2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Rod
[x] Cancel search: RodPage 1932 of 2643

POWER STEERING GEAR 6C – 15
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
4. Loosen the outer tie rod adjusting nut and remove
the outer tie rod by twisting it off the inner tie rod.
Installation Procedure
1. Reposition the adjusting nut to the marks on the
inner tie rod.
2. Install the outer tie rod by twisting it onto the inner
tie rod.
3. Connect the outer tie rod to the steering knuckle.
4. Perform a front toe adjustment. Refer to Section
2B, Wheel Alignment.
5. Tighten the adjusting nut.
Tighten
Tighten the outer tie rod adjusting nut to 64 NSm (47
lb–ft).
6. Install the outer tie rod nut.
Tighten
Tighten the outer tie rod nut to 50 NSm (37 lb–ft).
7. Install the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
Wheels.
DUST BOOT
Tools Required
KM–J–22610 Installer
Removal Procedure
1. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
2. Remove the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
Wheels.
3. Remove the outer tie rod. Refer to ”Outer Tie Rod”
in this section.
4. Remove the dust boot retaining clamps.
5. Remove the dust boot.
Page 1933 of 2643

6C – 16IPOWER STEERING GEAR
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Installation Procedure
1. Install the dust boot.
2. Install the tie rod end dust boot retaining clamp.
Install the cylinder end dust boot retaining clamp
with the installer KM–J–22610.
3. Install the outer tie rod. Refer to ”Outer Tie Rod” in
this section.
4. Install the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
Wheels.
5. Lower the vehicle.
STRAIGHT–AHEAD CHECK
After all the necessary operations on the steering gear are
completed (removing and installing, disassembling and
assembling), check the exact straight–ahead position of
the steering in each case.
With the vehicle on the floor, place the steering wheel in
the straight–ahead position. Mark the centerline of both
tires on the floor. Turn the steering wheel all the way to the
right and mark the new centerline of both tires on the floor.
Page 1939 of 2643
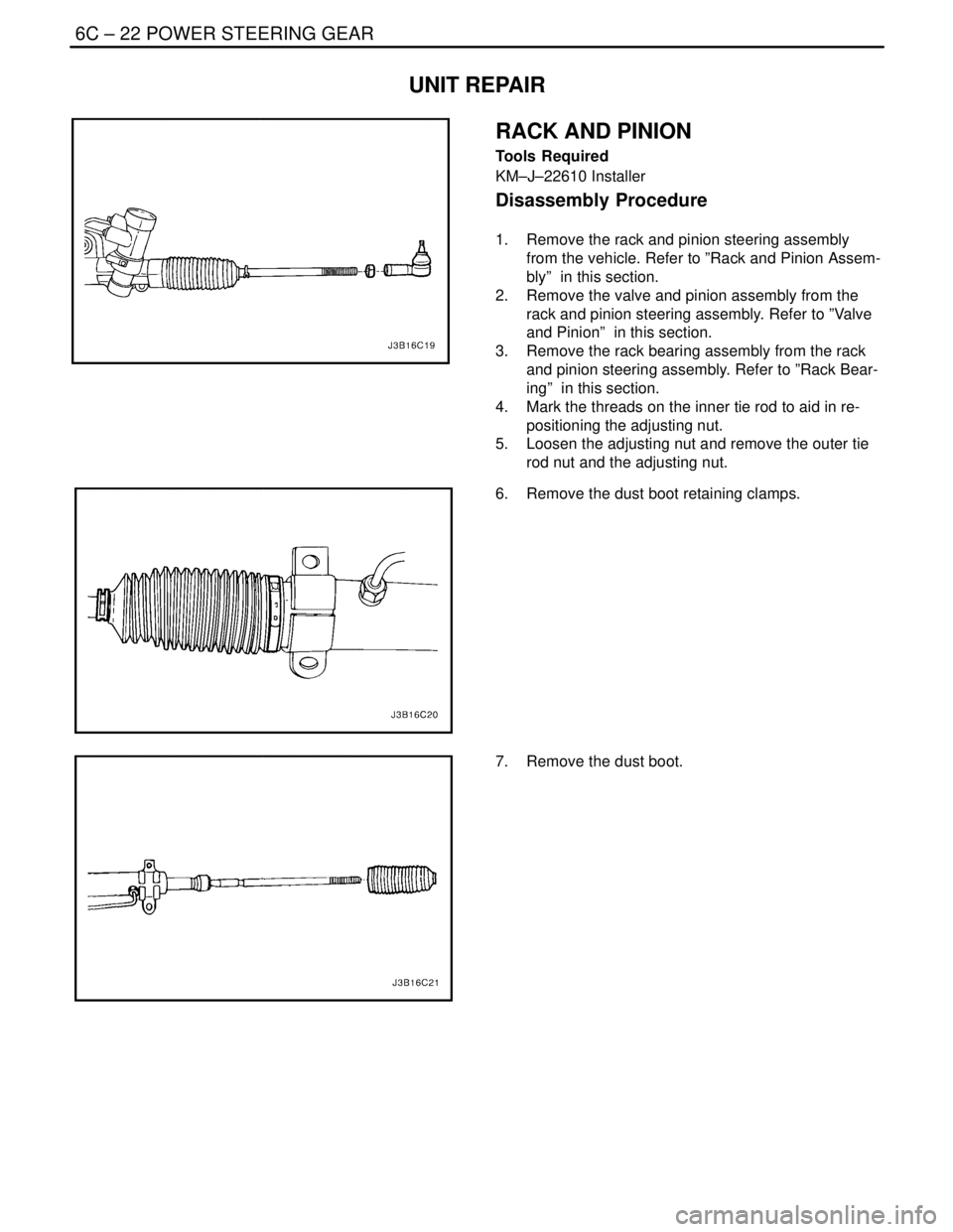
6C – 22IPOWER STEERING GEAR
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
UNIT REPAIR
RACK AND PINION
Tools Required
KM–J–22610 Installer
Disassembly Procedure
1. Remove the rack and pinion steering assembly
from the vehicle. Refer to ”Rack and Pinion Assem-
bly” in this section.
2. Remove the valve and pinion assembly from the
rack and pinion steering assembly. Refer to ”Valve
and Pinion” in this section.
3. Remove the rack bearing assembly from the rack
and pinion steering assembly. Refer to ”Rack Bear-
ing” in this section.
4. Mark the threads on the inner tie rod to aid in re-
positioning the adjusting nut.
5. Loosen the adjusting nut and remove the outer tie
rod nut and the adjusting nut.
6. Remove the dust boot retaining clamps.
7. Remove the dust boot.
Page 1940 of 2643
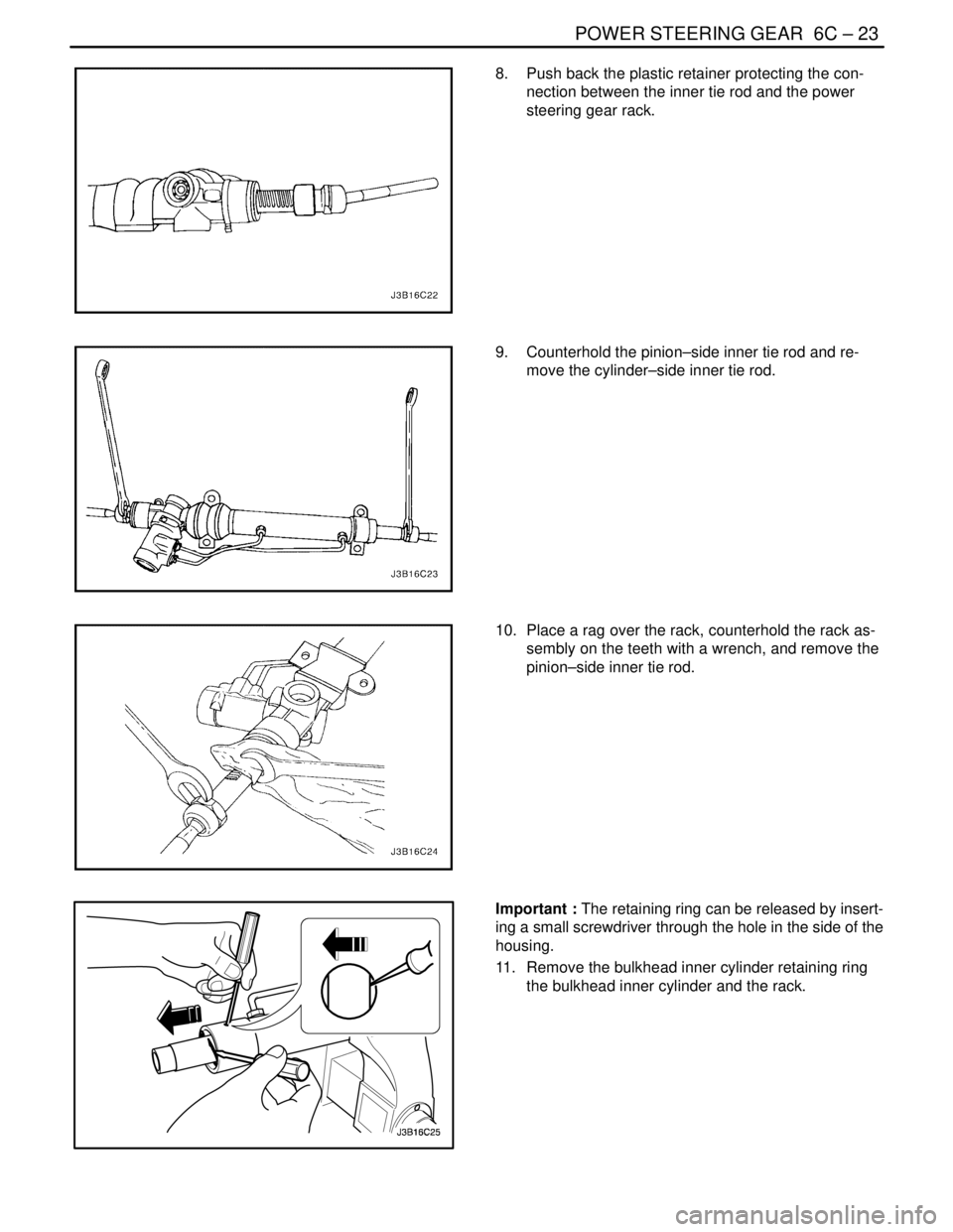
POWER STEERING GEAR 6C – 23
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
8. Push back the plastic retainer protecting the con-
nection between the inner tie rod and the power
steering gear rack.
9. Counterhold the pinion–side inner tie rod and re-
move the cylinder–side inner tie rod.
10. Place a rag over the rack, counterhold the rack as-
sembly on the teeth with a wrench, and remove the
pinion–side inner tie rod.
Important : The retaining ring can be released by insert-
ing a small screwdriver through the hole in the side of the
housing.
11. Remove the bulkhead inner cylinder retaining ring
the bulkhead inner cylinder and the rack.
Page 1941 of 2643
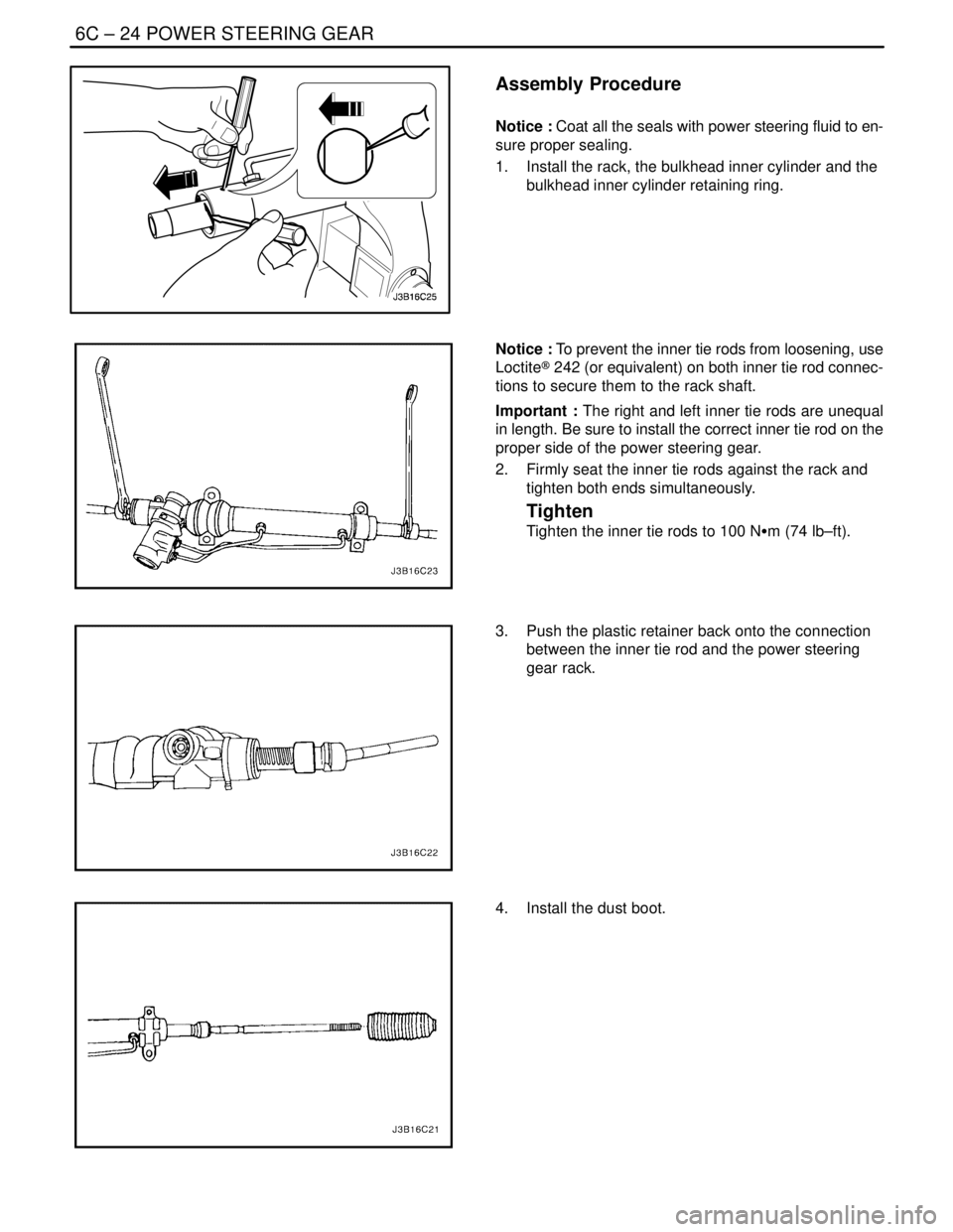
6C – 24IPOWER STEERING GEAR
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Assembly Procedure
Notice : Coat all the seals with power steering fluid to en-
sure proper sealing.
1. Install the rack, the bulkhead inner cylinder and the
bulkhead inner cylinder retaining ring.
Notice : To prevent the inner tie rods from loosening, use
Loctite® 242 (or equivalent) on both inner tie rod connec-
tions to secure them to the rack shaft.
Important : The right and left inner tie rods are unequal
in length. Be sure to install the correct inner tie rod on the
proper side of the power steering gear.
2. Firmly seat the inner tie rods against the rack and
tighten both ends simultaneously.
Tighten
Tighten the inner tie rods to 100 NSm (74 lb–ft).
3. Push the plastic retainer back onto the connection
between the inner tie rod and the power steering
gear rack.
4. Install the dust boot.
Page 1942 of 2643
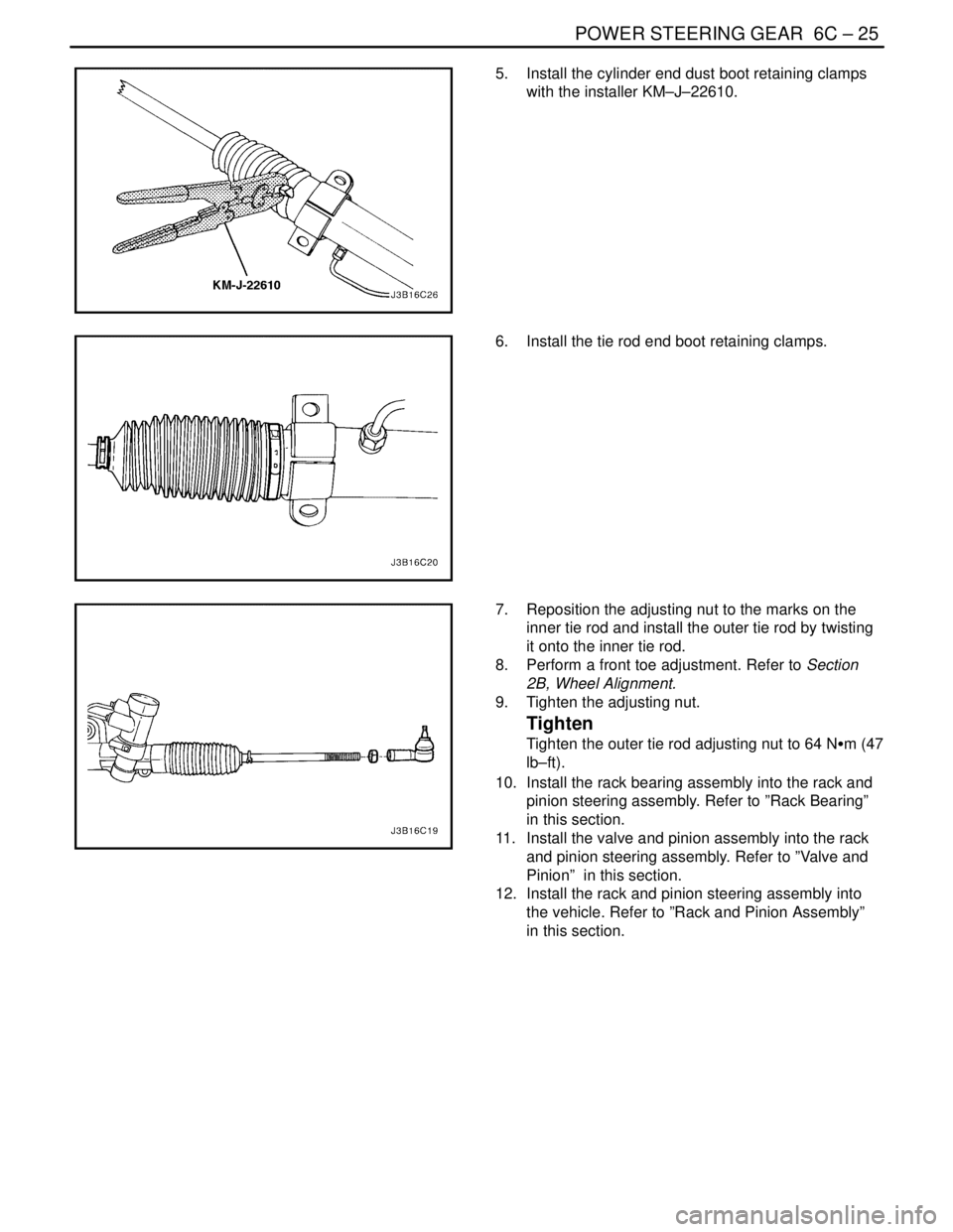
POWER STEERING GEAR 6C – 25
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
5. Install the cylinder end dust boot retaining clamps
with the installer KM–J–22610.
6. Install the tie rod end boot retaining clamps.
7. Reposition the adjusting nut to the marks on the
inner tie rod and install the outer tie rod by twisting
it onto the inner tie rod.
8. Perform a front toe adjustment. Refer to Section
2B, Wheel Alignment.
9. Tighten the adjusting nut.
Tighten
Tighten the outer tie rod adjusting nut to 64 NSm (47
lb–ft).
10. Install the rack bearing assembly into the rack and
pinion steering assembly. Refer to ”Rack Bearing”
in this section.
11. Install the valve and pinion assembly into the rack
and pinion steering assembly. Refer to ”Valve and
Pinion” in this section.
12. Install the rack and pinion steering assembly into
the vehicle. Refer to ”Rack and Pinion Assembly”
in this section.
Page 1950 of 2643

POWER STEERING GEAR 6C – 33
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
POWER RACK AND PINION
The power rack and pinion steering system has a rotary
control valve that directs hydraulic fluid coming from the
hydraulic pump to one side or the other side of the rack pis-
ton. The integral rack piston is attached to the rack. The
rack piston converts hydraulic pressure to a linear force
that moves the rack left or right. That force is then trans-
mitted through the tie rods to the steering knuckles, which
turn the wheels.
If power rack and pinion steering is not available, manual
rack and pinion control is used; however, with this system,
more steering effort is required. The movement of the
steering wheel is transferred to the pinion. The rotary
movement of the pinion is then transferred through the pin-
ion threads, which mesh with teeth on the rack, thereby
causing the rack to move in a linear direction.
A vane–type of hydraulic pump provides hydraulic pres-
sure for both steering systems.
SPEED SENSITIVE POWER
STEERING SYSTEM
The speed sensitive power steering (SSPS) system varies
the driver effort required to steer as the vehicle speed
changes. At low speeds, the system provides maximum
power assist for easy turning and parking maneuvers. At
higher speeds, the steering power is reduced to provide
the driver with firmer steering and directional stability. The
SSPS system accomplishes this by reducing the amount
of power steering fluid flow from the power steering pump
to the power steering gear as the vehicle speed increases.
When the vehicle is stationary, the SSPS system provides
maximum fluid flow to the steering gear. As the vehicle
speed increases, the fluid flow to the steering gear is de-
creased.
Control Module
The SSPS control module processes the vehicle speed in-
formation from the engine control module (ECM) and uses
the steering wheel rotation sensor to provide a control sig-
nal to the electronic variable orifice (EVO) actuator located
on the power steering pump.
Electronic Variable Orifice (EVO) Actuator
The electronic variable orifice (EVO) actuator is located on
the power steering pump and contains a solenoid– oper-
ated pintle valve. Fluid leaving the pump passes through
an orifice in the actuator tip. When the EVO actuator is
powered by the SSPS control module, the pintle moves
into the orifice and reduces the power steering fluid flow.As the vehicle speed increases, current from the SSPS
control module increases, and the pintle blocks more and
more of the orifice.
Steering Wheel Rotation Sensor
The steering wheel rotation sensor is located at the end of
the steering column housing and is used to send a signal
to the controller when abrupt or evasive steering maneu-
vers are needed.
Power Steering Pressure Hose
SSPS vehicles have a specific pressure hose assembly
which includes an in–line check valve in the rack and pin-
ion assembly. This reduces the amount of steering wheel
”kick” when driving over irregular road surfaces while oper-
ating at speeds with reduced flow rate and pressure.
Power Rack and Pinion
Except for differences in valve machining, the design of
the SSPS power rack and pinion assembly is the same as
for the a non–SSPS system. The steering wheel move-
ment is transferred to the pinion via the intermediate shaft.
The pinion moves the rack left or right through meshing the
pinion and the rack teeth. The force is then transmitted
through the tie rods and steering knuckle to steer the
wheels.
The power rack and pinion steering system has a rotary
control valve which directs the hydraulic fluid from the
power steering pump to one side or the other side of the
rack piston. The piston is attached to the rack and uses hy-
draulic pressure to move the rack left or right. The rotary
control valve regulates the degree of assist by responding
to the driver’s torque input.
If hydraulic assist is not available, manual control is main-
tained. However, under this condition, more steering effort
is required.
Power Steering Pump
The standard vane–type pump, which provides hydraulic
pressure for the system, incorporates a special discharge
fitting to hold the EVO actuator.
System Operation
System operation originates with input from the vehicle
speed sensor via the engine control module to the SSPS
control module. The SSPS control module sends a signal
to the SSPS actuator to vary the rate of fluid flow output
by the power steering pump.
Circuit Operation
The SSPS system uses inputs from the speed sensor and
steering wheel rotation sensor to the SSPS controller to
determine the desired amount of power steering assist.
The SSPS control module constantly compares the
amount of current flowing through the EVO actuator to the
desired current it has calculated. The EVO actuator has a
pintle that moves in and out of an orifice, regulating power
Page 1985 of 2643
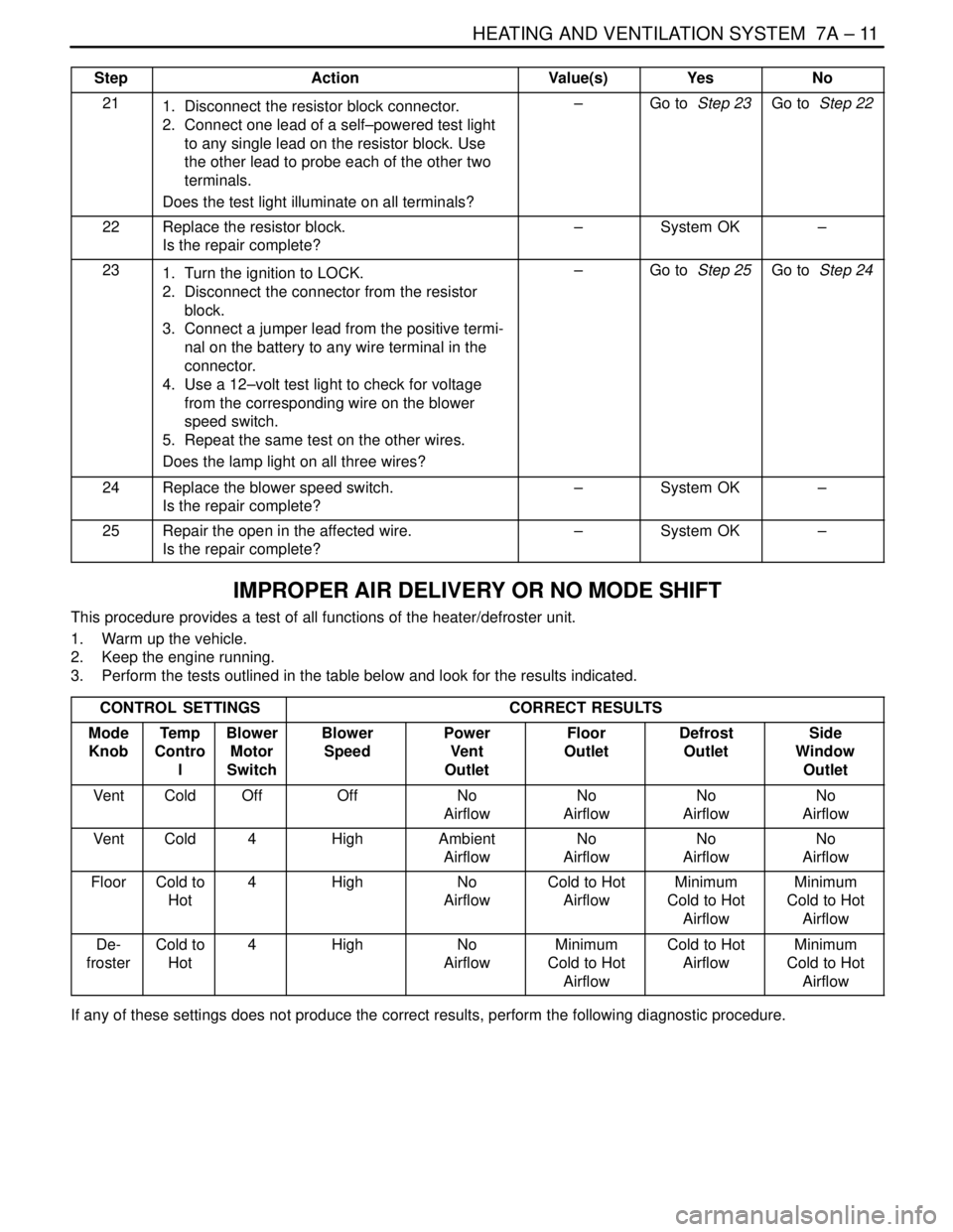
HEATING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM 7A – 11
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
211. Disconnect the resistor block connector.
2. Connect one lead of a self–powered test light
to any single lead on the resistor block. Use
the other lead to probe each of the other two
terminals.
Does the test light illuminate on all terminals?–Go to Step 23Go to Step 22
22Replace the resistor block.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
231. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the connector from the resistor
block.
3. Connect a jumper lead from the positive termi-
nal on the battery to any wire terminal in the
connector.
4. Use a 12–volt test light to check for voltage
from the corresponding wire on the blower
speed switch.
5. Repeat the same test on the other wires.
Does the lamp light on all three wires?–Go to Step 25Go to Step 24
24Replace the blower speed switch.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
25Repair the open in the affected wire.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
IMPROPER AIR DELIVERY OR NO MODE SHIFT
This procedure provides a test of all functions of the heater/defroster unit.
1. Warm up the vehicle.
2. Keep the engine running.
3. Perform the tests outlined in the table below and look for the results indicated.
CONTROL SETTINGS
CORRECT RESULTS
Mode
KnobTe m p
Contro
lBlower
Motor
SwitchBlower
SpeedPower
Vent
OutletFloor
OutletDefrost
OutletSide
Window
Outlet
VentColdOffOffNo
AirflowNo
AirflowNo
AirflowNo
Airflow
VentCold4HighAmbient
AirflowNo
AirflowNo
AirflowNo
Airflow
FloorCold to
Hot4HighNo
AirflowCold to Hot
AirflowMinimum
Cold to Hot
AirflowMinimum
Cold to Hot
Airflow
De-
frosterCold to
Hot4HighNo
AirflowMinimum
Cold to Hot
AirflowCold to Hot
AirflowMinimum
Cold to Hot
Airflow
If any of these settings does not produce the correct results, perform the following diagnostic procedure.