2003 DODGE RAM app
[x] Cancel search: appPage 2277 of 2895

OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 239) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in a direction
that would tend to slow it down.
Fig. 239 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
21 - 438 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2278 of 2895

STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 240).
Under stall conditions the turbine is stationary and
the oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of
the stator blades and tries to rotate them in a coun-
terclockwise direction. When this happens the over-
running clutch of the stator locks and holds the
stator from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil
strikes the stator blades and is redirected into a
ªhelpingº direction before it enters the impeller. This
circulation of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to
stator, and stator to impeller, can produce a maxi-
mum torque multiplication of about 1.75:1. As the
turbine begins to match the speed of the impeller, the
fluid that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The torque converter clutch is hydraulically
applied or released when fluid is feed or vented from
the hydraulic circuit by the torque converter control
(TCC) solenoid on the valve body. The torque con-
verter clutch is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The torque converter clutch engages
in fourth gear, and in third gear under various con-
ditions, such as when the O/D switch is OFF, or
when the vehicle is cruising on a level surface after
the vehicle has warmed up. The torque converterclutch may disengage momentarily when an increase
in engine load is sensed by the PCM, such as when
the vehicle begins to go uphill or the throttle pres-
sure is increased.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 241). Surface of converter lugs
should be 19mm (0.75 in.) to the rear of the straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
Fig. 240 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 439
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2279 of 2895

(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The drainback valve is located in the transmission
cooler outlet (pressure) line.
OPERATION
The valve prevents fluid from draining from the
converter into the cooler and lines when the vehicleis shut down for lengthy periods. Production valves
have a hose nipple at one end, while the opposite end
is threaded for a flare fitting. All valves have an
arrow (or similar mark) to indicate direction of flow
through the valve.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
The converter drainback check valve is located in
the cooler outlet (pressure) line near the radiator
tank. The valve prevents fluid drainback when the
vehicle is parked for lengthy periods. The valve check
ball is spring loaded and has an opening pressure of
approximately 2 psi.
The valve is serviced as an assembly; it is not
repairable. Do not clean the valve if restricted, or
contaminated by sludge, or debris. If the valve fails,
or if a transmission malfunction occurs that gener-
ates significant amounts of sludge and/or clutch par-
ticles and metal shavings, the valve must be
replaced.
The valve must be removed whenever the cooler
and lines are reverse flushed. The valve can be flow
tested when necessary. The procedure is exactly the
same as for flow testing a cooler.
If the valve is restricted, installed backwards, or in
the wrong line, it will cause an overheating condition
and possible transmission failure.
CAUTION: The drainback valve is a one-way flow
device. It must be properly oriented in terms of flow
direction for the cooler to function properly. The
valve must be installed in the pressure line. Other-
wise flow will be blocked and would cause an over-
heating condition and eventual transmission failure.
Fig. 241 Typical Method Of Checking Converter
Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 440 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2281 of 2895
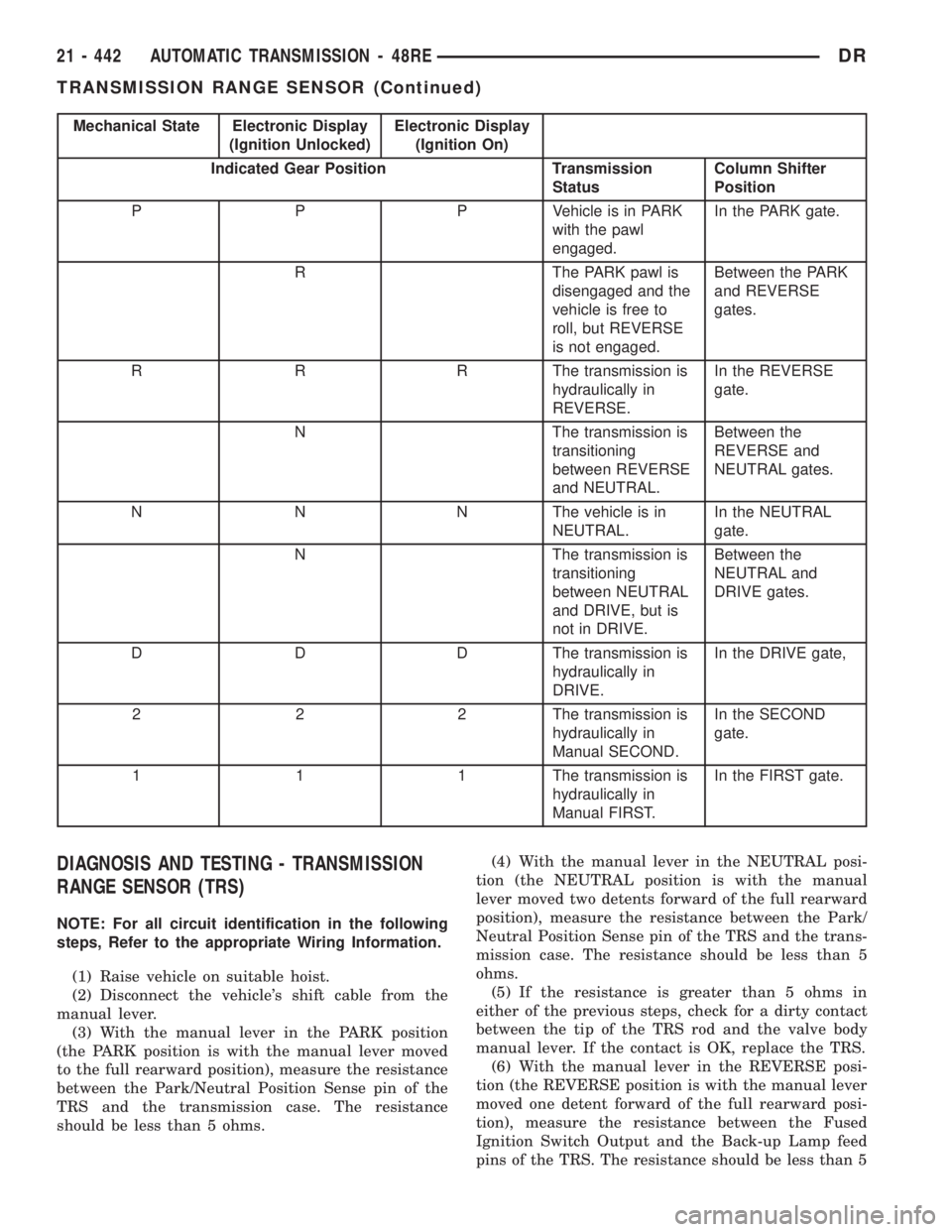
Mechanical State Electronic Display
(Ignition Unlocked)Electronic Display
(Ignition On)
Indicated Gear Position Transmission
StatusColumn Shifter
Position
P P P Vehicle is in PARK
with the pawl
engaged.In the PARK gate.
R The PARK pawl is
disengaged and the
vehicle is free to
roll, but REVERSE
is not engaged.Between the PARK
and REVERSE
gates.
R R R The transmission is
hydraulically in
REVERSE.In the REVERSE
gate.
N The transmission is
transitioning
between REVERSE
and NEUTRAL.Between the
REVERSE and
NEUTRAL gates.
N N N The vehicle is in
NEUTRAL.In the NEUTRAL
gate.
N The transmission is
transitioning
between NEUTRAL
and DRIVE, but is
not in DRIVE.Between the
NEUTRAL and
DRIVE gates.
D D D The transmission is
hydraulically in
DRIVE.In the DRIVE gate,
2 2 2 The transmission is
hydraulically in
Manual SECOND.In the SECOND
gate.
1 1 1 The transmission is
hydraulically in
Manual FIRST.In the FIRST gate.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSMISSION
RANGE SENSOR (TRS)
NOTE: For all circuit identification in the following
steps, Refer to the appropriate Wiring Information.
(1) Raise vehicle on suitable hoist.
(2) Disconnect the vehicle's shift cable from the
manual lever.
(3) With the manual lever in the PARK position
(the PARK position is with the manual lever moved
to the full rearward position), measure the resistance
between the Park/Neutral Position Sense pin of the
TRS and the transmission case. The resistance
should be less than 5 ohms.(4) With the manual lever in the NEUTRAL posi-
tion (the NEUTRAL position is with the manual
lever moved two detents forward of the full rearward
position), measure the resistance between the Park/
Neutral Position Sense pin of the TRS and the trans-
mission case. The resistance should be less than 5
ohms.
(5) If the resistance is greater than 5 ohms in
either of the previous steps, check for a dirty contact
between the tip of the TRS rod and the valve body
manual lever. If the contact is OK, replace the TRS.
(6) With the manual lever in the REVERSE posi-
tion (the REVERSE position is with the manual lever
moved one detent forward of the full rearward posi-
tion), measure the resistance between the Fused
Ignition Switch Output and the Back-up Lamp feed
pins of the TRS. The resistance should be less than 5
21 - 442 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 2284 of 2895

TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are sup-
plied to the transmission control module by the ther-
mistor (Fig. 250). The temperature readings are used
to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive
clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure.
Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room
temperature is approximately 2000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure
sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission
fluid at all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter
clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature
is below approximately 10ÉC (50ÉF).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126ÉC (260ÉF), the
PCM causes a 4-3 downshift and engage the con-
verter clutch. Engagement is according to the third
gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The overdrive OFF lamp in the instrument panel
illuminates when the shift back to third occurs. The
transmission will not allow fourth gear operation
until fluid temperature decreases to approximately
110ÉC (230ÉF).
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and transfer plate. The valve
body contains valves and check balls that control
fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch, bands,
and frictional clutches. The valve body contains the
following components (Fig. 251), (Fig. 252), (Fig.
253), and (Fig. 254):
²Regulator valve
²Regulator valve throttle pressure plug
²Line pressure sleeve
²Kickdown valve
²Kickdown limit valve
²1-2 shift valve
²1-2 control valve
²2-3 shift valve
²2-3 governor plug
²3-4 shift valve
²3-4 timing valve
²3-4 quick fill valve
²3-4 accumulator
²Throttle valve
²Throttle pressure plug
²Switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch lock-up valve
²Converter clutch lock-up timing Valve
²Shuttle valve
²Shuttle valve throttle plug
²Boost Valve
²9 check balls
By adjusting the spring pressure acting on the reg-
ulator valve, transmission line pressure can be
adjusted.
Fig. 250 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 445
Page 2295 of 2895

1-2 SHIFT VALVE
The 1-2 shift valve assembly (Fig. 262), or mecha-
nism, consists of: the 1-2 shift valve, governor plug,
and a spring on the end of the valve. After the man-
ual valve has been placed into a forward gear range,
line pressure is directed to the 1-2 shift valve. As the
throttle is depressed, throttle pressure is applied to
the right side of the 1-2 shift valve assembly. With
throttle pressure applied to the right side of the
valve, there is now both spring pressure and throttle
pressure acting on the valve, holding it against the
governor plug. As the vehicle begins to move and
build speed, governor pressure is created and is
applied to the left of the valve at the governor plug.
When governor pressure builds to a point where it
can overcome the combined force of the spring and
throttle pressure on the other side of the valve, the
valve will begin to move over to the right. As the
valve moves to the right, the middle land of the valve
will close off the circuit supplying the throttle pres-
sure to the right side of the valve. When the throttlepressure is closed off, the valve will move even far-
ther to the right, allowing line pressure to enter
another circuit and energize the front servo, applying
the front band (Fig. 263).
The governor plug serves a dual purpose:
²It allows the shift valves to move either left or
right, allowing both upshifts and downshifts.
²When in a manual selection position, it will be
hydraulically ªblockedº into position so no upshift can
occur.
The physical blocking of the upshift while in the
manual ª1º position is accomplished by the directing
of line pressure between both lands of the governor
plug. The line pressure reacts against the larger land
of the plug, pushing the plug back against the end
plate overcoming governor pressure. With the combi-
nation of the line pressure and spring pressure, the
valve cannot move, preventing any upshift.
Fig. 262 1-2 Shift Valve - Before Shift
Fig. 263 1-2 Shift Valve - After Shift
21 - 456 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 2296 of 2895

1-2 SHIFT CONTROL VALVE
It contains a valve with four lands and a spring. It
is used as both a ªrelayº and ªbalancedº valve.
The valve has two specific operations (Fig. 264):
²Aid in quality of the 1-2 upshift.
²Aid in the quality and timing of the 3-2 kick-
down ranges.
When the manual valve is set to the DRIVE posi-
tion and the transmission is in the first or second
gear range, 1-2 shift control or ªmodulated throttle
pressureº is supplied to the middle of the accumula-
tor piston by the 1-2 shift control valve. During the1-2 upshift, this pressure is used to control the kick-
down servo apply pressure that is needed to apply
the kickdown and accumulator pistons. Thus, the 1-2
shift point is ªcushionedº and the quality is
improved. During a WOT kickdown, kickdown pres-
sure is applied between the kickdown valve and the
1-2 shift control valve. This additional pressure is
directed to the 1-2 shift control's spring cavity, add-
ing to the spring load on the valve. The result of this
increased ªmodulatedº throttle pressure is a firmer
WOT upshift.
Fig. 264 1-2 Shift Control Valve
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 457
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 2297 of 2895

2-3 SHIFT VALVE
The 2-3 shift valve mechanism (Fig. 265) consists
of the 2-3 shift valve, governor plug and spring, and
a throttle plug. After the 1-2 shift valve has com-
pleted its operation and applied the front band, line
pressure is directed to the 2-3 shift valve through the
connecting passages from the 1-2 shift valve. The line
pressure will then dead±end at land #2 until the 2-3
valve is ready to make its shift. Now that the vehicle
is in motion and under acceleration, there is throttle
pressure being applied to the spring side of the valve
and between lands #3 and #4.
As vehicle speed increases, governor pressure
increases proportionately, until it becomes great
enough to overcome the combined throttle and spring
pressure on the right side of the valve. Since the
throttle pressure end of the 2-3 shift valve is larger
in diameter than the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shift will
always happen at a greater speed than the 1-2 shift.
When this happens, the governor plug is forced
against the shift valve moving it to the right. The
shift valve causes land #4 to close the passage sup-
plying throttle pressure to the 2-3 shift valve. With-
out throttle pressure present in the circuit now, the
governor plug will push the valve over far enough to
bottom the valve in its bore. This allows land #2 to
direct line pressure to the front clutch.
After the shift (Fig. 266), line pressure is directed
to the release side of the kickdown servo. This
releases the front band and applies the front clutch,shifting into third gear or direct drive. The rear
clutch remains applied, as it has been in the other
gears. During a manual ª1º or manual ª2º gear
selection, line pressure is sent between the two
lands of the 2-3 governor plug. This line pressure at
the governor plug locks the shift valve into the sec-
ond gear position, preventing an upshift into direct
drive. The theory for the blocking of the valve is the
same as that of the 1-2 shift valve.
If the manual ª2º or manual ª1º gear position is
selected from the drive position, the PCM will con-
trol the timing of the downshift by targeting for a
high governor pressure. When a safe vehicle speed
is reached, the PCM will switch to its normal con-
trol governor curve and the downshift will occur.
3-4 SHIFT VALVE
The PCM energizes the overdrive solenoid during
the 3-4 upshift (Fig. 267). This causes the solenoid
check ball to close the vent port allowing line pres-
sure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly on the
3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4 shift
valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving the
valve to the upshift position (Fig. 268). This action
exposes the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve,
3-4 quick fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately
to the overdrive piston.
Fig. 265 2-3 Shift Valve - Before Shift
21 - 458 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)