2003 GMC SIERRA DENALI wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 237 of 428

If the water isn’t too deep, drive slowly through it. At
faster speeds, water splashes on your ignition system
and your vehicle can stall. Stalling can also occur
if you
get your tailpipe under water. And, as long as your
tailpipe is under water, you’ll never be able to start your
engine. When you go through water, remember that
when your brakes get wet, it may take you longer
+- stop.
,,jving thr,,gh rushing water can be
dangerous. Deep water can sweep your vehicle
downstream and you and your passengers
could drown. If it’s only shallow water, it can
still wash away the ground from under your
tires, and you could lose traction and roll the
water.
~ vehicle over. Don’t drive through rushing
I
After Off-Road Driving
Remove any brush or debris that has collected on the
underbody, chassis or under the hood. These
accumulations can be a fire hazard.
After operation
in mud or sand, have the brake linings
cleaned and checked. These substances can cause
glazing and uneven braking. Check the body structure,
steering, suspension, wheels, tires and exhaust
system for damage. Also, check the fuel lines and
cooling system for any leakage.
Your vehicle will require more frequent service due
to
off-road use. Refer to the Maintenance Schedule
for additional information.
See
Driving in Rain and on Wet Roads on page 4-30 for
more information on driving through water.
4-28
Page 245 of 428

Highway Hypnosis
Is there actually such a condition as "highway
hypnosis"? Or is it just plain falling asleep at the wheel?
Call it highway hypnosis, lack of awareness, or
whatever.
There is something about an easy stretch of road with
the same scenery, along with the hum of the tires on the
road, the drone of the engine, and the rush
of the
wind against the vehicle that can make you sleepy. Don't
let it happen to you!
If it does, your vehicle can leave
the road in
less than a second, and you could crash and
be injured.
What can you do about highway hypnosis? First, be
aware that it can happen.
Then here are some tips:
Make sure your vehicle is well ventilated, with a
Keep your eyes moving. Scan the road ahead and
comfortably cool interior.
to the
sides. Check your mirrors and your
instruments frequently.
If you get sleepy, pull off the road into a rest,
service or parking area and take a nap, get some
exercise, or both. For safety, treat drowsiness
on the highway as an emergency.
Hill and Mountain Roads
Driving on steep hills or mountains is different from
driving in flat
or rolling terrain.
4-36
Page 246 of 428

If you drive regularly in steep country, or if you’re
planning to visit there, here are some tips that can make
your trips safer and more enjoyable. See
Operating
Your All-Wheel-Drive Vehicle
Off Paved Roads on
page
4-16 for information about driving off-road.
Keep your vehicle in good shape. Check all fluid
levels and also the brakes, tires, cooling system
and transmission. These parts can work hard
on mountain roads.
Know how to go down hills. The most important
thing to know is this: let your engine do some of
the slowing down. Shift to a lower gear when you go
down a steep or long hill.
If you don’t I R down, your -____ 3s COL- ge-
so hot that they wouldn’t work well. You would
then have poor braking or even none going
down a hill. You could crash. Shift down to let
your engine assist your brakes on a steep downhill slope. Coasting
UVwnlll..
..I NEUTRAL (N) G. .... h the
ignition
off is dangerous. Your brakes will have
to do all the work
of slowing down. They could
get
so hot that they wouldn’t work well. You
would then have poor braking or even none
going down a
hill. You could crash. Always
have your engine running and your vehicle in
gear when you go downhill.
Know how to go uphill. You may want to shift down to
a lower gear. The lower gears help cool your engine
and transmission, and you can climb the hill better.
roads in hills or mountains. Don’t swing wide or cut
across the center of the road. Drive at speeds that let
you stay in your own lane.
As you go over the top of a hill, be alert. There could
be something in your lane, like a stalled car or an
accident.
You may see highway signs on mountains that warn
of special problems. Examples are long grades,
passing or no-passing zones, a falling rocks area or
winding roads. Be alert to these and take appropriate
action.
Stay in your own lane when driving on two-lane
4-37
Page 248 of 428

Driving on Snow or Ice
Most of the time, those places where your tires meet
the road probably have good traction. the
least traction of all. You can get wet ice when it’s
about freezing (32°F; OOC) and freezing rain begins
to fall. Try to avoid driving on wet ice until salt and sand
crews can get there.
However,
if there is snow or ice between your tires and Whatever the condition - smooth ice, packed, blowing
the road, you can have a very slippery situation.
You’ll have a lot less traction or “grip” and will need to
be very careful. Accelerate gently. Try not to break the fragile traction.
If
or loose snow - drive with caution.
you accelerate too fast, the drive wheels will spin and
polish the surface under the tires even more.
m
What’s the worst time for this? “Wet ice.” Very cold
snow or ice can be slick and hard to drive on. But wet
ice can be even more trouble because it may offer Your
anti-lock brakes improve your vehicle’s stability
when you make a hard stop on a slippery road.
Even though you have an anti-lock braking system,
you’ll want to begin stopping sooner than you would on
dry pavement. See
Braking on page 4-6.
Allow greater following distance on any slippery
road.
0 Watch for slippery spots. The road might be fine
until you hit a spot that’s covered with ice. On
an otherwise clear road, ice patches may appear
in
shaded areas where the sun can’t reach: around
clumps
of trees, behind buildings or under bridges.
Sometimes the surface of a curve or an overpass
may remain icy when the surrounding roads
are clear.
If you see a patch of ice ahead of you,
brake before you are on it. Try not to brake
while you’re actually on the ice, and avoid sudden
steering maneuvers.
4-39
Page 251 of 428

If You Are Stuck: In Sand, Mud, Ice
or Snow
in order to free your vehicle when it is stuck, you will
need to spin the wheels, but you don’t want to spin your
wheels too fast. The method known as “rocking” can
help you aet out when you’re stuck, but you must
use cauti
.
If you let your tires spin at high speed, they
can explode, and you or others could be
injured.
And, the transmission or other parts of
the vehicle can overheat. That could cause an
CAUTION: (Continued) engine compartment fire or other
damage.
When you’re stuck, spin the wheels as little as
possible. Don’t spin the wheels above
25 mph
(55 km/h) as shown on the speedometer.
Nofice: Spinning your wheels can destroy parts of
your vehicle as well as the tires. If you spin the
wheels too fast while shifting your transmission back and forth, you can destroy your transmission.
For information about using tire chains on your
vehicle, see
Tire Chains on page 5-68.
4-42
Page 252 of 428
Rocking Your Vehicle To Get It Out
First, turn your steering wheel left and right. That will
clear the area around your front wheels. Then shift back
and forth between REVERSE
(R) and a forward gear,
spinning the wheels as little as possible. Release
the accelerator pedal while you shift, and press lightly
on the accelerator pedal when the transmission is
in gear. By slowly spinning your wheels in the forward
and reverse directions, you will cause a rocking
motion that may free your vehicle.
If that doesn’t get
you out after a few tries, you may need to be towed out.
Or, you can use your recovery hooks
if your vehicle
has them.
If you do need to be towed out, see Towing
Your Vehicle on page 4-45.
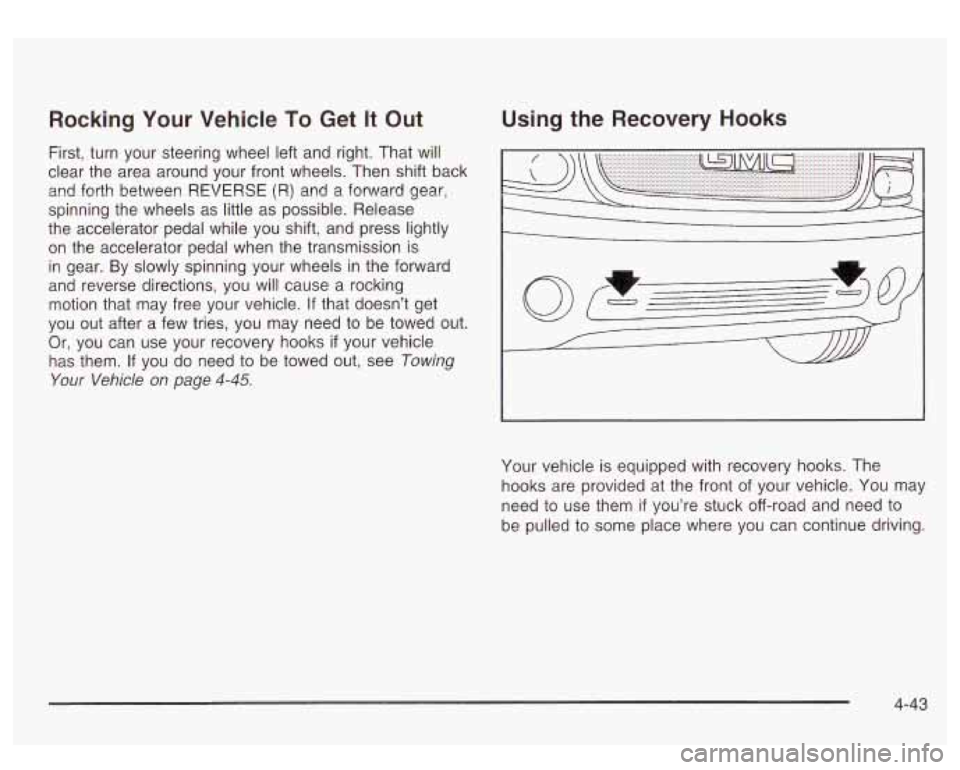
Using the Recovery Hooks
I
Your vehicle is equipped with recovery hooks. The
hooks are provided at the front of your vehicle. You may
need to use them
if you’re stuck off-road and need to
be pulled to some place where you can continue driving.
4-43
Page 254 of 428
Towing Loading Your Vehicle
Towing Your Vehicle
Consult your dealer or a professional towing service if
you need to have your disabled vehicle towed. See
Roadside Assistance Program on page 7-5.
If you want to tow your vehicle behind another vehicle
for recreational purposes (such as behind a motorhome),
see “Recreational Vehicle Towing” following.
Recreational Vehicle Towing
Recreational vehicle towing means towing your vehicle
behind another vehicle
- such as behind a motorhome.
The two most common types of recreational vehicle
towing are known as “dinghy towing” (towing your
vehicle with all four wheels on the ground) and “dolly
towing” (towing your vehicle with two wheels on
the ground and two wheels up on a device known
as a
“dolly”).
Your vehicle was not designed to be towed with any of
its wheels on the ground. If your vehicle must be
towed, see
Towing Your Vehicle on page 4-45.
Notice: Towing an all-wheel-drive vehicle with all
four wheels on the ground, or even with only two
of
its wheels on the ground, will damage drivetrain
components. Don’t tow an all-wheel-drive vehicle if
any
of its wheels will be on the ground.
COLD TIRE PRESSURE
00
The Certificationflire label is found on the rear edge of
the driver’s door.
The label shows the size of your original tires and the
inflation pressures needed to obtain the gross weight
capacity of your vehicle. This is called the GVWR (Gross
Vehicle Weight Rating). The GVWR includes the
weight of the vehicle, all occupants, fuel and cargo.
4-45
Page 256 of 428

Th.,,ds yo^ pur inside your vehicle can strike
and injure people in a sudden stop or turn, or
in a crash.
Put things in the trunk of your vehicle. In a
trunk, put them
as far forward as you can.
Try to spread the weight evenly.
Never stack heavier things, like suitcases,
inside the vehicle
so that some of them
are above the tops of the seats.
Don’t leave an unsecured child restraint in
your vehicle.
When you carry something inside the
vehicle, secure it whenever you can.
There’s also important loading information for off-road
driving in this manual. See “Loading Your Vehicle
for Off-Road Driving“ under
Operating Your
All- Wheel-Drive Vehicle Off Paved Roads on page 4- 16.
Payload
Payload capacity is the maximum load capacity that your
vehicle can carry. Be sure to include the weight of the
occupants as part of your load.
If you added any accessories or
equipment after your vehicle left the
factory, remember to subtract the weight of these things
from the payload. Your dealer can help you with this.
Remember not to exceed the Gross Axle Weight Rating
(GAWR) of the front or rear axle.
Two-Tiered Loading
By positioning four 2’’ x 6’’ wooden planks across the
width of the pickup box, you can create an upper
load platform. The planks must be inserted in the pickup
box depressions. The length of the planks must allow
for at least a
3/4 inch (2 cm) bearing surface on
each end of the plank.
When using this upper load platform, be sure the load is
securely tied down to prevent it from shifting. The
load’s center of gravity should be positioned in a zone
over the rear axle. The zone is located in the area
between the front of each wheel well and the rear of
each wheel well. The center of gravity height must not
extend above the top of the pickup box flareboard.
Any load that extends beyond the vehicle’s taillamp area
must be properly marked according to local laws and
regulations.
Remember not to exceed the Gross Axle Weight Rating
(GAWR) of the front or rear axle.
4-47