2002 MAZDA 6 coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 351 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–199
F2
NO.13 KNOCKING/PINGINGA6E408018881215
Diagnostic Procedure
13 KNOCKING/PINGING
DESCRIPTION•Excessive shrilly knocking sound from engine.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Poor fuel quality
•Air leakage from intake-air system
•Intake-air system restriction or clogging
•Variable swirl control (VSC) system malfunction
•Variable boost control (VBC) system malfunction
•Intake shutter valve stuck close
•VSC valve stuck close
•Glow system malfunction
•Low engine compression
•Improper valve timing
•Low coolant temperature
•Incorrect fuel injection timing
•Erratic signal from CKP sensor
•Erratic signal from CMP sensor
•ECT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•MAF/IAT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•IAT sensor No.2 or related circuit malfunction
•Boost sensor or related malfunction
•Fuel pressure sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Accelerator position sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Excessive fuel pressure
•Fuel return line clogging or restriction
•EGR system malfunction
•Exhaust system and/or catalyst converter restriction
•Turbocharger malfunction
•Charge air cooler malfunction
•Suction control valve malfunction (built-in supply pump)
Warning
The following troubleshooting flow chart contains the fuel system diagnosis and repair
procedures. Read the following warnings before performing the fuel system services:
•Fuel vapor is hazardous. It can easily ignite, causing serious injury and damage. Always keep
sparks and flames away from fuel.
•Fuel line spills and leakage are dangerous. Fuel can ignite and cause serious injury or death
and damage. Fuel can also irritate skin and eyes. To prevent this, always complete “BEFORE
REPAIR PROCEDURE” and “AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE” described in this manual.
STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
1 Does engine run cold? Yes Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.18 COOLING
SYSTEM CONCERNS—RUNS COLD”.
No Go to next step.
2 Inspect for following:
•Fuel quality (e.g.: including water
contamination, winter/summer blend)
•Fuel return line clogging and/or restriction
•Intake-air system restriction or clogging
•Exhaust system and/or catalyst converter
restriction or clogging
•Charge air cooler condition (restriction or
damaged)
Are all items okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Service as necessary.
Repeat Step 2.
3 Connect WDS or equivalent to DLC-2.
Access ECT PID.
Verify ECT PID is above 80 °C {176 °F}?Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect ECT PID.
Page 357 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–205
F2
NO.15 EMISSION COMPLIANCEA6E408018881217
Diagnostic Procedure
15 EMISSION COMPLIANCE
DESCRIPTION•Fails emissions test.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Poor fuel quality
•Vacuum leakage
•Air leakage from intake-air system
•Intake-air system restriction or clogging
•Variable swirl control (VSC) system malfunction
•Variable boost control (VBC) system malfunction
•Intake shutter valve stuck close
•VSC valve stuck close
•Turbocharger malfunction
•Guide blade valve malfunction
•Charge air cooler malfunction
•Glow system malfunction
•EGR system malfunction
•EGR water cooler malfunction
•Low coolant temperature
•Engine overheating
•Inadequate fuel pressure
•Fuel pressure limiter malfunction (built-in common rail)
•Suction control valve inspection (built-in supply pump)
•ECT sensor or related circuit malfunction
•MAF/IAT sensor related circuit malfunction
•IAT sensor No.2 or related circuit malfunction
•Fuel pressure sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Incorrect adjustment accelerator position sensor and/or idle switch
•Accelerator position sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Idle switch or related circuit malfunction
•Fuel line rclogging or restriction
•Supply pump malfunction
•Fuel injector malfunction
•Incorrect fuel injection timing
•Incorrect idle speed
•Erratic signal from CKP sensor
•Erratic signal from CMP sensor
•Boost sensor or related circuit malfunction
•Neutral switch or related circuit malfunction
•VSS or related circuit malfunction
•Low engine compression
•Improper valve timing
•Base engine malfunction
•Exhaust system and/or catalyst converter restriction
•Catalyst converter malfunction
•IDM or related circuit malfunction
Warning
The following troubleshooting flow chart contains the fuel system diagnosis and repair
procedures. Read the following warnings before performing the fuel system services:
•Fuel vapor is hazardous. It can easily ignite, causing serious injury and damage. Always keep
sparks and flames away from fuel.
•Fuel line spills and leakage are dangerous. Fuel can ignite and cause serious injury or death
and damage. Fuel can also irritate skin and eyes. To prevent this, always complete “BEFORE
REPAIR PROCEDURE” and “AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE” described in this manual.
STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
1 Is engine overheating? Yes Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.17 COOLING
SYSTEM CONCERNS—OVERHEATING”.
No Go to next step.
2 Does engine run cold? Yes Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.18 COOLING
SYSTEM CONCERNS—RUNS COLD”.
No Go to next step.
Page 362 of 909

F2–210
TROUBLESHOOTING
End Of SieNO.17 COOLING SYSTEM CONCERNS-OVERHEATINGA6E408018881219
Diagnostic Procedure
17
COOLING SYSTEM CONCERNS-OVERHEATING
DESCRIPTION•Engine runs at higher than normal temperature/overheats.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Cooling fan No.2 malfunction
•Cooling fan No.1 malfunction
•Low drive belt tension
•Drive belt damage
•Improper coolant level
•Thermostat malfunction
•Radiator clogging
•Improper water/anti-freeze mixture
•Improper or damaged radiator cap
•Radiator hose damage
•Coolant leakage (engine internal, turbocharger, external)
•A/C system malfunction
•EGR system malfunction
•Coolant heater system malfunction
STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
1 Inspect following:
•Engine coolant level
•Coolant leakage (around heater unit in
passenger compartment, coolant hoses and/
or radiator, and around coolant heater unit.)
•Water and anti-freeze mixture
•Radiator condition
•Collapsed or restricted radiator hoses
•Radiator pressure cap
•Drive belt tension
•Drive belt
•Fan rotational direction
Are all items okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Service as necessary.
Repeat Step 1.
2 Perform self-test function using WDS or
equivalent.
Turn engine switch to ON.
Retrieve any DTC.
Is DTC displayed?YesDTC is displayed:
Go to appropriate DTC test.
Communication error message is displayed:
Inspect for following:
•Open circuit between PCM control relay and PCM
terminal 53 or 79
•Open circuit PCM control relay and PCM terminal
69
•PCM control relay stuck open
•Open or poor GND circuit (PCM terminal 65, 85,
103 or 104)
•Poor connection vehicle body GND
NoNo DTC is displayed:
Go to next step.
Page 364 of 909

F2–212
TROUBLESHOOTING
NO.18 COOLING SYSTEM CONCERNS-RUNS COLDA6E408018881220
Diagnostic Procedure
End Of Sie
18 COOLING SYSTEM CONCERNS-RUNS COLD
DESCRIPTION•Engine takes excessive period for reaching normal operating temperature.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Thermostat malfunction
•Cooling fan No.2 system malfunction
•Cooling fan No.1 system malfunction
•Coolant heater system malfunction
STEP INSPECTION RESULTS ACTION
1 Is customer complaint “Lack of passenger
compartment heat”?Yes Inspect A/C heater system.
No Go to next step.
2 Does engine speed continue at fast idle? Yes Go to symptom troubleshooting “NO.7 SLOW
RETURN TO IDLE”.
No Go to next step.
3 Connect WDS or equivalent to DLC-2.
Access ECT PID.
Inspect for both ECT PID and temperature
gauge on instrument cluster readings.
Is ECT PID same as temperature gauge
reading?Yes Go to next step.
No If temperature gauge on instrument cluster indicates
normal range but ECT PID is not same as temperature
gauge reading, inspect ECT sensor.
If temperature gauge on instrument cluster indicates
cold range but ECT PID is normal, inspect
temperature gauge and heat gauge unit.
4 Remove thermostat and inspect operation.
(See E–9 THERMOSTAT REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
(See E–10 THERMOSTAT INSPECTION)
Is thermostat okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace thermostat.
5 Inspect cooling fan No.1 and cooling fan No.2
operations.
If both or either fan operate normally, inspect for
following:
•Cooling fan relay No.2 is stuck closed
•Short to GND between cooling fan relay No.2
and PCM terminal 76
•Circuit between cooling fan relay No.2 and
fan motor short to battery supply line
•Cooling fan relay No.1 is stuck closed
•Short to GND between cooling fan relay No.1
and PCM terminal 102
•Circuit between cooling fan relay No.1 and
fan motor short to battery supply line
•Short to GND between A/C switch and PCM
terminal 84
Are all circuits okay?Yes Perform coolant heater system inspection.
Repair or replace malfunctioning part according to
coolant heater system operation results.
No Repair or replace as necessary.
6 Verify test results.
•If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
•If malfunction remains, replace PCM. (See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
Page 427 of 909

K2–12
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Electronic Control Item and Control
Component Description (Electronic Control)
Control item Contents
Shift control•Detects engine load condition and vehicle speed. Shifts to the best gear
position according to the programmed automatic shift diagram.
Line pressure control•Generates line pressure matching the engine load condition and driving
conditions. Optimizes line pressure for each shift. When the ATF
temperature is low, automatically optimizes line pressure for quick clutch
engagement.
Revers inhibition control•When the shift lever is shifted to R position while the vehicle is running
forward at approx. 30 km/h{19 mph} or more, the TCM turns the neutral
shift solenoid valve on and drains the low and reverse brake hydraulic
pressure. Due to this, the transaxle shifts to neutral.
Shift transient control•Adjusts transient hydraulic pressure according to engine load and
vehicle driving conditions when shifting using the pressure control
solenoid, 2-4 brake solenoid valve, the high clutch solenoid valve, and
each accumulator control valve.
•Temporarily lowers engine torque during shift (up and down) to improve
shift feel
•The lock timing for the reduction brake band is controlled by the control
of the reduction timing solenoid valve ON/OFF timing.
•The lock timing for the clutch brake is controlled by the control of shift
solenoid A, B, and C ON/OFF timing.
Feedback control•Corrects clutch engagement pressure and timing on drain side to
compensate for changes in engine performance and changes in
transaxle
TCC control•Controls TCC according to the programmed TCC points
N-D select control•When a driving range is selected from P/N, the fuel injection amount is
controlled to prevent fluctuation in engine speed.
Slope mode control•Changes the shift point to prevent frequent shifting up/down when
climbing hills
OBD system•Detects and/or memorizes failure of input/output part and transaxle
condition
Part name Function
Input system TR switch•Detects selector lever ranges/positions
Input/turbine speed sensor•Detects reverse clutch drum revolution speed
Intermediate sensor•Detects output gear revolution speed
Vehicle speedometer sensor•Detects parking gear revolution speed
TFT sensor•Detects the ATF temperature
Brake switch•Detects the brake pedal depressed
Cruise control module (in cruise actuator)•When the cruise control is in use, the signal detects when the
difference between the target speed and actual speed
exceeds specification
M range switch•Detects selector lever shifted M range
Up switch•Detects up shift in M range
Down switch•Detects down shift in M range
CAN signal Throttle position signal•Input throttle opening angle from PCM
Engine torque signal
(without torque down)•Input engine torque from PCM
Engine torque signal (with
torque down)•Input engine torque from PCM
Engine torque signal (loss
torque)•Input engine loss torque from PCM
Torque reduced signal•Detects signals indicating torque down availability
Engine coolant
temperature signal•Input engine coolant temperature from PCM
Engine speed signal•Input engine speed from PCM
Battery OFF signal•Detect negative battery cable disconnected
4 wheel speed signal•Input wheel speed from ABS HU/CM or DSC HU/CM
Page 465 of 909

K2–50
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (CAN) DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901201Outline
•The TCM transmits/receives information using the CAN system. See Section T for detailed information
regarding the CAN system.
Structure/Operation
•The PCM inputs throttle opening angle, engine speed, engine torque, engine coolant temperature. to the TCM.
•The TCM operates shift and TCC controls based on the throttle opening angle, and controls line pressure and
other based on the throttle opening angle and the engine torque.
•The TCM outputs reduce torque signal, range signal, turbine speed, ATF temperature signal, and TCC signal to
the PCM.
•If there is an open or short circuit in the CAN wiring, the system determines that the CAN is abnormal and
switches to fail-safe mode.
Input
•Throttle position
•Engine torque (without torque down)
•Engine torque (with torque down)
•Engine torque (loss torque)
•Torque reduction request
•ECT
•Engine speed
•Buttery reconnection
Output
•Range position
•Turbine speed
•ATF temperature
•TCC
•Racing select
•Gear position
•Desired torque
•Desired gear position
•Upper torque limit
•Traveled distance
•MIL indicate request
•AT warning light indicate request
End Of Sie
Page 478 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–63
K2
Determination of Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Cancellation
The TCC control is canceled when any of the following condition are met:
•Engine coolant temperature is low.
•ATF temperature is low.
•Brake switch is on (when depressing the brake pedal).
•Accelerator depressing speed and accelerator opening angle are above the set value.
•Engine speed signal is below the set value.
•Failure is in the TCC control system detected by diagnosis function.
End Of Sie
SLOPE MODE CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901209•Climbing and the appropriate gear is determined by engine load and the vehicle acceleration.
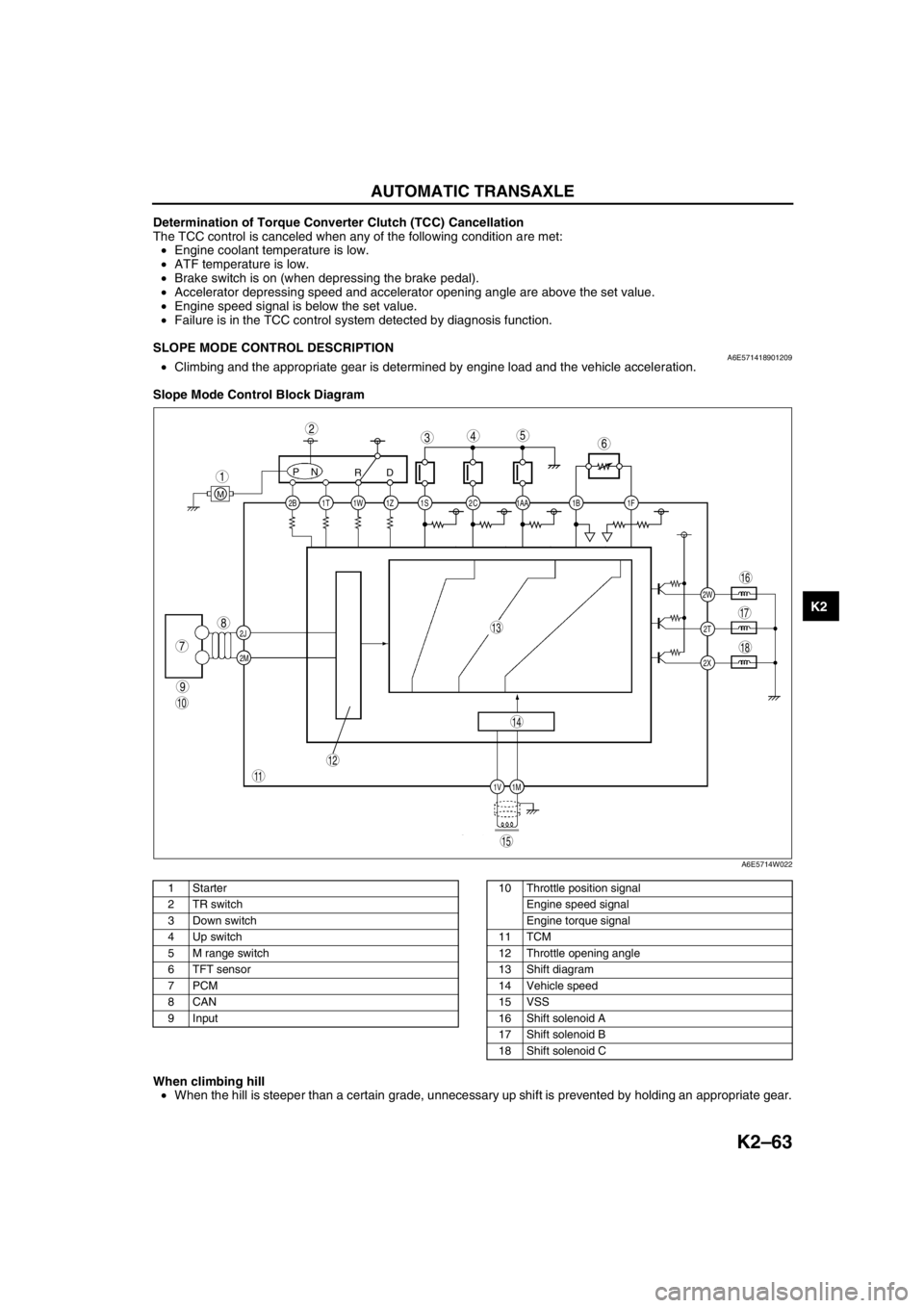
Slope Mode Control Block Diagram
.
When climbing hill
•When the hill is steeper than a certain grade, unnecessary up shift is prevented by holding an appropriate gear.
End Of Sie
2C 2B
2J
2M1AA 1S 1T 1Z1W 1B 1F
2W
1M 1V2T
2X
PN
RD
M
9
8
7
543
1
2
10
18
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W022
1Starter
2 TR switch
3 Down switch
4 Up switch
5 M range switch
6 TFT sensor
7PCM
8CAN
9 Input10 Throttle position signal
Engine speed signal
Engine torque signal
11 TCM
12 Throttle opening angle
13 Shift diagram
14 Vehicle speed
15 VSS
16 Shift solenoid A
17 Shift solenoid B
18 Shift solenoid C
Page 481 of 909

K2–66
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
P0711Transaxle fluid temperature (TFT)
sensor malfunction (stuck)•TFT sensor signal stays
outside normal temperature
range for 10 minute or more—Available
P0712Transaxle fluid temperature (TFT)
sensor circuit malfunction (short
circuit)•Signals form TFT sensor are
155 °C {311 °F} or greater
for 10 min.
•Inhibits feedback control
•Engine coolant temperature
signal are used for shifting.Available
P0713Transaxle fluid temperature (TFT)
sensor circuit malfunction (open
circuit)•Vehicle speed is 20 km/h
{12.4 mph} or greater, and
signals from TFT sensor are
–30 °C {–22 °F} or less for
150 seconds or moreAvailable
P0715Input/turbine speed sensor circuit
malfunction•Input/turbine speed sensor
is 600 rpm or less while
engine speed is 1500 rpm or
greater and vehicle speed is
40 km/h {24.8 mph} or
greater in D ranges.•Inhibits shift control Available
P0720Vehicle speedometer sensor
circuit malfunction•Parking gear rotation
detected by VSS is 150 rpm
or less while intermediate
sensor 1400 rpm or greater
in D range for 2 second or
more.•Inhibits SLOPE mode,
feedback control, torque
reduction controlAvailable
P0740Torque converter clutch (TCC)
system•RPM difference between
crankshaft (engine speed
signal) and reverse clutch
drum (input/turbine speed
sensor signal) exceeds the
pre-programmed value—Available
P0743Torque converter clutch (TCC)
solenoid valve malfunction (open/
short)•Open or short in torque
converter clutch solenoid
valve circuit (Voltage
different from on/off signal
relayed by CPU in TCM is
detected while TCM is
monitoring solenoid output
voltage.)•Stops driving of TCC
solenoid valve (OFF)Inhibition
P0748Pressure control solenoid
malfunction (open/short)•Open or short in pressure
control solenoid circuit
(Voltage different from on/off
signal relayed by CPU in
TCM is detected while TCM
is monitoring solenoid
output voltage.)•Stops driving of pressure
control solenoid, 2-4 brake
solenoid valve, and high
clutch solenoid valve (OFF)
•Inhibit feedback control.Available
P0751Shift solenoid A malfunction
(stuck off)•Difference between actual
gear ratio and gear ratio set
in TCM is large—Available
P0752Shift solenoid A malfunction
(stuck on)•Difference between actual
gear ratio and gear ratio set
in TCM is large—Available
P0753Shift solenoid A malfunction
(open/short)•Open or short in shift
solenoid A circuit (Voltage
different from on/off signal
relayed by CPU in TCM is
detected while TCM is
monitoring solenoid output
voltage.)•Stops driving all ON/OFF
type solenoids (OFF) and
TCC solenoid valve (OFF)Inhibition
P0756Shift solenoid B malfunction
(stuck off)•Difference between actual
gear ratio and gear ratio set
in TCM is large—Available
P0757Shift solenoid B malfunction
(stuck on)•Difference between actual
gear ratio and gear ratio set
in TCM is large—Available DTC
No.On-board diagnostic function Detection condition Fail-safe TCC