2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA fuel
[x] Cancel search: fuelPage 316 of 2643

1F – 70IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
111. Replace the fuse Ef18 or repair the wire be-
tween the fuel pump relay connector terminal
30 and the battery.
2. Install the fuel pump relay.
3. Turn the ignition OFF for 10 seconds.
4. Turn the ignition ON.
Does the fuel pump operate for the time specified?2 secSystem OK–
121. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the ECM.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Does the fuel pump operate for the time specified?2 secSystem OK–
131. Replace the fuse Ef18 or repair the wire be-
tween the fuel pump relay connector terminal
30 and the ignition system
2. Install the fuel pump relay.
3. Turn the ignition OFF for 10 seconds.
4. Turn the ignition ON.
Does the fuel pump operate for the time specified?2 secSystem OK–
Page 317 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 71
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MAIN RELAY CIRCUIT CHECK (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
When the ignition is turned On or to the START position,
the main relay is energized. The main relay then supply
voltage to the engine fuse block fuse Ef11. The Electronic
Ignition (EI) system ignition coil, Evaporative Emission
(EVAP) Canister Purge Solenoid and Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S) are supplied voltage through the engine
fuse block fuse Ef11. The fuel injectors are supplied volt-
age through the engine fuse block fuse Ef11.Diagnostic Aids
S An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor
connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a
broken wire inside the insulation.
S A fault main relay will cause a no start condition.
There will be no voltage supplied to the EI system
ignition coil, or the fuel injectors. Without voltage
supplied to these components, they will not oper-
ate.
Main Relay Circuit Check (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the engine fuse block fuse Ef11.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. With a test light connected to the ground,
probe the fuse terminals nearest the main relay
for fuse Ef11.
Is the light on at both terminal?–System OKGo to Step 2
2Is the light on at only one terminal?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
3Repair the open in the wiring between the main relay
connector terminal 87 and the fuse Ef11.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 319 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 73
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MAIN RELAY CIRCUIT CHECK (1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
When the ignition is turned On or to the START position,
the main relay is energized. The main relay then supply
voltage to the engine fuse block fuse F2. The Electronic
Ignition (EI) system ignition coil, Evaporative Emission
(EVAP) Canister Purge Solenoid and Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S) are supplied voltage through the engine
fuse block fuse F2. The fuel injectors are supplied voltage
through the engine fuse block fuse F2.Diagnostic Aids
S An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor
connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a
broken wire inside the insulation.
S A fault main relay will cause a no start condition.
There will be no voltage supplied to the EI system
ignition coil, or the fuel injectors. Without voltage
supplied to these components, they will not oper-
ate.
Main Relay Circuit Check (1.8L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the I/P fuse block fuse F2.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. With a test light connected to the ground,
probe the fuse terminals nearest the ignition
relay for fuse F2.
Is the light on at both terminal?–System OKGo to Step 2
2Is the light on at only one terminal?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
3Repair the open in the wiring between the ignition
relay connector terminal 87 and the fuse F2.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 321 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 75
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE CHECK
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the changes in the intake manifold pressure which result
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and rpm
changes. The MAP sensor converts these changes into a
voltage output. The engine control module (ECM) sends
a 5–volt reference voltage to the MAP sensor. As the in-
take manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of the
MAP sensor also changes. A low voltage (high vacuum)
output of 1 to 2 volts is present at idle. A high voltage (low
vacuum) output of 4.0 to 4.8 volts is present at wide open
throttle. The MAP sensor is also used under certain condi-
tions to measure baro–metric pressure. This allows the
ECM to make adjustments for altitude changes. The ECMuses the MAP sensor for fuel delivery and ignition timing
changes.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. Applying 34 kPa (10 inches Hg) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor should cause the voltage to change.
Subtract the second voltage reading from the first.
That voltage value should be more than 1.5 volts.
When applying vacuum to the MAP sensor, the
change in the voltage should happen instantly. A
slow voltage change indicates a faulty MAP sensor.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor from the bracket and
twist the MAP sensor. Output changes more than
0.1 volt indicate a faulty connector or connection.
Page 323 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 77
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE CHECK (1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the changes in the intake manifold pressure which result
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and rpm
changes. The MAP sensor converts these changes into a
voltage output. The engine control module (ECM) sends
a 5–volt reference voltage to the MAP sensor. As the in-
take manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of the
MAP sensor also changes. A low voltage (high vacuum)
output of 1 to 2 volts is present at idle. A high voltage (low
vacuum) output of 4.0 to 4.8 volts is present at wide open
throttle. The MAP sensor is also used under certain condi-
tions to measure baro–metric pressure. This allows the
ECM to make adjustments for altitude changes. The ECMuses the MAP sensor for fuel delivery and ignition timing
changes.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. Applying 34 kPa (10 inches Hg) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor should cause the voltage to change.
Subtract the second voltage reading from the first.
That voltage value should be more than 1.5 volts.
When applying vacuum to the MAP sensor, the
change in the voltage should happen instantly. A
slow voltage change indicates a faulty MAP sensor.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor from the bracket and
twist the MAP sensor. Output changes more than
0.1 volt indicate a faulty connector or connection.
Page 325 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 79
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA (Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (0°C, 19°C). The char-
acteristics of the airflow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TPS is lower for small angles that
permits to be more precise during the idle speed control.
Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated mechanically by
a classical bowdencable.
The main throttle idle actuator (MTIA) provides a voltagesignal that changes in relation to the throttle plate angle.
The signal voltage will vary from about nearly 5.0 V at idles
to about 0.2V to 0.4 V at wide–open throttle. The TPS is
one of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel
control and other functions such as idle, wide open
throttle, deceleration enleanment, and acceleration en-
richment.
Diagnostic Aids
If the idle is too high, stop the engine. Fully extend the main
throttle idle actuator (MTIA) with a IAC driver. Start the en-
gine. If the idle speed is above 800 rpm, locate and repair
the vacuum leak. Also, check for a binding throttle plate or
throttle linkage or an incorrect base idle setting.
Page 356 of 2643
1F – 110IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
FUEL INJECTOR BALANCE TEST
A fuel injector tester is used to energize the injector for a
precise amount of time, thus spraying a measured amount
of fuel into the intake manifold. This causes a drop in the
fuel rail pressure that can be recorded and used tocompare each of the fuel injectors. All of the fuel injectors
should have the same pressure drop.
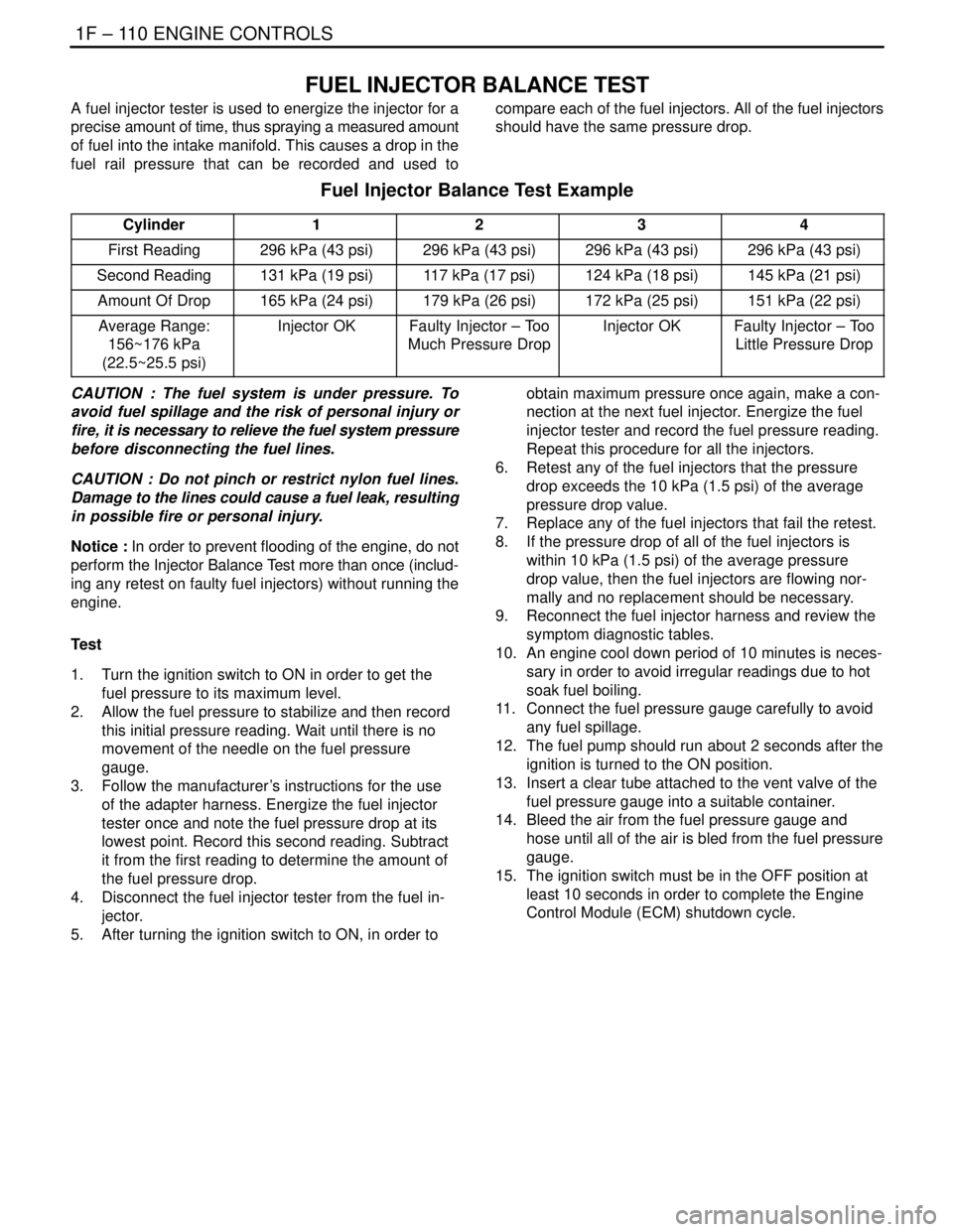
Fuel Injector Balance Test Example
Cylinder1234
First Reading296 kPa (43 psi)296 kPa (43 psi)296 kPa (43 psi)296 kPa (43 psi)
Second Reading131 kPa (19 psi)117 kPa (17 psi)124 kPa (18 psi)145 kPa (21 psi)
Amount Of Drop165 kPa (24 psi)179 kPa (26 psi)172 kPa (25 psi)151 kPa (22 psi)
Average Range:
156~176 kPa
(22.5~25.5 psi)Injector OKFaulty Injector – Too
Much Pressure DropInjector OKFaulty Injector – Too
Little Pressure Drop
CAUTION : The fuel system is under pressure. To
avoid fuel spillage and the risk of personal injury or
fire, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system pressure
before disconnecting the fuel lines.
CAUTION : Do not pinch or restrict nylon fuel lines.
Damage to the lines could cause a fuel leak, resulting
in possible fire or personal injury.
Notice : In order to prevent flooding of the engine, do not
perform the Injector Balance Test more than once (includ-
ing any retest on faulty fuel injectors) without running the
engine.
Test
1. Turn the ignition switch to ON in order to get the
fuel pressure to its maximum level.
2. Allow the fuel pressure to stabilize and then record
this initial pressure reading. Wait until there is no
movement of the needle on the fuel pressure
gauge.
3. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the use
of the adapter harness. Energize the fuel injector
tester once and note the fuel pressure drop at its
lowest point. Record this second reading. Subtract
it from the first reading to determine the amount of
the fuel pressure drop.
4. Disconnect the fuel injector tester from the fuel in-
jector.
5. After turning the ignition switch to ON, in order toobtain maximum pressure once again, make a con-
nection at the next fuel injector. Energize the fuel
injector tester and record the fuel pressure reading.
Repeat this procedure for all the injectors.
6. Retest any of the fuel injectors that the pressure
drop exceeds the 10 kPa (1.5 psi) of the average
pressure drop value.
7. Replace any of the fuel injectors that fail the retest.
8. If the pressure drop of all of the fuel injectors is
within 10 kPa (1.5 psi) of the average pressure
drop value, then the fuel injectors are flowing nor-
mally and no replacement should be necessary.
9. Reconnect the fuel injector harness and review the
symptom diagnostic tables.
10. An engine cool down period of 10 minutes is neces-
sary in order to avoid irregular readings due to hot
soak fuel boiling.
11. Connect the fuel pressure gauge carefully to avoid
any fuel spillage.
12. The fuel pump should run about 2 seconds after the
ignition is turned to the ON position.
13. Insert a clear tube attached to the vent valve of the
fuel pressure gauge into a suitable container.
14. Bleed the air from the fuel pressure gauge and
hose until all of the air is bled from the fuel pressure
gauge.
15. The ignition switch must be in the OFF position at
least 10 seconds in order to complete the Engine
Control Module (ECM) shutdown cycle.
Page 357 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 111
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
CLEARING TROUBLE CODES
Notice : To prevent Engine Control Module (ECM) dam-
age, the key must be OFF when disconnecting or recon-
necting the power to the ECM (for example battery cable,
ECM pigtail connector, ECM fuse, jumper cables,
etc.).When the ECM sets a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC), the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) lamp will be
turned on only for type A, B and E but a DTC will be stored
in the ECM’s memory for all types of DTC. If the problemis intermittent, the MIL will go out after 10 seconds if the
fault is no longer present. The DTC will stay in the ECM’s
memory until cleared by scan tool. Removing battery volt-
age for 10 seconds will clear some stored DTCs.
DTCs should be cleared after repairs have been com-
pleted. Some diagnostic tables will tell you to clear the
codes before using the chart. This allows the ECM to set
the DTC while going through the chart, which will help to
find the cause of the problem more quickly.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
DTCFunctionError
TypeIlluminate MIL
P0107Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Low VoltageAYES
P0108Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor High VoltageAYES
P0112Intake Air Temperature Sensor Low VoltageEYES
P0113Intake Air Temperature Sensor High VoltageEYES
P0117Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Low VoltageAYES
P0118Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor High VoltageAYES
P0122Throttle Position Sensor Low VoltageAYES
P0123Throttle Position Sensor High VoltageAYES
P0131Front Heated Oxygen Sensor Low VoltageAYES
P0132Front Heated Oxygen Sensor High VoltageAYES
P0133Front Heated Oxygen Sensor No ActivityEYES
P0135Front Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit Not FunctioningEYES
P0137Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor Low VoltageEYES
P0138Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor High VoltageEYES
P0140Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor No ActivityEYES
P0141Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater MalfuctionEYES
P0171Fuel Trim System Too LeanEYES
P0172Fuel Trim System Too RichEYES
P0222Main Throttle Idle Actuactor (MTIA) Low VoltageAYES
P0223Main Throttle Idle Actuactor (MTIA) High VoltageAYES
P0261Injector 1 Low VoltageAYES
P0262Injector 1 High VoltageAYES
P0264Injector 2 Low VoltageAYES
P0265Injector 2 High VoltageAYES
P0267Injector 3 Low VoltageAYES
P0268Injector 3 High VoltageAYES
P0270Injector 4 Low VoltageAYES
P0271Injector 4 High VoltageAYES
P0300Multiple Cylinder Misfire (Catalyst Damage)ABLINKING