2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 78 of 2585

(7) Clean all foreign material off the threads of the
outer C/V joint stub shaft. Install the washer and
hub nut (Fig. 16) on the stub shaft of the outer C/V
joint.
(8) Lower vehicle.
(9) Set the park brake.This is required to keep
the driveshaft from rotating when tightening
and torquing the hub nut and driveshaft inner
joint to driveline module mounting nuts.
(10) Raise vehicle.
(11) Tighten the driveshaft inner joint to drive line
module output shaft mounting bolts to a torque of 61
N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
(12) Tighten the outer C/V joint hub nut (Fig. 16)
to a torque of 244 N´m (180 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the spring washer (Fig. 17) on the stub
shaft of the outer C/V joint.
(14) Install the nut retainer and cotter pin (Fig.
18) on the stub shaft of the outer C/V joint.
(15) Install the wheel speed sensor on the hub/
bearing and adapter. Install the wheel speed sensor
attaching bolt (Fig. 19). Tighten the wheel speed sen-
sor attaching bolt to a torque of 12 N´m (105 in. lbs).
Fig. 16 Hub Nut And Washer
1 - CALIPER
2 - HUB NUT
3 - WASHER
4 - ROTOR
5 - ADAPTER
Fig. 17 Spring Washer
1 - HUB NUT
2 - STUB SHAFT
3 - ROTOR
4 - SPRING WASHER
Fig. 18 Cotter Pin And Nut Retainer
1 - CALIPER
2 - COTTER PIN
3 - ROTOR
4 - NUT RETAINER
5 - OUTER C/V JOINT
RSREAR SUSPENSION2-35
HUB / BEARING (Continued)
Page 79 of 2585

(16) Install wheel and tire. (Refer to 22 - TIRES/
WHEELS - INSTALLATION)
(17) Tighten the wheel mounting stud nuts in
proper sequence until all nuts are torqued to half
specification. Then repeat the tightening sequence to
the full specified torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(18) Lower vehicle.
CAUTION: Before moving vehicle, pump the brake
pedal several times to insure the vehicle has a firm
brake pedal to adequately stop vehicle.
(19) Road test vehicle to ensure proper operation
of the brake system.
JOUNCE BUMPER
DESCRIPTION
There are two jounce bumpers used in the rear
suspension. One mounts to each frame rail above the
rear axle.
OPERATION
The jounce bumper limits suspension travel and
metal-to-metal contact of the rear axle with the
frame under full jounce conditions.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - AWD, HEAVY DUTY, CARGO
(1) Using slip-joint pliers grasp the base of the
jounce bumper. Turn the base counterclockwise (Fig.
20).
(2) Remove the jounce bumper from the frame rail.
REMOVAL - FRONT-WHEEL-DRIVE
(1) Remove the bolt attaching the jounce bumper
to frame rail (Fig. 21).
(2) Remove the jounce bumper from the frame rail.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - AWD, HEAVY DUTY, CARGO
(1) Install jounce bumper through bumper support
plate and thread into welded nut in frame rail.
(2) Tighten the jounce bumper to 33 N´m (290 in.
lbs.) torque.
INSTALLATION - FRONT-WHEEL-DRIVE
(1) Hook the forward end of the jounce bumper
bracket in the mounting hole of the frame rail, then
install the mounting bolt in the opposite end, secur-
ing the bumper to the frame rail. Tighten the jounce
bumper mounting bolt to 33 N´m (290 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 19 Wheel Speed Sensor
1 - MOUNTING BOLT
2 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 20 Jounce Bumper
1 - JOUNCE BUMPER
Fig. 21 Jounce Bumper - FWD
1-JOUNCE BUMPER
2 - 36 REAR SUSPENSIONRS
HUB / BEARING (Continued)
Page 82 of 2585

(6) Using the jack standsslowlylower the rear
axle, permitting the rear springs to hang free.
(7) Loosen and remove the 4 bolts at the front
mount of the rear leaf spring (Fig. 26).
(8) Loosen and remove the 2 bolts and the 2 pin
nuts from the spring shackle for the rear leaf spring
(Fig. 29). Then remove the inner half of the spring
shackle from the outer half hanger of the spring
hanger and the spring.
(9) Remove the rear leaf spring from the outer half
of the spring shackle.
(10) Remove the leaf spring from the vehicle.(11) Loosen and remove the pivot bolt from the
front mount of the rear leaf spring. (Fig. 30).INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Pivot bolt must face inboard to prevent
structural damage during installation of spring.
(1) Install the front eyelet of the rear leaf spring
into the spring mount. Install the pivot bolt and nut.
Do not tighten the pivot bolt at this time.
(2) Position the front spring mount for the rear
leaf spring against the floor pan of the vehicle.
Install the 4 mounting bolts for the front spring
Fig. 26 LIFTING POINT AND SPRING MOUNT
1 - BODY SILL AREA
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - SPRING MOUNTING BRACKET
4 - LEAF SPRING
5 - HOIST LIFT ARM
6 - WOODEN BLOCK
Fig. 27 Rear Shock Absorber Mounting Bolt
1 - SHOCK BOLT
Fig. 28 Axle Plate Bolts
1 - LEAF SPRING
2 - AXLE PLATE BOLTS (4)
3 - AXLE PLATE
4 - AXLE
Fig. 29 All-Wheel-Drive Rear Suspension
1 - SHACKLE
2 - REAR MOUNT (HANGER)
3 - LEAF SPRING (MULTI-LEAF)
4 - AWD REAR AXLE
RSREAR SUSPENSION2-39
SPRING - AWD (Continued)
Page 87 of 2585

be necessary to place a wooden block between the
spring and vehicle to hold forward end of the spring
in place.
(6) Remove leaf spring forward pivot bolt, then
remove mounting bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position spring mounting bracket over spring
eye and install pivot bolt through center of bushing
from theoutboardside.
NOTE: The pivot bolt must be installed from the
outboard side to allow proper bracket to body
mounting.
(2) Install the nut on the pivot bolt and lightly
tighten. Do not fully tighten bolt at this time.
(3) Raise the under-hoist utility jack or transmis-
sion jack, guiding the forward mounting bracket into
place against the body. It may help to use a drift
punch placed through the hole centered between the
mounting bolt holes in the bracket and the pilot hole
in the body of the vehicle as a guide. When the four
mounting bolt holes line up with their threads in the
body, Install the mounting bolts (Fig. 37). Tighten the
four mounting bolts to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Raise or lower the jack until shock absorber
lower eye aligns with threads in axle housing. Install
shock absorber lower mounting bolt. Do not fully
tighten bolt at this time.
(5) Lower the vehicle and remove hoist arms and
block of wood from under vehicle.
(6) Tighten the spring front pivot bolt to 156 N´m
(115 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Tighten the lower shock absorber mounting
bolt to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.) torque.
SPRING MOUNTS - REAR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the attaching nuts and bolts from the
leaf spring rear shackle (Fig. 38) and (Fig. 39).
(2) Install a jackstand under the side of the axle
having the leaf spring mount removed. Using the
jackstand, support the weight of the axle and leaf
spring.(3) Remove the lower mounting bolt from the
shock absorber.
(4) Remove the bolts attaching the leaf spring rear
mount to the body of the vehicle (Fig. 40).
(5) Lower the jackstand and the rear of the leaf
spring. Remove the shackle from the leaf spring
bushing.
Fig. 38 Leaf Spring Shackle Nuts (FWD)
1 - SHACKLE PLATE
Fig. 39 All-Wheel-Drive Rear Suspension
1 - SHACKLE
2 - REAR MOUNT (HANGER)
3 - LEAF SPRING (MULTI-LEAF)
4 - AWD REAR AXLE
2 - 44 REAR SUSPENSIONRS
SPRING MOUNTS - FRONT (Continued)
Page 88 of 2585

INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The following sequence must be fol-
lowed when tightening the pin nuts on the rear
hanger for the rear leaf spring. First the hanger pin
nuts must be tightened to the specified torque.
Then tighten the retaining bolts for the inner to
outer half of the spring hanger to the specified
torque. This sequence must be followed to avoid
bending the spring hanger.
(1) For installation, reverse removal procedure. Do
not tighten rear spring shackle nuts fully until vehi-
cle is lowered and the full vehicle weight is applied
to the rear wheels. Tighten rear spring mount bolts
to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.). Tighten shackle nuts to 61
N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
STABILIZER BAR
DESCRIPTION
Some front-wheel-drive models use a stabilizer bar.
It is mounted behind the rear axle. All-wheel-drive
models use a stabilizer bar that is mounted in front
of the rear axle.
The stabilizer bar interconnects both sides of the
rear axle and attaches to the rear frame rails using 2
rubber isolated link arms.
Both type stabilizer bars have the same basic com-
ponents. Attachment to the rear axle tube, and rear
frame rails is through rubber-isolated bushings.
The 2 rubber isolated links are connected to the
rear frame rails by brackets. These brackets are
bolted to the bottom of the frame rails.
OPERATION
Jounce and rebound movements affecting one
wheel are partially transmitted to the opposite wheel
to reduce body roll.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - AWD
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(2) Remove the bolts securing the stabilizer bar to
links on each end of the bar.
(3) While holding the stabilizer bar in place,
remove the bolts that attach the stabilizer bar bush-
ing retainers to the rear axle.
(4) Remove the stabilizer bar from the vehicle.
(5) If the links need to be serviced, remove the
upper link arm to bracket bolt. Then remove link
arm from frame rail attaching bracket.
REMOVAL - FWD
(1) Raise vehicle. See Hoisting in Lubrication and
Maintenance.
(2) Remove the bolts securing the stabilizer bar to
links on each side of bar.
(3) While holding the stabilizer bar in place,
remove the bolts that attach the stabilizer bar bush-
ing retainers to the rear axle.
(4) Remove the stabilizer bar from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - AWD
(1) Install the stabilizer bar on the rear axle.
(2) Install bushing retainer bolts. Do not tighten at
this time.
(3) Install bolts connecting links to stabilizer bar.
Do not tighten at this time.
(4) Lower the vehicle so that the full weight of the
vehicle is on all four tires. With the vehicle at its
curb height, tighten the following bolts to the torques
listed:
²Stabilizer bar bushing retainer-to-axle bracket
bolts Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
²Stabilizer bar-to-link bolts Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
INSTALLATION - FWD
(1) Lift the stabilizer bar onto the rear axle and
install the two retainer mounting bolts. DO NOT
TIGHTEN.
(2) Install the bolts attaching the stabilizer bar
links to the stabilizer bar. DO NOT TIGHTEN.
Fig. 40 Rear Spring Mount
1 - LEAF SPRING MOUNT
RSREAR SUSPENSION2-45
SPRING MOUNTS - REAR (Continued)
Page 89 of 2585

(3) Lower the vehicle so that the full weight of the
vehicle is on all four tires. With the vehicle at its
curb height, tighten the following bolts to the torques
listed:
²Stabilizer bar bushing retainer-to-axle bracket
bolts Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
²Stabilizer bar-to-link Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
TRACK BAR
DESCRIPTION
On front-wheel-drive applications of this vehicle
that are equipped with single leaf rear springs, a
track bar is used on the rear axle (Fig. 1).
The track bar connects the rear axle to the frame/
body of the vehicle. The track bar is isolated from the
body of the vehicle by an isolator bushing located in
each end of the track bar.
OPERATION
The track bar prevents excessive side-to-side move-
ment of the rear axle. The track bar is used to keep
the location of the axle in the correct position for
optimum handling and control of the vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the nut and bolt mounting the track
bar to the rear axle (Fig. 41).
(2) Remove the nut and bolt attaching the track
bar to the track bar mount on the body of the vehicle.
Remove the track bar from the track bar mount.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the track bar first into the body mount
for the track bar (Fig. 42). Install the track bar bolt
with the head of the bolt facing toward the rear of
the vehicle (Fig. 43). Do not tighten.
(2) Install the track bar into its mounting bracket
on the rear axle (Fig. 41). Install the track bar bolt
with the head of the bolt facing toward the rear of
the vehicle. Do not tighten.
(3) Lower the vehicle to the ground until the full
weight of the vehicle is supported by the wheels.
Tighten both track bar attaching bolts to a torque of
95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 41 Track Bar Mounting To Axle (Typical)
1 - LOWER TRACK BAR BOLT INSTALLATION
Fig. 42 Track Bar Installation (Typical)
1 - TRACK BAR REPLACEMENT
Fig. 43 Track Bar Bolt Installation
1 - TRACK BAR BOLT
2 - 46 REAR SUSPENSIONRS
STABILIZER BAR (Continued)
Page 90 of 2585
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION - WHEEL ALIGNMENT.......47
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUSPENSION
AND STEERING......................50
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL
ALIGNMENT.........................52STANDARD PROCEDURE - CURB HEIGHT
MEASUREMENT......................55
SPECIFICATIONS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT...................56
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION - WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Vehicle wheel alignment is the positioning of all
interrelated front and rear suspension angles. These
angles affect the handling and steering of the vehicle
when it is in motion. Proper wheel alignment is
essential for efficient steering, good directional stabil-
ity, and proper tire wear.
The method of checking a vehicle's front and rear
wheel alignment varies depending on the manufac-
turer and type of equipment used. The manufactur-
er's instructions should always be followed to ensure
accuracy of the alignment, except when
DaimlerChrysler Corporation's wheel alignment spec-
ifications differ.
On this vehicle, the suspension angles that can be
adjusted are as follows:
²Front Camber (with camber bolt package and
standard procedure)
²Front Toe
Check the wheel alignment and make all wheel
alignment adjustments with the vehicle standing at
its proper curb height specification. Curb height is
the normal riding height of the vehicle. It is mea-
sured from a certain point on the vehicle to the
ground or a designated area while the vehicle is sit-
ting on a flat, level surface. Refer to Curb Height
Measurement in this section for additional informa-
tion.
Typical wheel alignment angles and measurements
are described in the following paragraphs.
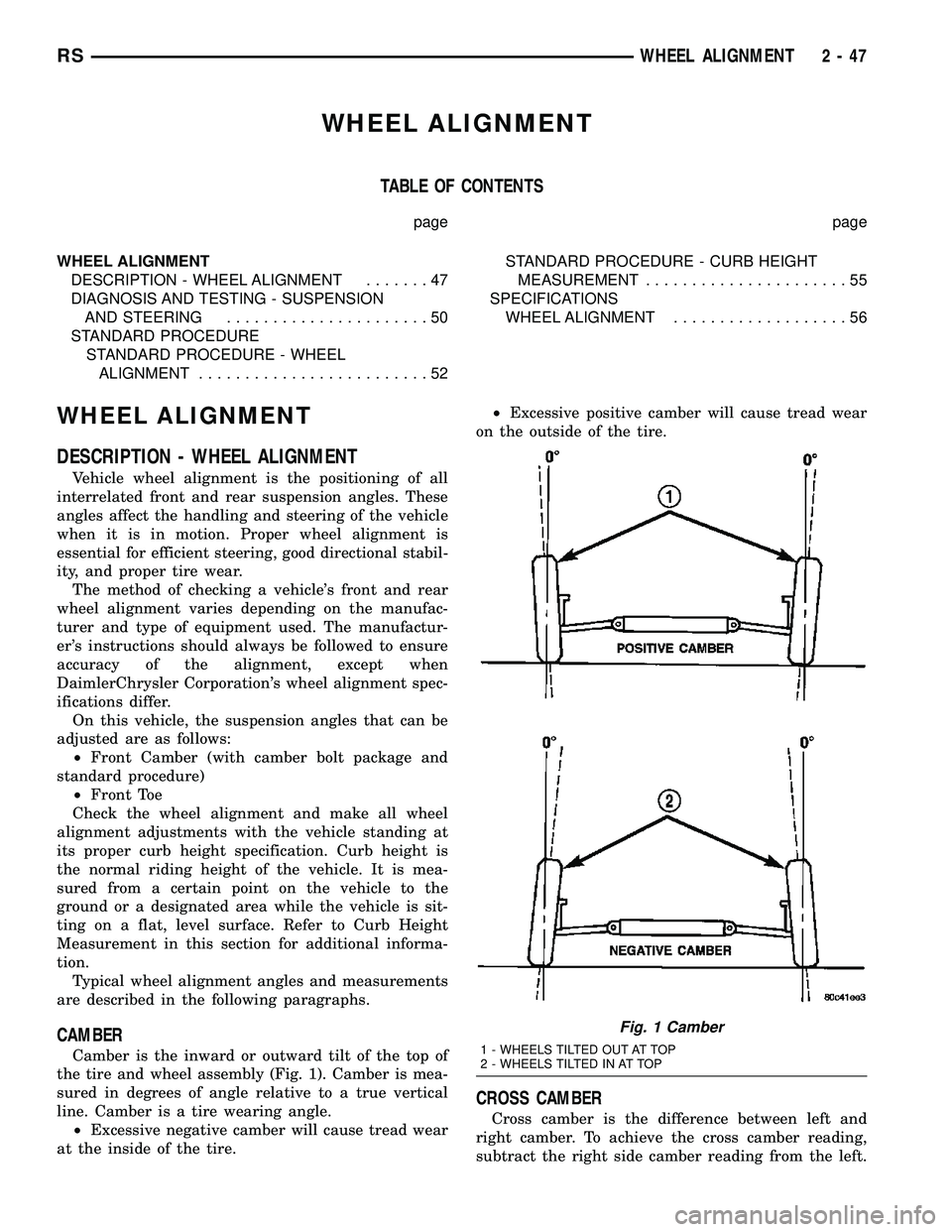
CAMBER
Camber is the inward or outward tilt of the top of
the tire and wheel assembly (Fig. 1). Camber is mea-
sured in degrees of angle relative to a true vertical
line. Camber is a tire wearing angle.
²Excessive negative camber will cause tread wear
at the inside of the tire.²Excessive positive camber will cause tread wear
on the outside of the tire.
CROSS CAMBER
Cross camber is the difference between left and
right camber. To achieve the cross camber reading,
subtract the right side camber reading from the left.
Fig. 1 Camber
1 - WHEELS TILTED OUT AT TOP
2 - WHEELS TILTED IN AT TOP
RSWHEEL ALIGNMENT2-47
Page 91 of 2585
For example, if the left camber is +0.3É and the right
camber is 0.0É, the cross camber would be +0.3É.
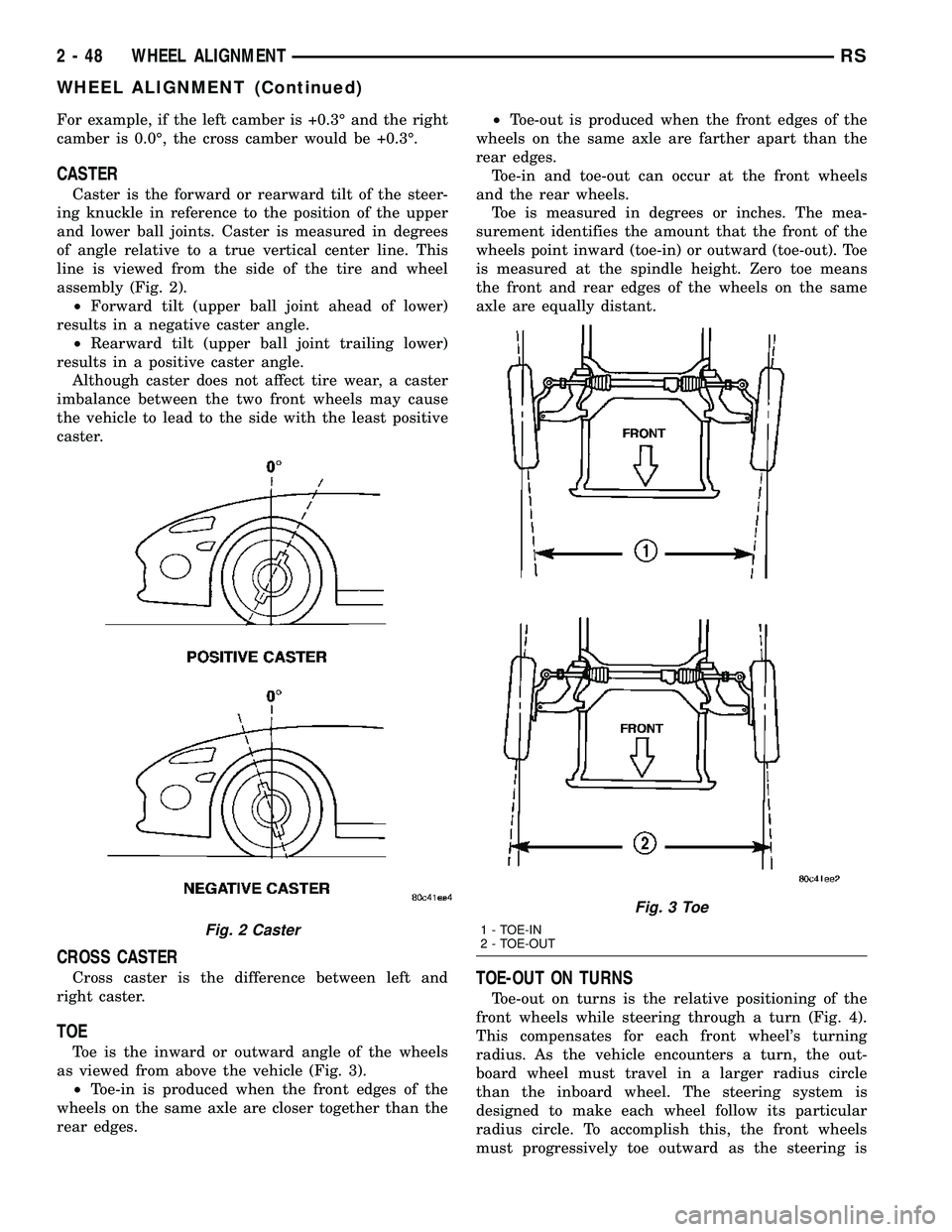
CASTER
Caster is the forward or rearward tilt of the steer-
ing knuckle in reference to the position of the upper
and lower ball joints. Caster is measured in degrees
of angle relative to a true vertical center line. This
line is viewed from the side of the tire and wheel
assembly (Fig. 2).
²Forward tilt (upper ball joint ahead of lower)
results in a negative caster angle.
²Rearward tilt (upper ball joint trailing lower)
results in a positive caster angle.
Although caster does not affect tire wear, a caster
imbalance between the two front wheels may cause
the vehicle to lead to the side with the least positive
caster.
CROSS CASTER
Cross caster is the difference between left and
right caster.
TOE
Toe is the inward or outward angle of the wheels
as viewed from above the vehicle (Fig. 3).
²Toe-in is produced when the front edges of the
wheels on the same axle are closer together than the
rear edges.²Toe-out is produced when the front edges of the
wheels on the same axle are farther apart than the
rear edges.
Toe-in and toe-out can occur at the front wheels
and the rear wheels.
Toe is measured in degrees or inches. The mea-
surement identifies the amount that the front of the
wheels point inward (toe-in) or outward (toe-out). Toe
is measured at the spindle height. Zero toe means
the front and rear edges of the wheels on the same
axle are equally distant.
TOE-OUT ON TURNS
Toe-out on turns is the relative positioning of the
front wheels while steering through a turn (Fig. 4).
This compensates for each front wheel's turning
radius. As the vehicle encounters a turn, the out-
board wheel must travel in a larger radius circle
than the inboard wheel. The steering system is
designed to make each wheel follow its particular
radius circle. To accomplish this, the front wheels
must progressively toe outward as the steering is
Fig. 2 Caster
Fig. 3 Toe
1 - TOE-IN
2 - TOE-OUT
2 - 48 WHEEL ALIGNMENTRS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)