
(Fig. 5) (Fig. 6). The clutches may be tested by apply-
ing air pressure to their respective passages. The
valve body must be removed and Tool 6056 installed.
To make air pressure tests, proceed as follows:
NOTE: The compressed air supply must be free of
all dirt and moisture. Use a pressure of 30 psi.
Remove oil pan and valve body. See Valve body
removal.
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the overdrive clutch apply
passage and watch for the push/pull piston to move
forward. The piston should return to its starting
position when the air pressure is removed.
REVERSE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the reverse clutch apply pas-
sage and watch for the push/pull piston to move rear-
ward. The piston should return to its starting
position when the air pressure is removed.
2/4 CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the feed hole located on the
2/4 clutch retainer. Look in the area where the 2/4
piston contacts the first separator plate and watch
carefully for the 2/4 piston to move rearward. The
piston should return to its original position after the
air pressure is removed.
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the low/reverse clutch feed
hole (rear of case, between 2 bolt holes). Then, look
in the area where the low/reverse piston contacts the
first separator plate. Watch carefully for the piston to
move forward. The piston should return to its origi-
nal position after the air pressure is removed.
UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
Because this clutch piston cannot be seen, its oper-
ation is checked by function. Air pressure is applied
to the low/reverse and the 2/4 clutches. This locks the
output shaft. Use a piece of rubber hose wrapped
around the input shaft and a pair of clamp-on pliers
to turn the input shaft. Next apply air pressure to
the underdrive clutch. The input shaft should not
rotate with hand torque. Release the air pressure
and confirm that the input shaft will rotate.
Fig. 5 Air Pressure Test Plate
1 - TOOL 6056
2 - ACCUMULATORS
Fig. 6 Testing Reverse Clutch
1 - TOOL 6056
2 - AIR NOZZLE
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 153
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1615 of 2339
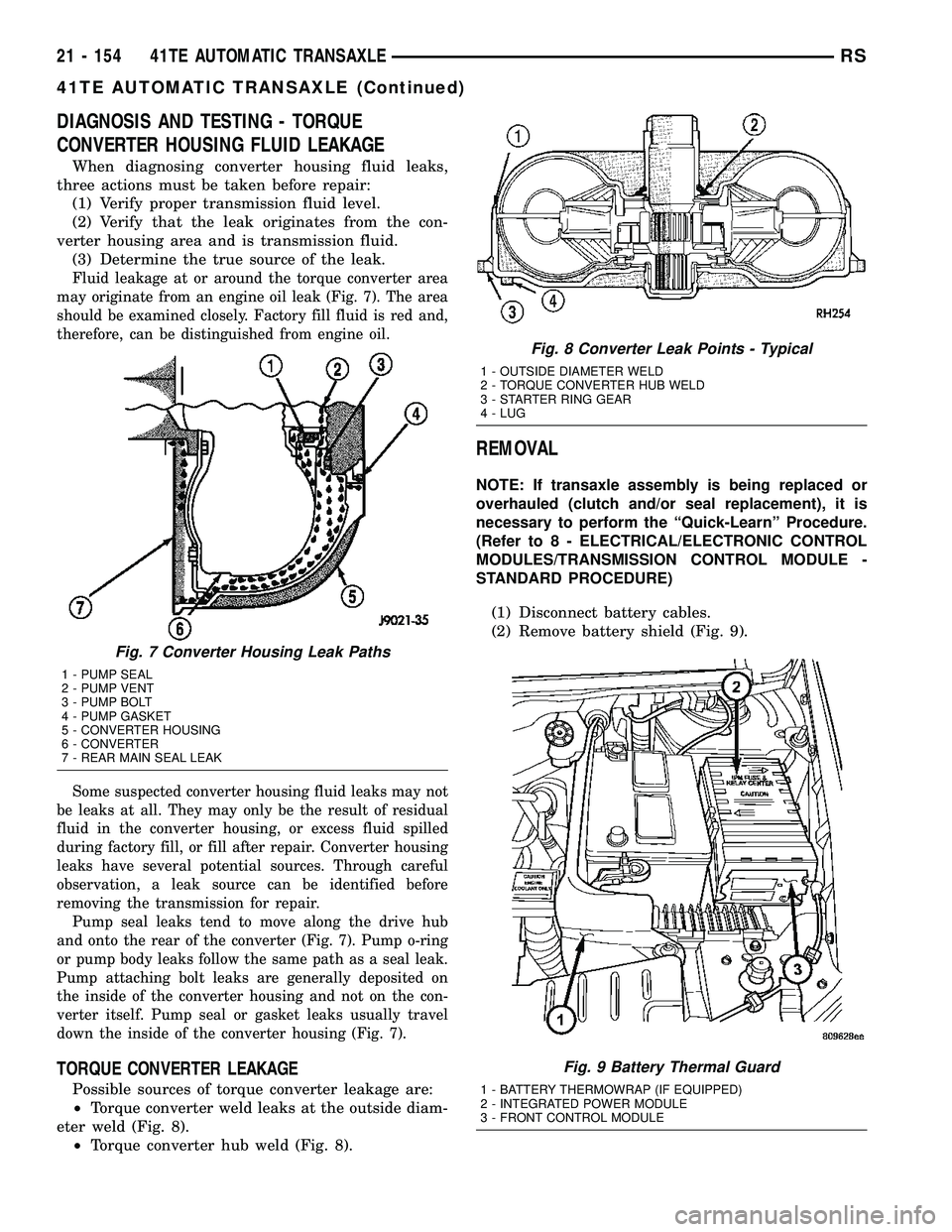
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
three actions must be taken before repair:
(1) Verify proper transmission fluid level.
(2) Verify that the leak originates from the con-
verter housing area and is transmission fluid.
(3) Determine the true source of the leak.
Fluid leakage at or around the torque converter area
may originate from an engine oil leak (Fig. 7). The area
should be examined closely. Factory fill fluid is red and,
therefore, can be distinguished from engine oil.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may not
be leaks at all. They may only be the result of residual
fluid in the converter housing, or excess fluid spilled
during factory fill, or fill after repair. Converter housing
leaks have several potential sources. Through careful
observation, a leak source can be identified before
removing the transmission for repair.
Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter (Fig. 7). Pump o-ring
or pump body leaks follow the same path as a seal leak.
Pump attaching bolt leaks are generally deposited on
the inside of the converter housing and not on the con-
verter itself. Pump seal or gasket leaks usually travel
down the inside of the converter housing (Fig. 7).
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
²Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diam-
eter weld (Fig. 8).
²Torque converter hub weld (Fig. 8).
REMOVAL
NOTE: If transaxle assembly is being replaced or
overhauled (clutch and/or seal replacement), it is
necessary to perform the ªQuick-Learnº Procedure.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield (Fig. 9).
Fig. 7 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
Fig. 8 Converter Leak Points - Typical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
Fig. 9 Battery Thermal Guard
1 - BATTERY THERMOWRAP (IF EQUIPPED)
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
21 - 154 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1619 of 2339
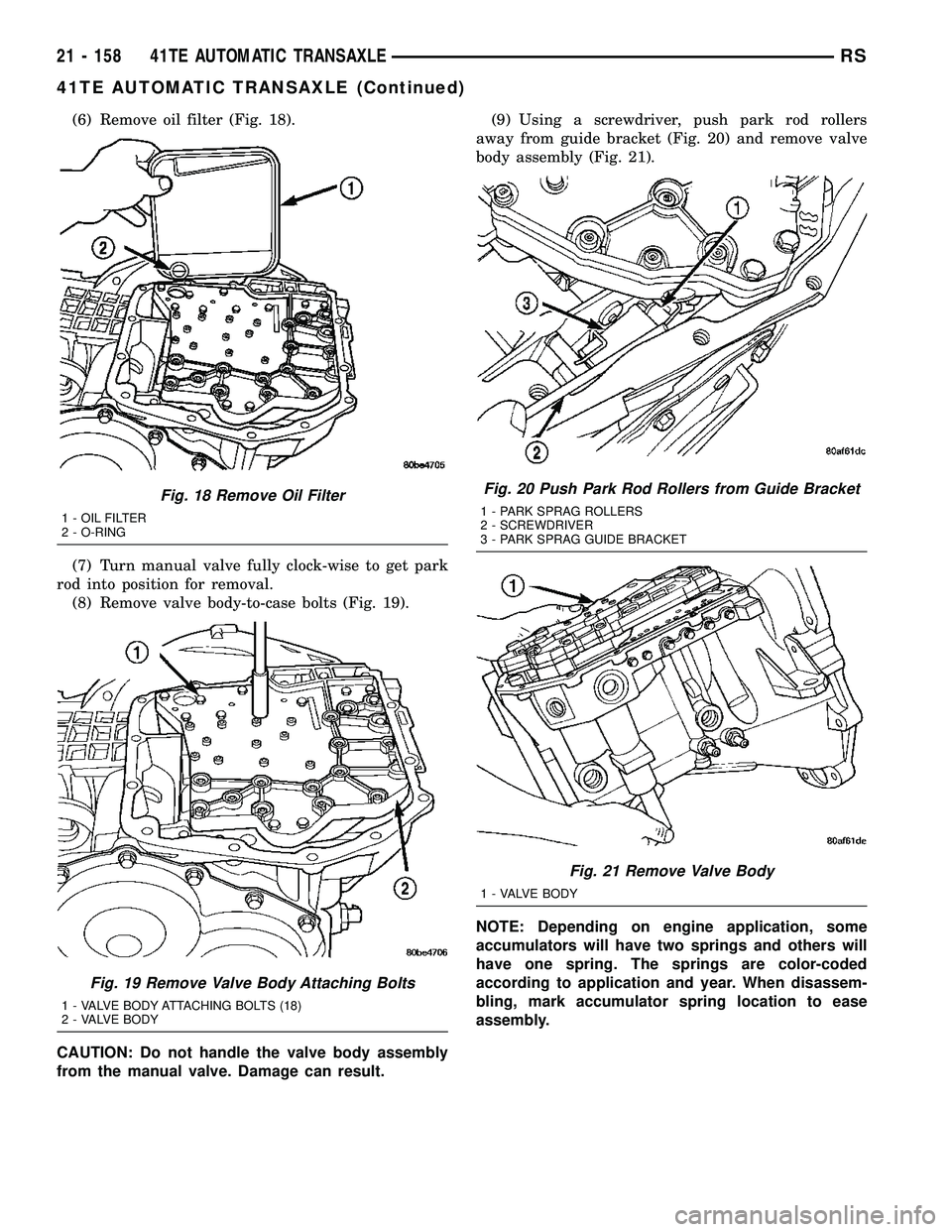
(6) Remove oil filter (Fig. 18).
(7) Turn manual valve fully clock-wise to get park
rod into position for removal.
(8) Remove valve body-to-case bolts (Fig. 19).
CAUTION: Do not handle the valve body assembly
from the manual valve. Damage can result.(9) Using a screwdriver, push park rod rollers
away from guide bracket (Fig. 20) and remove valve
body assembly (Fig. 21).
NOTE: Depending on engine application, some
accumulators will have two springs and others will
have one spring. The springs are color-coded
according to application and year. When disassem-
bling, mark accumulator spring location to ease
assembly.
Fig. 18 Remove Oil Filter
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
Fig. 19 Remove Valve Body Attaching Bolts
1 - VALVE BODY ATTACHING BOLTS (18)
2 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 20 Push Park Rod Rollers from Guide Bracket
1 - PARK SPRAG ROLLERS
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - PARK SPRAG GUIDE BRACKET
Fig. 21 Remove Valve Body
1 - VALVE BODY
21 - 158 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)