2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 93 of 2643

1C1 – 50I1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
33. Remove the crankshaft pulley bolt.
34. Remove the crankshaft pulley.
35. Disconnect the vacuum lines at the charcoal canis-
ter purge solenoid.
36. Disconnect the electrical connector at the charcoal
canister purge (CCP) solenoid and at the knock
sensor.
37. Disconnect the electrical connector at the oil pres-
sure switch and at the exhaust gas recirculation
(EGR) solenoid.
38. Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor (CPS)
connector.
39. Remove the transaxle torque converter bolts, if au-
tomatic transaxle equipped.
40. Remove the stater motor. Refer to Section 1E, En-
gine Electrical.
41. Remove the transaxle bell housing bolts.
42. Support the transaxle with a floor jack.
43. Install the engine lifting device.
44. Disconnect the right engine mount bracket from the
engine mount and the engine by removing the at-
taching bolts and the nuts.
45. Remove the right engine mount from the engine
block. Refer to ”Engine Mount” in this section.
46. Separate the engine block from the transaxle.
47. Remove the engine.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the engine into the engine compartment.
2. Align the engine alignment pins to the transaxle.
3. Install the transaxle bell housing bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the transaxle bell housing bolts to 75 NSm (55
lb–ft).
4. Install the right engine mount to the engine block.
Refer to ”Engine Mount” in this section.
Page 98 of 2643

1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C1 – 55
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
9. Inspect the engine block deck surface for flatness
using a straight edge and a feeler gauge. Refer to
”Engine Specifications” in this section.
10. Inspect the bearing bore for concentricity and align-
ment using a bore gauge. Refer to ”Engine Specifi-
cations” in this section. If the bearing bore is be-
yond specifications, replace the engine block.
11. Inspect the engine block cylinder bore for wear,
runout, ridging and taper using a bore gauge. Refer
to ”Engine Specifications” in this section.
12. Inspect the engine block cylinder bore for glazing.
Lightly hone the cylinder bore as necessary.
Installation Procedure
1. Align the notch on the piston and the connecting
rod so that the proper sides will be facing the front
of the engine.
2. Install the piston pin guide through the piston and
the connecting rod.
3. Coat the piston pin with clean oil.
4. Install the piston pin into the opposite side of the
piston.
5. Install the piston pin into the piston and connecting
rod assembly using the piston pin service set
KM–427.
6. Select a set of new piston rings.
7. Measure the piston ring gap using a feeler gauge.
Refer to ”Engine Specifications” in this section.
8. Increase the piston ring gap by carefully filing off
excess material if the piston ring gap is below spec-
ifications.
9. Measure the piston ring side clearance using a feel-
er gauge. Refer to ”Engine Specifications’’ in this
section.
10. If the piston ring is too thick, try another piston ring.
11. If no piston ring can be found that fits to specifica-
tions, the piston ring may be ground to size with
emery paper placed on a sheet of glass.
Page 105 of 2643
1C1 – 62I1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
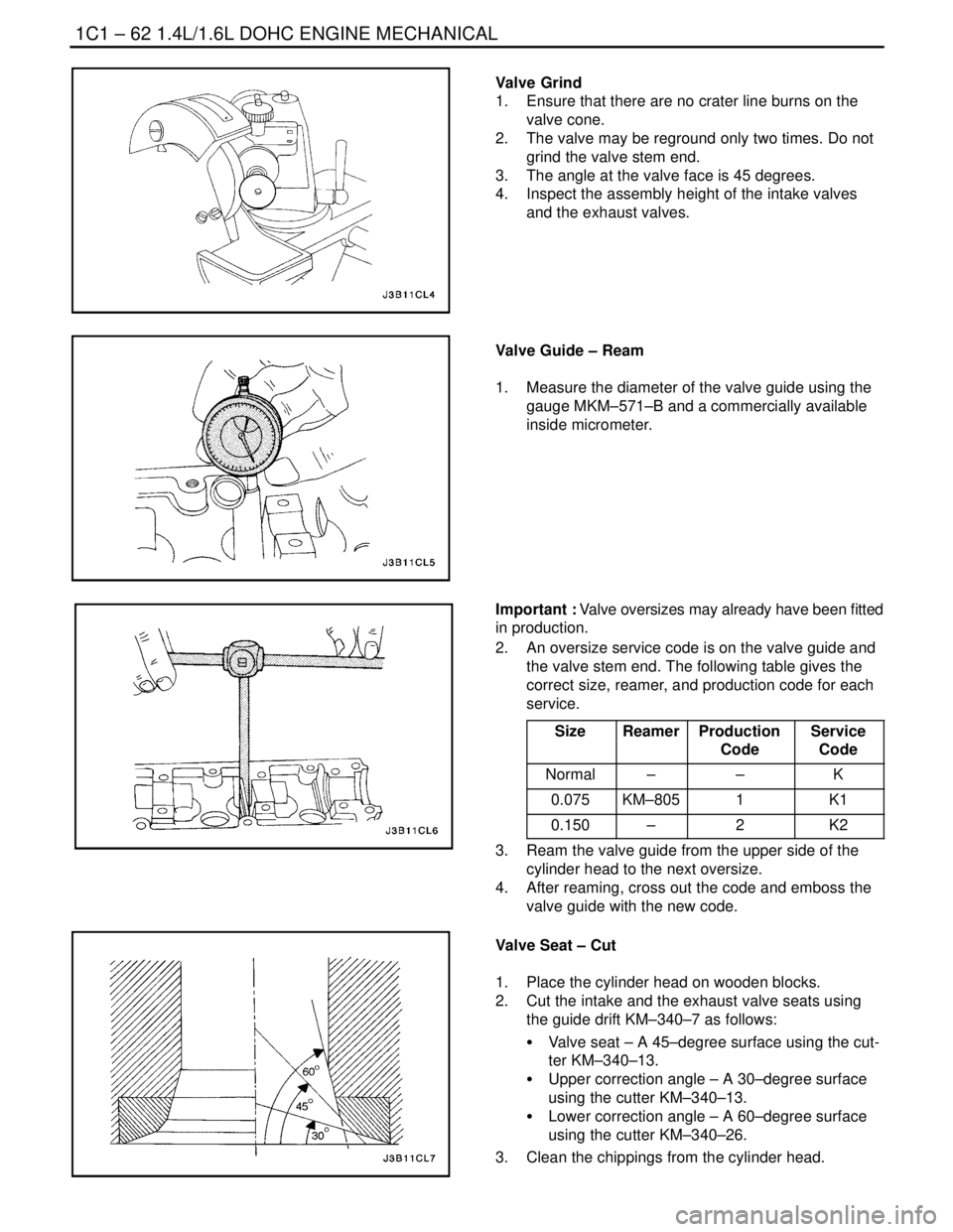
Valve Grind
1. Ensure that there are no crater line burns on the
valve cone.
2. The valve may be reground only two times. Do not
grind the valve stem end.
3. The angle at the valve face is 45 degrees.
4. Inspect the assembly height of the intake valves
and the exhaust valves.
Valve Guide – Ream
1. Measure the diameter of the valve guide using the
gauge MKM–571–B and a commercially available
inside micrometer.
Important : Valve oversizes may already have been fitted
in production.
2. An oversize service code is on the valve guide and
the valve stem end. The following table gives the
correct size, reamer, and production code for each
service.
Size
ReamerProduction
CodeService
Code
Normal––K
0.075KM–8051K1
0.150–2K2
3. Ream the valve guide from the upper side of the
cylinder head to the next oversize.
4. After reaming, cross out the code and emboss the
valve guide with the new code.
Valve Seat – Cut
1. Place the cylinder head on wooden blocks.
2. Cut the intake and the exhaust valve seats using
the guide drift KM–340–7 as follows:
S Valve seat – A 45–degree surface using the cut-
ter KM–340–13.
S Upper correction angle – A 30–degree surface
using the cutter KM–340–13.
S Lower correction angle – A 60–degree surface
using the cutter KM–340–26.
3. Clean the chippings from the cylinder head.
Page 112 of 2643
1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C1 – 69
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
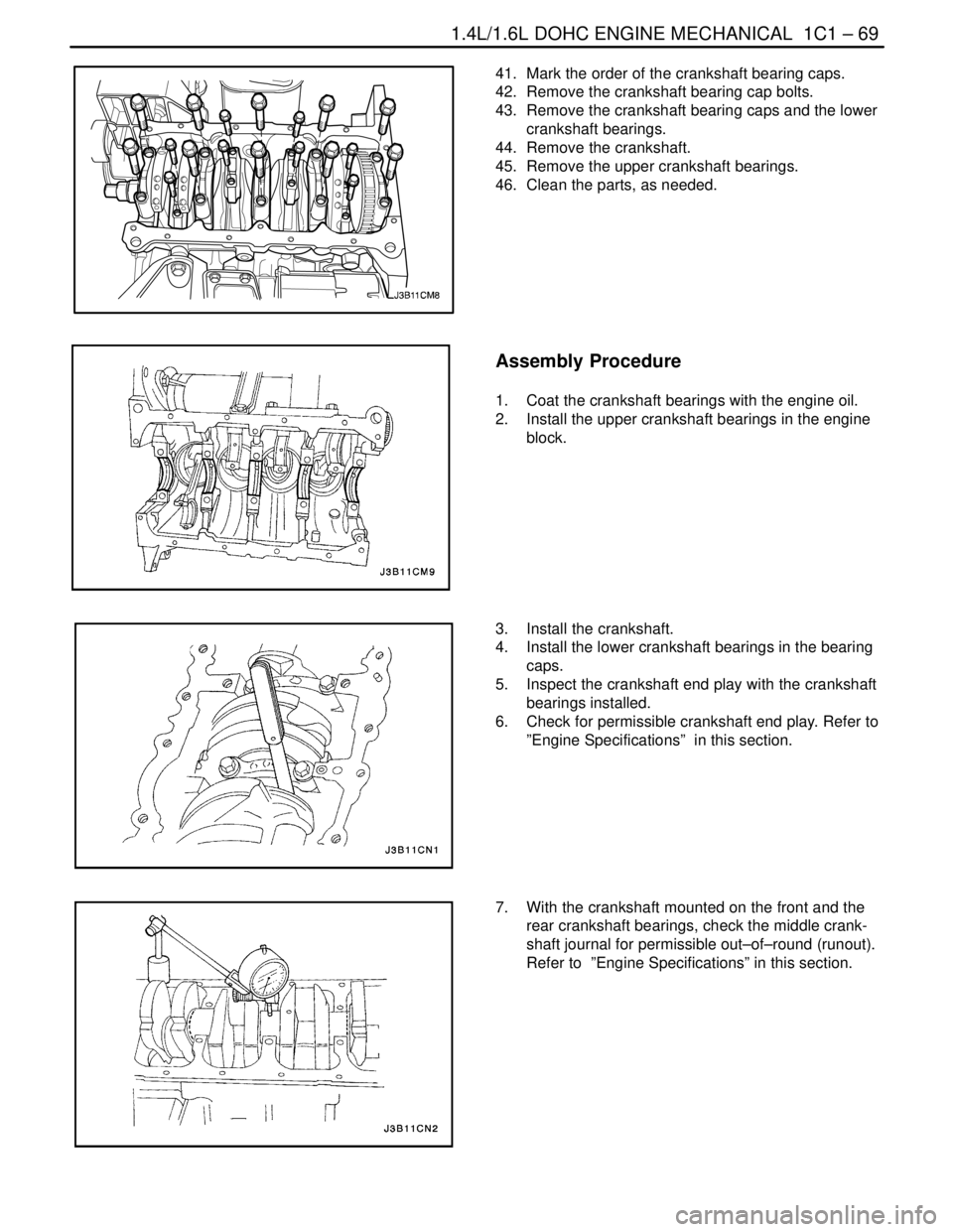
41. Mark the order of the crankshaft bearing caps.
42. Remove the crankshaft bearing cap bolts.
43. Remove the crankshaft bearing caps and the lower
crankshaft bearings.
44. Remove the crankshaft.
45. Remove the upper crankshaft bearings.
46. Clean the parts, as needed.
Assembly Procedure
1. Coat the crankshaft bearings with the engine oil.
2. Install the upper crankshaft bearings in the engine
block.
3. Install the crankshaft.
4. Install the lower crankshaft bearings in the bearing
caps.
5. Inspect the crankshaft end play with the crankshaft
bearings installed.
6. Check for permissible crankshaft end play. Refer to
”Engine Specifications” in this section.
7. With the crankshaft mounted on the front and the
rear crankshaft bearings, check the middle crank-
shaft journal for permissible out–of–round (runout).
Refer to ”Engine Specifications” in this section.
Page 113 of 2643
1C1 – 70I1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Important : Grease the crankshaft journals and lubri–cate
the crankshaft bearings slightly so that the plastic gauging
thread does not tear when the crankshaft bearing caps are
removed.
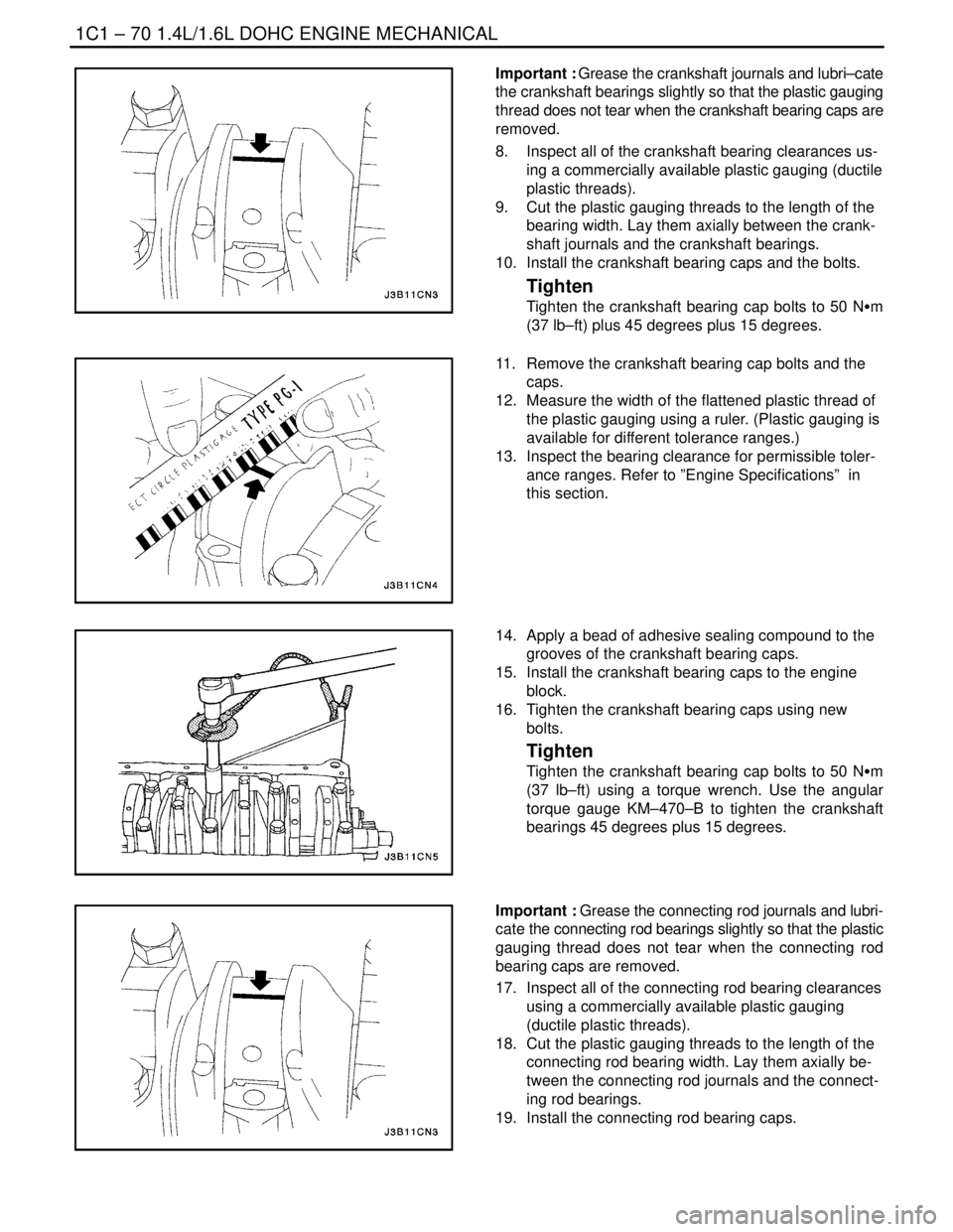
8. Inspect all of the crankshaft bearing clearances us-
ing a commercially available plastic gauging (ductile
plastic threads).
9. Cut the plastic gauging threads to the length of the
bearing width. Lay them axially between the crank-
shaft journals and the crankshaft bearings.
10. Install the crankshaft bearing caps and the bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the crankshaft bearing cap bolts to 50 NSm
(37 lb–ft) plus 45 degrees plus 15 degrees.
11. Remove the crankshaft bearing cap bolts and the
caps.
12. Measure the width of the flattened plastic thread of
the plastic gauging using a ruler. (Plastic gauging is
available for different tolerance ranges.)
13. Inspect the bearing clearance for permissible toler-
ance ranges. Refer to ”Engine Specifications” in
this section.
14. Apply a bead of adhesive sealing compound to the
grooves of the crankshaft bearing caps.
15. Install the crankshaft bearing caps to the engine
block.
16. Tighten the crankshaft bearing caps using new
bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the crankshaft bearing cap bolts to 50 NSm
(37 lb–ft) using a torque wrench. Use the angular
torque gauge KM–470–B to tighten the crankshaft
bearings 45 degrees plus 15 degrees.
Important : Grease the connecting rod journals and lubri-
cate the connecting rod bearings slightly so that the plastic
gauging thread does not tear when the connecting rod
bearing caps are removed.
17. Inspect all of the connecting rod bearing clearances
using a commercially available plastic gauging
(ductile plastic threads).
18. Cut the plastic gauging threads to the length of the
connecting rod bearing width. Lay them axially be-
tween the connecting rod journals and the connect-
ing rod bearings.
19. Install the connecting rod bearing caps.
Page 117 of 2643
1C1 – 74I1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
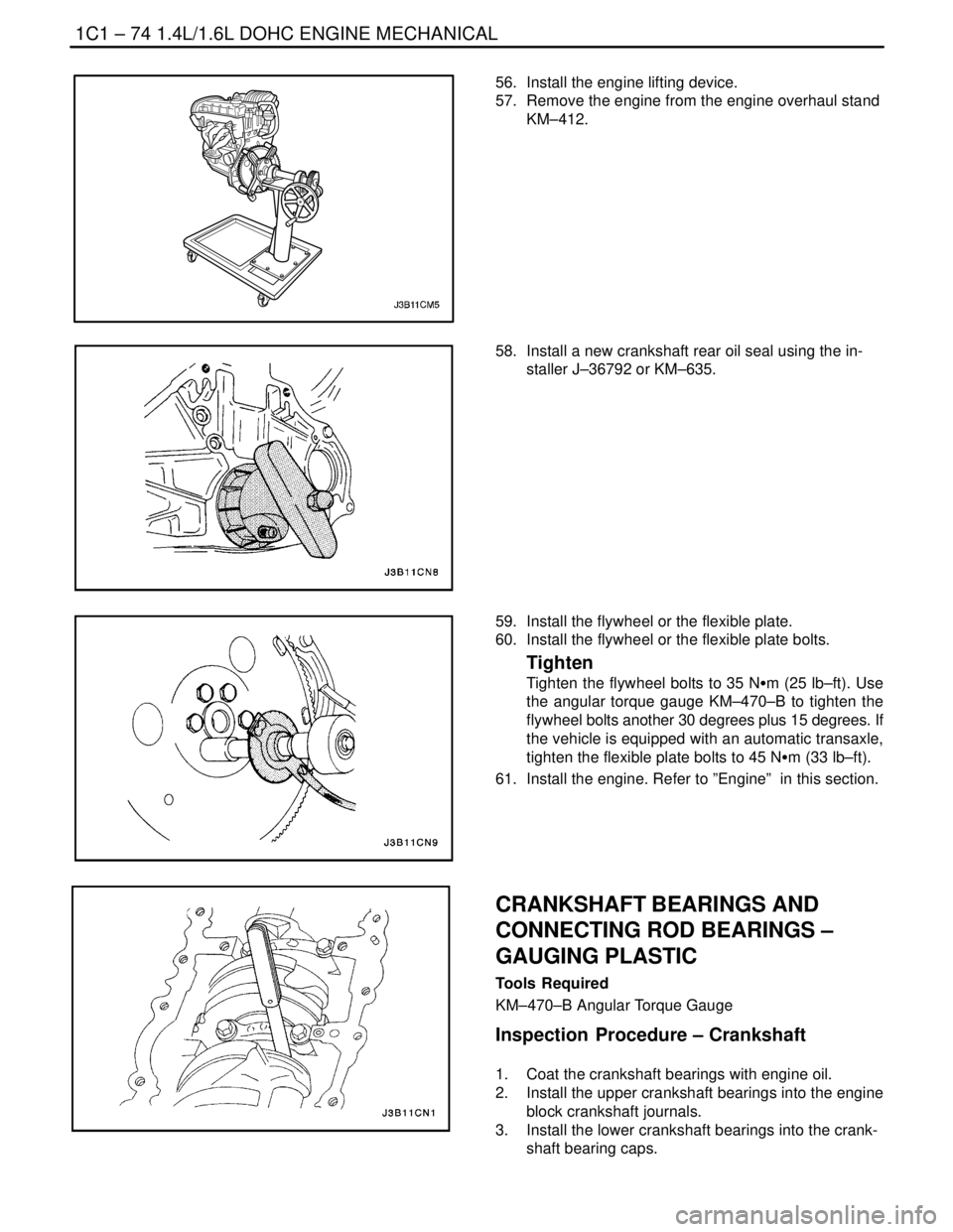
56. Install the engine lifting device.
57. Remove the engine from the engine overhaul stand
KM–412.
58. Install a new crankshaft rear oil seal using the in-
staller J–36792 or KM–635.
59. Install the flywheel or the flexible plate.
60. Install the flywheel or the flexible plate bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the flywheel bolts to 35 NSm (25 lb–ft). Use
the angular torque gauge KM–470–B to tighten the
flywheel bolts another 30 degrees plus 15 degrees. If
the vehicle is equipped with an automatic transaxle,
tighten the flexible plate bolts to 45 NSm (33 lb–ft).
61. Install the engine. Refer to ”Engine” in this section.
CRANKSHAFT BEARINGS AND
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS –
GAUGING PLASTIC
Tools Required
KM–470–B Angular Torque Gauge
Inspection Procedure – Crankshaft
1. Coat the crankshaft bearings with engine oil.
2. Install the upper crankshaft bearings into the engine
block crankshaft journals.
3. Install the lower crankshaft bearings into the crank-
shaft bearing caps.
Page 120 of 2643

1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C1 – 77
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
CYLINDER HEAD AND GASKET
The cylinder head is made of an aluminum alloy. The cylin-
der head uses cross–flow intake and exhaust ports. A
spark plug is located in the center of each combustion
chamber. The cylinder head houses the dual camshafts.
CRANKSHAFT
The crankshaft has eight integral weights which are cast
with it for balancing. Oil holes run through the center of the
crankshaft to supply oil to the connecting rods, the bear-
ings, the pistons, and the other components. The end
thrust load is taken by the thrust washers installed at the
center journal.
TIMING BELT
The timing belt coordinates the crankshaft and the dual
overhead camshafts and keeps them synchronized. The
timing belt also turns the water pump. The timing belt and
the pulleys are toothed so that there is no slippage be-
tween them. There are two idler pulleys. An automatic ten-
sioner pulley maintains the timing belt’s correct tension.
The timing belt is made of a tough reinforced rubber similar
to that used on the serpentine accessory drive belt. The
timing belt requires no lubrication.
OIL PUMP
The oil pump draws engine oil from the oil pan and feeds
it under pressure to the various parts of the engine. An oil
strainer is mounted before the inlet of the oil pump to re-
move impurities which could clog or damage the oil pump
or other engine components. When the drive gear rotates,
the driven gear rotates. This causes the space between
the gears to constantly open and narrow, pulling oil in from
the oil pan when the space opens and pumping the oil out
to the engine as it narrows.
At high engine speeds, the oil pump supplies a much high-
er amount of oil than is required for lubrication of the en-
gine. The oil pressure regulator prevents too much oil from
entering the engine lubrication passages. During normal
oil supply, a coil spring and valve keep the bypass closed,
directing all of the oil pumped to the engine. When the
amount of oil being pumped increases, the pressure be-
comes high enough to overcome the force of the spring.This opens the valve of the oil pressure regulator, allowing
the excess oil to flow through the valve and drain back to
the oil pan.
OIL PAN
The engine oil pan is mounted to the bottom of the cylinder
block. The engine oil pan houses the crankcase and is
made of cast metal.
Engine oil is pumped from the oil pan by the oil pump. After
it passes through the oil filter, it is fed through two paths
to lubricate the cylinder block and the cylinder head. In one
path, the oil is pumped through the oil passages in the
crankshaft to the connecting rods, then to the pistons and
the cylinders. It then drains back to the oil pan. In the sec-
ond path, the oil is pumped through the oil passages to the
camshaft. The oil passes through the internal passage-
ways in the camshafts to lubricate the valve assemblies
before draining back to the oil pan.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
A single four–port, rear–takedown manifold is used with
this engine. The manifold is designed to direct escaping
exhaust gases out of the combustion chambers with a
minimum of back pressure. The oxygen sensor is
mounted to the exhaust manifold.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
The intake manifold has four independent long ports and
uses inertial supercharging to improve engine torque at
low and moderate speeds. The plenum is attached to the
intake manifold.
CAMSHAFTS
This engine is a dual overhead camshaft (DOHC) type,
which means there are two camshafts. One camshaft op-
erates the intake valves, and the other camshaft operates
the exhaust valves. The camshafts sit in journals on the
top of the engine in the cylinder head and are held in place
by camshaft caps. The camshaft journals of the cylinder
head are drilled to create oil passages. Engine oil travels
to the camshafts under pressure where it lubricates each
camshaft journal. The oil returns to the oil pan through
drain holes in the cylinder head. The camshaft lobes are
machined into the solid camshaft to open and close the in-
take and the exhaust valves precisely the correct amount
at the correct time. The camshaft lobes are oiled by splash
action from pressurized oil escaping from the camshaft
journals.
Page 121 of 2643

SECTION : 1C2
1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
CAUTION : Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool
or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable will help
prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS1C2–2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Specifications 1C2–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fastener Tightening Specifcations 1C2–4. . . . . . . . . .
SPECIAL TOOLS1C2–6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Special Tools Table 1C2–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
COMPONENT LOCATOR1C2–8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Upper End 1C2–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lower End 1C2–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR1C2–12 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE 1C2–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshaft Cover 1C2–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cylinder Head and Gasket 1C2–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshafts 1C2–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Timing Belt Check and Adjust 1C2–24. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Timing Belt 1C2–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Pan 1C2–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Pump 1C2–33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Mount 1C2–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Manifold 1C2–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Exhaust Manifold 1C2–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshaft Gears 1C2–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Timing Belt Cover 1C2–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine 1C2–46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pistions and Rods 1C2–51. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UNIT REPAIR 1C2–56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cylinder Head and Valve Train Components 1C2–56.
Crankshaft 1C2–63. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Bearing and Connecting Rod
Beadings – Gauging Plastics 1C2–72. . . . . . . . . . . .
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION1C2–75 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cylinder Head and Gasket 1C2–75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft 1C2–75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Timing Belt 1C2–75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Pump 1C2–75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Pan 1C2–75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Exhaust Manifold 1C2–75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Manifold 1C2–75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshaft 1C2–75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .