2002 MAZDA 6 oil temperature
[x] Cancel search: oil temperaturePage 317 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–165
F2
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSTIC INDEXA6E408018881201
TROUBLESHOOTING
No. TROUBLESHOOTING ITEM DESCRIPTION PAGE
1 Melting of main or other fuses—(See F2–173 NO.1 MELTING
OF MAIN OR OTHER FUSES)
2 MIL illuminates MIL is illuminated incorrectly.(See F2–174 NO.2 MIL
ILLUMINATES)
3 Will not crank Starter does not work.(See F2–174 NO.3 WILL NOT
CRANK)
4Hard start/long crank/erratic start/
erratic crankStarter cranks engine at normal speed but
engine requires excessive cranking time
before starting.(See F2–176 NO.4 HARD
START/LONG CRANK/
ERRATIC START/ERRATIC
CRANK)
5 Engine stalls After start/at idleEngine stops unexpectedly at idle and/or
after start.(See F2–178 NO.5 ENGINE
STALLS-AFTER START/AT
IDLE)
6 Cranks normally but will not startStarter cranks engine at normal speed but
engine will not run.(See F2–181 NO.6 CRANKS
NORMALLY BUT WILL NOT
START)
7 Slow return to idleEngine takes more time than normal to
return to idle speed.(See F2–184 NO.7 SLOW
RETURN TO IDLE)
8 Engine runs rough/rolling idleEngine speed fluctuates between specified
idle speed and lower speed and engine
shakes excessively.(See F2–186 NO.8 ENGINE
RUNS ROUGH/ROLLING
IDLE)
9 Fast idle/runs onEngine speed continues at fast idle after
warm-up.
Engine runs after engine switch is turned to
OFF.(See F2–189 NO.9 FAST
IDLE/RUNS ON)
10 Low idle/stalls during decelerationEngine stops unexpectedly at beginning of
deceleration or recovery from deceleration.(See F2–190 NO.10 LOW
IDLE/STALLS DURING
DECELERATION)
11Engine stalls/quitsAcceleration/
cruiseEngine stops unexpectedly at beginning of
acceleration or during acceleration.
Engine stops unexpectedly while cruising.
(See F2–192 NO.11 ENGINE
STALLS/QUITS, ENGINE
RUNS ROUGH, MISSES,
BUCK/JERK, HESITATION/
STUMBLE, SURGES) Engine runs roughAcceleration/
cruiseEngine speed fluctuates during acceleration
or cruising.
MissesAcceleration/
cruiseEngine misses during acceleration or
cruising.
Buck/jerkAcceleration/
cruise/
decelerationVehicle bucks/jerks during acceleration,
cruising, or deceleration.
Hesitation/stumble AccelerationMomentary pause at beginning of
acceleration or during acceleration.
SurgesAcceleration/
cruiseMomentary minor irregularity in engine
output.
12 Lack/loss of powerAcceleration/
cruisePerformance is poor under load (e.g. power
down when climbing hills).(See F2–195 NO.12 LACK/
LOSS OF POWER-
ACCELERATION/CRUISE)
13 Knocking/pingingExcessive shrilly knocking sound from
engine.(See F2–199 NO.13
KNOCKING/PINGING)
14 Poor fuel economy Fuel economy is unsatisfactory.(See F2–202 NO.14 POOR
FUEL ECONOMY)
15 Emissions compliance Fails emissions test.(See F2–205 NO.15
EMISSION COMPLIANCE)
16 High oil consumption/leakage Oil consumption is excessive.(See F2–209 NO.16 HIGH OIL
CONSUMPTION/LEAKAGE)
17Cooling system
concernsOverheatingEngine runs at higher than normal
temperature/overheats.(See F2–210 NO.17 COOLING
SYSTEM CONCERNS-
OVERHEATING)
Page 374 of 909

F2–222
TROUBLESHOOTING
NO.23 A/C DOES NOT WORK SUFFICIENTLYA6E408018881225
Diagnostic Procedure
End Of Sie
23 A/C DOES NOT WORK SUFFICIENTLY
DESCRIPTION•A/C compressor magnetic clutch does not engage when A/C switch is turned on.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Improper refrigerant charge amount
•Open A/C switch magnetic clutch
•Open circuit between A/C relay and A/C magnetic clutch
•Poor GND of A/C magnetic clutch
•Improper A/C magnetic clutch clearance
•Refrigerant pressure switch is stuck open
•A/C relay is stuck open
•Improper A/C cut-off control
•Open circuit between A/C switch and PCM through both refrigerant pressure switch and A/C amplifier
STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
1 Perform self-test function using WDS or
equivalent.
Turn engine switch to ON.
Retrieve any DTC.
Is DTC displayed?YesDTC is displayed:
Go to appropriate DTC test.
Communication error message is displayed:
Inspect for following:
•Open circuit between PCM control relay and PCM
terminal 53 or 79
•Open circuit PCM control relay and PCM terminal
69
•PCM control relay stuck open
•Open or poor GND circuit (PCM terminal 65, 85,
103 or 104)
•Poor connection vehicle body GND
YesNo DTC is displayed:
Go to appropriate DTC test.
2 Disconnect A/C compressor connector.
Start engine and turn A/C switch to ON.
Is there correct voltage at terminal of A/C
compressor magnetic clutch connector?
Specification
More than 10.5 VYes Inspect for GND condition of magnetic clutch on A/C
compressor.
If GND condition is okay, inspect magnetic clutch coil
for open circuit.
No Go to next step.
3 Disconnect refrigerant pressure switch
connector.
Connect jumper wire between terminals of
refrigerant pressure switch connector.
Turn engine switch to ON.
Turn A/C switch on and set blower fan at any
speed.
Measure PCM terminal 84 voltage.
Is voltage below 1.0 V?Yes Inspect refrigerant pressure switch operation.
If switch is okay, go to next step.
No Inspect for following:
•A/C switch is stuck open
•Open circuit between refrigerant pressure switch
and PCM terminal 84
•Open circuit of blower motor fan switch and
resistor (if blower motor does not operate)
•Evaporator temperature sensor and A/C amplifier
4 Inspect A/C cut-off operation.
Does A/C cut-off work properly?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace malfunctioning part according to A/C
cut-off system inspection results.
5 Remove jumper wire from switch connector.
Reconnect connector to refrigerant pressure
switch.
Start engine and turn A/C switch on.
Does fan operate?Yes Inspect for stuck open A/C relay.
Replace if necessary.
No Inspect following and repair or replace as necessary:
•Refrigerant charging amount
•Seized A/C compressor
6 Verify test results.
•If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
•If malfunction remains, replace PCM. (See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
Page 416 of 909
![MAZDA 6 2002 Workshop Manual Suplement K2–1
K2
K2AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE [JA5AX-EL]
OUTLINE.............................................................. K2-3
FEATURES ........................................................ K2-3
SPECIFICATI MAZDA 6 2002 Workshop Manual Suplement K2–1
K2
K2AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE [JA5AX-EL]
OUTLINE.............................................................. K2-3
FEATURES ........................................................ K2-3
SPECIFICATI](/manual-img/28/57057/w960_57057-415.png)
K2–1
K2
K2AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE [JA5AX-EL]
OUTLINE.............................................................. K2-3
FEATURES ........................................................ K2-3
SPECIFICATIONS ............................................. K2-3
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.................................. K2-4
OUTLINE ........................................................... K2-4
CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW .............................. K2-6
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
STRUCTURAL VIEW...................................... K2-8
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE CONTROL SYSTEM
WIRING DIAGRAM ....................................... K2-10
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE BLOCK
DIAGRAM ..................................................... K2-11
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DEVICE
RELATIONSHIP CHART .............................. K2-13
POWERTRAIN DESCRIPTION ....................... K2-15
TORQUE CONVERTER DESCRIPTION......... K2-40
OIL PUMP DESCRIPTION .............................. K2-41
CENTRIFUGAL BALANCE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION ............................................. K2-42
CONTROL VALVE BODY DESCRIPTION ...... K2-43
TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE
(TFT) SENSOR DESCRIPTION ................... K2-45
INPUT/TURBINE SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION ............................................. K2-45
INTERMEDIATE SENSOR DESCRIPTION..... K2-46
VEHICLE SPEEDOMETER SENSOR
DESCRIPTION ............................................. K2-46
SOLENOID VALVE DESCRIPTION ................ K2-47
CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (CAN)
DESCRIPTION ............................................. K2-50
TRANSAXLE CONTROL MODULE
(TCM) DESCRIPTION .................................. K2-51
SHIFT CONTROL DESCRIPTION .................. K2-51
MANUAL MODE SHIFT CONTROL
DESCRIPTION ............................................. K2-52
LINE PRESSURE CONTROL DESCRIPTION K2-54
FEEDBACK CONTROL DESCRIPTION ......... K2-57
N-D SELECT CONTROL DESCRIPTION........ K2-59
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH
(TCC) CONTROL DESCRIPTION ................ K2-59
SLOPE MODE CONTROL DESCRIPTION ..... K2-63
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD)
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION.............................. K2-64
COOLING SYSTEM DESCRIPTION ............... K2-69
LOCATION INDEX............................................. K2-70
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE LOCATION
INDEX ........................................................... K2-70
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE................................ K2-72
MECHANICAL SYSTEM TEST ....................... K2-72
ROAD TEST .................................................... K2-75AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID
(ATF) INSPECTION ...................................... K2-78
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID
(ATF) REPLACEMENT ................................. K2-80
TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH
INSPECTION ................................................ K2-80
TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION .......................... K2-81
TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH
ADJUSTMENT .............................................. K2-83
TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE
(TFT) SENSOR INSPECTION ...................... K2-84
TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE
(TFT) SENSOR REMOVAL/INSTALLATION K2-85
INPUT/TURBINE SPEED SENSOR
INSPECTION ................................................ K2-85
INPUT/TURBINE SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION .......................... K2-86
INTERMEDIATE SENSOR INSPECTION ....... K2-86
INTERMEDIATE SENSOR
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION .......................... K2-86
VEHICLE SPEEDOMETER SENSOR
(VSS) INSPECTION...................................... K2-87
VEHICLE SPEEDOMETER SENSOR
(VSS) REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ............... K2-87
SOLENOID VALVE INSPECTION ................... K2-88
SOLENOID VALVE
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION .......................... K2-90
TCM INSPECTION .......................................... K2-90
TCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION .................... K2-96
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE AND
TRANSFER REMOVAL/INSTALLATION...... K2-99
OIL SEAL REMOVAL/INSTALLATION .......... K2-104
CONTROL VALVE BODY
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................ K2-105
OIL COOLER FLUSHING .............................. K2-106
OIL COOLER REMOVAL/INSTALLATION .... K2-108
OIL COOLER DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY .. K2-110
DRIVE PLATE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION... K2-112
TRANSFER....................................................... K2-114
TRANSFER OIL INSPECTION ...................... K2-114
TRANSFER OIL REPLACEMENT ................. K2-114
TRANSFER REMOVAL/INSTALLATION....... K2-115
BREATHER PLUG
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................ K2-116
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SHIFT
MECHANISM................................................. K2-117
SELECTOR LEVER INSPECTION ................ K2-117
SELECTOR LEVER COMPONENT
INSPECTION .............................................. K2-117
SELECTOR CABLE ADJUSTMENT .............. K2-118
SELECTOR LEVER
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................ K2-119
SELECTOR LEVER
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ...................... K2-122
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC............................... K2-123
FOREWORD .................................................. K2-123 FEATURES
SERVICE
Page 486 of 909

LOCATION INDEX
K2–71
K2
End Of Sie
1 Automatic transaxle fluid (ATF)
(See K2–78 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID
(ATF) INSPECTION)
(See K2–80 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID
(ATF) REPLACEMENT)
2 Transaxle range (TR) switch
(See K2–80 TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH
INSPECTION)
(See K2–81 TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
(See K2–83 TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH
ADJUSTMENT)
3 Transaxle fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
(See K2–84 TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE
(TFT) SENSOR INSPECTION)
(See K2–85 TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE
(TFT) SENSOR REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
4 Input/turbine speed sensor
(See K2–85 INPUT/TURBINE SPEED SENSOR
INSPECTION)
(See K2–86 INPUT/TURBINE SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
5 Intermediate sensor
(See K2–86 INTERMEDIATE SENSOR
INSPECTION)
(See K2–86 INTERMEDIATE SENSOR REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
6 Vehicle speedometer sensor (VSS)
(See K2–87 VEHICLE SPEEDOMETER SENSOR
(VSS) INSPECTION)
(See K2–87 VEHICLE SPEEDOMETER SENSOR
(VSS) REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
7 Solenoid valve
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE INSPECTION)
(See K2–90 SOLENOID VALVE REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
8TCM
(See K2–90 TCM INSPECTION)
(See K2–96 TCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)9 Transfer oil
(See K2–114 TRANSFER OIL INSPECTION)
(See K2–114 TRANSFER OIL REPLACEMENT)
10 Automatic transaxle
(See K2–99 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE AND
TRANSFER REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
11 Transfer
(See K2–115 TRANSFER REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
(See K2–116 BREATHER PLUG REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
12 Oil seal
(See K2–104 OIL SEAL REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
13 Control valve body
(See K2–105 CONTROL VALVE BODY REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
14 Oil cooler
(See K2–106 OIL COOLER FLUSHING)
(See K2–108 OIL COOLER REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
(See K2–110 OIL COOLER DISASSEMBLY/
ASSEMBLY)
15 Drive plate
(See K2–112 DRIVE PLATE REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
16 Selector lever
(See K2–117 SELECTOR LEVER INSPECTION)
(See K2–117 SELECTOR LEVER COMPONENT
INSPECTION)
(See K2–119 SELECTOR LEVER REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
(See K2–122 SELECTOR LEVER DISASSEMBLY/
ASSEMBLY)
17 Selector cable
(See K2–118 SELECTOR CABLE ADJUSTMENT)
Page 489 of 909

K2–74
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Evaluation of line pressure test
Stall Speed Test
1. Perform mechanical system test preparation. (See K2–72 Mechanical System Test Preparation.)
2. Connect a tachometer.
3. Start the engine.
4. Shift the selector lever to D range.
Caution
•Do not maintain WOT in any gear range for more than 5 seconds or transaxle damage will occur.
•If engine speed recorded by the tachometer exceeds maximum specified rpm, release the
accelerator pedal immediately. Clutch or band slippage is indicator.
5. Firmly depress the brake pedal with the left foot, and gently depress the accelerator pedal to the floor (WOT)
with the right.
6. When the engine speed no longer increases, quickly read the engine speed and release the accelerator pedal.
7. Shift the selector the to N position and let the engine idle for 1 minute or more to cool the ATF.
8. Perform stall tests for the remaining ranges and position in the same manner.
•R position
•Mrange (1GR, 2GR)
Engine stall speed
ATF temperature : 60—70 °C {140—158 °F}
Turn off all electrical loads
2,200—2,600 rpm
9. Turn off the engine.
Evaluation of stall test
Condition Possible cause
IdleBelow specificationLow pressure in all rangesWorn oil pump
Poor operation of each solenoid
Fluid leaking from oil strainer, oil pump, pressure regulator
valve, torque converter relief valve, and/or pressure relief valve
Pressure regulator valve or pilot valve sticking
Damaged pressure regulator valve spring or pilot valve spring
Low pressure in D and M
rangeFluid leaking from hydraulic circuit of low clutch
Low pressure in R position
onlyFluid leaking from hydraulic circuit of reverse clutch
Fluid leaking from hydraulic circuit of low and reverse brake
clutch
Above specification High pressure in all rangesThrottle position sensor out of adjustment
TFT sensor malfunction
Poor operation of shift solenoid
Pilot valve sticking
Pressure reducing valve or plug sticking
Stall Below specification Low pressure in all rangesThrottle position sensor out of adjustment
Pressure control solenoid malfunction
Poor operation of shift solenoid
Pilot valve sticking
Pressure reducing valve or plug sticking
Condition Possible cause
Above specificationIn all forward ranges and R
positionInsufficient line pressure
Worm oil pump
Poor operation of low clutch
Poor adjustment or malfunction of TR switch
Oil leaking from oil pump, control valve, and/or transmission
case
Pressure regulator valve or pilot valve sticking
In all forward ranges Low clutch slippage
Low one-way clutch slippage
Reduction one-way clutch slippage
In R positionLow and reverse brake slippage
Reverse clutch slippage
Reduction brake slippage
Below specificationIn all forward ranges and R
positionEngine out of tune
One-way clutch slippage within torque converter
Page 490 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–75
K2
Time Lag Test
1. Perform mechanical system test preparation. (See K2–72 Mechanical System Test Preparation.)
2. Start the engine.
3. Warm up the engine until the ATF temperature reaches 60—70°C {140—158°F}. Shift the selector lever from N
position to D range.
4. Use a stopwatch to measure the time it takes from shifting until engagement is felt. Take three measurements
for each test and average the results using the following formula.
Formula
Average time lag = (Time 1 + Time 2 + Time 3) / 3
5. Perform the test for the following shifts in the same manner.
•N position → P position
Time lag
N → D range ... approx. 0.5—1.0 second
N → R position ... approx. 0.6— 1.0 second
Evaluation of time lag test
End Of SieROAD TESTA6E571401030210Road Test Preparation
1. Inspect the engine coolant. (See Section E.)
2. Inspect the engine oil. (See D–8 ENGINE OIL INSPECTION.)
3. Inspect the ATF levels. (See K2–78 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID (ATF) INSPECTION.)
4. Inspect the idle speed and ignition timing in P position. (See F1–22 IDLE SPEED INSPECTION (4WD).)
5. Bring up the engine and transaxle to normal operating temperature.
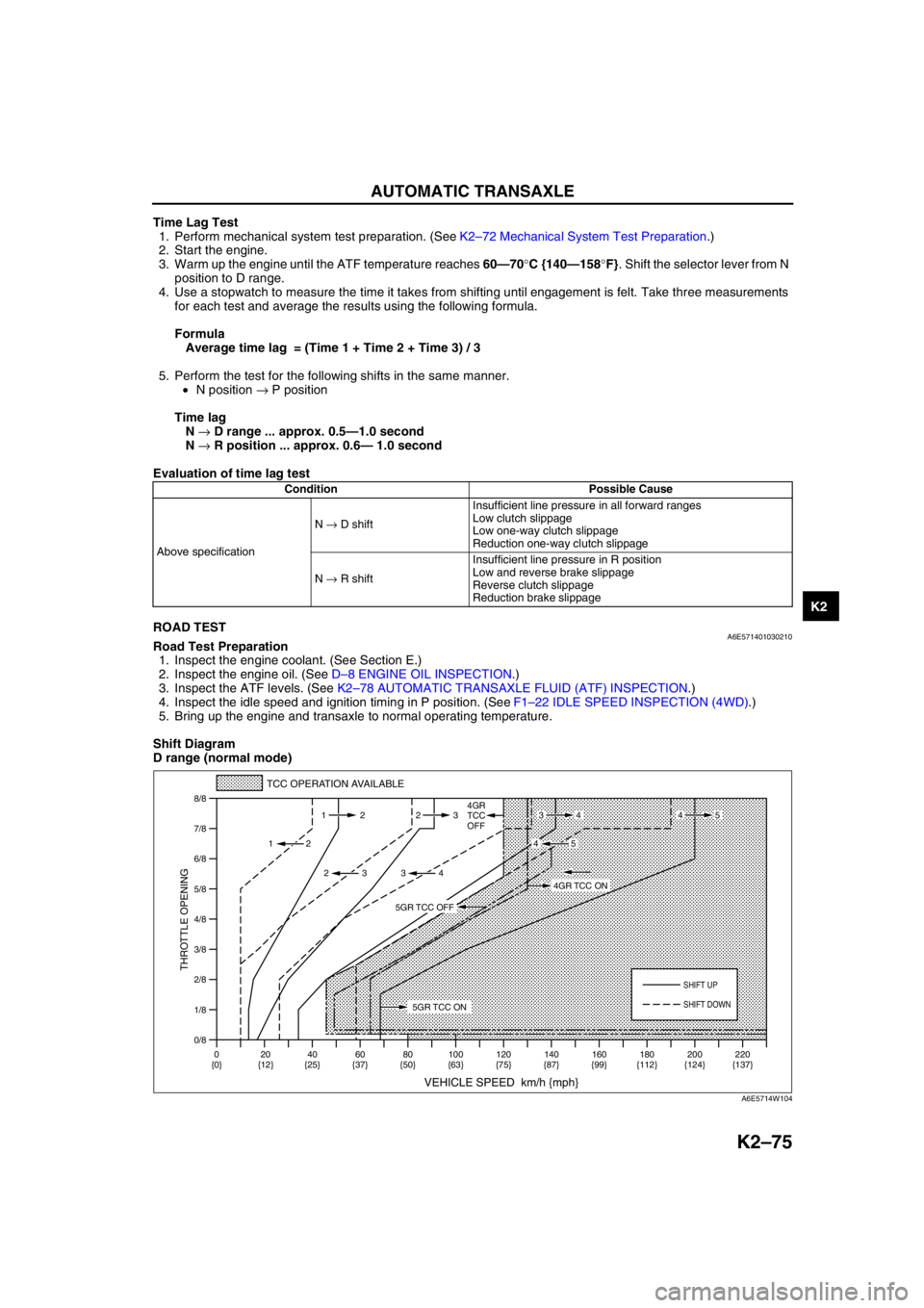
Shift Diagram
D range (normal mode)
Condition Possible Cause
Above specificationN → D shiftInsufficient line pressure in all forward ranges
Low clutch slippage
Low one-way clutch slippage
Reduction one-way clutch slippage
N → R shiftInsufficient line pressure in R position
Low and reverse brake slippage
Reverse clutch slippage
Reduction brake slippage
0/8 1/8
2/8
3/8
4/8
5/8
6/8
7/8
8/8
TCC OPERATION AVAILABLE
VEHICLE SPEED km/h {mph}
THROTTLE OPENING
SHIFT UP
4GR
TCC
OFF
SHIFT DOWN
0
{0}20
{12}40
{25}60
{37}80
{50}100
{63}120
{75}140
{87}160
{99}180
{112}220
{137} 200
{124} 112 23
2
2 232
34
4534
45
5GR TCC ON
4GR TCC ON
5GR TCC OFF
A6E5714W104
Page 494 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–79
K2
Automatic Transaxle Fluid (ATF) Level Inspection
Caution
•The ATF amount varies according to ATF's temperature. Therefore, when checking the ATF level or
replacing the ATF, use a thermometer to measure the temperature then adjust the ATF amount to
the specified level according to the specified temperature.
1. Park the vehicle on level ground.
2. Apply the parking brake and position wheel chocks securely to prevent the vehicle from rolling.
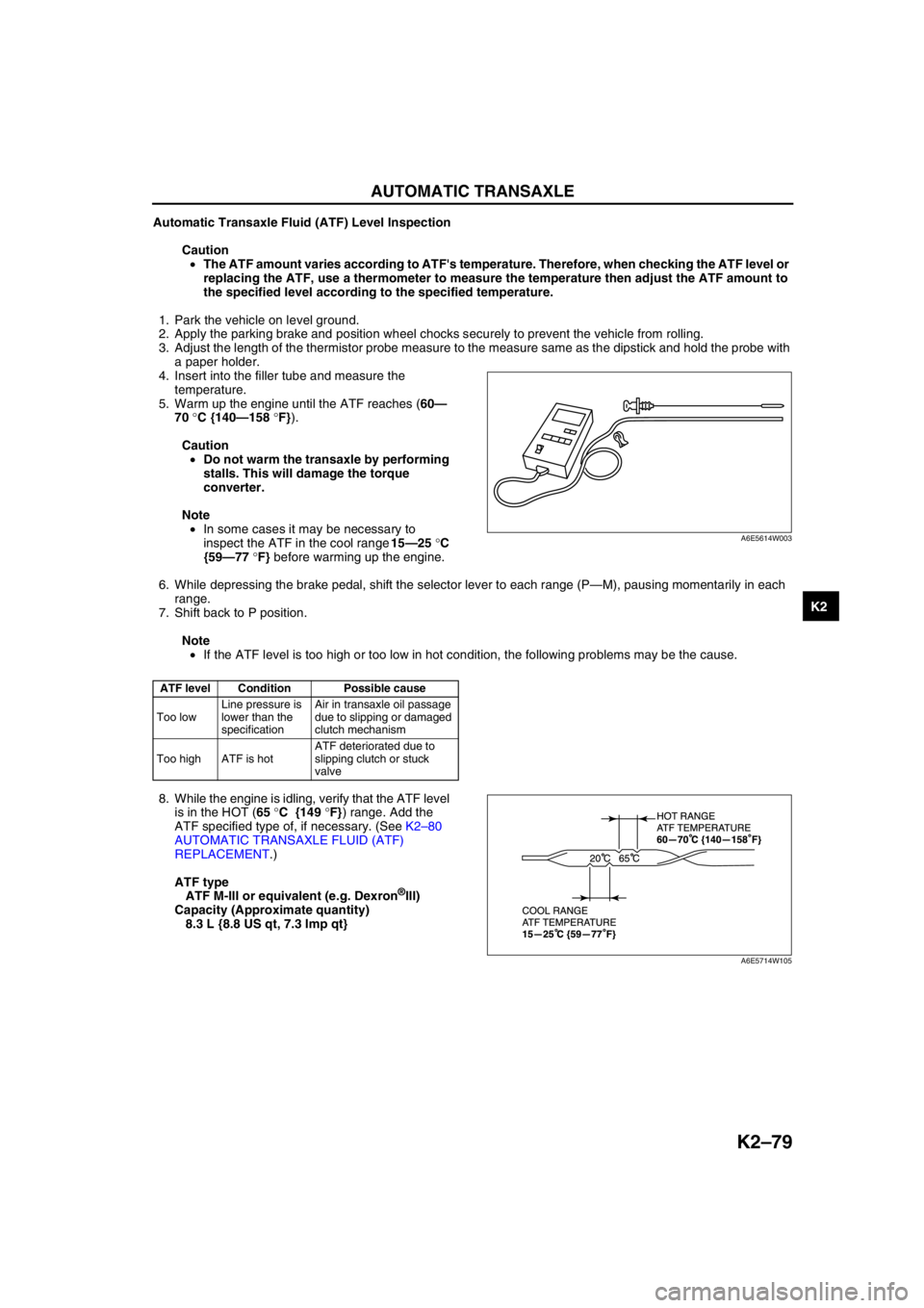
3. Adjust the length of the thermistor probe measure to the measure same as the dipstick and hold the probe with
a paper holder.
4. Insert into the filler tube and measure the
temperature.
5. Warm up the engine until the ATF reaches (60—
70 °C {140—158 °F}).
Caution
•Do not warm the transaxle by performing
stalls. This will damage the torque
converter.
Note
•In some cases it may be necessary to
inspect the ATF in the cool range 15—25 °C
{59—77 °F} before warming up the engine.
6. While depressing the brake pedal, shift the selector lever to each range (P—M), pausing momentarily in each
range.
7. Shift back to P position.
Note
•If the ATF level is too high or too low in hot condition, the following problems may be the cause.
8. While the engine is idling, verify that the ATF level
is in the HOT (65 °C {149 °F}) range. Add the
ATF specified type of, if necessary. (See K2–80
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID (ATF)
REPLACEMENT.)
ATF type
ATF M-III or equivalent (e.g. Dexron
®III)
Capacity (Approximate quantity)
8.3 L {8.8 US qt, 7.3 Imp qt}
End Of Sie
ATF level Condition Possible cause
Too lowLine pressure is
lower than the
specificationAir in transaxle oil passage
due to slipping or damaged
clutch mechanism
Too high ATF is hotATF deteriorated due to
slipping clutch or stuck
valve
A6E5614W003
A6E5714W105
Page 499 of 909

K2–84
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE (TFT) SENSOR INSPECTIONA6E5714190102021. Disconnect the terminal component No.2
connector.
2. Remove the oil dipstick.
3. Insert the thermistor probe into the filler tube.
4. Start the engine.
5. Measure resistance between the terminals G and
H.
•If not as specified, replace the TFT sensor.
(See K2–99 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE AND
TRANSFER REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.)
(See Automatic Transaxle Workshop Manual
JA5A-EL.)
6. Connect the terminal component No.2 connector.
End Of Sie
ATF temperature (°C {°F}) Resistance (kilohm)
-20 {-4} 15.87—17.54
0 {32} 5.73—6.33
20 {68} 2.38—2.63
40 {104} 1.10—1.22
60 {140} 0.56—0.62
80 {176} 0.31—0.34
100 {212} 0.18—0.20
120 {248} 0.11—0.12
130 {266} 0.09—0.10
TERMINAL COMPONENT No.2
A6E5714W117
A6E5614W003
ACEG
BDFH
A6E5714W118
INCREASES
RESISTANCE (ohm)
ATF TEMPERATURE INCREASESCHARACTERISTIC
OF TFT SENSOR
A6E5714W119