2003 CHEVROLET ASTRO change wheel
[x] Cancel search: change wheelPage 135 of 386

Cruise Control
Your vehicle may have this feature. With cruise control,
you can maintain a speed
of about 25 mph (40 km/h)
or more without keeping your foot on the accelerator.
This can really help on long trips. Cruise control
does not work at speeds below about
25 mph (40 km/h).
When you apply your brakes, the cruise control shuts
off.
Cruise con,. _. ,an be dang-. DUS where
you can’t drive safely at a steady speed.
So, don’t use your cruise control on
winding roads or in heavy traffic.
Cruise control can be dangerous on
slippery roads. On such roads, fast
changes in tire traction can cause needless wheel spinning, and you could
lose control. Don’t use cruise control on
slippery roads.
I
If yvu leave your cruise control on when you’re
not using cruise, you might hit a button and go
into cruise when you don’t want to. You could
be startled and even lose control. Keep the
cruise control switch
off until you want to use
cruise control.
1. Move the cruise control switch to ON.
2. Get up to the speed you want.
3. Press in the SET
button at the end of the
lever and release it.
4. Take your foot off the accelerator pedal.
3-1 0
Page 147 of 386

Outlet Adjustment Operation Tips
1. Clear away any ice, snow or leaves from the
air inlets at the base of the windshield that
may block the flow of air into your vehicle.
2. Use of non-GM approved hood deflectors may
adversely affect the performance of the system.
3. Keep the path under the front seats clear of
objects to help circulate the air inside of your
vehicle more effectively.
Move the thumbwheel in the center of the outlets up or
down to change the direction
of airflow.
3-22
Page 183 of 386

Let’s say the road is wet and you’re driving safely.
Suddenly, an animal jumps out in front of you.
You slam on the brakes and continue braking.
Here’s what happens with
ABS:
A computer senses that wheels are slowing down.
If one of the wheels is about to stop rolling, the computer
will separately work the brakes at each front wheel
and at both rear wheels. The anti-lock system can
change the brake pressure
faster than any driver could. The computer is
programmed to make the most of available tire and
road conditions. This can help you steer around
the obstacle while braking hard. As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates
on wheel speed and controls braking pressure
accordingly.
4-8
Page 184 of 386

Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time you need
to get your foot up to the brake pedal or always
decrease stopping distance. If you get too close to the
vehicle in front of you, you won’t have time to apply
your brakes
if that vehicle suddenly slows or stops.
Always leave enough room up ahead to stop, even
though you have anti-lock brakes.
Using Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down
firmly and let anti-lock work for you. You may feel
the brakes vibrate, or you may notice some noise, but
this is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
With anti-lock, you can steer and brake at the same
time. In many emergencies, steering can help you more
than even the very best braking.
Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine
stops or the system is not functioning, you can steer but
it will take much more effort.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on
the news happen on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each of us is subject
to the same laws of physics when driving on curves.
The traction of the tires against the road surface makes
it possible for the vehicle to change its path when
you turn the front wheels. If there’s no traction, inertia
will keep the vehicle going in the same direction.
If you’ve ever tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice,
you’ll understand this.
The traction you can get in a curve depends on the
condition of your tires and the road surface, the angle at
which the curve is banked, and your speed. While you’re
in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control.
4-9
Page 188 of 386

Check your mirrors, glance over your shoulder, and
start your left lane change signal before moving out
of the right lane to pass. When you are far enough
ahead of the passed vehicle to see its front in your
inside mirror, activate your right lane change signal
and move back into the right lane. (Remember that
your right outside mirror is convex. The vehicle you
just passed may seem to be farther away from you
than it really is.)
Try not to pass more than one vehicle at a time OD
two-lane roads. Reconsider before passing the
next vehicle.
Don’t overtake a slowly moving vehicle too rapidly.
Even though the brake lamps are not flashing, it may
be slowing down or starting to turn.
If you’re being passed, make it easy for the following
driver to get ahead of you. Perhaps you can ease a
little to the right.
Loss of Control
Let’s review what driving experts say about what happens
when the three control systems (brakes, steering and
acceleration) don’t have enough friction where the tires
meet the road to do what the driver has asked.
In any emergency, don’t give up. Keep trying to steer
and constantly seek an escape route or area of
less danger.
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions, and by not “overdriving”
those conditions. But skids are always possible.
The three types of skids correspond to your vehicle’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels
aren’t rolling. In the steering or cornering skid, too much
speed or steering in a curve causes tires to slip and lose
cornering force. And in the acceleration skid, too much
throttle causes the driving wheels to spin.
A cornering skid is best handled by easing your foot off
the accelerator pedal.
4-1
3
Page 213 of 386

Following Distance
Stay at least twice as far behind the vehicle ahead as
you would when driving your vehicle without a trailer.
This can help you avoid situations that require
heavy braking and sudden turns.
Passing
You’ll need more passing distance up ahead when
you’re towing a trailer. And, because you’re a good deal
longer, you’ll need to go much farther beyond the
passed vehicle before you can return to your lane.
Backing Up
Hold the bottom of the steering wheel with one hand.
Then, to move the trailer to the left, just move that hand
to the left.
To move the trailer to the right, move your
hand to the right. Always back up slowly and,
if possible,
have someone guide you.
Making Turns
Notice: Making very sharp turns while trailering
could cause the trailer to come in contact with the
vehicle. Your vehicle could be damaged. Avoid
making very sharp turns while trailering.
When you’re turning with a trailer, make wider turns than
normal.
Do this so your trailer won’t strike soft shoulders,
curbs, road signs, trees or other objects. Avoid jerky or
sudden maneuvers. Signal well in advance.
Turn Signals When Towing a Trailer
When you tow a trailer, your vehicle has to have extra
wiring (included in the optional trailering package).
The arrows on your instrument panel will flash whenever
you signal a turn or lane change. Properly hooked up,
the trailer lamps will also flash, telling other drivers
you’re about to turn, change lanes or stop.
When towing a trailer, the arrows on your instrument
panel will flash for turns even
if the bulbs on the trailer
are burned out. Thus, you may think drivers behind
you are seeing your signal when they are not. It’s
important to check occasionally to be sure the trailer
bulbs are still working.
4-38
Page 282 of 386
Make sure the spare tire is stored securely. Push,
pull, and then try to rotate or turn the tire.
If it moves,
use the ratchevwheel wrench to tighten the cable.
See
Changing a Flat Tire on page 5-71.
The purpose Gf regular rotation is lo achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first rotation
is the most important. See “Part
A: Scheduled
Maintenance Services,” in Section
6, for scheduled
rotation intervals. After
the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and rear
inflation pressures as shown on the CertificationA-ire
label. Make certain that all wheel nuts are properly
tightened. See “Wheel Nut Torque” under
Capacities and
Specifications
on page 5-99.
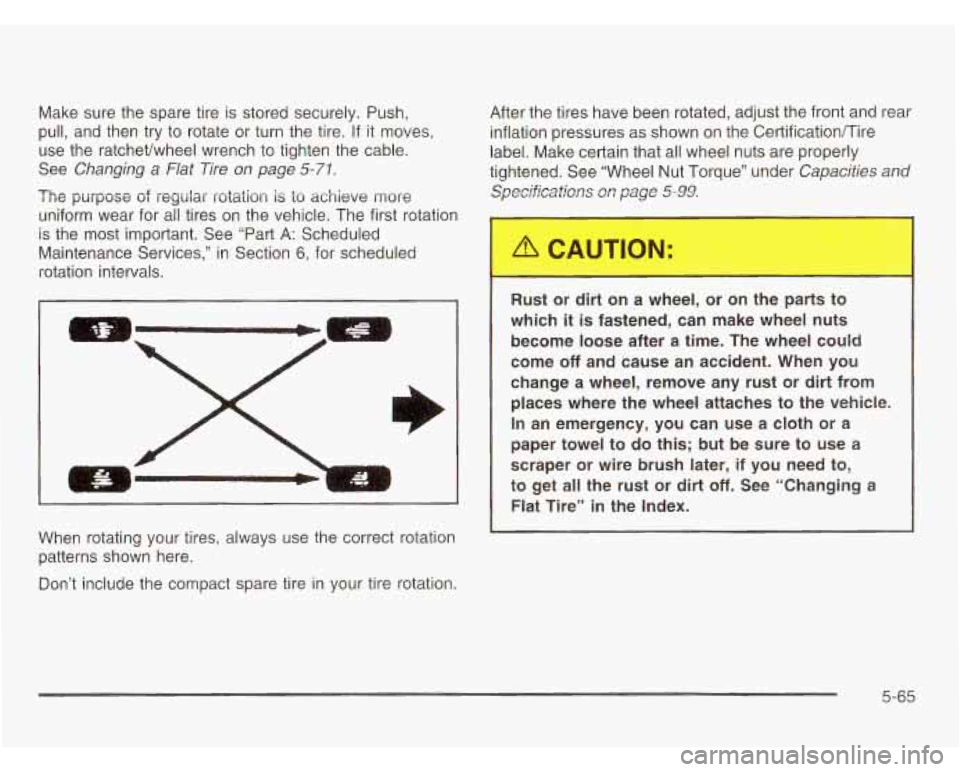
When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation
patterns shown here.
ts to
-
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the par
which
it is fastened, can make wheel nuts
become loose after a time. The wheel could
come
off and cause an accident. When you
change a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from
places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle.
In an emergency, you can use a cloth or a
paper towel to do
this; but be sure to use a
scraper
or wire brush later, if you need to,
to get all the rust or dirt
off. See “Changing a
Flat Tire” in the Index.
Don’t include the compact spare tire in your tire rotation.
5-65
Page 287 of 386

Used Replacement Wheels
Putting a uscu wheel on your vehicle is
dangerous. You can’t know how it’s been used or how far
it’s been driven. It could fail suddenly
and cause a crash. If you have to replace a
wheel, use a new
GM original equipment wheel.
Tire Chains
Notice: Use tire chains only where legal and only
when you must. Use only
SAE Class ”S” type chains
that are the proper size for your tires. Install them on the rear axle tires and tighten them as tightly
as possible with the ends securely fastened.
Drive slowly and follow the chain manufacturer’s
instructions.
If you can hear the chains contacting
your vehicle, stop and retighten them. If the contact
continues, slow down until
it stops. Driving too
fast or spinning
the wheels with chains on will
damage your vehicle.
If a Tire Goes Flat
It’s unusual for a tire to “blow out” while you’re driving,
especially
if you maintain your tires properly. If air
goes out of a tire, it’s much more likely to leak out
slowly. But
if you should ever have a “blowout”, here are
a few tips about what to expect and what to do:
If a front tire fails, the flat tire will create a drag that
pulls the vehicle toward that side. Take your foot off the
accelerator pedal and grip the steering wheel firmly.
Steer to maintain lane position, and then gently brake to
a stop well out of the traffic lane.
A rear blowout, particularly on a curve, acts much like a
skid and may require the same correction you’d use
in a skid. In any rear blowout, remove your foot from the
accelerator pedal. Get the vehicle under control by
steering the way you want the vehicle to go. It may be
very bumpy and noisy, but you can still steer. Gently
brake to a stop
- well off the road if possible.
If a tire goes flat, the next part shows how to use your
jacking equipment to change a flat tire safely.
5-70