2004 ISUZU TF SERIES injector
[x] Cancel search: injectorPage 2627 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–51
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
The IAT sensor is a thermistor. A temperature changes
the resistance value. And it changes voltage. In other
words it measures a temperature value. Low air
temperature produces a high resistance.
The ECM supplies 5 volts signal to the IAT sensor
through resisters in the ECM and measures the voltage.
The signal voltage will be high when the air temperature
is cold, and it will be low when the air temperature is
hot.
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
The VSS is a magnet rotated by the transmission output
shaft. The VSS uses a hall element. It interacts with the
magnetic field treated by the rotating magnet. It outputs
pulse signal. The 12 volts operating supply from the
meter fuse.
Heated Oxygen (O2) Sensor
The heated ox ygen sensor consists of a 4-wire low
temperature activated zirconia ox ygen analyzer element
with heater for operating temperature of 315°C, and
there is one mounted on each ex haust pipe.
A constant 450millivolt is supplied by the ECM between
the two supply terminals, and oxygen concentration in
the ex haust gas is reported to the ECM as returned
signal voltage.
The ox ygen present in the ex haust gas reacts with the
sensor to produce a voltage output. This voltage should
constantly fluctuate from approx imately 100mV to
1000mV and the ECM calculates the pulse width
commanded for the injectors to produce the proper
combustion chamber mix ture.
Low ox ygen sensor output voltage is a lean mix ture
which will result in a rich commanded to compensate.
High ox ygen sensor output voltage is a rich mix ture
which result in a lean commanded to compensate.
When the engine is first started the system is in “Open
Loop” operation. In “Open Loop”, the ECM ignores the
signal from the ox ygen sensors. When various
conditions (ECT, time from start, engine speed &
ox ygen sensor output) are met, the system enters
“Closed Loop” operation. In “Closed Loop”, the ECM
calculates the air fuel ratio based on the signal from the
ox ygen sensors.
Heated ox ygen sensors are used to minimize the
amount of time required for closed loop fuel control to
begin operation and allow accurate catalyst monitoring.
The ox ygen sensor heater greatly decreases the
amount of time required for fuel control sensors to
become active.
Oxygen sensor heaters are required by catalyst monitor
and sensors to maintain a sufficiently high temperature
which allows accurate ex haust ox ygen content readings
further away from the engine.
C haract erist ic of I A T Sen sor -Ref erence-
10 100 1000 10000 100000
- 20 - 10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
I nt ake A i r T emp. ( deg . C ) ( Tec h2 R eadi ng )
Resistance (ohm) (Solid Line)
Page 2628 of 4264

6E–52 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR FUEL
METERING
The fuel metering system starts with the fuel in the fuel
tank. An electric fuel pump, located in the fuel tank,
pumps fuel to the fuel rail through an in-line fuel filter.
The pump is designed to provide fuel at a pressure
above the pressure needed by the injectors.
A fuel pressure regulator in the fuel rail keeps fuel
available to the fuel injectors at a constant pressure.
A return line delivers unused fuel back to the fuel tank.
The basic function of the air/fuel metering system is to
control the air/fuel delivery to the engine. Fuel is
delivered to the engine by individual fuel injectors
mounted in the intake manifold.
The main control sensor is the heated ox ygen sensor
located in the ex haust system. The heated ox ygen
sensor reports to the ECM how much oxygen is in the
ex haust gas. The ECM changes the air/fuel ratio to the
engine by controlling the amount of time that fuel
injector is “On”.
The best mix ture to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7
parts of air to 1 part of gasoline by weight, which allows
the catalytic converter to operate most efficiently.
Because of the constant measuring and adjusting of the
air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system is called a “closed
loop” system.
The ECM monitors signals from several sensors in
order to determine the fuel needs of the engine. Fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions called “mode”.
All modes are controlled by the ECM.
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
When battery voltage is low, the ECM will compensate
for the weak spark by increasing the following:
The amount of fuel delivered.
The idle RPM.
Clear Flood Mode
Clear a flooded engine by pushing the accelerator pedal
down all the way. The ECM then de-energizes the fuel
injectors. The ECM holds the fuel injectors de-energized
as long as the throttle remains above 75% and the
engine speed is below 800 RPM. If the throttle position
becomes less than 75%, the ECM again begins to pulse
the injectors ON and OFF, allowing fuel into the
cylinders.
Deceleration Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) Mode
The ECM reduces the amount of fuel injected when it
detects a decrease in the throttle position and the air
flow. When deceleration is very fast, the ECM may cut
off fuel completely. Until enable conditions meet the
engine revolution less 1000 rpm or manifold absolute
pressure less than 10 kPa.
Engine Speed/ Vehicle Speed/ Fuel Disable
Mode
The ECM monitors engine speed. It turns off the fuel
injectors when the engine speed increases above 6000
RPM. The fuel injectors are turned back on when
engine speed decreases below 3500 RPM.
Acceleration Mode
The ECM provides ex tra fuel when it detects a rapid
increase in the throttle position and the air flow.
Fuel Cutoff Mode
No fuel is delivered by the fuel injectors when the
ignition is OFF. This prevents engine run-on. In addition,
the ECM suspends fuel delivery if no reference pulses
are detected (engine not running) to prevent engine
flooding.
Starting Mode
When the ignition is first turned ON, the ECM energizes
the fuel pump relay for two seconds to allow the fuel
pump to build up pressure. The ECM then checks the
engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor and the
throttle position sensor to determine the proper air/fuel
ratio for starting.
The ECM controls the amount of fuel delivered in the
starting mode by adjusting how long the fuel injectors
are energized by pulsing the injectors for very short
times.
Run Mode
The run mode has the following two conditions:
Open loop
Closed loop
When the engine is first started, the system is in “open
loop” operation. In “Open Loop,” the ECM ignores the
signal from the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S). It
calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the TP,
ECT, and MAP sensors.
The system remains in “Open Loop” until the following
conditions are met:
The HO2S has a varying voltage output showing that
it is hot enough to operate properly (this depends on
temperature).
The ECT has reached a specified temperature.
A specific amount of time has elapsed since starting
the engine.
Engine speed has been greater than a specified RPM
since start-up.
The specific values for the above conditions vary with
different engines and are stored in the programmable
read only memory (PROM). When these conditions are
met, the system enters “closed loop” operation. In
“closed loop,” the ECM calculates the air/fuel ratio
(injector on-time) based on the signal from the HO2S.
This allows the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7:1.
Page 2629 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–53
Fuel Metering System Components
The fuel metering system is made up of the following
parts.
Fuel injector
Throttle body
Fuel rail
Fuel pressure regulator
ECM
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
Idle air control (IAC) valve
Fuel pump
Fuel Injector
The group fuel injection fuel injector is a solenoid
operated device controlled by the ECM. The ECM
energizes the solenoid, which opens a valve to allow
fuel delivery.
The fuel is injected under pressure in a conical spray
pattern at the opening of the intake valve. Ex cess fuel
not used by the injectors passes through the fuel
pressure regulator before being returned to the fuel
tank.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm-operated
relief valve mounted on the fuel rail with fuel pump
pressure on one side and manifold pressure on the
other side. The fuel pressure regulator maintains the
fuel pressure available to the injector at three times
barometric pressure adjusted for engine load. It may be
serviced separately.
If the pressure is too low or poor performance, DTC
P0131 or P1171 will be the result. If the pressure is too
high, DTC P0132 or P1167 will be the result. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis for information on diagnosing
fuel pressure conditions.
Fuel Rail
The fuel rail is mounted to the top of the engine and
distributes fuel to the individual injectors. Fuel is
delivered to the fuel inlet tube of the fuel rail by the fuel
lines. The fuel goes through the fuel rail to the fuel
pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator
maintains a constant fuel pressure at the injectors.
Remaining fuel is then returned to the fuel tank.
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit
When the key is first turned ON, the ECM energizes the
fuel pump relay for two seconds to build up the fuel
pressure quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the ECM shuts the fuel pump off and waits
until the engine is cranked. When the engine is cranked
and the 58X crankshaft position signal has been
detected by the ECM, the ECM supplies 12 volts to the
fuel pump relay to energize the electric in-tank fuel
pump.
An inoperative fuel pump will cause a “no-start”
condition. A fuel pump which does not provide enoughpressure will result in poor performance.
Thottle Body Unit
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the
amount of air delivered to the engine. The Thottle
position sensor and IAC valve are also mounted on the
throttle body.
Vacuum ports located behind the throttle plate provide
the vacuum signals needed by various components.
Engine coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in
the throttle body to warm the throttle valve and to
prevent icing.
Page 2647 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–71
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code
The purpose of the “Diagnostic Trouble Codes” mod e i s
to display stored trouble code in the ECM.
When “Clear DTC Information” is selected, a “Clear
DTC Information”, warning screen appears.
This screen informs you that by cleaning DTC's “all
stored DTC information in the ECM will be erased”.
After clearing codes, confirm system operation by test
driving the vehicle.
Use the “DTC Information” mode to search for a specific
type of stored DTC information.
History
This selection will display only DTCs that are stored in
the ECM's history memory. It will not display Type B
DTCs that have not requested the MIL (“Check EngineLamp”). It will display all type A and B DTCs that
requested the MIL and have failed within the last 40
warm-up cycles. In addition, it will display all type C and
D DTCs that have failed within the last 40 warm-up
cycles.
MIL SVC or Message Request
This selection will display only DTCs that are requesting
the MIL. Type C and Type D DTCs cannot be displayed
using the MIL. Type C and D DTCs cannot be displayed
using this option.
This selection will report type B DTCs only after the MIL
has been requested.
Last Test Failed
This selection will display only DTCs that have failed the
last time the test run. The last test may have run during
a previous ignition cycle of a type A or type B DTC is
displayed. For type C and type D DTCs, the last failure
must have occurred during the current ignition cycle to
appear as last test fail.
Test Failed Since Code Cleared
The selection will display all active and history DTCs
that have reported a test failure since the last time
DTCs were cleared. DTCs that last failed more that 40
warm-up cycles before this option is selected will not be
displayed.
No Run Since Code Cleared
This selection will display up to DTCs that have not run
since the DTCs were last cleared. Since any displayed
DTCs have not run, their condition (passing or failing) is
unknown.
Failed This Ignition
This selection will display all DTCs that have failed
during the present ignition cycle.
F1: Data Display
The purpose of the “Data Display” mode is to
continuously monitor data parameters.
The current actual values of all important sensors and
signals in the system are display through F1 mode.
See the “Typical Scan Data” section.
F2: Snapshot
“Snapshot” allows you to focus on making the condition
occur, rather than trying to view all of the data in
anticipation of the fault.
The snapshot will collect parameter information around
a trigger point that you select.
F3: Miscellaneous Test:
The purpose of “Miscellaneous Test” mode is to check
for correct operation of electronic system actuators.
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code
F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority
F1: Clear DTC Information
F2: DTC Information
F0: History
F1: MIL SVS or Message Requested
F2: Last Test Failed
F3: Test Failed Since Code Cleared
F4: Not Run Since Code Cleared
F5: Failed This Ignition
F1: Data Display
F0: Engine Data
F1: O2 Sensor Data
F2: Snapshot
F3: Miscellaneous Test
F0: Lamps
F0: Malfunction Indicator Lamps
F1: Relays
F0: Fuel Pump Relay
F1: A/C Clutch Relay
F2: EVAP
F0: Purge Solenoid
F3: IAC System
F0: IAC Control
F1: IAC Reset
F4: Injector Balance Test
Page 2648 of 4264
6E–72 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
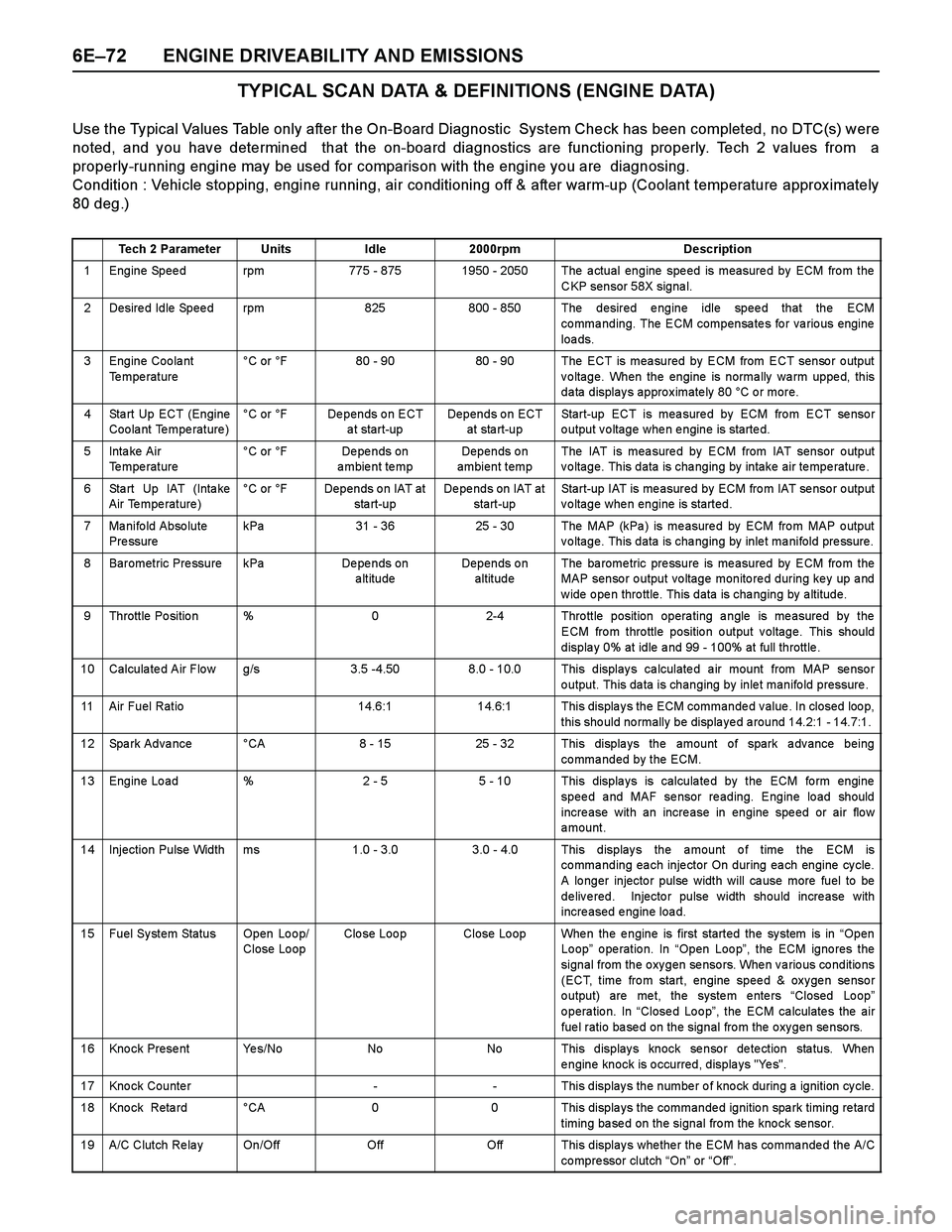
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS (ENGINE DATA)
Use the Typical Values Table only after the On-Board Diagnostic System Check has been completed, no DTC(s) were
noted, and you have determined that the on-board diagnostics are functioning properly. Tech 2 values from a
properly-running engine may be used for comparison with the engine you are diagnosing.
Condition : Vehicle stopping, engine running, air conditioning off & after warm-up (Coolant temperature approx imately
80 deg.)
Tech 2 ParameterUnitsIdle2000rpmDescription
1 Engine Speed rpm775 - 8751950 - 2050 The actual engine speed is measured by ECM from the
CKP sensor 58X signal.
2 Desired Idle Speed rpm825800 - 850 The desired engine idle speed that the ECM
commanding. The ECM compensates for various engine
loa ds.
3 Engine Coolant
Te mpe rature°C or °F80 - 9080 - 90 The ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor output
voltage. When the engine is normally warm upped, this
data displays approximately 80 °C or more.
4 Sta rt Up ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature)°C or °FDepends on ECT
a t start-upDepends on ECT
at sta rt-upStart-up ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor
output voltage when engine is started.
5Inta ke Air
Temperature °C or °FDe pe nds on
ambient tempDepends on
ambient tempThe IAT is mea sure d by ECM from IAT sensor o utput
voltage. This data is changing by intake air temperature.
6 Sta rt Up IAT (Inta ke
Air Temperature)°C or °FDepends on IAT at
sta rt-upDepends on IAT at
start-upStart-up IAT is me asured by ECM fro m IAT se nso r o utput
voltage when engine is started.
7 Manifold Absolute
Pre ssurekPa31 - 3625 - 30The MAP (kPa ) is me asure d by ECM fro m MAP o utput
voltage. This data is changing by inlet manifold pressure.
8 Barometric Pressure kPaDe pe nds on
altitudeDepends on
altitudeThe ba rome tric pre ssure is me asured by ECM fro m the
MAP sensor output voltage monitored during key up and
w ide o pe n thro ttle. This data is cha nging by a ltitude.
9 Throttle Position %02-4 Throttle position operating angle is measured by the
ECM from throttle position output voltage. This should
displa y 0% at idle a nd 99 - 100% at full throttle .
10 Calculated Air Flow g/s3.5 -4.508.0 - 10.0 This displays calculated air mount from MAP sensor
output. This data is changing by inlet manifold pressure .
11 Air Fuel Ratio14.6:114.6:1 This displays the ECM commanded value. In closed loop,
this should normally be displayed around 14.2:1 - 14.7:1.
12 Spark Advance °CA8 - 1525 - 32 This displays the amount of spark advance being
commanded by the ECM.
13 Engine Load %2 - 55 - 10 This displays is calculated by the ECM form engine
speed and MAF sensor reading. Engine load should
incre ase with an incre ase in engine spe ed or air flo w
amount.
14 Injection Pulse Width ms1.0 - 3.0 3.0 - 4.0 This displays the amount of time the ECM is
commanding each injector On during each engine cycle.
A lo nger injecto r pulse width will ca use more fuel to be
delivered. Injector pulse width should increase with
increased engine load.
15 Fuel System Status Open Loop/
Close LoopClo se Loo pClose Loop When the engine is first started the system is in “Open
Loop” operation. In “Open Loop”, the ECM ignores the
signal from the oxygen sensors. When various conditions
(ECT, time from start, engine speed & oxygen sensor
o utput) are me t, the syste m e nte rs “Closed Lo op”
o pera tio n. In “Close d Lo o p”, the ECM ca lculate s the air
fuel ratio based on the signal from the oxygen sensors.
16 Knock Present Yes/NoNoNo This displays knock sensor detection status. When
engine knock is occurred, displays "Yes".
17 Knock Counter-- This displays the number of knock during a ignition cycle.
18 Kno ck Reta rd °CA00 This displa ys the commande d ignitio n spa rk timing re tard
timing based on the signal from the knock sensor.
19 A/C Clutch Re la y On/OffOffOff This display s whe the r the ECM has co mma nde d the A/C
co mpre ssor clutch “On” or “Off”.
Page 2651 of 4264
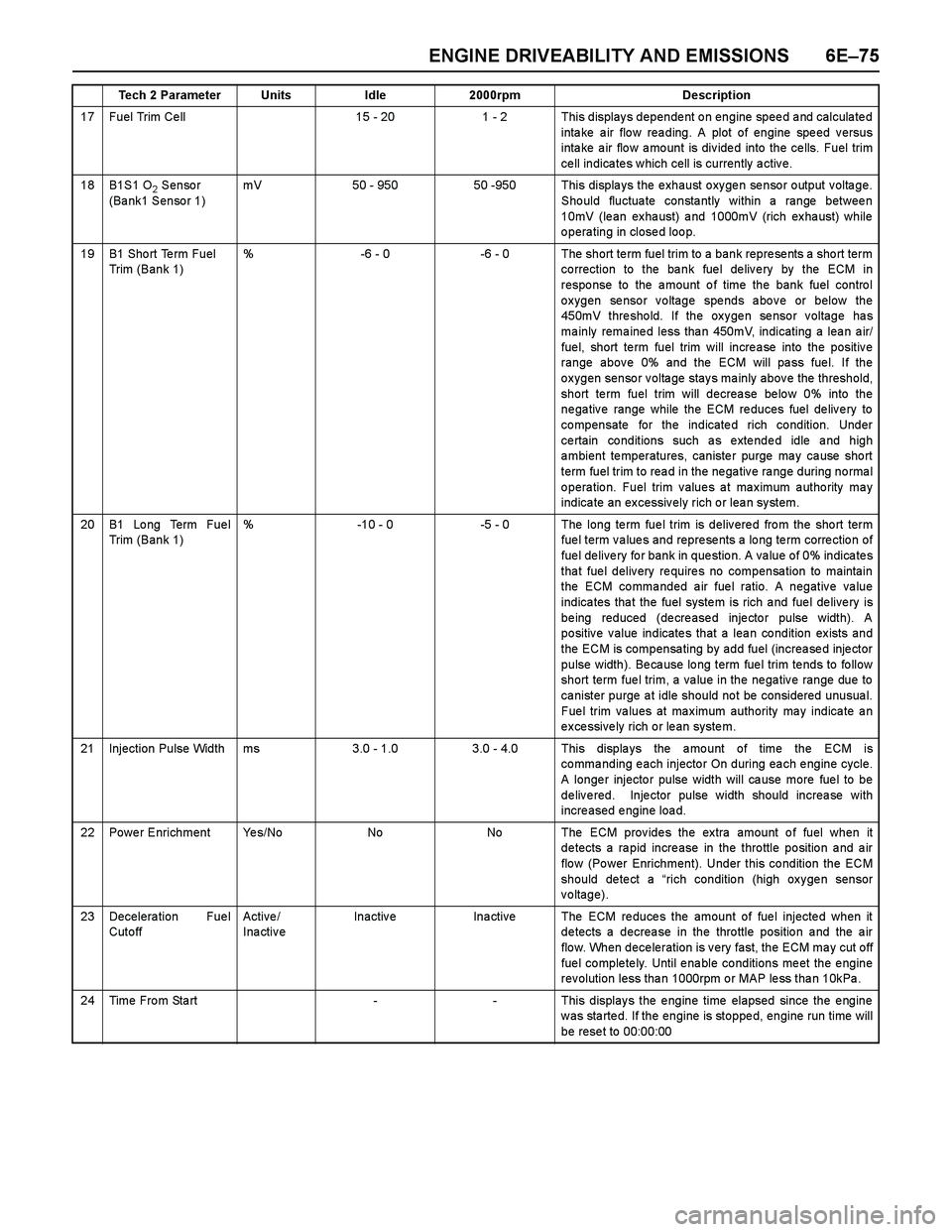
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–75
17 Fuel Trim Ce ll15 - 201 - 2 This displays dependent on engine speed and calculated
intake air flow reading. A plot of engine speed versus
inta ke a ir flo w a mo unt is div ide d into the ce lls. Fuel trim
ce ll indica te s w hich cell is currently a ctiv e.
18B1S1 O2 Sensor
(Bank1 Sensor 1)mV50 - 95050 -950 This displays the exhaust oxygen sensor output voltage.
Should fluctuate constantly within a range between
10mV (lean exhaust) and 1000mV (rich exhaust) while
operating in closed loop.
19B1 Sho rt Te rm Fuel
Trim (Bank 1)%-6 - 0-6 - 0 The short term fuel trim to a bank represents a short term
co rrection to the ba nk fue l de liv e ry by the ECM in
response to the amount of time the bank fuel control
oxygen sensor voltage spends above or below the
450mV threshold. If the oxygen sensor voltage has
ma inly rema ine d less tha n 450mV, indicating a lea n a ir/
fue l, short te rm fuel trim will incre a se into the positiv e
range above 0% and the ECM will pass fuel. If the
oxygen sensor voltage stays mainly above the threshold,
short term fuel trim will decrease below 0% into the
negative range while the ECM reduces fuel delivery to
compensate for the indicated rich condition. Under
ce rtain co nditions such a s e xte nde d idle a nd high
ambient temperatures, canister purge may cause short
term fuel trim to rea d in the ne ga tiv e ra nge during no rma l
operation. Fuel trim values at maximum authority may
indica te an ex cessiv ely rich o r lea n sy stem.
20B1 Lo ng Term Fue l
Trim (Bank 1)%-10 - 0-5 - 0 The long te rm fue l trim is deliv ere d fro m the sho rt term
fuel term values and represents a long term correction of
fuel delivery for bank in question. A value of 0% indicates
that fuel delivery requires no compensation to maintain
the ECM commanded air fuel ratio. A negative value
indica tes tha t the fuel syste m is rich a nd fue l de live ry is
being reduced (decreased injector pulse width). A
positive value indicates that a lean condition exists and
the ECM is compensating by add fuel (increased injector
pulse width). Be ca use lo ng term fue l trim te nds to fo llow
short term fuel trim, a value in the negative range due to
canister purge at idle should not be considered unusual.
Fuel trim values at maximum authority may indicate an
excessively rich or lean system.
21Injection Pulse Widthms3.0 - 1.03.0 - 4.0 This displays the amount of time the ECM is
co mma nding e ach injecto r On during ea ch e ngine cycle.
A longer injector pulse width will cause more fuel to be
delivered. Injector pulse width should increase with
increased engine load.
22Power EnrichmentYe s / N oNoNo The ECM provides the extra amount of fuel when it
detects a rapid increase in the throttle position and air
flo w (Po wer Enrichment). Under this co ndition the ECM
should detect a “rich condition (high oxygen sensor
voltage).
23Decelera tion Fue l
Cut o ff Active /
InactiveInactiveIna ctiveThe ECM reduces the amount of fuel injected when it
detects a decrease in the throttle position and the air
flow. When deceleration is very fast, the ECM may cut off
fue l co mple te ly. Until e na ble co nditions me et the e ngine
rev olution less tha n 1000rpm o r MAP le ss tha n 10kPa .
24Time From Start--This displays the engine time elapsed since the engine
w as sta rte d. If the engine is stoppe d, engine run time will
be rese t to 00:00:00
Tech 2 ParameterUnitsIdle2000rpmDescription
Page 2653 of 4264
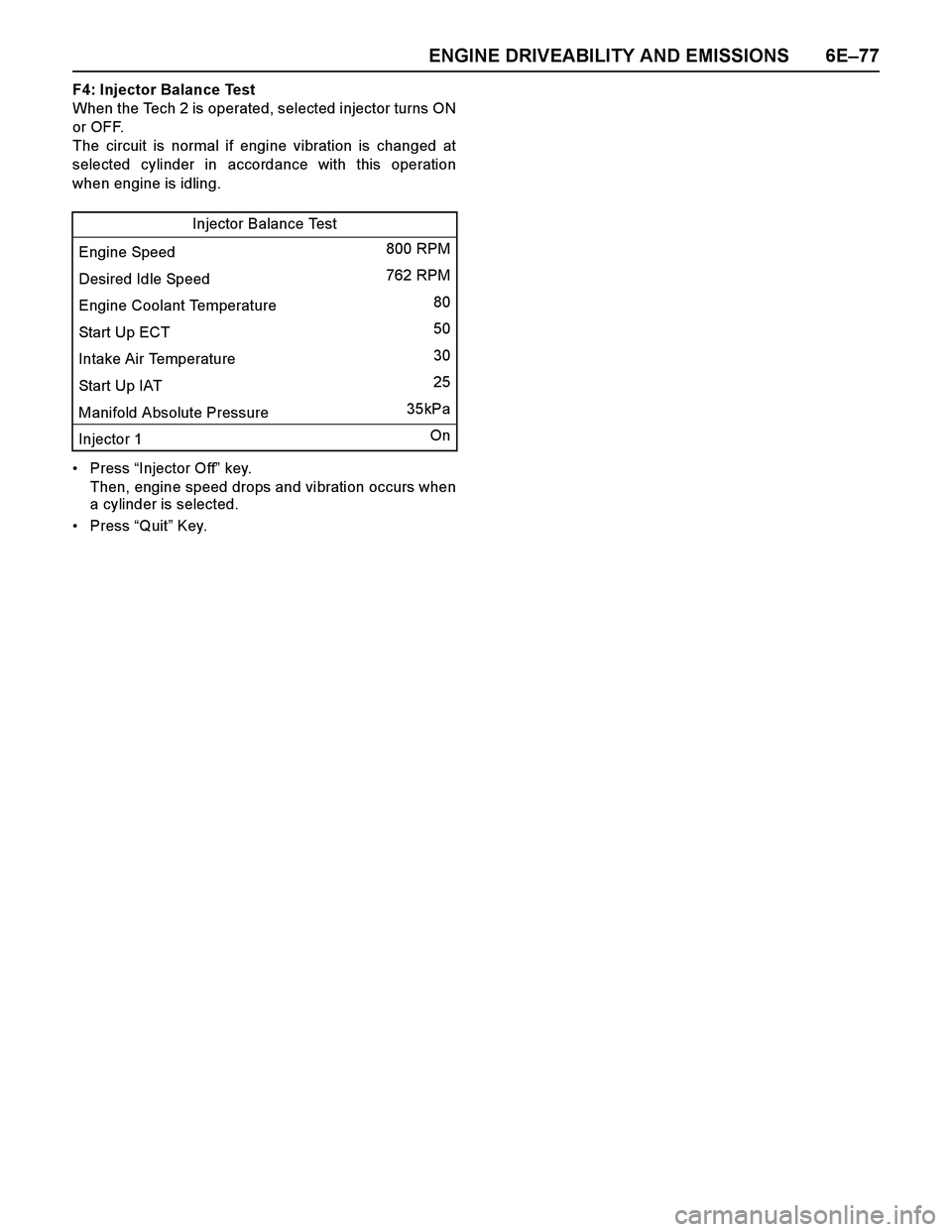
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–77
F4: Injector Balance Test
When the Tech 2 is operated, selected injector turns ON
or OFF.
The circuit is normal if engine vibration is changed at
selected cylinder in accordance with this operation
when engine is idling.
Press “Injector Off” key.
Then, engine speed drops and vibration occurs when
a cylinder is selected.
Press “Quit” Key.Injector Balance Test
Engine Speed 800 RPM
Desired Idle Speed 762 RPM
Engine Coolant Temperature 80
Start Up ECT 50
Intake Air Temperature 30
Start Up IAT 25
Manifold Absolute Pressure 35kPa
Injector 1 On
Page 2674 of 4264
6E–98 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FUEL METERING SYSTEM CHECK
Some failures of the fuel metering system will result in
an “Engine Cranks But Will Not Run” symptom. If this
condition ex ists, refer to the Cranks But Will Not Run
chart. This chart will determine if the problem is caused
by the ignition system, the ECM, or the fuel pump
electrical circuit.
Refer to Fuel System Electrical Test for the fuel system
wiring schematic.
If there is a fuel delivery problem, refer to Fuel System
Diagnosis, which diagnoses the fuel injectors, the fuel
pressure regulator, and the fuel pump.
Followings are applicable to the vehicles with
closed Loop System:
If a malfunction occurs in the fuel metering system, it
usually results in either a rich HO2S signal or a lean
HO2S signal. This condition is indicated by the HO2S
voltage, which causes the ECM to change the fuel
calculation (fuel injector pulse width) based on the
HO2S reading. Changes made to the fuel calculation
will be indicated by a change in the long term fuel trim
values which can be monitored with a Scan Tool. Ideal
long term fuel trim values are around 0%; for a lean
HO2S signal, the ECM will add fuel, resulting in a fuel
trim value above 0%. Some variations in fuel trim values
are normal because all engines are not ex actly the
same. If the evaporative emission canister purge is 02
status may be rich condition. 02 status indicates the
lean condition, refer to DTC P1171 for items which can
cause a lean HO2S signal.
FUEL INJECTOR COIL TEST PROCEDURE
AND FUEL INJECTOR BALANCE TEST
PROCEDURE
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. Relieve the fuel pressure by connecting 5-8840-
0378-0 T-Joint to the fuel pressure connection on the
fuel rail.
Caution: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury, wrap a shop towel around the
fuel pressure connection. The towel will absorb
any fuel leakage that occurs during the
connection of the fuel pressure gauge. Place the
towel in an approved container when the
connection of the fuel pressure gauge is
complete.
Place the fuel pressure gauge bleed hose in an
approved gasoline container.
With the ignition switch OFF open the valve on the
fuel pressure gauge.
3. Record the lowest voltage displayed by the DVM
after the first second of the test. (During the first
second, voltage displayed by the DVM may be
inaccurate due to the initial current surge.)
Injector Specifications:
The voltage displayed by the DVM should be
within the specified range.
The voltage displayed by the DVM may increase
throughout the test as the fuel injector windings
warm and the resistance of the fuel injector
windings changes.Resistance OhmsVoltage Specification at
10°C-35°C (50°F-95°F)
11.8-12.6 5.7-6.6