2002 NISSAN TERRANO weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 6 of 1767

Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ªAIR
BAGº and ªSEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERº
The Supplemental Restraint System such as ªAIR BAGº and ªSEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERº used along with
a seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or severity of injury to the driver and front passenger in a frontal collision.
The SRS system composition which is available to NISSAN MODEL R20 is as follows (The composition var-
ies according to the destination.):
Driver air bag module (located in the center of the steering wheel), front passenger air bag module (located
on the instrument panel on passenger side), seat belt pre-tensioner, a diagnosis sensor unit, warning lamp,
wiring harness and spiral cable.
Information necessary to service the system safely is included in theRS sectionof this Service Manual.
WARNING:
ITo avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death
in the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be performed
by an authorized NISSAN dealer.
IImproper maintenance, including incorrect removal and installation of the SRS, can lead to per-
sonal injury caused by unintentional activation of the system. For removal of Spiral Cable and Air
Bag Module, see the RS section.
IDo not use electrical test equipment on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. Spiral cable and wiring harnesses covered with yellow insulation either just before
the harness connectors or for the complete harness are related to the SRS.
Precautions
IBefore proceeding with disassembly, thoroughly clean the outside of the transmission. It is important to
prevent the internal parts from becoming contaminated by dirt or other foreign matter.
IDisassembly should be done in a clean work area.
IUse lint-free cloth or towels for wiping parts clean. Common shop rags can leave fibers that could inter-
fere with the operation of the transmission.
IPlace disassembled parts in order for easier and proper assembly.
IAll parts should be carefully cleaned with a general purpose, non-flammable solvent before inspection or
reassembly.
IGaskets, seals and O-rings should be replaced any time the transmission is disassembled.
IIt is very important to perform functional tests whenever they are indicated.
IThe valve body contains precision parts and requires extreme care when parts are removed and serviced.
Place removed parts in a parts rack in order to replace them in correct positions and sequences. Care will
also prevent springs and small parts from becoming scattered or lost.
IProperly installed valves, sleeves, plugs, etc. will slide along bores in valve body under their own weight.
IBefore assembly, apply a coat of recommended ATF to all parts. Apply petroleum jelly to protect O-rings
and seals, and to hold bearings and washers in place during assembly. Do not use grease.
IExtreme care should be taken to avoid damage to O-rings, seals and gaskets when assembling.
IAfter overhaul, refill the transmission with new ATF.
IWhen the A/T drain plug is removed, only some of the fluid is drained. Old A/T fluid will remain in torque
converter and ATF cooling system.
Always follow the procedures under ªChanging A/T Fluidº in the MA section when changing A/T fluid.
PREPARATION AND PRECAUTIONS
AT- 4
Page 12 of 1767
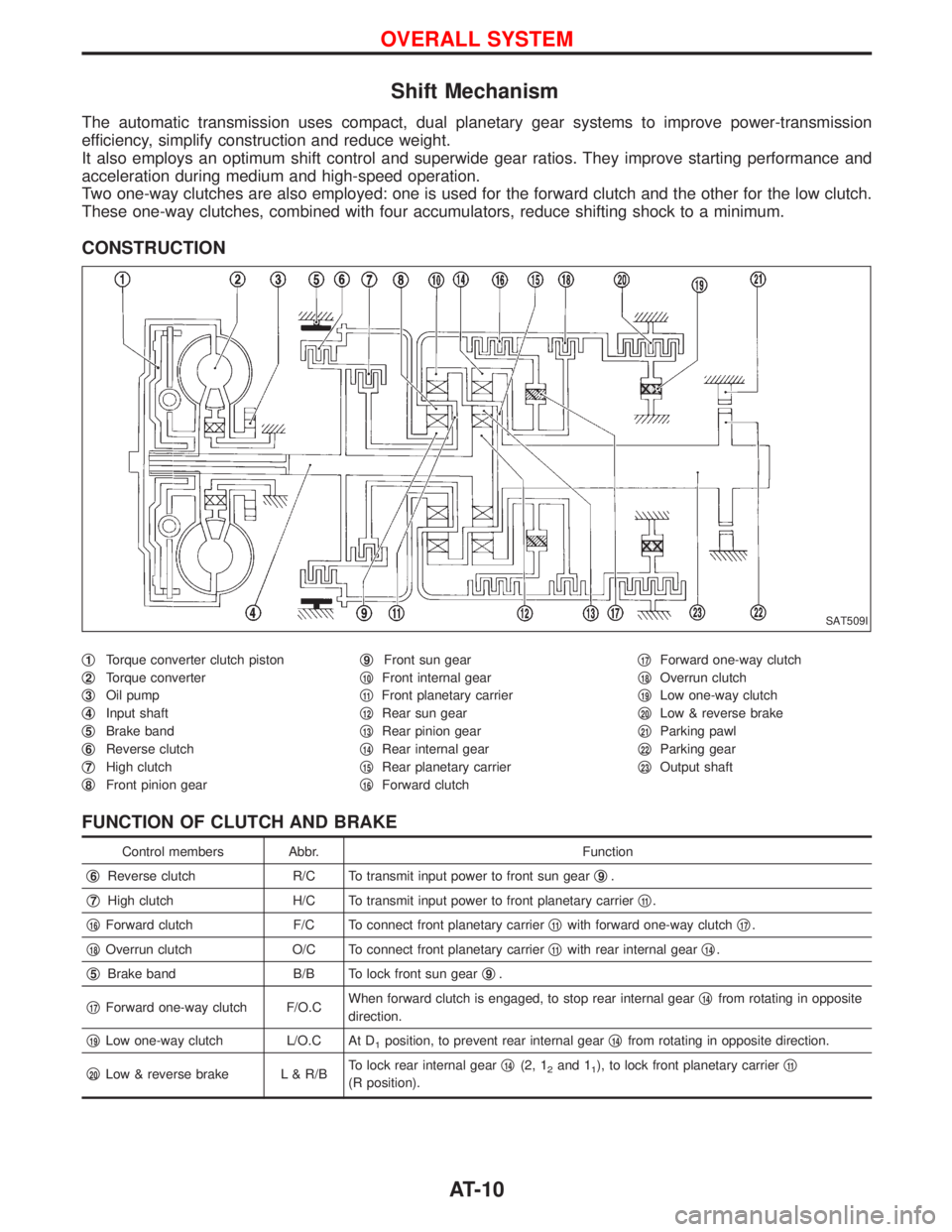
Shift Mechanism
The automatic transmission uses compact, dual planetary gear systems to improve power-transmission
efficiency, simplify construction and reduce weight.
It also employs an optimum shift control and superwide gear ratios. They improve starting performance and
acceleration during medium and high-speed operation.
Two one-way clutches are also employed: one is used for the forward clutch and the other for the low clutch.
These one-way clutches, combined with four accumulators, reduce shifting shock to a minimum.
CONSTRUCTION
q1Torque converter clutch piston
q
2Torque converter
q
3Oil pump
q
4Input shaft
q
5Brake band
q
6Reverse clutch
q
7High clutch
q
8Front pinion gearq
9Front sun gear
q
10Front internal gear
q
11Front planetary carrier
q
12Rear sun gear
q
13Rear pinion gear
q
14Rear internal gear
q
15Rear planetary carrier
q
16Forward clutchq
17Forward one-way clutch
q
18Overrun clutch
q
19Low one-way clutch
q
20Low & reverse brake
q
21Parking pawl
q
22Parking gear
q
23Output shaft
FUNCTION OF CLUTCH AND BRAKE
Control members Abbr. Function
q
6Reverse clutch R/C To transmit input power to front sun gearq9.
q
7High clutch H/C To transmit input power to front planetary carrierq11.
q
16Forward clutch F/C To connect front planetary carrierq11with forward one-way clutchq17.
q
18Overrun clutch O/C To connect front planetary carrierq11with rear internal gearq14.
q
5Brake band B/B To lock front sun gearq9.
q
17Forward one-way clutch F/O.CWhen forward clutch is engaged, to stop rear internal gearq14from rotating in opposite
direction.
q
19Low one-way clutch L/O.C At D1position, to prevent rear internal gearq14from rotating in opposite direction.
q
20Low & reverse brake L & R/BTo lock rear internal gearq14(2, 12and 11), to lock front planetary carrierq11
(R position).
SAT509I
OVERALL SYSTEM
AT-10
Page 677 of 1767
4. Clean spray hole of nozzle body by using Tool.
To prevent spray hole from canting, always clean it by start-
ing with inner side and working towards the outside.
5. Decarbonate nozzle needle tip by using Tool.
6. Check needle sink.
(1) Pull needle about halfway out from body and then release it.
(2) Needle should sink into body very smoothly from just its own
weight.
(3) Repeat this test and rotate needle slightly each time.
If needle fails to sink smoothly from any position, replace both
needle and body as a unit.
Assembly (No.2-4nozzle)
Assembly is in the reverse order of disassembly.
Holder to nozzle nut:
:29-49N×m (3.0 - 5.0 kg-m, 22 - 36 ft-lb)
SEF833
SEF834
SEF835
SEF967
INJECTION NOZZLETD27Ti
Cleaning (No.2-4nozzle) (Cont'd)
EC-315
Page 859 of 1767

Bulb Replacement
The headlamp is a semi-sealed beam type which uses a replacable
halogen bulb. The bulb can be replaced from the engine compart-
ment side without removing the headlamp body.
IGrasp only the plastic base when handling the bulb. Never
touch the glass envelope.
1. Disconnect the battery cable.
2. Disconnect the harness connector from the back side of the
bulb.
3. Pull off the rubber cap.
4. Press end of the retaining pin together to release bulb.
5. Remove the headlamp bulb. Do not shake or rotate the bulb
when removing it.
6. Install the new bulb in reverse order of removal.
CAUTION:
IDo not leave the bulb out of the headlamp reflector for a
long period of time as dust, moisture, smoke, etc. may
enter the headlamp body and affect the performance of the
headlamp. Thus, the headlamp bulb should not be
removed from the headlamp reflector until just before a
replacement bulb is to be installed.
Aiming Adjustment
When performing headlamp aiming adjustment, use an aiming
machine, aiming wall screen or headlamp tester. For operating
instructions, of any aimer, it should be in good repair, calibrated and
used according to respective operation manuals supplied with the
unit.
If any aimer is not available, aiming adjustment can be done as
follows:
For details, refer to the regulations in your own country.
CAUTION:
a. Keep all tires inflated to correct pressures.
b. Place vehicle and tester on one and same flat surface.
c. See that there is noload in vehicle other than coolant,
engine oil filled up to correct level, full fuel tank and the
driver (or equivalent weight placed in driver's position).
CAUTION:
Be sure aiming switch is set to ª0º when performing aiming
adjustment on vehicles equipped with headlamp aiming con-
trol.
NEL623
HEADLAMP
EL-43
Page 869 of 1767

Front Fog Lamp Aiming Adjustment
When performing fog lamp aiming adjustment, use an aiming
machine, aiming wall screen or headlamp tester. The aimer should
be in good operational condition, calibrated and used according to
the relevant operation manuals supplied with the unit.
If an aimer is not available, aiming adjustment can be done as fol-
lows:
For details, refer to the regulations in your own country.
CAUTION:
IKeep all tires inflated to correct pressures.
IPlace vehicle and tester on one and the same flat surface.
IEnsure that there is no-load in the vehicle other than
coolant, engine oil (filled up to correct level), full fuel tank
and the driver (or equivalent weight placed in driver's posi-
tion).
For details of front fog lamp aiming adjustment, refer to ªAiming
Adjustmentº, EL-43.
Check the distance between the vehicle and the ground illumina-
tion point of the main axis of the fog lamp beam. Keep the distance
to approximately 40 m (131 ft).
NEL331
EXTERIOR LAMP
EL-53
Page 1148 of 1767

8. Remove the crankshaft pulley.
ITo fix the crankshaft, clamp the bar between the drive plate
holding bolts, and set by touching the engine sub-attachment
(SST).
IAs another method, set by clamping a hammer handle, etc. in
the counterweight portion of the crankshaft.
CAUTION:
IDo not damage the crankshaft.
IMake sure that no foreign objects get inside the engine.
IDo not damage or magnetize the signal detection protru-
sions of the crankshaft pulley.
IAfter removing timing chain, never rotate crankshaft, or
the piston will push the valve up and damage the valve.
9. Remove the gear case.
IUsing the grooved places shown in the figure, remove the gear
case by using a screwdriver and a seal cutter (SST).
10. Remove the front oil seal from the gear case by using a screw-
driver.
CAUTION:
Do not damage the gear case.
11. Fix the internal mechanism setting bolt [part No.: 81-20620-28,
screw dia.: M6, dimension below neck: 20 mm (0.79 in)] to the
bolt hole of the idler gear (A) and tighten to the specification.
: 2.5 - 3.4 N×m (0.25 - 0.35 kg-m, 22 - 30 in-lb)
CAUTION:
IOnly use the genuine setting bolt, or the idler gear (A) will
be damaged.
IDo not rotate the crankshaft as the head of the setting
bolts interferes with the gear case.
IDo not remove the setting bolt from the idler gear (A) until
the timing chain and all of the parts in connection have
been installed.
IIf these bolts are not installed, internal mechanism will
disengage after the idler gear is removed. This will prohibit
the idler gear from being reusable.
FEM050
YEM030
FEM052
SEM377G
TIMING GEARZD
Removal (Cont'd)
EM-40
Page 1182 of 1767

INew connecting rods are classified into 8 weight classes at
factory. The same class connecting rods are used on a engine.
Weight grade symbol Weight class g (oz)
H 1,261 - 1,264 (44.5 - 44.6)
I 1,264 - 1,267 (44.6 - 44.7)
K 1,267 - 1,270 (44.7 - 44.8)
L 1,270 - 1,273 (44.8 - 44.9)
M 1,273 - 1,276 (44.9 - 45.0)
O 1,276 - 1,279 (45.0 - 45.1)
P 1,279 - 1,282 (45.1 - 45.2)
S 1,282 - 1,285 (45.2 - 45.3)
CYLINDER BLOCK TOP SURFACE DISTORTION
IUsing scraper, remove gasket installed onto cylinder block sur-
face. Remove contamination such as oil, scale, and carbon.
CAUTION:
Keep broken pieces of gasket clear of oil and coolant pas-
sages.
IUse straightedge and feeler gauge to check block upper sur-
face for distortion.
Limit: 0.1 mm (0.004 in)
MAIN BEARING HOUSING INNER DIAMETER
IInstall main bearing caps without main bearings. Tighten
mounting bolts to the specified torque.
IUse bore gauge to measure main bearing housing inner diam-
eter.
Standard:
74.981 - 75.000 mm (2.9520 - 2.9528 in) dia.
IIf out of specification, replace cylinder block and lower cylinder
block.
PISTON TO CYLINDER BORE CLEARANCE
Cylinder bore inner diameter
IUsing bore gauge, measure cylinder inner diameters at 6 posi-
tions; top, middle, and bottom (A, B, C) in 2 directions (X, Y).
Cylinder inner diameter (Standard):
96.000 - 96.030 mm (3.7795 - 3.7807 in) dia.
Wear limit: 0.2 mm (0.008 in)
Out-of-round limit (X - Y): 0.02 mm (0.0008 in)
Taper limit (A - C): 0.02 mm (0.0008 in)
FEM106
FEM107
FEM108
FEM109
CYLINDER BLOCKZD
Inspection (Cont'd)
EM-74
Page 1184 of 1767

Selective combination chart
Unit: mm (in)
q: Preferable combination
g: Allowable combination
X: NG combinationPiston grade
12
95.950 - 95.960
(3.7776 - 3.7779)95.960 - 95.970
(3.7779 - 3.7783)
Cylinder
bore grade
(Cylinder
block bore
inner
diameter)196.000 - 96.010
(3.7795 - 3.7799)qX
296.010 - 96.020
(3.7799 - 3.7803)gq
396.020 - 96.030
(3.7803 - 3.7807)gq
IPiston grade 3 (95.980/95.970) is applicable at factory only.
INew pistons are classified into 4 weight classes at factory. The
same class pistons are used on a engine.
Weight grade symbol Weight class g (oz)
E 600 - 605 (21.2 - 21.3)
F 605 - 610 (21.3 - 21.5)
G 610 - 615 (21.5 - 21.7)
H 615 - 620 (21.7 - 21.9)
CRANKSHAFT JOURNAL OUTER DIAMETER
Use micrometer to measure journal outer diameter.
Standard: 70.907 - 70.920 mm (2.7916 - 2.7921 in) dia.
CRANKSHAFT PIN OUTER DIAMETER
Use micrometer to measure pin outer diameter.
Standard: 56.913 - 56.926 mm (2.2407 - 2.2412 in) dia.
CRANKSHAFT OUT-OF-ROUND AND TAPER
IUsing micrometer, measure each journal and pin at 4 points
shown in the figure.
IOut-of-round value is indicated by difference in dimensions
between directions A and B at points 1 and 2.
ITaper value is indicated by difference in dimensions between
points 1 and 2 in directions A and B.
Out-of-round limit: 0.01 mm (0.0004 in)
Taper limit: 0.01 mm (0.0004 in)
CRANKSHAFT RUNOUT
IPlace V-block onto surface plate to support journals at both
ends of crankshaft.
IPosition dial indicator vertically onto No. 3 journal.
IRotate crankshaft to read needle movement on dial indicator.
ICrankshaft bend value is 1/2 of needle movement.
Limit: 0.03 mm (0.0012 in)
FEM114
FEM115
FEM116
CYLINDER BLOCKZD
Inspection (Cont'd)
EM-76