Page 1992 of 2585
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump is located in the pump housing inside
the bell housing of the transaxle case (Fig. 255). The
oil pump consists of an inner and outer gear, a hous-
ing, and a cover that also serves as the reaction shaft
support.
OPERATION
As the torque converter rotates, the converter hub
rotates the inner and outer gears. As the gears
rotate, the clearance between the gear teeth
increases in the crescent area, and creates a suction
at the inlet side of the pump. This suction draws
fluid through the pump inlet from the oil pan. As the
clearance between the gear teeth in the crescent area
decreases, it forces pressurized fluid into the pump
outlet and to the valve body.
DISASSEMBLY
When disassembling the transaxle it is necessary
to inspect the oil pump for wear and damage. (1) Remove the reaction shaft support bolts.
(2) Remove reaction shaft support from pump
housing (Fig. 256). (3) Remove the pump gears (Fig. 257) and check
for wear and damage on pump housing and gears. (4) Re-install the gears and check clearances. (5) Measure the clearance between the outer gear
and the pump pocket (Fig. 258). Clearance should be
0.089±0.202 mm (0.0035-0.0079 in.). (6) Measure clearance between outer gear and
crescent. Clearance should be 0.060-0.298 mm
(0.0023-0.0117 in.). (7) Measure clearance between inner gear and
crescent. Clearance should be 0.093-0.385 mm
(0.0036-0.0151 in.).
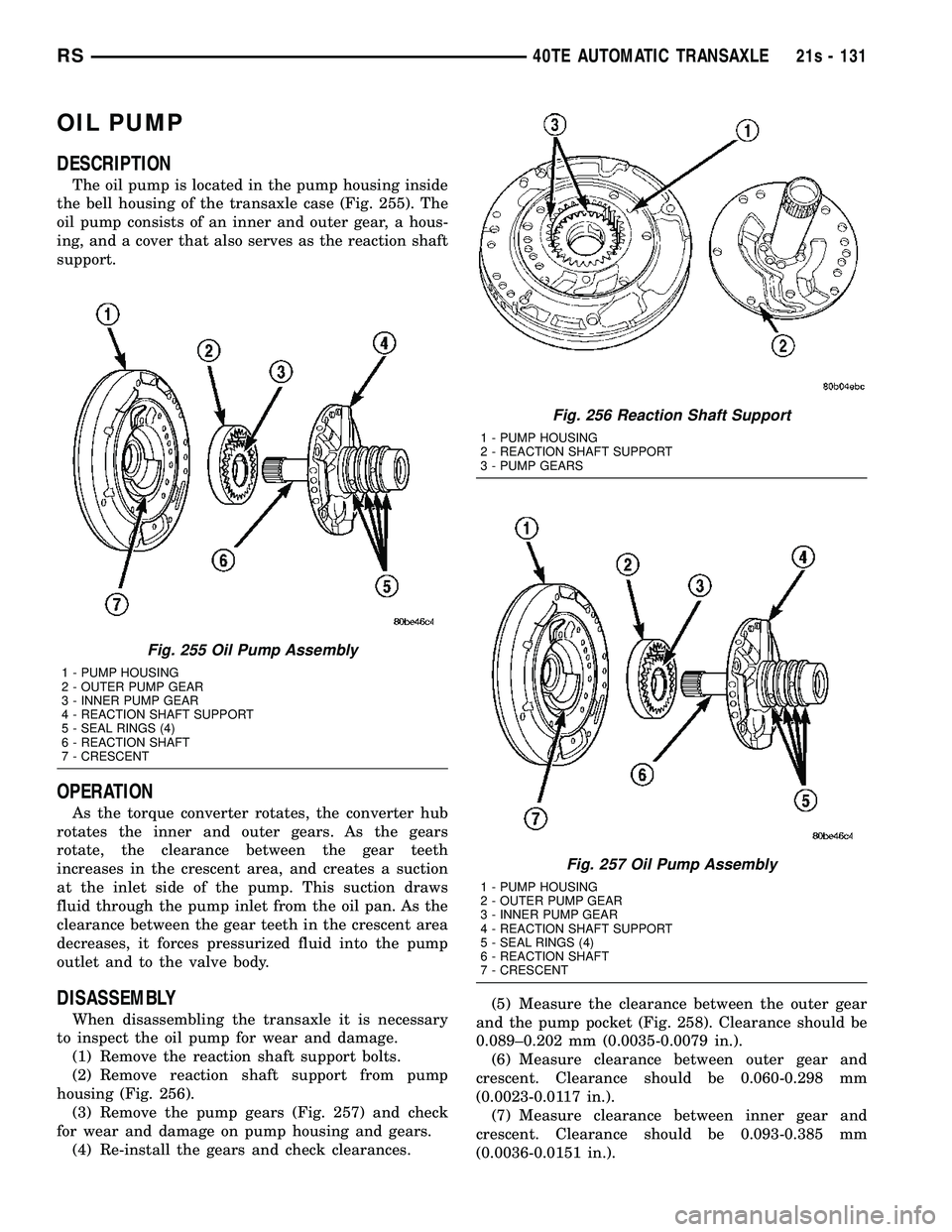
Fig. 255 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - OUTER PUMP GEAR
3 - INNER PUMP GEAR
4 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
5 - SEAL RINGS (4)
6 - REACTION SHAFT
7 - CRESCENT
Fig. 256 Reaction Shaft Support
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
3 - PUMP GEARS
Fig. 257 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - OUTER PUMP GEAR
3 - INNER PUMP GEAR
4 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
5 - SEAL RINGS (4)
6 - REACTION SHAFT
7 - CRESCENT
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 131
Page 1993 of 2585
(8) Position an appropriate piece of Plastigage
across both pump gears. (9) Align the Plastigage to a flat area on the reac-
tion shaft support housing. (10) Install the reaction shaft to the pump hous-
ing. Tighten the bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.). (11) Remove bolts and carefully separate the hous-
ings. Measure the Plastigage following the instruc-
tions supplied. (12) Clearance between outer gear side and the
reaction shaft support should be 0.020-0.046 mm
(0.0008-0.0018 in.). Clearance between inner gear
side and the reaction shaft support should be 0.020-
0.046 mm (0.0008-0.0018 in.).
ASSEMBLY
(1) Assemble oil pump as shown in (Fig. 259)
(2) Install and torque reaction shaft support-to-oil
pump housing bolts to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION
The planetary geartrain is located between the
input clutch assembly and the rear of the transaxle
case. The planetary geartrain consists of two sun
gears, two planetary carriers, two annulus (ring)
gears, and one output shaft (Fig. 260).
OPERATION
The planetary geartrain utilizes two planetary gear
sets that connect the transmission input shaft to the
output shaft. Input and holding clutches drive or lock
different planetary members to change output ratio
or direction.
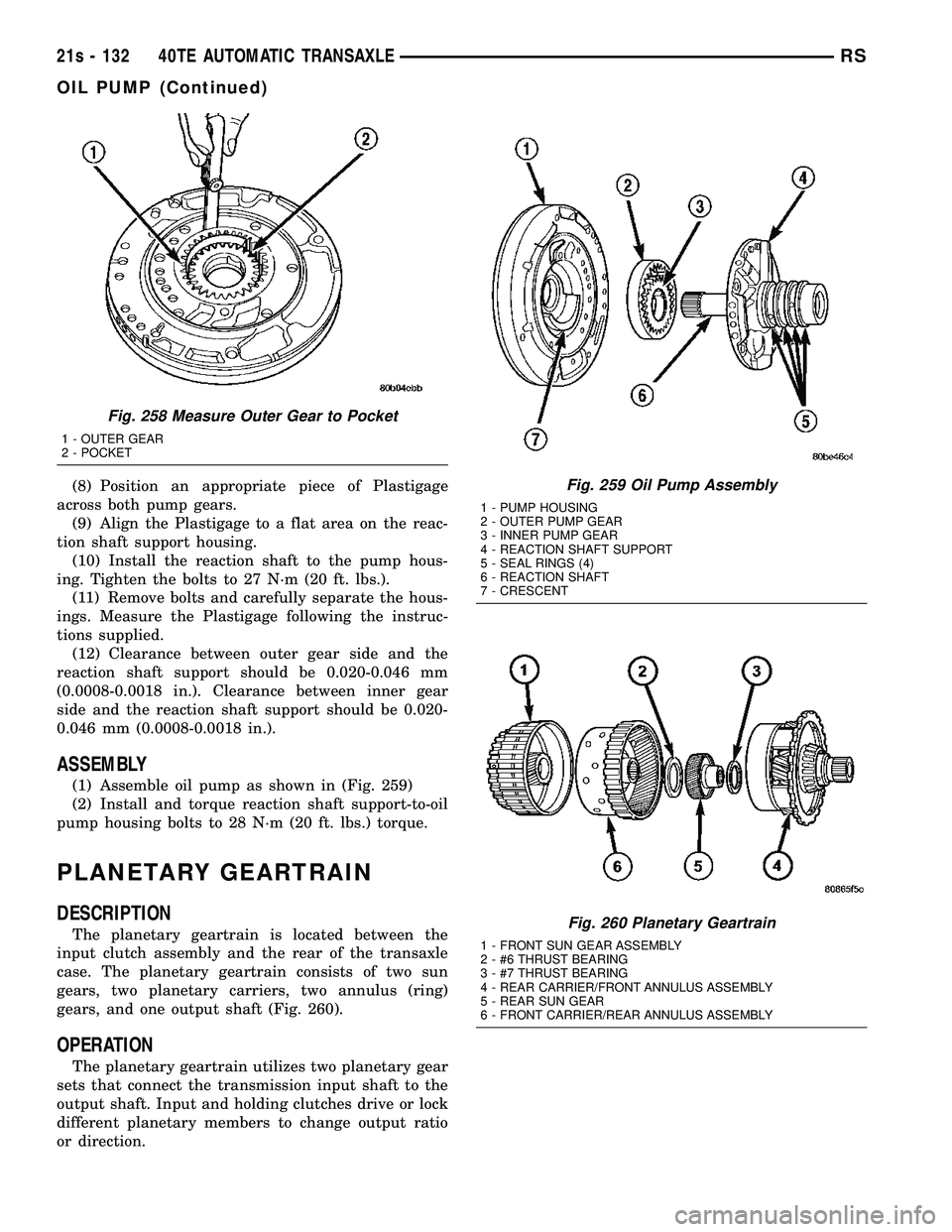
Fig. 258 Measure Outer Gear to Pocket
1 - OUTER GEAR
2 - POCKET
Fig. 259 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - OUTER PUMP GEAR
3 - INNER PUMP GEAR
4 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
5 - SEAL RINGS (4)
6 - REACTION SHAFT
7 - CRESCENT
Fig. 260 Planetary Geartrain
1 - FRONT SUN GEAR ASSEMBLY
2 - #6 THRUST BEARING
3 - #7 THRUST BEARING
4 - REAR CARRIER/FRONT ANNULUS ASSEMBLY
5 - REAR SUN GEAR
6 - FRONT CARRIER/REAR ANNULUS ASSEMBLY
21s - 132 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 2000 of 2585

(5) Remove input speed sensor (Fig. 278).
(6) Remove three (3) solenoid/pressure switch
assembly-to-transaxle case bolts (Fig. 279).
(7) Remove solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
gasket (Fig. 280). Use care to prevent gasket mate-
rial and foreign objects from become lodged in the
transaxle case ports.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If solenoid/pressure switch assembly is
being replaced, it is necessary to perform the TCM
Quick Learn Procedure. (Refer t o 8 - ELECTRICAL/
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Install solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
new gasket to transaxle (Fig. 280). (2) Install and torque three (3) bolts (Fig. 279) to
13 N´m (110 in. lbs.). (3) Install input speed sensor (Fig. 278) and torque
to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.). (4) Connect input speed sensor connector (Fig.
277). (5) Install solenoid/pressure switch 8-way connec-
tor and torque to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) (Fig. 277). (6) Install air cleaner assembly.
(7) Connect battery negative cable.
(8) If solenoid/pressure switch assembly was
replaced, perform TCM Quick Learn procedure.
(Refer t o 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 278 Input Speed Sensor
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 279 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly-to- Case Bolts
1 - BOLTS
2 - SOLENOID AND PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 280 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly and Gasket
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
2 - GASKET
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 139
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY (Continued)
Page 2001 of 2585
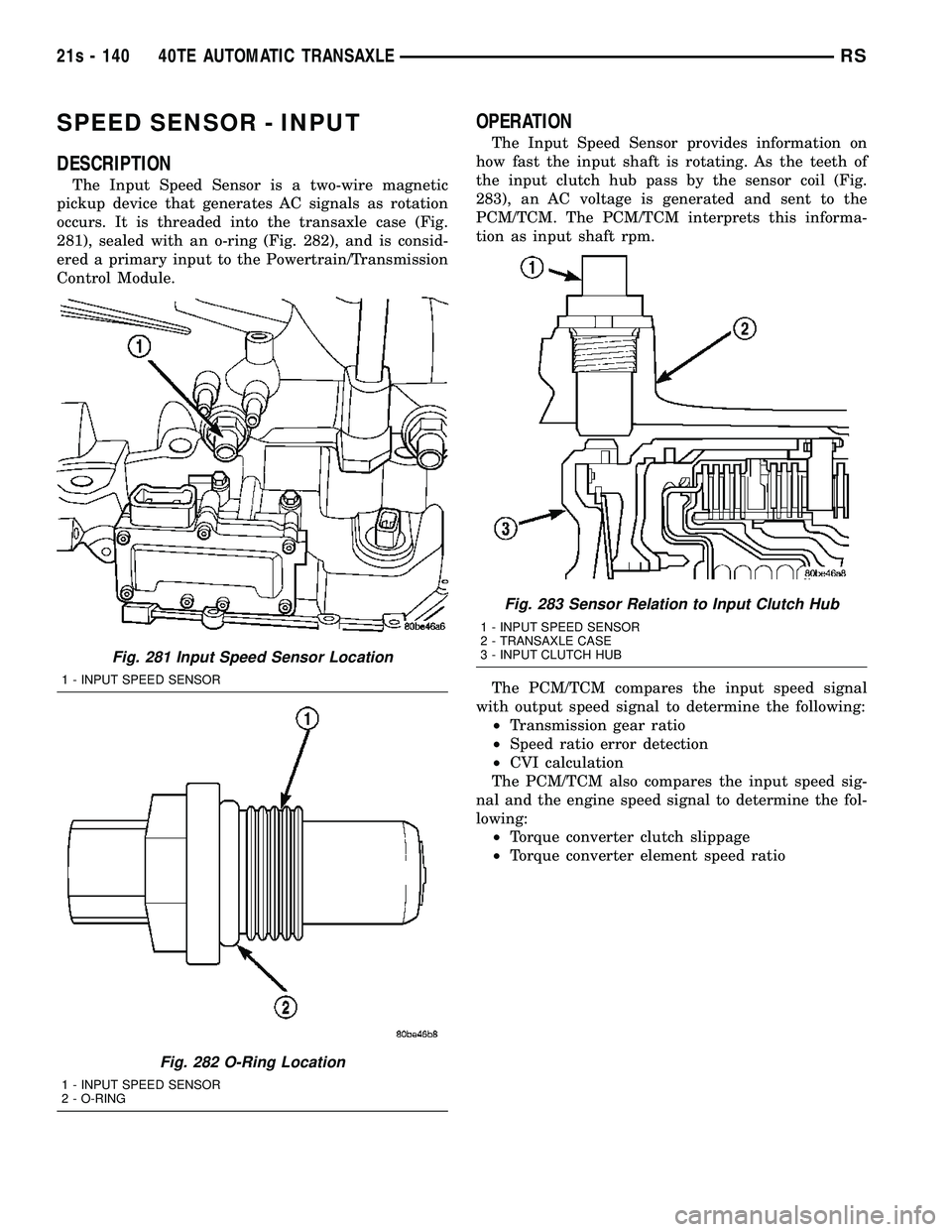
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The Input Speed Sensor is a two-wire magnetic
pickup device that generates AC signals as rotation
occurs. It is threaded into the transaxle case (Fig.
281), sealed with an o-ring (Fig. 282), and is consid-
ered a primary input to the Powertrain/Transmission
Control Module.
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil (Fig.
283), an AC voltage is generated and sent to the
PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this informa-
tion as input shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input speed signal
with output speed signal to determine the following: ² Transmission gear ratio
² Speed ratio error detection
² CVI calculation
The PCM/TCM also compares the input speed sig-
nal and the engine speed signal to determine the fol-
lowing: ² Torque converter clutch slippage
² Torque converter element speed ratio
Fig. 281 Input Speed Sensor Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 282 O-Ring Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
Fig. 283 Sensor Relation to Input Clutch Hub
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - TRANSAXLE CASE
3 - INPUT CLUTCH HUB
21s - 140 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 2005 of 2585
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 293) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The con-
verter clutch engages in third gear. The torque con-
verter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid) pump. The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
Fig. 293 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
6 - DRIVE PLATE
21s - 144 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 2006 of 2585
IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 294) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving member of the system.
Fig. 294 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE
SECTION 5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 145
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2007 of 2585
TURBINE
The turbine (Fig. 295) is the output, or driven,
member of the converter. The turbine is mounted
within the housing opposite the impeller, but is not
attached to the housing. The input shaft is inserted
through the center of the impeller and splined into
the turbine. The design of the turbine is similar to
the impeller, except the blades of the turbine are
curved in the opposite direction.
Fig. 295 Turbine
1 - TURBINE VANE
2 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - INPUT SHAFT 4 - PORTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER COVER
5 - ENGINE ROTATION
6 - OIL FLOW WITHIN TURBINE SECTION
21s - 146 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2008 of 2585

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 296) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 297).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 298) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock±free power transfer, it
is natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impel-
ler and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston was added to the turbine, and a friction mate-
rial was added to the inside of the front cover to pro-
vide this mechanical lock-up.
Fig. 296 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 297 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 298 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 147
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)