2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE frame
[x] Cancel search: framePage 1964 of 2199

REAR SEAT CUSHION COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove rear seat cushion (Refer to 23 - BODY/
SEATS/REAR SEAT CUSHION - REMOVAL).
(2) From the underside of the seat, disengage
J-straps attaching cover to seat cushion base panel.
(3) Remove push-in fasteners attaching cushion
cover to seat cushion base panel (Fig. 14).
(4) Roll back cover.
(5) Disengage hog rings attaching cushion cover to
seat cushion foam pad.
(6) Separate cushion cover from seat cushion foam
pad.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position cushion cover on seat cushion foam
pad.
(2) Engage hog rings attaching cushion cover to
seat cushion foam pad.
(3) Align cushion cover and engage J-straps
attaching cushion cover to seat cushion base panel.
(4) Install push-in fasteners attaching cushion
cover to seat cushion base panel.
(5) Install rear seat cushion (Refer to 23 - BODY/
SEATS/REAR SEAT CUSHION - INSTALLATION).
REAR SEAT CUSHION
RELEASE LATCH
REMOVAL
(1) Unlatch seat and pivot seat upward.
(2) Disengage J-strap at seat cushion base panel.
(3) Roll back cushion cover.(4) Remove screws attaching latch to base panel.
(5) Separate latch from base panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position latch on base panel.
(2) Install screws attaching latch to base panel.
Tighten screws to 8 N´m (75 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Route the cushion release strap from the loop
on the latch through the slot in the trim cover.
(4) Engage J-strap at seat cushion base panel.
(5) latch seat.
FOLDING REAR SEAT BACK
LATCH HANDLE
REMOVAL
(1) Pull handle to release latch.
(2) Remove screws attaching release handle to seat
back frame.
(3) Using a small flat blade, disengage retainers
securing latch release cable housing to latch release
handle.
(4) Rotate cable end until barrel end aligns with
key hole slot in latch release handle.
(5) Disengage cable barrel end from release han-
dle.
(6) Separate latch release handle from seat back
(Fig. 15).
Fig. 14 Push-in Fasteners
1 - CUSHION COVER
2 - SEAT CUSHION BASE PANEL
3 - PUSH-IN FASTENER
Fig. 15 Rear Seat Release Handle
1 - REAR SEAT FOLDING RELEASE HANDLE
WJSEATS 23 - 91
Page 1965 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Route cable end into latch release handle.
(2) Rotate cable end until barrel end aligns with
key hole slot in latch release handle and insert into
handle.
(3) Engage retainers securing latch release cable
housing to latch release handle.
(4) Position latch release handle in seat back.
Ensure seat back cover is properly aligned.
(5) Install screws attaching release handle to seat
back frame.
FOLDING REAR SEAT BACK
LATCH/HINGE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove seat back (Refer to 23 - BODY/SEATS/
REAR SEAT BACK - REMOVAL).
(2) Disengage J-straps on outboard side of seat
back.
(3) Disengage release cable from latch.
(4) Remove bolts attaching latch/hinge to seat back
frame.
(5) Separate latch/hinge from seat back frame.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position latch/hinge on seat back frame.
(2) Install bolts attaching latch/hinge to seat back
frame. Tighten bolts to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Engage latch release cable.
(4) Engage J-straps on outboard side of seat back.
(5) Install seat back (Refer to 23 - BODY/SEATS/
REAR SEAT BACK - INSTALLATION).
23 - 92 SEATSWJ
FOLDING REAR SEAT BACK LATCH HANDLE (Continued)
Page 1966 of 2199

STATIONARY GLASS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DOOR GLASS
REMOVAL.............................93
INSTALLATION.........................93
QUARTER WINDOW
REMOVAL.............................93INSTALLATION.........................93
WINDSHIELD
REMOVAL.............................94
INSTALLATION.........................95
DOOR GLASS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove door trim panel.
(2) Remove waterdam.
(3) Remove inner belt weatherstrip.
(4) Remove bolt attaching bottom of rear glass run
channel to door.
(5) Pull run channel downward and separate from
door.
(6) Remove screws attaching stationary door glass
frame to door (Fig. 1) and (Fig. 2).
(7) Separate stationary door glass from door.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position stationary door glass in door.
(2) Install screws attaching stationary door glass
frame to door.
(3) Install glass run channel.
(4) Install inner belt weatherstrip.
(5) Install waterdam.
(6) Install door trim panel.
QUARTER WINDOW
REMOVAL
(1) Cut urethane bonding from around quarter
window glass using a suitable sharp cold knife. A
pneumatic cutting device can be used if available.
(2) Separate glass from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Open a window before installing glass.
This will avoid pressurizing the passenger compart-
ment. If a door or liftgate is slammed before ure-
thane is cured, water leaks can result.
The window opening fence should be cleaned of old
urethane bonding material.
(1) Clean inside of glass with Mopar Glass Cleaner
and lint-free cloth.
(2) Apply PVC (vinyl) primer 25 mm (1 in.) wide
around edge of glass. Wipe with clean/dry lint-free
cloth.
Fig. 1 Stationary Door Glass
1 - DOOR
2 - STATIONARY DOOR GLASS
Fig. 2 Stationary Door Glass
1 - STATIONARY DOOR GLASS
2 - DOOR
WJSTATIONARY GLASS 23 - 93
Page 1972 of 2199
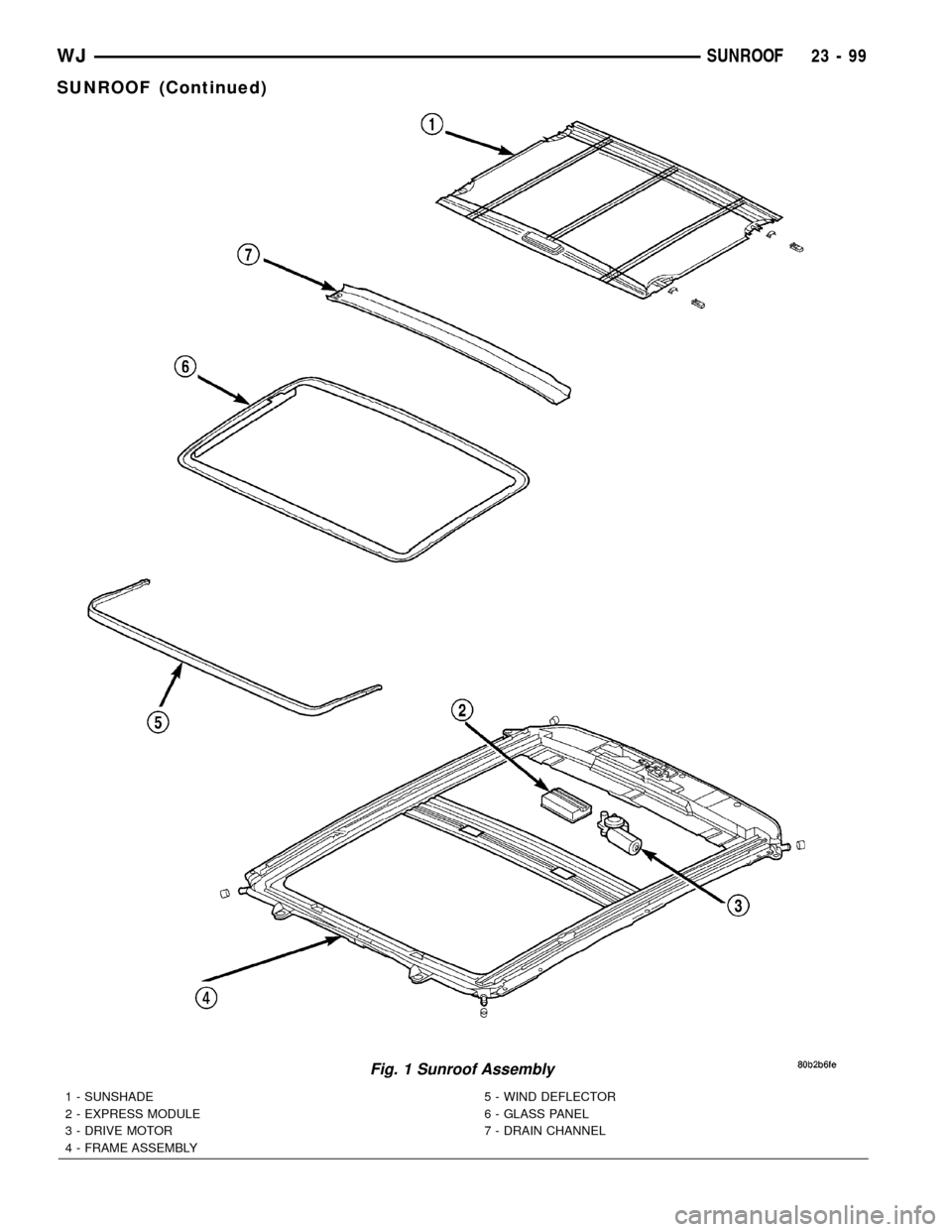
Fig. 1 Sunroof Assembly
1 - SUNSHADE
2 - EXPRESS MODULE
3 - DRIVE MOTOR
4 - FRAME ASSEMBLY5 - WIND DEFLECTOR
6 - GLASS PANEL
7 - DRAIN CHANNEL
WJSUNROOF 23 - 99
SUNROOF (Continued)
Page 2157 of 2199

DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connect
the DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0030 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0031 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0032 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0036 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0037 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0038 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0043 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0044 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0051 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0052 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2176 of 2199

OPERATION - TASK MANAGER
The Task Manager determines which tests happen
when and which functions occur when. Many of the
diagnostic steps required by OBD II must be per-
formed under specific operating conditions. The Task
Manager software organizes and prioritizes the diag-
nostic procedures. The job of the Task Manager is to
determine if conditions are appropriate for tests to be
run, monitor the parameters for a trip for each test,
and record the results of the test. Following are the
responsibilities of the Task Manager software:
²Test Sequence
²MIL Illumination
²Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
²Trip Indicator
²Freeze Frame Data Storage
²Similar Conditions Window
Test Sequence
In many instances, emissions systems must fail
diagnostic tests more than once before the PCM illu-
minates the MIL. These tests are know as 'two trip
monitors.' Other tests that turn the MIL lamp on
after a single failure are known as 'one trip moni-
tors.' A trip is defined as 'start the vehicle and oper-
ate it to meet the criteria necessary to run the given
monitor.'
Many of the diagnostic tests must be performed
under certain operating conditions. However, there
are times when tests cannot be run because another
test is in progress (conflict), another test has failed
(pending) or the Task Manager has set a fault that
may cause a failure of the test (suspend).
²Pending
Under some situations the Task Manager will not
run a monitor if the MIL is illuminated and a fault is
stored from another monitor. In these situations, the
Task Manager postpones monitorspendingresolu-
tion of the original fault. The Task Manager does not
run the test until the problem is remedied.
For example, when the MIL is illuminated for an
Oxygen Sensor fault, the Task Manager does not run
the Catalyst Monitor until the Oxygen Sensor fault is
remedied. Since the Catalyst Monitor is based on sig-
nals from the Oxygen Sensor, running the test would
produce inaccurate results.
²Conflict
There are situations when the Task Manager does
not run a test if another monitor is in progress. In
these situations, the effects of another monitor run-
ning could result in an erroneous failure. If thiscon-
flictis present, the monitor is not run until the
conflicting condition passes. Most likely the monitor
will run later after the conflicting monitor has
passed.
For example, if the Fuel System Monitor is inprogress, the Task Manager does not run the EGR
Monitor. Since both tests monitor changes in air/fuel
ratio and adaptive fuel compensation, the monitors
will conflict with each other.
²Suspend
Occasionally the Task Manager may not allow a two
trip fault to mature. The Task Manager willsus-
pendthe maturing of a fault if a condition exists
that may induce an erroneous failure. This prevents
illuminating the MIL for the wrong fault and allows
more precis diagnosis.
For example, if the PCM is storing a one trip fault
for the Oxygen Sensor and the EGR monitor, the
Task Manager may still run the EGR Monitor but
will suspend the results until the Oxygen Sensor
Monitor either passes or fails. At that point the Task
Manager can determine if the EGR system is actu-
ally failing or if an Oxygen Sensor is failing.MIL Illumination
The PCM Task Manager carries out the illumina-
tion of the MIL. The Task Manager triggers MIL illu-
mination upon test failure, depending on monitor
failure criteria.
The Task Manager Screen shows both a Requested
MIL state and an Actual MIL state. When the MIL is
illuminated upon completion of a test for a third trip,
the Requested MIL state changes to OFF. However,
the MIL remains illuminated until the next key
cycle. (On some vehicles, the MIL will actually turn
OFF during the third key cycle) During the key cycle
for the third good trip, the Requested MIL state is
OFF, while the Actual MIL state is ON. After the
next key cycle, the MIL is not illuminated and both
MIL states read OFF.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
With OBD II, different DTC faults have different
priorities according to regulations. As a result, the
priorities determine MIL illumination and DTC era-
sure. DTCs are entered according to individual prior-
ity. DTCs with a higher priority overwrite lower
priority DTCs.
Priorities
²Priority 0 ÐNon-emissions related trouble codes
²Priority 1 Ð One trip failure of a two trip fault
for non-fuel system and non-misfire.
²Priority 2 Ð One trip failure of a two trip fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) or misfire.
²Priority3ÐTwotrip failure for a non-fuel sys-
tem and non-misfire or matured one trip comprehen-
sive component fault.
²Priority4ÐTwotrip failure or matured fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) and misfire or one trip cat-
alyst damaging misfire.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 21
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2177 of 2199

Non-emissions related failures have no priority.
One trip failures of two trip faults have low priority.
Two trip failures or matured faults have higher pri-
ority. One and two trip failures of fuel system and
misfire monitor take precedence over non-fuel system
and non-misfire failures.
DTC Self Erasure
With one trip components or systems, the MIL is
illuminated upon test failure and DTCs are stored.
Two trip monitors are components requiring failure
in two consecutive trips for MIL illumination. Upon
failure of the first test, the Task Manager enters a
maturing code. If the component fails the test for a
second time the code matures and a DTC is set.
After three good trips the MIL is extinguished and
the Task Manager automatically switches the trip
counter to a warm-up cycle counter. DTCs are auto-
matically erased following 40 warm-up cycles if the
component does not fail again.
For misfire and fuel system monitors, the compo-
nent must pass the test under a Similar Conditions
Window in order to record a good trip. A Similar Con-
ditions Window is when engine RPM is within 375
RPM and load is within 10% of when the fault
occurred.
NOTE: It is important to understand that a compo-
nent does not have to fail under a similar window of
operation to mature. It must pass the test under a
Similar Conditions Window when it failed to record
a Good Trip for DTC erasure for misfire and fuel
system monitors.
DTCs can be erased anytime with a DRB III. Eras-
ing the DTC with the DRB III erases all OBD II
information. The DRB III automatically displays a
warning that erasing the DTC will also erase all
OBD II monitor data. This includes all counter infor-
mation for warm-up cycles, trips and Freeze Frame.
Trip Indicator
TheTripis essential for running monitors and
extinguishing the MIL. In OBD II terms, a trip is a
set of vehicle operating conditions that must be met
for a specific monitor to run. All trips begin with a
key cycle.
Good Trip
The Good Trip counters are as follows:
²Specific Good Trip
²Fuel System Good Trip
²Misfire Good Trip
²Alternate Good Trip (appears as a Global Good
Trip on DRB III)
²Comprehensive Components
²Major Monitor
²Warm-Up CyclesSpecific Good Trip
The term Good Trip has different meanings
depending on the circumstances:
²If the MIL is OFF, a trip is defined as when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst Monitor
have been completed in the same drive cycle.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by the Fuel
Monitor or Misfire Monitor (both continuous moni-
tors), the vehicle must be operated in the Similar
Condition Window for a specified amount of time.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by a Task
Manager commanded once-per-trip monitor (such as
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Catalyst Monitor, Purge
Flow Monitor, Leak Detection Pump Monitor, EGR
Monitor or Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor), a good
trip is when the monitor is passed on the next start-
up.
²If the MIL is ON and any other emissions DTC
was set (not an OBD II monitor), a good trip occurs
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Mon-
itor have been completed, or two minutes of engine
run time if the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst
Monitor have been stopped from running.
Fuel System Good Trip
To count a good trip (three required) and turn off
the MIL, the following conditions must occur:
²Engine in closed loop
²Operating in Similar Conditions Window
²Short Term multiplied by Long Term less than
threshold
²Less than threshold for a predetermined time
If all of the previous criteria are met, the PCM will
count a good trip (three required) and turn off the
MIL.
Misfire Good Trip
If the following conditions are met the PCM will
count one good trip (three required) in order to turn
off the MIL:
²Operating in Similar Condition Window
²1000 engine revolutions with no misfire
Warm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRB III. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
25 - 22 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2178 of 2199

Freeze Frame Data Storage
Once a failure occurs, the Task Manager records
several engine operating conditions and stores it in a
Freeze Frame. The Freeze Frame is considered one
frame of information taken by an on-board data
recorder. When a fault occurs, the PCM stores the
input data from various sensors so that technicians
can determine under what vehicle operating condi-
tions the failure occurred.
The data stored in Freeze Frame is usually
recorded when a system fails the first time for two
trip faults. Freeze Frame data will only be overwrit-
ten by a different fault with a higher priority.
CAUTION: Erasing DTCs, either with the DRB III or
by disconnecting the battery, also clears all Freeze
Frame data.
Similar Conditions Window
The Similar Conditions Window displays informa-
tion about engine operation during a monitor. Abso-
lute MAP (engine load) and Engine RPM are stored
in this window when a failure occurs. There are two
different Similar conditions Windows: Fuel System
and Misfire.
FUEL SYSTEM
²Fuel System Similar Conditions WindowÐ
An indicator that 'Absolute MAP When Fuel Sys Fail'
and 'RPM When Fuel Sys Failed' are all in the same
range when the failure occurred. Indicated by switch-
ing from 'NO' to 'YES'.
²Absolute MAP When Fuel Sys FailÐ The
stored MAP reading at the time of failure. Informs
the user at what engine load the failure occurred.
²Absolute MAPÐ A live reading of engine load
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²RPM When Fuel Sys FailÐ The stored RPM
reading at the time of failure. Informs the user at
what engine RPM the failure occurred.
²Engine RPMÐ A live reading of engine RPM
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²Adaptive Memory FactorÐ The PCM utilizes
both Short Term Compensation and Long Term Adap-
tive to calculate the Adaptive Memory Factor for
total fuel correction.
²Upstream O2S VoltsÐ A live reading of the
Oxygen Sensor to indicate its performance. For
example, stuck lean, stuck rich, etc.
²SCW Time in Window (Similar Conditions
Window Time in Window)Ð A timer used by thePCM that indicates that, after all Similar Conditions
have been met, if there has been enough good engine
running time in the SCW without failure detected.
This timer is used to increment a Good Trip.
²Fuel System Good Trip CounterÐATrip
Counter used to turn OFF the MIL for Fuel System
DTCs. To increment a Fuel System Good Trip, the
engine must be in the Similar Conditions Window,
Adaptive Memory Factor must be less than cali-
brated threshold and the Adaptive Memory Factor
must stay below that threshold for a calibrated
amount of time.
²Test Done This TripÐ Indicates that the
monitor has already been run and completed during
the current trip.
MISFIRE
²Same Misfire Warm-Up StateÐ Indicates if
the misfire occurred when the engine was warmed up
(above 160É F).
²In Similar Misfire WindowÐ An indicator
that 'Absolute MAP When Misfire Occurred' and
'RPM When Misfire Occurred' are all in the same
range when the failure occurred. Indicated by switch-
ing from 'NO' to 'YES'.
²Absolute MAP When Misfire OccurredÐ
The stored MAP reading at the time of failure.
Informs the user at what engine load the failure
occurred.
²Absolute MAPÐ A live reading of engine load
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²RPM When Misfire OccurredÐ The stored
RPM reading at the time of failure. Informs the user
at what engine RPM the failure occurred.
²Engine RPMÐ A live reading of engine RPM
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²Adaptive Memory FactorÐ The PCM utilizes
both Short Term Compensation and Long Term Adap-
tive to calculate the Adaptive Memory Factor for
total fuel correction.
²200 Rev CounterÐ Counts 0±100 720 degree
cycles.
²SCW Cat 200 Rev CounterÐ Counts when in
similar conditions.
²SCW FTP 1000 Rev CounterÐ Counts 0±4
when in similar conditions.
²Misfire Good Trip CounterÐ Counts up to
three to turn OFF the MIL.
²Misfire DataÐ Data collected during test.
²Test Done This TripÐ Indicates YES when the
test is done.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 23
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)