2003 DODGE RAM app
[x] Cancel search: appPage 1477 of 2895
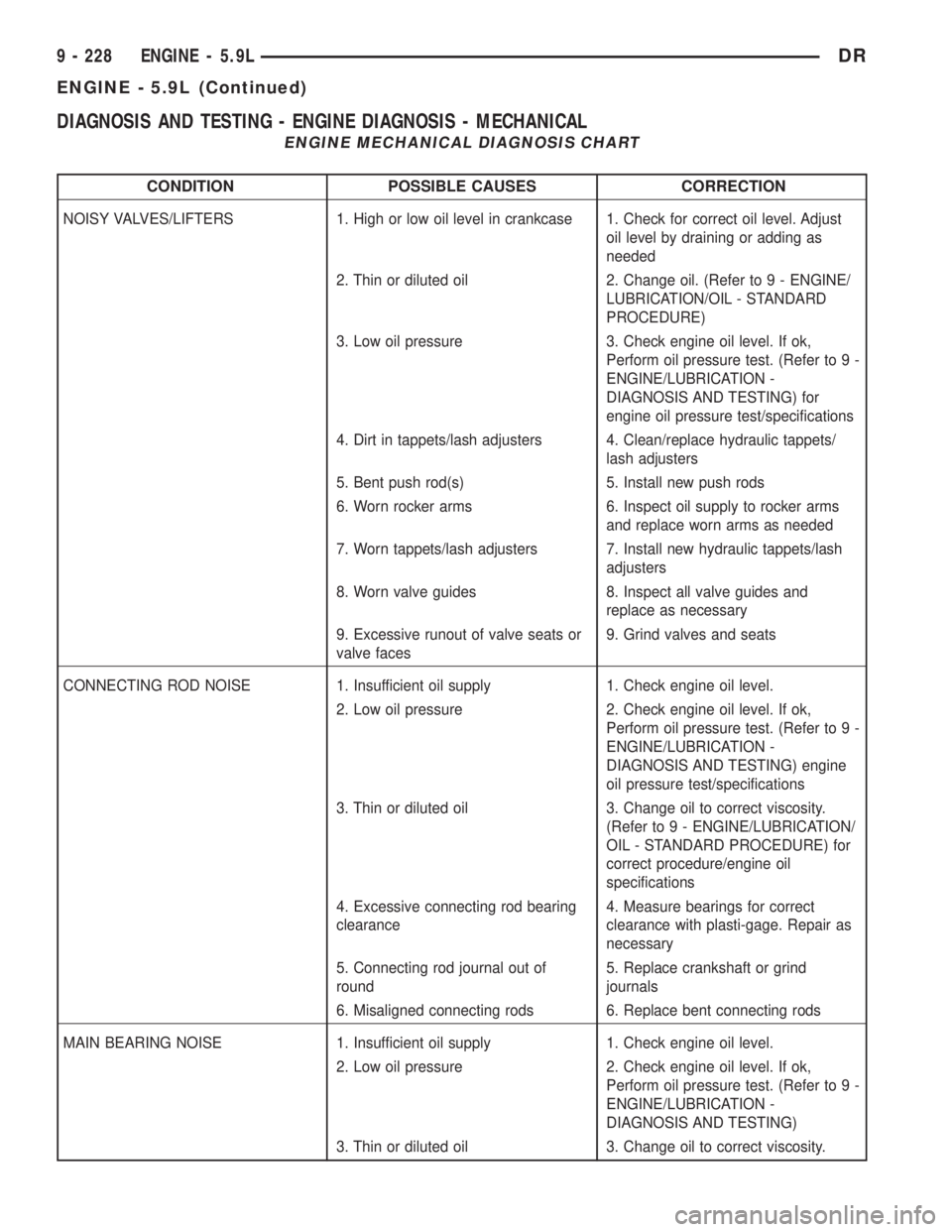
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
ENGINE MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES/LIFTERS 1. High or low oil level in crankcase 1. Check for correct oil level. Adjust
oil level by draining or adding as
needed
2. Thin or diluted oil 2. Change oil. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
3. Low oil pressure 3. Check engine oil level. If ok,
Perform oil pressure test. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for
engine oil pressure test/specifications
4. Dirt in tappets/lash adjusters 4. Clean/replace hydraulic tappets/
lash adjusters
5. Bent push rod(s) 5. Install new push rods
6. Worn rocker arms 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms
and replace worn arms as needed
7. Worn tappets/lash adjusters 7. Install new hydraulic tappets/lash
adjusters
8. Worn valve guides 8. Inspect all valve guides and
replace as necessary
9. Excessive runout of valve seats or
valve faces9. Grind valves and seats
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure 2. Check engine oil level. If ok,
Perform oil pressure test. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) engine
oil pressure test/specifications
3. Thin or diluted oil 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/
OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE) for
correct procedure/engine oil
specifications
4. Excessive connecting rod bearing
clearance4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance with plasti-gage. Repair as
necessary
5. Connecting rod journal out of
round5. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals
6. Misaligned connecting rods 6. Replace bent connecting rods
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure 2. Check engine oil level. If ok,
Perform oil pressure test. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
3. Thin or diluted oil 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
9 - 228 ENGINE - 5.9LDR
ENGINE - 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1481 of 2895

STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTV
MopartATF RTV is a specifically designed black
silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and seal-
ing properties to seal components exposed to auto-
matic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKER
MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
material is for use between two machined surfaces.
Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANT
MopartGasket Sealant is a slow drying, perma-
nently soft sealer. This material is recommended for
sealing threaded fittings and gaskets against leakage
of oil and coolant. Can be used on threaded and
machined parts under all temperatures. This mate-
rial is used on engines with multi-layer steel (MLS)
cylinder head gaskets. This material also will pre-
vent corrosion. MopartGasket Sealant is available in
a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16 oz. can w/applicator.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier than using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC
LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
9 - 232 ENGINE - 5.9LDR
ENGINE - 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1486 of 2895
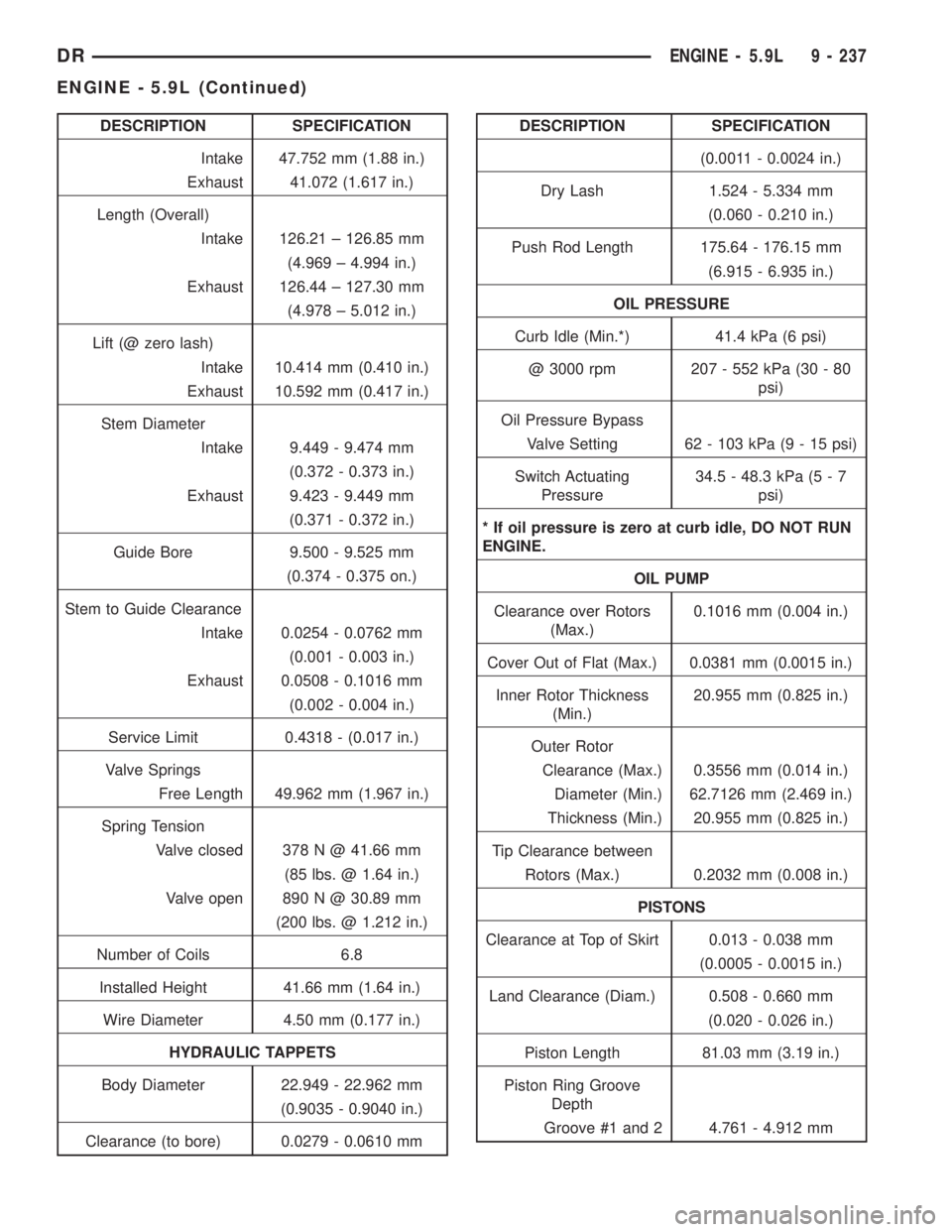
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Intake 47.752 mm (1.88 in.)
Exhaust 41.072 (1.617 in.)
Length (Overall)
Intake 126.21 ± 126.85 mm
(4.969 ± 4.994 in.)
Exhaust 126.44 ± 127.30 mm
(4.978 ± 5.012 in.)
Lift (@ zero lash)
Intake 10.414 mm (0.410 in.)
Exhaust 10.592 mm (0.417 in.)
Stem Diameter
Intake 9.449 - 9.474 mm
(0.372 - 0.373 in.)
Exhaust 9.423 - 9.449 mm
(0.371 - 0.372 in.)
Guide Bore 9.500 - 9.525 mm
(0.374 - 0.375 on.)
Stem to Guide Clearance
Intake 0.0254 - 0.0762 mm
(0.001 - 0.003 in.)
Exhaust 0.0508 - 0.1016 mm
(0.002 - 0.004 in.)
Service Limit 0.4318 - (0.017 in.)
Valve Springs
Free Length 49.962 mm (1.967 in.)
Spring Tension
Valve closed 378 N @ 41.66 mm
(85 lbs. @ 1.64 in.)
Valve open 890 N @ 30.89 mm
(200 lbs. @ 1.212 in.)
Number of Coils 6.8
Installed Height 41.66 mm (1.64 in.)
Wire Diameter 4.50 mm (0.177 in.)
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
Body Diameter 22.949 - 22.962 mm
(0.9035 - 0.9040 in.)
Clearance (to bore) 0.0279 - 0.0610 mmDESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
(0.0011 - 0.0024 in.)
Dry Lash 1.524 - 5.334 mm
(0.060 - 0.210 in.)
Push Rod Length 175.64 - 176.15 mm
(6.915 - 6.935 in.)
OIL PRESSURE
Curb Idle (Min.*) 41.4 kPa (6 psi)
@ 3000 rpm 207 - 552 kPa (30 - 80
psi)
Oil Pressure Bypass
Valve Setting 62 - 103 kPa (9 - 15 psi)
Switch Actuating
Pressure34.5 - 48.3 kPa (5 - 7
psi)
* If oil pressure is zero at curb idle, DO NOT RUN
ENGINE.
OIL PUMP
Clearance over Rotors
(Max.)0.1016 mm (0.004 in.)
Cover Out of Flat (Max.) 0.0381 mm (0.0015 in.)
Inner Rotor Thickness
(Min.)20.955 mm (0.825 in.)
Outer Rotor
Clearance (Max.) 0.3556 mm (0.014 in.)
Diameter (Min.) 62.7126 mm (2.469 in.)
Thickness (Min.) 20.955 mm (0.825 in.)
Tip Clearance between
Rotors (Max.) 0.2032 mm (0.008 in.)
PISTONS
Clearance at Top of Skirt 0.013 - 0.038 mm
(0.0005 - 0.0015 in.)
Land Clearance (Diam.) 0.508 - 0.660 mm
(0.020 - 0.026 in.)
Piston Length 81.03 mm (3.19 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth
Groove #1 and 2 4.761 - 4.912 mm
DRENGINE - 5.9L 9 - 237
ENGINE - 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1487 of 2895
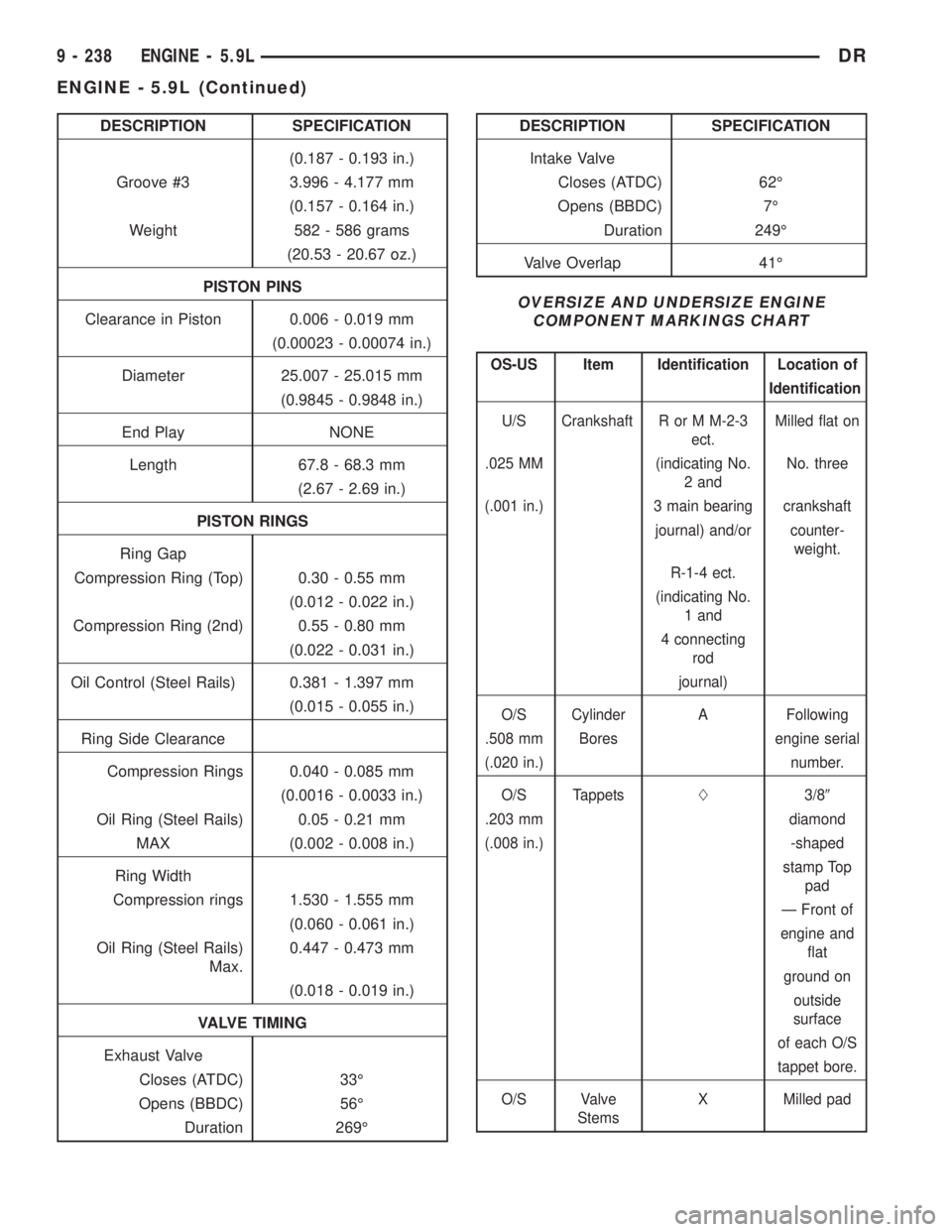
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
(0.187 - 0.193 in.)
Groove #3 3.996 - 4.177 mm
(0.157 - 0.164 in.)
Weight 582 - 586 grams
(20.53 - 20.67 oz.)
PISTON PINS
Clearance in Piston 0.006 - 0.019 mm
(0.00023 - 0.00074 in.)
Diameter 25.007 - 25.015 mm
(0.9845 - 0.9848 in.)
End Play NONE
Length 67.8 - 68.3 mm
(2.67 - 2.69 in.)
PISTON RINGS
Ring Gap
Compression Ring (Top) 0.30 - 0.55 mm
(0.012 - 0.022 in.)
Compression Ring (2nd) 0.55 - 0.80 mm
(0.022 - 0.031 in.)
Oil Control (Steel Rails) 0.381 - 1.397 mm
(0.015 - 0.055 in.)
Ring Side Clearance
Compression Rings 0.040 - 0.085 mm
(0.0016 - 0.0033 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) 0.05 - 0.21 mm
MAX (0.002 - 0.008 in.)
Ring Width
Compression rings 1.530 - 1.555 mm
(0.060 - 0.061 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Rails)
Max.0.447 - 0.473 mm
(0.018 - 0.019 in.)
VALVE TIMING
Exhaust Valve
Closes (ATDC) 33É
Opens (BBDC) 56É
Duration 269ÉDESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Intake Valve
Closes (ATDC) 62É
Opens (BBDC) 7É
Duration 249É
Valve Overlap 41É
OVERSIZE AND UNDERSIZE ENGINE
COMPONENT MARKINGS CHART
OS-US Item Identification Location of
Identification
U/S Crankshaft R or M M-2-3
ect.Milled flat on
.025 MM (indicating No.
2 andNo. three
(.001 in.) 3 main bearing crankshaft
journal) and/or counter-
weight.
R-1-4 ect.
(indicating No.
1 and
4 connecting
rod
journal)
O/S Cylinder A Following
.508 mm Bores engine serial
(.020 in.) number.
O/S TappetsL3/89
.203 mm diamond
(.008 in.) -shaped
stamp Top
pad
Ð Front of
engine and
flat
ground on
outside
surface
of each O/S
tappet bore.
O/S Valve
StemsX Milled pad
9 - 238 ENGINE - 5.9LDR
ENGINE - 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1488 of 2895

OS-US Item Identification Location of
.127 mm adjacent to
two
(.005 in.) 3/89tapped
holes on
each
end of
cylinder
head.
TORQUE
TORQUE CHART 5.9L ENGINE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Camshaft Sprocket Bolt 68 50 Ð
Camshaft Thrust Plate Bolts 24 Ð 210
Timing Chain Case Cover
Bolts41 30 Ð
Connecting Rod Cap Bolts 61 45 Ð
Main Bearing Cap Bolts 115 85 Ð
Crankshaft Pulley Bolts 24 Ð 210
Cylinder Head Bolts
Step 1 68 50 Ð
Step 2 143 105 Ð
Cylinder Head Cover Bolts 11 Ð 95
Engine Support Bracket to
Block Bolts (4WD)41 30 Ð
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder
Head Bolts/Nuts34 25 Ð
Flywheel Bolts 75 55 Ð
Front Insulator Through
bolt/nut95 70 Ð
Front Insulator to Support
Bracket
Stud Nut (4WD) 41 30 Ð
Through Bolt/Nut (4WD) 102 75 Ð
Front Insulator to Block Bolts
(2WD)95 70 Ð
Generator Mounting Bolt 41 30 Ð
Intake Manifold Bolts Refer to Procedure
Oil Pan Bolts 24 Ð 215
Oil Pan Drain Plug 34 25 Ð
Oil Pump Attaching Bolts 41 30 Ð
Oil Pump Cover Bolts 11 Ð 95
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Rear Insulator to Bracket
Through-Bolt (2WD)68 50 Ð
Rear Insulator to
Crossmember Support
Bracket Nut (2WD)41 30 Ð
Rear Insulator to
Crossmember Nuts (4WD)68 50 Ð
Rear Insulator to
Transmission Bolts (4WD)68 50 Ð
Rear Insulator Bracket Bolts
(4WD Automatic)68 50 Ð
Rear Support Bracket to
Crossmember Flange Nuts41 30 Ð
Rear Support Plate to
Transfer Case Bolts41 30 Ð
Rocker Arm Bolts 28 21 Ð
Spark Plugs 41 30 Ð
Starter Motor Mounting Bolts 68 50 Ð
Thermostat Housing Bolts 25 Ð 225
Throttle Body Bolts 23 Ð 200
Torque Converter Drive Plate
Bolts31 Ð 270
Transfer Case to Insulator
Mounting Plate Nuts204 105 Ð
Transmission Support Bracket
Bolts (2WD)68 50 Ð
Vibration Damper Bolt 244 180 Ð
Water Pump to Timing Chain
Case Cover Bolts41 30 Ð
DRENGINE - 5.9L 9 - 239
ENGINE - 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1492 of 2895

CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONÐCYLINDER HEAD
The cast iron cylinder heads (Fig. 6) are mounted
to the cylinder block using ten bolts. The spark plugs
are located in the peak of the wedge between the
valves.
DESCRIPTION - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
GASKET
The cylinder head cover gasket (Fig. 7) is a steel-
backed silicone gasket, designed for long life usage.
OPERATION
OPERATIONÐCYLINDER HEAD
The cylinder head closes the combustion chamber
allowing the pistons to compress the air fuel mixture
to the correct ratio for ignition. The valves located in
the cylinder head open and close to either allow clean
air into the combustion chamber or to allow the
exhaust gases out, depending on the stroke of the
engine.
OPERATION - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
GASKET
The steel-backed silicone gasket is designed to seal
the cylinder head cover for long periods of time
through extensive heat and cold, without failure. The
gasket is designed to be reusable.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET FAILURE
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
þ Loss of engine power
þ Engine misfiring
þ Poor fuel economy
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
þ Engine overheating
þ Loss of coolant
þ Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
þ Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test in this
section. An engine cylinder head gasket leaking
between adjacent cylinders will result in approxi-
mately a 50±70% reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
Fig. 6 Cylinder Head AssemblyÐV-8 Gas Engines
1 - EXHAUST VALVE
2 - SPARK PLUGS
3 - EXHAUST VALVES
4 - SPARK PLUGS
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - INTAKE VALVES
7 - INTAKE VALVES
Fig. 7 Cylinder Head Cover Gasket V-8 Gas Engines
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER GASKET
DRENGINE - 5.9L 9 - 243
Page 1498 of 2895

(3) Measure valve stems for wear. If wear exceeds
0.051 mm (0.002 inch), replace the valve.
(4) Coat valve stems with lubrication oil and insert
them in cylinder head.
(5) If valves or seats are reground, check valve
stem height. If valve is too long, replace cylinder
head.
(6) Install new seals on all valve guides. Install
valve springs and valve retainers.
(7) Compress valve springs with Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A and adapter 6716A,
install locks and release tool. If valves and/or seats
are ground, measure the installed height of springs.
Make sure the measurement is taken from bottom of
spring seat in cylinder head to the bottom surface of
spring retainer. If spacers are installed, measure
from the top of spacer. If height is greater than 42.86
mm (1-11/16 inches), install a 1.587 mm (1/16 inch)
spacer in head counterbore. This should bring spring
height back to normal 41.27 to 42.86 mm (1-5/8 to
1-11/16 inch).
(8) Install cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER
ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Remove cylinder head cover and gasket (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER
HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the rocker arm bolts and pivots (Fig.
18). Place them on a bench in the same order as
removed.(3) Remove the push rods and place them on a
bench in the same order as removed.
INSTALLATION
(1) Rotate the crankshaft until the ªV8º mark lines
up with the TDC mark on the timing chain case
cover. This mark is located 147É ATDC from the No.1
firing position.
(2) Install the push rods in the same order as
removed.
(3) Install rocker arm and pivot assemblies in the
same order as removed. Tighten the rocker arm bolts
to 28 N´m (21 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION: DO NOT rotate or crank the engine dur-
ing or immediately after rocker arm installation.
Allow the hydraulic roller tappets adequate time to
bleed down (about 5 minutes).
(4) Install cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
ENGINE BLOCK
CLEANING
Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all core
hole plugs for evidence of leakage.
INSPECTION
Examine block for cracks or fractures.
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper. Refer to Honing Cylinder Bores in
the Service Procedures portion of this Section.
Inspect the oil line plug, the oil line plug is located
in the vertical passage at the rear of the block
between the oil-to-filter and oil-from-filter passages
(Fig. 19). Improper installation or missing plug could
cause erratic, low, or no oil pressure.
The oil plug must come out the bottom. Use flat
dowel, down the oil pressure sending unit hole from
the top, to remove oil plug.
Fig. 17 Measuring Valve Guide Wear
1 - VALVE
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3339
Fig. 18 Rocker Arms
1 - ROCKER ARMS
2 - CYLINDER HEAD
DRENGINE - 5.9L 9 - 249
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1499 of 2895

(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit from back of
block.
(2) Insert a 3.175 mm (1/8 in.) finish wire, or
equivalent, into passage.
(3) Plug should be 190.0 to 195.2 mm (7-1/2 to
7-11/16 in.) from machined surface of block (Fig. 19).
If plug is too high, use a suitable flat dowel to posi-
tion properly.
(4) If plug is too low, remove oil pan and No. 4
main bearing cap. Use suitable flat dowel to position
properly. Coat outside diameter of plug with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount Adhesive. Plug should be
54.0 to 57.7 mm (2-1/8 to 2-5/16 in.) from bottom of
the block.CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK)
REMOVALÐCAMSHAFT
NOTE: The camshaft has an integral oil pump and
distributor drive gear (Fig. 20).
(1) Remove the radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the A/C Condenser (if equipped)
(3) Remove the engine cover.
(4) Remove intake manifold (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(6) Remove timing case cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL) and timing chain (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN
AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(7) Remove rocker arms.
(8) Remove push rods and tappets. Identify each
part so it can be installed in its original location.
(9) Remove distributor and lift out the oil pump
and distributor drive shaft.
(10) Remove camshaft thrust plate, note location of
oil tab (Fig. 21).
(11) Install a long bolt into front of camshaft to aid
in removal of the camshaft. Remove camshaft, being
careful not to damage cam bearings with the cam
lobes.
INSTALLATIONÐCAMSHAFT
(1) Lubricate camshaft lobes and camshaft bearing
journals and insert the camshaft to within 51 mm (2
inches) of its final position in cylinder block.
(2) Install Camshaft Holder Tool C-3509 with
tongue back of distributor drive gear (Fig. 22).
Fig. 19 Oil Line Plug
1 - RIGHT OIL GALLERY
2 - CYLINDER BLOCK
3 - OIL FROM FILTER TO SYSTEM
4 - OIL TO FILTER
5 - FROM OIL PUMP
6 - CRANKSHAFT
7 - PLUG
Fig. 20 Camshaft and Sprocket Assembly
1 - THRUST PLATE
2 - OIL PUMP AND DISTRIBUTOR DRIVE GEAR INTEGRAL WITH
CAMSHAFT
3 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
9 - 250 ENGINE - 5.9LDR
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)