2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Iat
[x] Cancel search: IatPage 776 of 2643
1F – 530IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
2. Verifies the fault is present.
3. If DTC P1112 can be repeated only by duplicating
the Fail Records conditions, refer to the Tempera-
ture Vs. Resistance Value Chart. The chart may be
used to test the IAT sensor at various temperaturesto evaluate the possibility of a ”shifted” sensor that
may be shorted above or below a certain tempera-
ture. If this is the case, replace the IAT sensor.
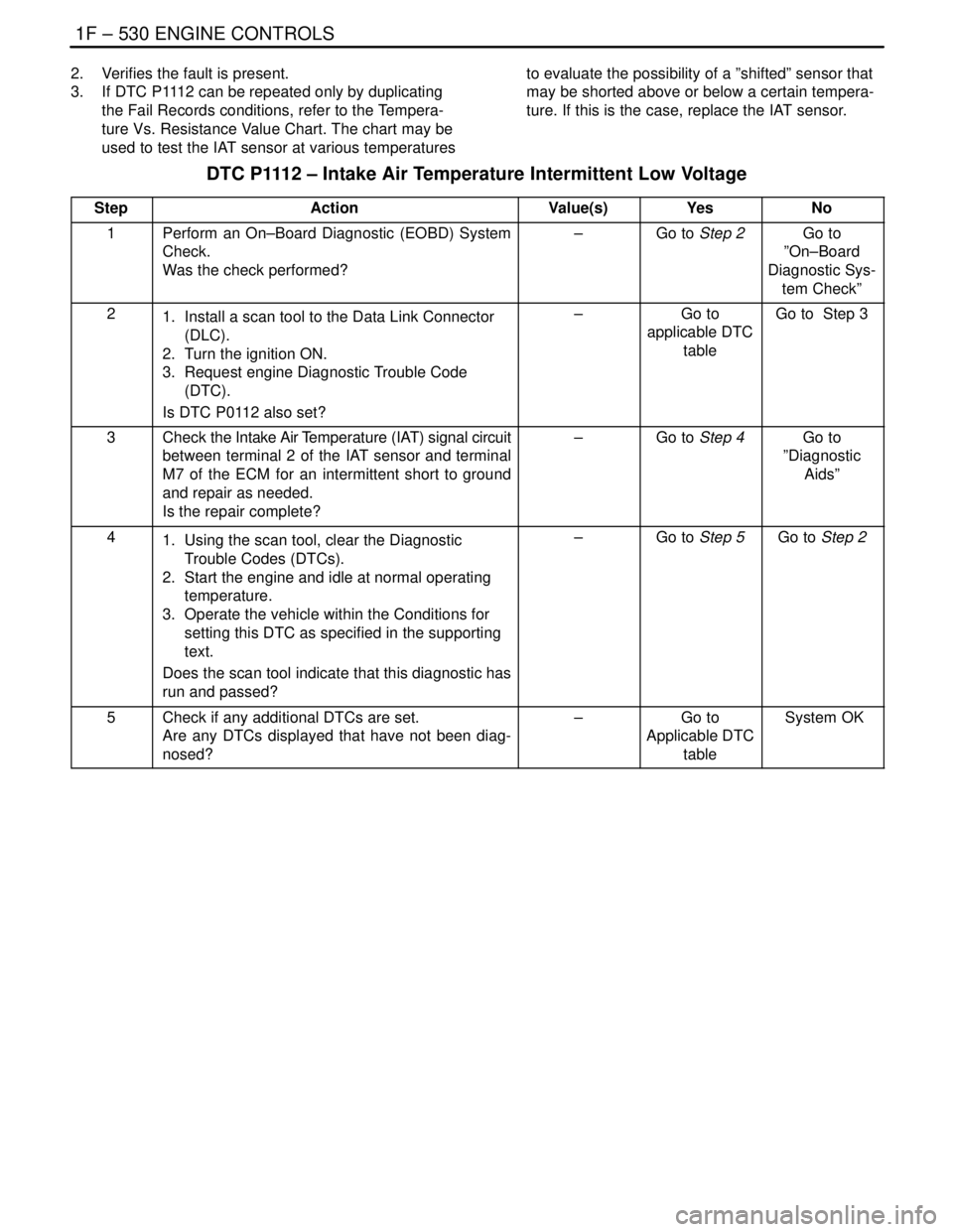
DTC P1112 – Intake Air Temperature Intermittent Low Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Request engine Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC).
Is DTC P0112 also set?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableGo to Step 3
3Check the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) signal circuit
between terminal 2 of the IAT sensor and terminal
M7 of the ECM for an intermittent short to ground
and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 4Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids”
41. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 2
5Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
table System OK
Page 791 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 545
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
51. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the HO2S1 connector.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. Using a voltmeter, measure the voltage be-
tween following terminals.
5. Terminal 4 of Engine Control Module (ECM)
side HO2S1 connector and ground.
6. Terminal 3 of ECM side HO2S1 connector and
ground.
Are both voltages in the specified value?3–5 vGo to Step 6Go to Step 8
61. With the HO2S1 disconnected, jumper the
ECM side HO2S1 connector terminals 4 and 3.
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Using a scan tool, monitor the HO2S1 voltage.
Does the scan tool indicates less than 10 millivolts
and immediately return to about 450 millivolts when
the jumper is removed?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 9
7Repair conditions as needed.
Is the action complete?–Go to Step 14–
8Check for faulty ECM connections or terminal dam-
ages and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 9
9Repair open, short, or grounded signal circuit.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Step 11
10Remove the HO2S1 and examine it for sign of:
S Fuel contamination.
S Improper room temperature vulcanizing sealant
(white powdery coating on the sensor)
S Engine oil/coolant consumption.
Are sign of contamination observed?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 13
111. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 13
12Determine and correct the cause of contamination.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14
13Replace the HO2S1.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14–
141. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 15Go to Step 2
15Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 796 of 2643

1F – 550IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1336
58X CRANK POSITION TOOTH ERROR NOT LEARNED
Circuit Description
In order to detect engine misfire at higher engine speeds,
the Engine Control Module (ECM) must know of any varia-
tion between the crankshaft sensor pulses. Most varia-
tions are due to the machining of the crankshaft reluctor
wheel. However, other sources of variation are also pos-
sible. A Crankshaft Position (CKP) system variation learn-
ing procedure must be performed any time a change is
made to the crankshaft sensor to crankshaft relationship
of if the ECM is replaced or reprogrammed. The ECM
measures the variations and then calculates compensa-
tion factors needed to enable the ECM to accurately de-
tect engine misfire at all speeds and loads. A scan tool
must be used to command the ECM to learn these varia-
tions. If for any reason the ECM is unable to learn these
variations or they are out of an acceptable range, the ECM
will set Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1336. An ECM
that has not had the CKP system variation learning proce-
dure performed due to replacement or reprogramming will
also set DTC P1336.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Tooth error not learned if the manufacture enable
counter is set to zero.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0132, P0201, P0202, P0203,
P0204, P0325 , 0327, P0336, P0337, P0341,
P0342, P0351, P0352, P0402, P1404, P0404,
P0405, P0406 and P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffer.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn OFF after four consecutive igni-
tion cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a
fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.Diagnostic Aids
CAUTION : To avoid personal injury when performing
the crankshaft position system variation learning
procedure, always set the vehice parking brake and
block the drive wheels. Release the throttle immedi-
ately when the engine starts to decelerate. Once the
learn procedure is completed, engine control will be
returned to the operator, and the engine will respond
to throttle position.
DTC P1336 will only set if the ECM has not learned the
CKP system variation. The ECM only needs to learn this
variation once per life cycle of the vehicle unless the crank
sensor to crankshaft relationship is disturbed. Removing
a part is considered a disturbance. A fully warmed engine
is critical to learning the variation correctly. If a valid learn
occurs, no other learns can be completed that ignition
cycle.
If the engine cuts out before the specified learn procedure
engine speed or at normal fuel cutoff rpm, the ECM is not
in the learn procedure mode.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the fault occurred. The information is then stored on
the scan tool for later reference.
2. Engine temperature is critical to properly learn the
CKP system variation. Failure to properly warm the
engine before performing this procedure will result
in an inaccurate measurement of the CKP system
variation. The ECM learns this variation as the en-
gine is decelerating and then allows engine control
to be returned to the operator. All accessories must
be OFF when learning the CKP system angle varia-
tion. If the A/C is not disabled when the learn pro-
cedure is enabled, the ECM will disable the A/C.
3. If after the specified number attempts the ECM
cannot learn the CKP system variation, then the
variation is too large and no further attempts should
be made until the variation problem is corrected.
4. Being unable to learn the procedure indicates that
the variation is out of range.
5. After the CKP system variation has been learned,
wait above 10 seconds with ignition switch OFF to
prevent being cleared the learned value.
Page 797 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 551
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P1336 – 58X Crank Position Tooth Error Not Learned
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
3. Put the vehicle in PARK or NEUTRAL.
4. Start the engine and operate to normal operat-
ing temperature.
5. Turn all accessories OFF.
6. Enable the TEC (Tooth Error Correction)
LEARN PROCEDURE with the scan tool.
7. Raise the engine rpm to the specified value,
then release the throttle as soon as the engine
cuts out.
Does the scan tool indicate that the Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) system variation has been learned?65°C (149°F)
4000 rpmGo to Step 5Go to Step 3
3Attempt the CKP system variation procedure as
many times as the specified value.
Does the scan tool indicate that the CKP system
variation has been learned?10Go to Step 5Go to Step 4
4Check for a problem with the CKP sensor to crank-
shaft relationship.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 5–
51. Turn the ignition OFF and wait above specified
value.
2. Turn the ignition ON, with engine OFF.
3. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
4. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
5. Operate the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as supported in the text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran
and passed?10 secGo to Step 6Go to Step 2
6Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 807 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 561
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1396
ABS WSS SIGNAL VARIATION
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) determines linear
wheel speed excessive variation. The wheel speed varia-
tion test detects at least one missing edge from the wheel
speed sensor signal.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S WSS variation is greater than 18km/h (11.2 mph).
S Vehicle speed is greater than 10km/h (6.2 mph).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC set as Failure Records data only.
This information will not be stored as Freeze Frame
data.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:S Poor connection at the ECM – Inspect the harness
connections for backed–out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or dam-
aged terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connec-
tion.
S Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe
the G sensor display on the scan tool while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sen-
sor. A change in the display will indicate the loca-
tion of the fault.
An open signal circuit of open PWM serial data line be-
tween the ECM and the EBCM will be the cause of this
DTC.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to specific step(s) on the diag-
nostic table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
6. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
Page 808 of 2643
1F – 562IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
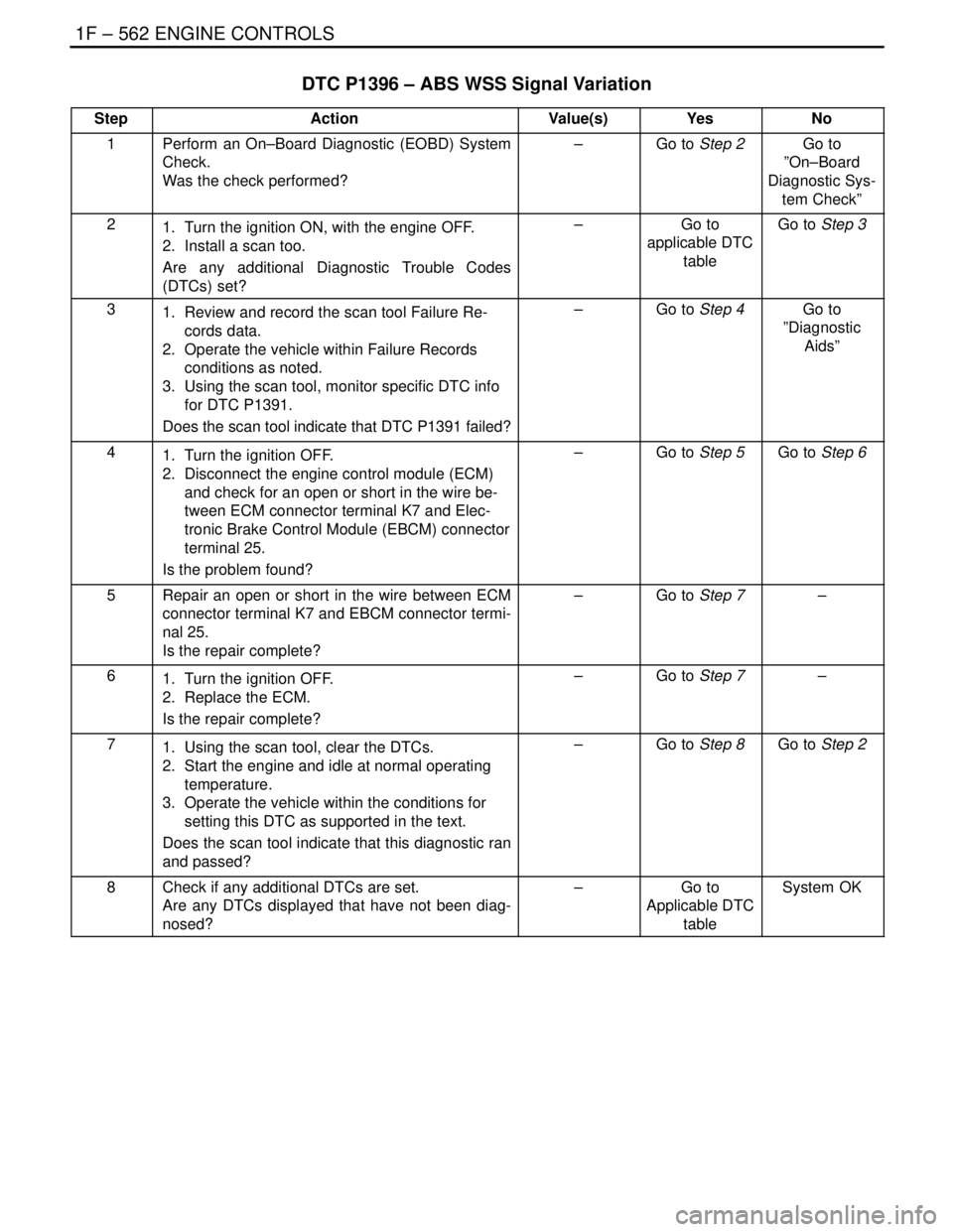
DTC P1396 – ABS WSS Signal Variation
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Install a scan too.
Are any additional Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTCs) set?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableGo to Step 3
31. Review and record the scan tool Failure Re-
cords data.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using the scan tool, monitor specific DTC info
for DTC P1391.
Does the scan tool indicate that DTC P1391 failed?–Go to Step 4Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids”
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the engine control module (ECM)
and check for an open or short in the wire be-
tween ECM connector terminal K7 and Elec-
tronic Brake Control Module (EBCM) connector
terminal 25.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Repair an open or short in the wire between ECM
connector terminal K7 and EBCM connector termi-
nal 25.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7–
61. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7–
71. Using the scan tool, clear the DTCs.
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as supported in the text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran
and passed?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 2
8Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 811 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 565
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1404
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION CLOSED VALVE
PINTLE ERROR
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber.When the air/fuelmixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced.
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with an En-
gine Control Module (ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM
controls the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle
Position (TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sen-
sors. The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate
when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through
the ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the De-
sired EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-
back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR Position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
Position.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Difference between current and learned low posi-
tion is greater than 10%.S Desired EGR position is equal to 0.
S Engine is running.
S Ignition voltage is between 11.7 and 16 volts.
S Intake Air Temperature (IAT) is greater than 3°C
(37.4°F).
S DTCs P0112, P0113, P0405, P0406, and P0502
are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
S EGR is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after three consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 80 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Due to moisture associated with exhaust systems, the
EGR valve may freeze and stick in cold weather. After the
vehicle is brought into a warm shop for repairs, the valve
warms and the problem disappears. By watching the Actu-
al EGR and Desired EGR Positions on a cold vehicle with
a scan tool, the fault can be easily verified. Check the
Page 822 of 2643
1F – 576IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
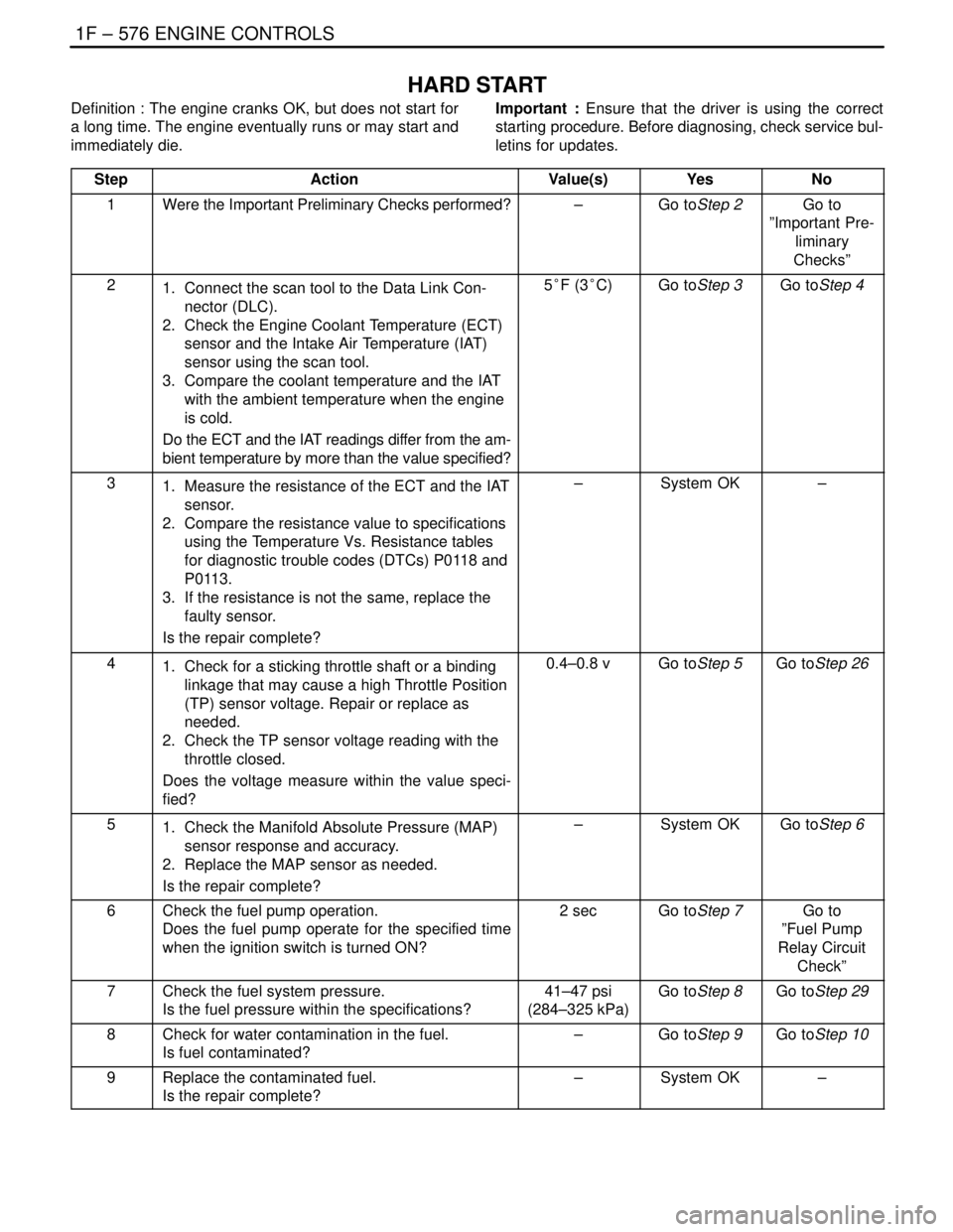
HARD START
Definition : The engine cranks OK, but does not start for
a long time. The engine eventually runs or may start and
immediately die.Important : Ensure that the driver is using the correct
starting procedure. Before diagnosing, check service bul-
letins for updates.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Were the Important Preliminary Checks performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”Important Pre-
liminary
Checks”
21. Connect the scan tool to the Data Link Con-
nector (DLC).
2. Check the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
sensor and the Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
sensor using the scan tool.
3. Compare the coolant temperature and the IAT
with the ambient temperature when the engine
is cold.
Do the ECT and the IAT readings differ from the am-
bient temperature by more than the value specified?5°F (3°C)Go toStep 3Go toStep 4
31. Measure the resistance of the ECT and the IAT
sensor.
2. Compare the resistance value to specifications
using the Temperature Vs. Resistance tables
for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) P0118 and
P0113.
3. If the resistance is not the same, replace the
faulty sensor.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
41. Check for a sticking throttle shaft or a binding
linkage that may cause a high Throttle Position
(TP) sensor voltage. Repair or replace as
needed.
2. Check the TP sensor voltage reading with the
throttle closed.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?0.4–0.8 vGo toStep 5Go toStep 26
51. Check the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
sensor response and accuracy.
2. Replace the MAP sensor as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OKGo toStep 6
6Check the fuel pump operation.
Does the fuel pump operate for the specified time
when the ignition switch is turned ON?2 secGo toStep 7Go to
”Fuel Pump
Relay Circuit
Check”
7Check the fuel system pressure.
Is the fuel pressure within the specifications?41–47 psi
(284–325 kPa)Go toStep 8Go toStep 29
8Check for water contamination in the fuel.
Is fuel contaminated?–Go toStep 9Go toStep 10
9Replace the contaminated fuel.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–