2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Lamp
[x] Cancel search: LampPage 818 of 2643
1F – 572IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1650
SPI COMMUNICATION BETWEEN ERROR WITH SIDM
CHIP
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) is the control center of
the fuel injection system. It constantly looks at the informa-
tion from various sensors, and controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM also performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize opera-
tional problems, alert the driver through the Malfunction In-
dicator Lamp (MIL) (Check Engine), and store a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) or DTCs which identify the
problem areas to aid the technician in making repairs. An
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
(EEPROM) is used to house the program information and
the calibrations required for engine, transmission, and
powertrain diagnostics operation. The Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) will stored, when the ECM detects SPI com-
munication between main CPU and output driver I/C is
corrupted.
Conditions for Setting the DTCS Ignition switch is turned to ON.
S Battery voltage is greater than 11 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
DTC P1650 – SPI Communication Between Error with SIDM Chip
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 3–
31. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 2
4Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 819 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 573
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1655
SPI COMMUNICATION BETWEEN ERROR WITH PSVI
CHIP
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) is the control center of
the fuel injection system. It constantly looks at the informa-
tion from various sensors, and controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM also performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize opera-
tional problems, alert the driver through the Malfunction In-
dicator Lamp (MIL) (Check Engine), and store a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) or DTCs which identify the
problem areas to aid the technician in making repairs. An
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
(EEPROM) is used to house the program information and
the calibrations required for engine, transmission, and
powertrain diagnostics operation. The Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) will stored, when the ECM detects corrupted
serial peripheral interface (SPI) comunication between
main CPU and output driver I/C.
Conditions for Setting the DTCS Ignition switch is turned to ON.
S Battery voltage is greater than 11 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
DTC P1655 – SPI Communication Between Error with PSVI Chip
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 3–
31. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 2
4Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 820 of 2643
1F – 574IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
IMPORTANT PRELIMINARY CHECKS
Important : Several symptom procedures call for a careful visual/physical inspection. Always perform the visual/physical
test first. Visual inspections may lead to correcting a problem without further checks and can save valuable time.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the check complete?–Go toStep 2Go to”On–
Board Diagnos-
tic System
Check”
21. Inspect all of the engine control module (ECM)
ground connections.
2. Inspect all of the vacuum hoses for splits,
kinks, and proper connections.
3. Check for air leaks at all of the mounting areas
of the intake manifold sealing surfaces.
4. Inspect the ignition wires for cracking, hard-
ness, proper routing, and carbon tracking.
5. Inspect the wiring for proper connections,
pinches, and cuts.
Are all checks complete?–Go to Appropri-
ate Symptom
Table–
INTERMITTENTS
Definition : The problem may or may not illuminate the
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) or store a diagnostic
trouble code (DTC).Important : Do not use the DTC tables for intermittent
problems. A fault must be present in order to locate the
problem. If a fault is intermittent, use of DTC tables may
result in the replacement of good parts.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Were the Important Preliminary Checks performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”Important Pre-
liminary
Checks”
21. Perform a careful inspection of any suspect
circuits.
2. Inspect for poor mating of the connector
halves, or terminals not fully seated into the
connector body.
3. Inspect for improperly formed or damaged ter-
minals.
4. Inspect for poor terminal to wire connections.
This requires removing the terminal from the
connector body to inspect it.
Are any problems present?–Go toStep 3Go toStep 4
3Repair the electrical connections as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
4Road test the vehicle with a voltmeter connected to
a suspected circuit or a scan tool connected to the
Data Link Connector (DLC).
Did the voltmeter or the scan tool indicate an abnor-
mal voltage or scan reading?–Go toStep 5Go toStep 6
Page 821 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 575
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
5Replace the sensor in the affected circuit, if a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) was stored for this circuit
(except for the DTCs P0171 and P0172.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
6Does an intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) or DTC occur?–Go toStep 7Go toStep 8
71. Check for a faulty relay, electronic control mod-
ule (ECM) driven solenoid, or switch.
2. Check for improper installation of electrical de-
vices, such as lights, two–way radios, electric
motors, etc.
3. Inspect the ignition control wires for proper
routing (away from ignition wires, ignition sys-
tem components, and the generator).
4. Check for a short–to–ground in the MIL circuit
or the DLC ”test” terminal.
5. Inspect the ECM ground connections.
6. Correct or repair the affected circuits as need-
ed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
81. Check for a loss of DTC memory.
2. 2. Disconnect the Throttle Position Sensor.
3. Run the engine at idle until the MIL comes on.
4. Turn the ignition OFF.
Is DTC P0122 stored in memory?–Go toStep 10Go toStep 9
9Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
10Does the vehicle stall while driving?–Go toStep 11Go toStep 12
11Monitor the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1)
and the injector base pulse width with the scan tool.
Does the scan tool display a steady low voltage
(about 0 mv) for the HO2S1 sensor with the control
module commanding an injector base pulse width of
the value specified?8 msGo toStep 9Go toStep 12
121. Check for an open diode across the A/C clutch
and for other open diodes.
2. Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 840 of 2643

1F – 594IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELIEF
Procedure
CAUTION : The fuel system is under pressure. To
avoid fuel spillage and the risk of personal injury or
fire, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system pressure
before disconnecting the fuel lines.
1. Remove the fuel cap.
2. Remove the fuel pump fuse Ef18 from the engine
fuse block.
3. Start the engine and allow the engine to stall.
4. Crank the engine for an additional 10 seconds.
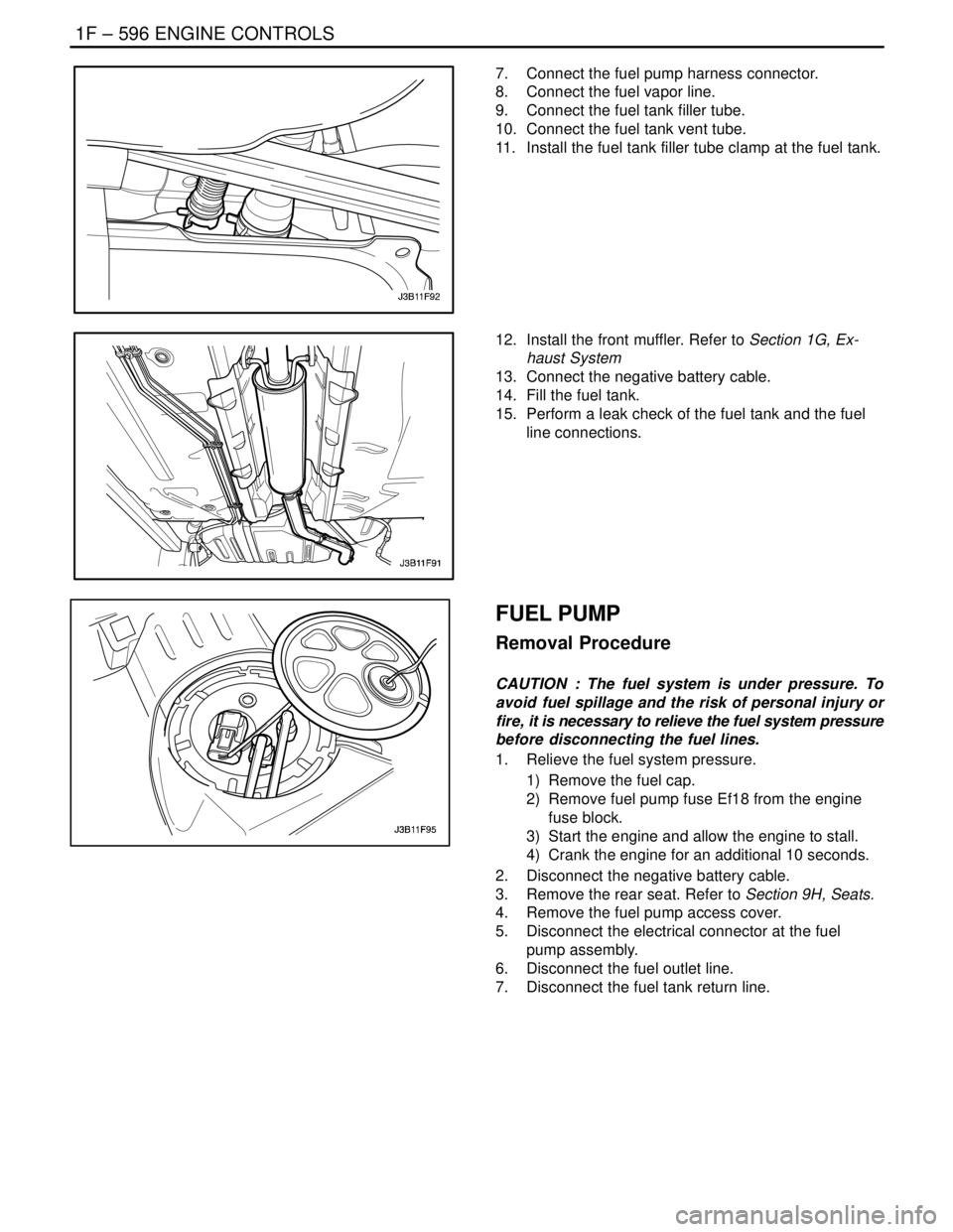
FUEL TANK
Removal Procedure
CAUTION : The fuel system is under pressure. To
avoid fuel spillage and the risk of personal injury or
fire, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system pressure
before disconnecting the fuel lines.
1. Relieve the fuel pressure. Refer to ” Fuel System
Pressure Relief ” in this section.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Drain the fuel tank.
4. Remove the front muffler. Refer to Section 1G, Ex-
haust System
5. Remove the fuel tank filler tube clamp at the fuel
tank.
6. Disconnect the fuel tank filler tube.
7. Disconnect the fuel vapor line near the fuel tank
filler tube.
8. Disconnect the fuel pump harness connector.
Page 842 of 2643

1F – 596IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
7. Connect the fuel pump harness connector.
8. Connect the fuel vapor line.
9. Connect the fuel tank filler tube.
10. Connect the fuel tank vent tube.
11. Install the fuel tank filler tube clamp at the fuel tank.
12. Install the front muffler. Refer to Section 1G, Ex-
haust System
13. Connect the negative battery cable.
14. Fill the fuel tank.
15. Perform a leak check of the fuel tank and the fuel
line connections.
FUEL PUMP
Removal Procedure
CAUTION : The fuel system is under pressure. To
avoid fuel spillage and the risk of personal injury or
fire, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system pressure
before disconnecting the fuel lines.
1. Relieve the fuel system pressure.
1) Remove the fuel cap.
2) Remove fuel pump fuse Ef18 from the engine
fuse block.
3) Start the engine and allow the engine to stall.
4) Crank the engine for an additional 10 seconds.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Remove the rear seat. Refer to Section 9H, Seats.
4. Remove the fuel pump access cover.
5. Disconnect the electrical connector at the fuel
pump assembly.
6. Disconnect the fuel outlet line.
7. Disconnect the fuel tank return line.
Page 844 of 2643

1F – 598IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Installation Procedure
1. Install the new fuel filter into the retaining clamp.
Note the flow direction.
2. Install the fuel filter.
3. Connect the inlet/outlet lines. Secure the lines with
the connector lock.
4. Install the fuel filter cover.
5. Install the fuel filter mounting bracket assembly bolt
with the fuel filter ground.
Tighten
Tighten the fuel filter mounting bracket assembly
bolts to 4 NSm (35 lb–ft).
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
7. Perform a leak test of the fuel filter.
FUEL RAIL AND INJECTORS
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
CAUTION : The fuel system is under pressure. To
avoid fuel spillage and the risk of personal injury or
fire, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system pressure
before disconnecting the fuel lines.
1. Relieve the fuel system pressure. Refer to ”Fuel
Pump”in this section.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Remove the intake manifold bracket bolts.
4. Remove the intake manifold bracket.
5. Disconnect the fuel injector harness connectors.
6. Remove the fuel feed line.
7. Remove the fuel rail mounting bolts.
Notice : Before removal, the fuel rail assembly may be
cleaned with a spray–type cleaner, following package in-
structions. Do not immerse the fuel rails in liquid cleaning
solvent. Use care in removing the fuel rail assembly to pre-
vent damage to the electrical connectors and the injector
spray tips. Prevent dirt and other contaminants from enter-
ing open lines and passages. Fittings should be capped
and holes plugged during service.
Important : If an injector becomes separated from the rail
and remains in the cylinder head, replace the injector O–
ring seals and the retaining clip.
Page 871 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 625
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CANISTER
The Evaporative (EVAP) Emission canister is an emission
control device containing activated charcoal granules.
The EVAP emission canister is used to store fuel vapors
from the fuel tank. Once certain conditions are met, the en-
gine control module (ECM) activates the EVAP canister
purge solenoid, allowing the fuel vapors to be drawn into
the engine cylinders and burned.
POSITIVE CRANKCASE
VENTILATION SYSTEM OPERATION
A Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system is used to
provide complete use of the crankcase vapors. Fresh air
from the air cleaner is supplied to the crankcase. The fresh
air is mixed with blowby gases which are then passed
through a vacuum hose into the intake manifold.
Periodically inspect the hoses and the clamps. Replace
any crankcase ventilation components as required.
A restricted or plugged PCV hose may cause the following
conditions:
S Rough idle
S Stalling or low idle speed
S Oil leaks
S Oil in the air cleaner
S Sludge in the engine
A leaking PCV hose may cause the following conditions:
S Rough idle
S Stalling
S High idle speed
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor (a resistor which changes value based on tem-
perature) mounted in the engine coolant stream. Low cool-
ant temperature produces a high resistance (100,000
ohms at –40 °F [–40 °C]) while high temperature causes
low resistance (70 ohms at 266 °F [130 °C]).
The engine control module (ECM) supplies 5 volts to the
ECT sensor through a resistor in the ECM and measures
the change in voltage. The voltage will be high when the
engine is cold, and low when the engine is hot. By measur-
ing the change in voltage, the ECM can determine the
coolant temperature. The engine coolant temperature af-
fects most of the systems that the ECM controls. A failure
in the ECT sensor circuit should set a diagnostic trouble
code P0117 or P0118. Remember, these diagnostic
trouble codes indicate a failure in the ECT sensor circuit,
so proper use of the chart will lead either to repairing a wir-
ing problem or to replacing the sensor to repair a problem
properly.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
The Throttle Position (TP) sensor is a potentiometer con-
nected to the throttle shaft of the throttle body. The TP sen-
sor electrical circuit consists of a 5 volt supply line and a
ground line, both provided by the engine control module
(ECM). The ECM calculates the throttle position by moni-
toring the voltage on this signal line. The TP sensor output
changes as the accelerator pedal is moved, changing the
throttle valve angle. At a closed throttle position, the output
of the TP sensor is low, about 0.5 volt. As the throttle valve
opens, the output increases so that, at Wide Open Throttle
(WOT), the output voltage will be about 5 volts.
The ECM can determine fuel delivery based on throttle
valve angle (driver demand). A broken or loose TP sensor
can cause intermittent bursts of fuel from the injector and
an unstable idle, because the ECM thinks the throttle is
moving. A problem in any of the TP sensor circuits should
set a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0121 or P0122.
Once the DTC is set, the ECM will substitute a default val-
ue for the TP sensor and some vehicle performance will
return. A DTC P0121 will cause a high idle speed.
CATALYST MONITOR OXYGEN
SENSORS
Three–way catalytic converters are used to control emis-
sions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and
oxides of nitrogen (NOx). The catalyst within the convert-
ers promotes a chemical reaction. This reaction oxidizes
the HC and CO present in the exhaust gas and converts
them into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide. The
catalyst also reduces NOx by converting it to nitrogen. The
engine control module (ECM) can monitor this process us-
ing the HO2S1 and HO2S2 sensor. These sensors pro-
duce an output signal which indicates the amount of oxy-
gen present in the exhaust gas entering and leaving the
three–way converter. This indicates the catalyst’s ability to
efficiently convert exhaust gasses. If the catalyst is operat-
ing efficiently, the HO2S1 sensor signals will be more ac-
tive than the signals produced by the HO2S2 sensor. The
catalyst monitor sensors operate the same way as the fuel
control sensors. The sensor’s main function is catalyst
monitoring, but they also have a limited role in fuel control.
If a sensor output indicates a voltage either above or below
the 450 mv bias voltage for an extended period of time, the
ECM will make a slight adjustment to fuel trim to ensure
that fuel delivery is correct for catalyst monitoring.
A problem with the HO2S1 sensor circuit will set DTC
P0131, P0132, P0133 or P0134 depending, on the special
condition. A problem with the HO2S2 sensor signal will set
DTC P0137, P0138, P0140 or P0141, depending on the
special condition.
A fault in the Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2) heat-
er element or its ignition feed or ground will result in lower
oxygen sensor response. This may cause incorrect cata-
lyst monitor diagnostic results.