2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Ground
[x] Cancel search: GroundPage 1667 of 2643

AISIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A2 – 77
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0753
SHIFT SOLENOID 1 (SS1) ELECTRICAL
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S TCM detects that the ON signal of the Shift Sole-
noid 1 (SS1) monitor during 0.5 seconds when SS1
driver outputs the OFF signal.(When the SS1 circuit
is open or short to battery).
S TCM detects that the OFF signal of the Shift Sole-
noid 1 (SS1) monitor during 0.3 seconds when SS1
driver outputs the ON signal.(When the SS1 circuit
is short to ground).
S The above detection 2 times at shifting continuous-
ly.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S TCM will request the illumination of MIL and store
DTC when TCM detects a failure on the first ignition
cycle.
S No lockup control
S No engine torque reduction control
S No engagement pressure control
S No timing solenoid control for N–D
S No self–learning control
S After failure decision : emergency modeTCM Shifting Pattern (Range : D)
Normal
SS1 FAIL
GearSS1SS2GearSS1SS2
1 stONON3 rdFAILOFF
2 ndONOFF3 rdFAILOFF
3 rdOFFOFF3 rdFAILOFF
4 thOFFON4 thFAILON
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
S The TCM turns off the MIL when no further failures
detected for three consecutive ignition cycles.
S The scan tool can clear the DTC from the TCM his-
tory.
S The TCM clears the DTC from the TCM history
memory after forty consecutive warm up cycles
without fault.
S TCM detects the ON signal of the SS1 monitor dur-
ing 160 ms when SS1 driver outputs the ON signal
and TCM detects the OFF signal of the SS1 moni-
tor during 160 ms when SS1 driver outputs the
OFF signal.
Page 1668 of 2643
5A2 – 78IAISIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Cause of Failure
S Wiring harness or connector between Shift Sole-noid 1 (SS1) and TCM
S SS1
S TCM
DTC P0753 Shift Solenoid 1 (SS1) Electrical
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Install the Scan tool.
3. With the engine OFF, turn the ignition switch to
the ON position.
4. Select Store Freeze Frame/Failure Records
from the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Information
menu.
5. Store Freeze Frame/Failure Records.
6. Select Clear DTC Information from the Diag-
nostic Trouble Codes Information menu.
7. Clear DTC Information.
8. Perform one vehicle drive cycle.
Is the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) ON?–Go to Step 2Repair the tem-
porary connec-
tion failure of
connector (Re-
fer to ”Wiring
Harness and
Connector In-
spection” in this
section.)
21. Select Request DTC by Status from the Diag-
nostic Trouble Codes Information menu.
2. Request DTC by Status.
Is DTC P0753 displayed?–Go to Step 3Repair the tem-
porary connec-
tion failure of
connector (Re-
fer to ”Wiring
Harness and
Connector In-
spection” in this
section.)
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Inspect the resistance between the vehicle har-
ness and Shift Solenoid 1 (SS1). Refer to ”Unit
Inspection” in this section.
3. Disconnect the TCM connector (X–1) and in-
spect the resistance between the terminal A16
and A23.
Is the measurement within the specified value?20°C (68°F)
11–16 WGo to Step 4Go to Step 5
41. Estimate the failure of between the vehicle wir-
ing harness connector and TCM.
2. Inspect the connector. Refer to ”Wiring Har-
ness and Connector Inspection” in this section.
3. Inspect the connection condition between the
connectors (C–1).
Is the connection condition OK?–Go to Step 6Repair the wir-
ing harness
connectors.
51. Estimate the failure of between the vehicle har-
ness and SS1.
2. Disconnect the connector (X–3) of T/M wire
and inspect the resistance between SS1 con-
nector terminal 5 and ground.
Is the measurement within the specified value?20°C (68°F)
11–16 WGo to Step 7Go to Step 8
Page 1672 of 2643

5A2 – 82IAISIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0758
SHIFT SOLENOID 2 (SS2) ELECTRICAL
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S TCM detects that the ON signal of the Shift Sole-
noid 2 (SS2) monitor during 0.5 seconds when SS2
driver outputs the OFF signal.(When the SS2 circuit
is open or short to battery).
S TCM detects that the OFF signal of the Shift Sole-
noid 2 (SS2) monitor during 0.3 seconds when SS2
driver outputs the ON signal.(When the SS2 circuit
is short to ground).
S The above detection 2 times at shifting continuous-
ly.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S TCM will request the illumination of MIL and store
DTC when TCM detects a failure on the first ignition
cycle.
S No lockup control
S No engine torque reduction control
S No engagement pressure control
S No timing solenoid control for N–D
S No self–learning control
S After failure decision : emergency modeTCM Shifting Pattern (Range : D)
Normal
SS2 FAIL
GearSS1SS2GearSS1SS2
1 stONON2 ndONFAIL
2 ndONOFF2 ndONFAIL
3 rdOFFOFF3 rdOFFFAIL
4 thOFFON3 rdOFFFAIL
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
S The TCM turns off the MIL when no further failures
detected for three consecutive ignition cycles.
S The scan tool can clear the DTC from the TCM his-
tory.
S The TCM clears the DTC from the TCM history
memory after forty consecutive warm up cycles
without fault.
S TCM detects the ON signal of the SS2 monitor dur-
ing 160 ms when SS2 driver outputs the ON signal
and TCM detects the OFF signal of the SS2 moni-
tor during 160 ms when SS2 driver outputs the
OFF signal.
Page 1673 of 2643
AISIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A2 – 83
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Cause of Failure
S Wiring harness or connector between Shift Sole-noid 2 (SS2) and TCM
S SS2
S TCM
DTC P0758 Shift Solenoid 2 (SS2) Electrical
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Install the Scan tool.
3. With the engine OFF, turn the ignition switch to
the ON position.
4. Select Store Freeze Frame/Failure Records
from the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Information
menu.
5. Store Freeze Frame/Failure Records.
6. Select Clear DTC Information from the Diag-
nostic Trouble Codes Information menu.
7. Clear DTC Information.
8. Perform one vehicle drive cycle.
Is the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) ON?–Go to Step 2Repair the tem-
porary connec-
tion failure of
connector (Re-
fer to ”Wiring
Harness and
Connector In-
spection” in this
section.)
21. Select Request DTC by Status from the Diag-
nostic Trouble Codes Information menu.
2. Request DTC by Status.
Is DTC P0758 displayed?–Go to Step 3Repair the tem-
porary connec-
tion failure of
connector (Re-
fer to ”Wiring
Harness and
Connector In-
spection” in this
section.)
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Inspect the resistance between the vehicle har-
ness and Shift Solenoid 2 (SS2). Refer to ”Unit
Inspection” in this section.
3. Disconnect the TCM connector (X–1) and in-
spect the resistance between the terminal A15
and A23.
Is the measurement within the specified value?20°C (68°F)
11–16 WGo to Step 4Go to Step 5
41. Estimate the failure of between the vehicle wir-
ing harness connector and TCM.
2. Inspect the connector. Refer to ”Wiring Har-
ness and Connector Inspection” in this section.
3. Inspect the connection condition between the
connectors (C–1).
Is the connection condition OK?–Go to Step 6Repair the wir-
ing harness
connectors.
51. Estimate the failure of between the vehicle har-
ness and SS2.
2. Disconnect the connector (X–3) of T/M wire
and inspect the resistance between SS2 con-
nector terminal 10 and ground.
Is the measurement within the specified value?20°C (68°F)
11–16 WGo to Step 7Go to Step 8
Page 1675 of 2643

AISIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A2 – 85
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0785
TIMING SOLENOID (ST) ELECTRICAL
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S TCM detects that the ON signal of the Timing Sole-
noid (ST) monitor during 0.5 seconds when ST driv-
er outputs the OFF signal.(When the ST circuit is
open or short to battery).
S TCM detects that the OFF signal of the Timing So-
lenoid (ST) monitor during 0.1 seconds when ST
driver outputs the ON signal.(When the ST circuit is
short to ground).
S The above detection 3 times at shifting continuous-
ly.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S TCM will request the illumination of MIL and store
DTC when TCM detects a failure on the first ignition
cycle.
S After failure decision : emergency modeConditions for Clearing the DTC
S The TCM turns off the MIL when no further failures
detected for three consecutive ignition cycles.
S The scan tool can clear the DTC from the TCM his-
tory.
S The TCM clears the DTC from the TCM history
memory after forty consecutive warm up cycles
without fault.
S TCM detects the ON signal of the ST monitor dur-
ing 100 ms when ST driver outputs the ON signal
and TCM detects the OFF signal of the ST monitor
during 160 ms when ST driver outputs the OFF sig-
nal.
Cause of Failure
S Wiring harness or connector between Timing Sole-
noid (ST) and TCM
S ST
S TCM
Page 1676 of 2643
5A2 – 86IAISIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P0785 Timing Solenoid (ST) Electrical
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Install the Scan tool.
3. With the engine OFF, turn the ignition switch to
the ON position.
4. Select Store Freeze Frame/Failure Records
from the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Information
menu.
5. Store Freeze Frame/Failure Records.
6. Select Clear DTC Information from the Diag-
nostic Trouble Codes Information menu.
7. Clear DTC Information.
8. Perform one vehicle drive cycle.
Is the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) ON?–Go to Step 2Repair the tem-
porary connec-
tion failure of
connector (Re-
fer to ”Wiring
Harness and
Connector In-
spection” in this
section.)
21. Select Request DTC by Status from the Diag-
nostic Trouble Codes Information menu.
2. Request DTC by Status.
Is DTC P0785 displayed?–Go to Step 3Repair the tem-
porary connec-
tion failure of
connector (Re-
fer to ”Wiring
Harness and
Connector In-
spection” in this
section.)
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Inspect the resistance between the vehicle har-
ness and Timing Solenoid (ST). Refer to ”Unit
Inspection” in this section.
3. Disconnect the TCM connector (X–1) and in-
spect the resistance between the terminal A24
and A23.
Is the measurement within the specified value?20°C (68°F)
11–16 WGo to Step 4Go to Step 5
41. Estimate the failure of between the vehicle wir-
ing harness connector and TCM.
2. Inspect the connector. Refer to ”Wiring Har-
ness and Connector Inspection” in this section.
3. Inspect the connection condition between the
connectors (C–1).
Is the connection condition OK?–Go to Step 6Repair the wir-
ing harness
connectors.
51. Estimate the failure of between the vehicle har-
ness and ST.
2. Disconnect the connector (X–3) of T/M wire
and inspect the resistance between ST con-
nector terminal 2 and ground.
Is the measurement within the specified value?20°C (68°F)
11–16 WGo to Step 7Go to Step 8
61. Replace the master TCM.
2. Perform the reproducing test under user condi-
tion after confirming no DTC.
Is DTC displayed?–Repair the tem-
porary connec-
tion failure of
connector (Re-
fer to ”Wiring
Harness and
Connector In-
spection” in this
section.)Replace the
TCM
Page 1809 of 2643
AISIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A2 – 219
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
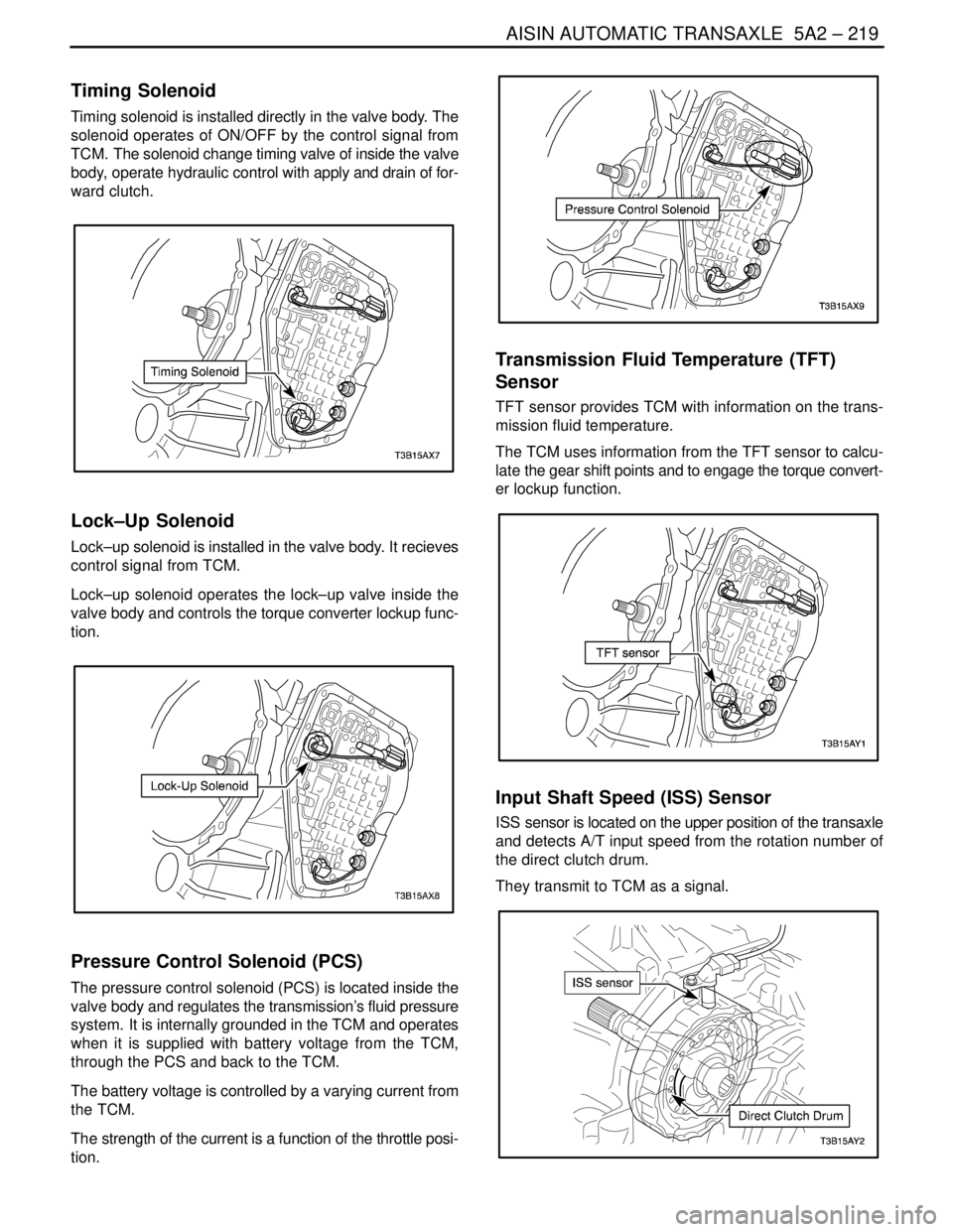
Timing Solenoid
Timing solenoid is installed directly in the valve body. The
solenoid operates of ON/OFF by the control signal from
TCM. The solenoid change timing valve of inside the valve
body, operate hydraulic control with apply and drain of for-
ward clutch.
Lock–Up Solenoid
Lock–up solenoid is installed in the valve body. It recieves
control signal from TCM.
Lock–up solenoid operates the lock–up valve inside the
valve body and controls the torque converter lockup func-
tion.
Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS)
The pressure control solenoid (PCS) is located inside the
valve body and regulates the transmission’s fluid pressure
system. It is internally grounded in the TCM and operates
when it is supplied with battery voltage from the TCM,
through the PCS and back to the TCM.
The battery voltage is controlled by a varying current from
the TCM.
The strength of the current is a function of the throttle posi-
tion.
Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT)
Sensor
TFT sensor provides TCM with information on the trans-
mission fluid temperature.
The TCM uses information from the TFT sensor to calcu-
late the gear shift points and to engage the torque convert-
er lockup function.
Input Shaft Speed (ISS) Sensor
ISS sensor is located on the upper position of the transaxle
and detects A/T input speed from the rotation number of
the direct clutch drum.
They transmit to TCM as a signal.
Page 1829 of 2643

FIVE–SPEED MANUAL TRANSAXLE 5B – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSIS
ISOLATE NOISE
Identify the cause of any noise before attempting to repair
the clutch, the transaxle, or their related link–ages.
Symptoms of trouble with the clutch or the manual trans-
axle include:
S A great effort required to shift gears.
S The sound of gears clashing and grinding.
S Gear blockout.
Any of these conditions requires a careful analysis. Make
the following checks before disassembling the clutch or
the transaxle for repairs.
Road Travel Noise
Many noises that appear to come from the transaxle may
actually originate with other sources such as the:
S Tires.
S Road surfaces.
S Wheel bearings.
S Engine.
S Exhaust system.
These noises may vary according to the:
S Size of the vehicle.
S Type of the vehicle.
S Amount of insulation used in the body of the ve-
hicle.
Transaxle Noise
Transaxle gears, like any mechanical device, are not ab-
solutely quiet and will make some noise during normal op-
eration.
To verify suspected transaxle noises:
1. Select a smooth, level asphalt road to reduce tire
and resonant body noise.
2. Drive the vehicle far enough to warm up all the lu-
bricants thoroughly.
3. Record the speed and the gear range of the trans-
axle when the noise occurs.
4. Check for noises with the vehicle stopped, but with
the engine running.
5. Determine if the noise occurs while the vehicle op-
erates in:
S Drive – under a light acceleration or a heavy
pull.
S Float – maintaining a constant speed with a light
throttle on a level road.
S Coast – with the transaxle in gear and the
throttle partly or fully closed.
S All of the above.
Bearing Noise
Differential Side Bearing Noise
Differential side bearing noise and wheel bearing noise
can be confused easily. Since side bearings are pre–
loaded, a differential side bearing noise should not dimin-
ish much when the differential/transaxle is run with the
wheels off the ground.
Wheel Bearing Noise
Wheel bearings produce a rough growl or grating sound
that will continue when the vehicle is coasting and the
transaxle is in NEUTRAL. Since wheel bearings are not
pre–loaded, a wheel bearing noise should diminish con-
siderably when the wheels are off the ground.
Other Noise
Brinelling
A brinelled bearing causes a ”knock” or ”click” approxi-
mately every second revolution of the wheel because the
bearing rollers do not travel at the same speed as the
wheel. In operation, the effect is characterized by a low–
pitched noise.
A brinelled bearing is caused by excessive thrust which
pushes the balls up on the pathway and creates a triangu-
lar–shaped spot in the bearing race. A brinelled bearing
can also be caused from pressing one race into position
by applying pressure on the other race.
A false indication of a brinelled bearing occurs as a result
of vibration near the area where the bearing is mounted.
Brinelling is identified by slight indentations, resulting in a
washboard effect in the bearing race.
Lapping
Lapped bearing noise occurs when fine particles of abra-
sive materials such as scale, sand, or emery circulate
through the oil in the vehicle, causing the surfaces of the
roller and the race to wear away. Bearings that wear loose
but remain smooth, without spalling or pitting, are the re-
sult of dirty oil.
Locking
Large particles of foreign material wedged between the
roller and the race usually causes one of the races to turn,
creating noise from a locked bearing. Pre–loading regular
taper roller bearings to a value higher than that specified
also can result in locked bearings
Pitting
Pitting on the rolling surface comes from normal wear and
the introduction of foreign materials.
Spalling
Spalled bearings have flaked or pitted rollers or races
caused by an overload or an incorrect assembly that re-
sults in a misalignment, a cocking of bearings, or adjust-
ments that are too tight.
After completing these checks, refer to the ”Diagnosis
Chart” in this section.