Page 466 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–51
K2
TRANSAXLE CONTROL MODULE (TCM) DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901202Outline
•The TCM controls the automatic transaxle operations. The TCM outputs a control signal to the transaxle
according to the signal from other sensors and/or switches.
•In driving mode, there are three mode selections: NORMAL, high temp, and SLOPE. The TCM automatically
selects the proper mode according to driving condition.
End Of Sie
SHIFT CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901203Outline
Features
•The TCM selects and determines the shift diagram based on the results of the range and driving mode
judgements. Then, based on the shift diagram, the TCM sends the signal to the duty-cycle type solenoid valves
and the ON/OFF type solenoid valves, according to the VSS signal and the throttle opening signal, to perform
shifting.
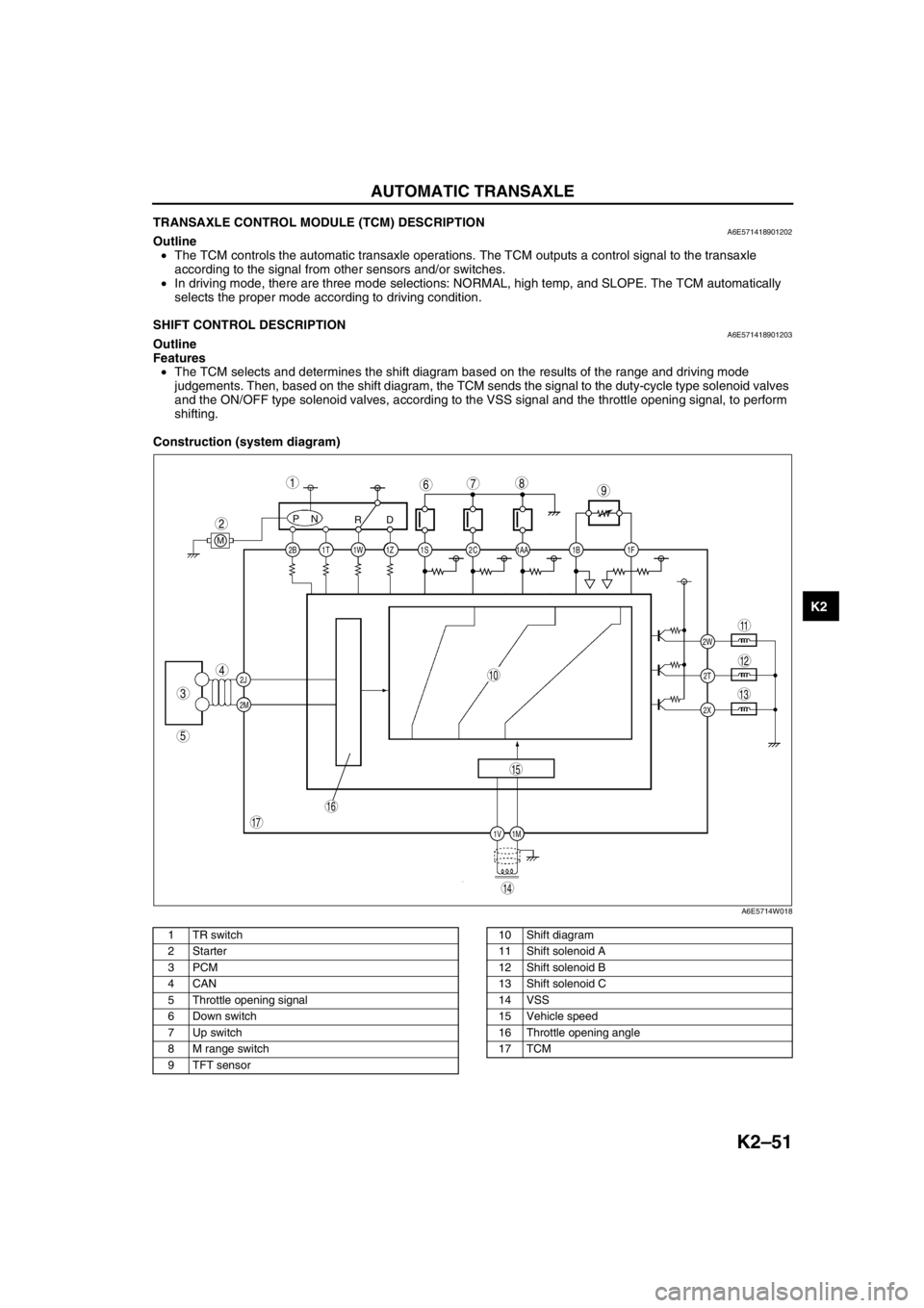
Construction (system diagram)
.
2C 2B
2J
2M1AA 1S 1T 1Z1W 1B 1F
2W
1M 1V2T
2X
PN
RD
M
987
5
4
3
1
2
10
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W018
1 TR switch
2Starter
3PCM
4CAN
5 Throttle opening signal
6 Down switch
7 Up switch
8 M range switch
9 TFT sensor10 Shift diagram
11 Shift solenoid A
12 Shift solenoid B
13 Shift solenoid C
14 VSS
15 Vehicle speed
16 Throttle opening angle
17 TCM
Page 468 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–53
K2
Operation
Manual mode shift
•When the selector lever is shifted over from the D to M range position, the M range switch in the selector lever
component turns on, sending a manual mode command signal to the PCM which activates the manual mode
shift control.
•When in manual mode and the selector lever is operated in the back (+) direction, the up switch in the selector
lever component is turned on and an up-shift command signal is inputted to the PCM.
—The PCM, triggered by the up-shift command signal, carries out shifting by outputting an operation signal to
the shift solenoid if the ATF temperature is not low (for 3GR only), vehicle speed is higher than the set
speed and the gear position is 3GR or lower.
•Conversely, when the selector lever is operated in the forward (-) direction, the down switch in the selector lever
component turns on, and a down-shift command signal is inputted to the PCM.
—The PCM, triggered by the down-shift command signal, carries out shifting by outputting an operation
signal to the shift solenoid if the vehicle speed is less than the set speed and the gear position is 2GR or
above.
•The PCM utilizes a specialized M range automatic shift diagram when down shifting. This restriction of manual
downshifting is carried out to reduce load on the ATX and prevent engine over-revving.
13 Instrument cluster
14 Input15 Selector lever component
-M range switch
-Up switch
-Down switch
16 TR switch
17 ABS HU/CM or DSC HU/CM
18 TFT sensor
Condition Shift control Note
2GR→3GR up-shift command
at low speed•To reduce load on the ATX, upshifting is
inhibited until vehicle reaches speed
possible for upshifting
— 3GR→4GR up-shift command
at low speed
3GR→4GR up-shift command,
low ATF temperature•To reduce load on the ATX, upshifting to
4GR is inhibited
4GR→3GR down-shift
command, above set speed•To prevent engine over-rev, downshifting is
inhibited until vehicle reaches speed
possible for downshifting•Selector indicator “M” light and gear
position indicator light flash to alert
driver
3GR→2GR down-shift
command, above set speed
2GR→1GR down-shift
command, above set speed
In 4GR deceleration, speed
goes below coast-down set
speed (deceleration down-
shift)•To assure drive stability, automatically
downshifts from 4GR to 3GR
— In 3GR deceleration, speed
goes below coast-down set
speed (deceleration down-
shift)•To assure drive stability, automatically
downshifts from 3GR to 1GR
In 2GR deceleration, speed
goes below coast-down set
speed (deceleration down-
shift)•To assure driving stability, automatically
downshifts from 2GR to 1GR
Page 470 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–55
K2
Construction (System diagram)
.
1T 1Z 1W
1AA
2C 2Y
1S
1H2B 1K
1X
1M
1V
1N
2F
2J
2M
1F
1B
9
8
7
5
4
3
1
2
10
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W019
1 Intermediate sensor
2 VSS
3 Input/turbine speed sensor
4 Throttle position signal
5 Engine torque signal
6 TFT sensor
7TCM8TR switch
9 Pressure control solenoid
10 M range switch
11 Up switch
12 Down switch
13 Cruise control module
Page 473 of 909
K2–58
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Construction (system diagram)
.
1T 1Z 1W
2B
2Y
2V
2U
2P 1K
1X 1M
1V
1N
2F
2J
2M
1F
1B
9
8
7
5
4
3
1
2
10
19
18
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W020
1 VSS
2 Input/turbine speed sensor
3 Intermediate sensor
4 Input5 Throttle position signal
Torque reduce signal
Engine torque signal
6Output
7 Reduce torque signal
Page 474 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–59
K2
Operation
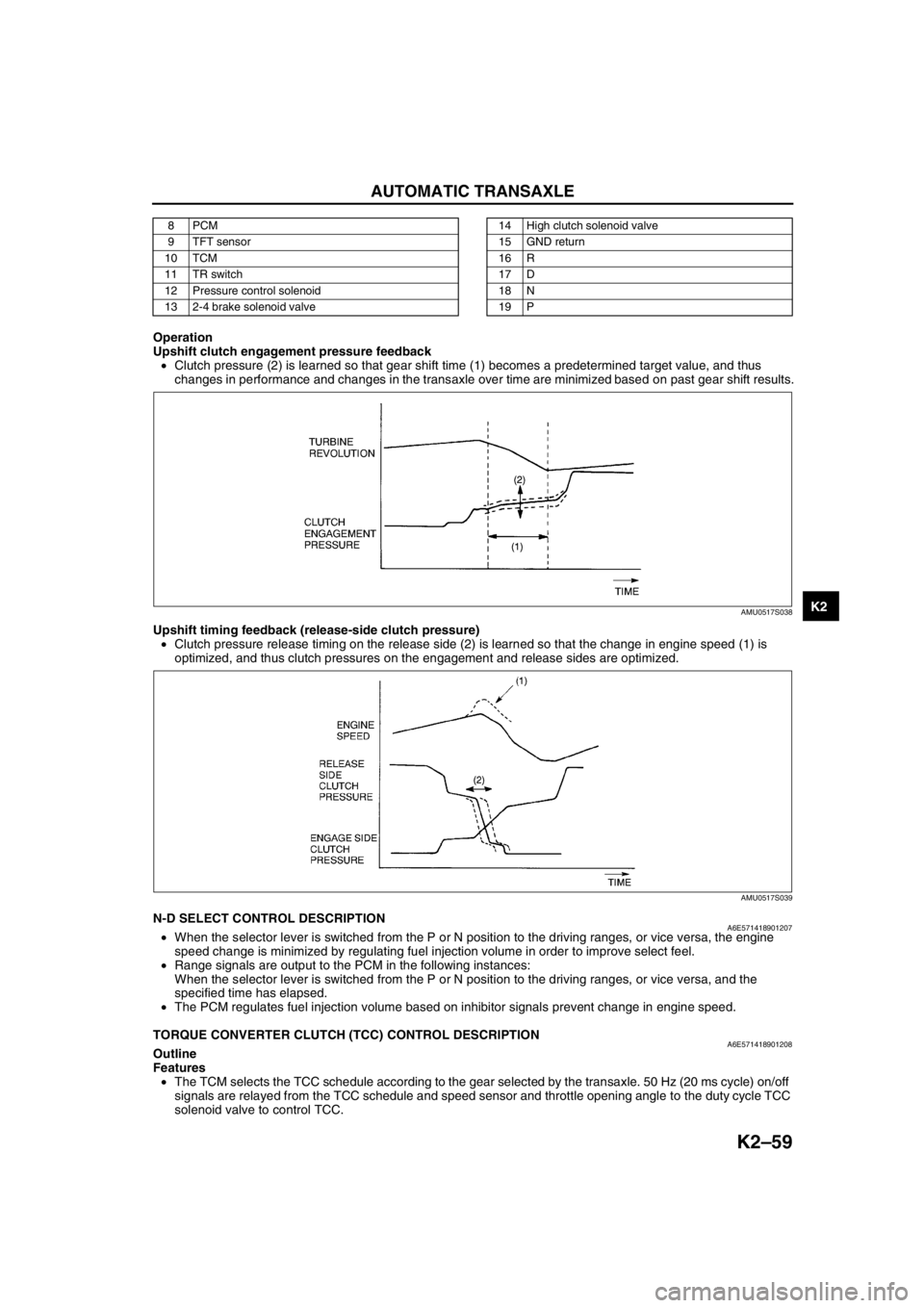
Upshift clutch engagement pressure feedback
•Clutch pressure (2) is learned so that gear shift time (1) becomes a predetermined target value, and thus
changes in performance and changes in the transaxle over time are minimized based on past gear shift results.
Upshift timing feedback (release-side clutch pressure)
•Clutch pressure release timing on the release side (2) is learned so that the change in engine speed (1) is
optimized, and thus clutch pressures on the engagement and release sides are optimized.
End Of SieN-D SELECT CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901207•When the selector lever is switched from the P or N position to the driving ranges, or vice versa, the engine
speed change is minimized by regulating fuel injection volume in order to improve select feel.
•Range signals are output to the PCM in the following instances:
When the selector lever is switched from the P or N position to the driving ranges, or vice versa, and the
specified time has elapsed.
•The PCM regulates fuel injection volume based on inhibitor signals prevent change in engine speed.
End Of Sie
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC) CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901208Outline
Features
•The TCM selects the TCC schedule according to the gear selected by the transaxle. 50 Hz (20 ms cycle) on/off
signals are relayed from the TCC schedule and speed sensor and throttle opening angle to the duty cycle TCC
solenoid valve to control TCC.
8PCM
9 TFT sensor
10 TCM
11 TR switch
12 Pressure control solenoid
13 2-4 brake solenoid valve14 High clutch solenoid valve
15 GND return
16 R
17 D
18 N
19 P
AMU0517S038
AMU0517S039
Page 475 of 909
K2–60
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Construction (system diagram)
.
1T 1Z 1W
2B
1S 1M
1V
1N
2F
2J
2M
1F
1B
9
8
7
5
4
3
1
2
10
15
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W021
1 VSS
2 Input/turbine speed sensor
3 Engine speed signal
4 Throttle position signal
5 TCC signal
6PCM
7CAN
8 TFT sensor9TCM
10 TR switch
11 TCC solenoid valve
12 R
13 D
14 N
15 P
Page 478 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–63
K2
Determination of Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Cancellation
The TCC control is canceled when any of the following condition are met:
•Engine coolant temperature is low.
•ATF temperature is low.
•Brake switch is on (when depressing the brake pedal).
•Accelerator depressing speed and accelerator opening angle are above the set value.
•Engine speed signal is below the set value.
•Failure is in the TCC control system detected by diagnosis function.
End Of Sie
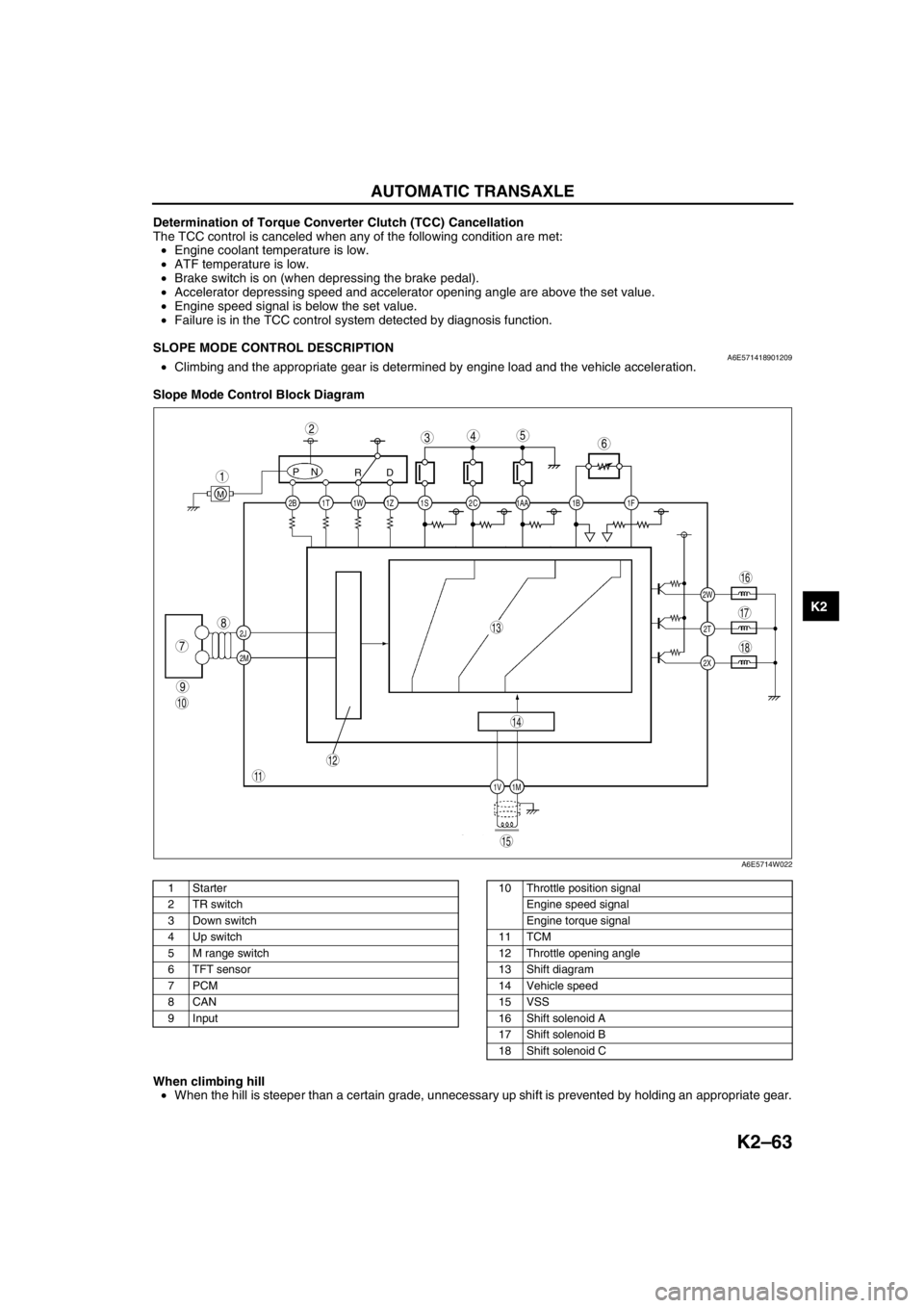
SLOPE MODE CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901209•Climbing and the appropriate gear is determined by engine load and the vehicle acceleration.
Slope Mode Control Block Diagram
.
When climbing hill
•When the hill is steeper than a certain grade, unnecessary up shift is prevented by holding an appropriate gear.
End Of Sie
2C 2B
2J
2M1AA 1S 1T 1Z1W 1B 1F
2W
1M 1V2T
2X
PN
RD
M
9
8
7
543
1
2
10
18
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W022
1Starter
2 TR switch
3 Down switch
4 Up switch
5 M range switch
6 TFT sensor
7PCM
8CAN
9 Input10 Throttle position signal
Engine speed signal
Engine torque signal
11 TCM
12 Throttle opening angle
13 Shift diagram
14 Vehicle speed
15 VSS
16 Shift solenoid A
17 Shift solenoid B
18 Shift solenoid C
Page 479 of 909
K2–64
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
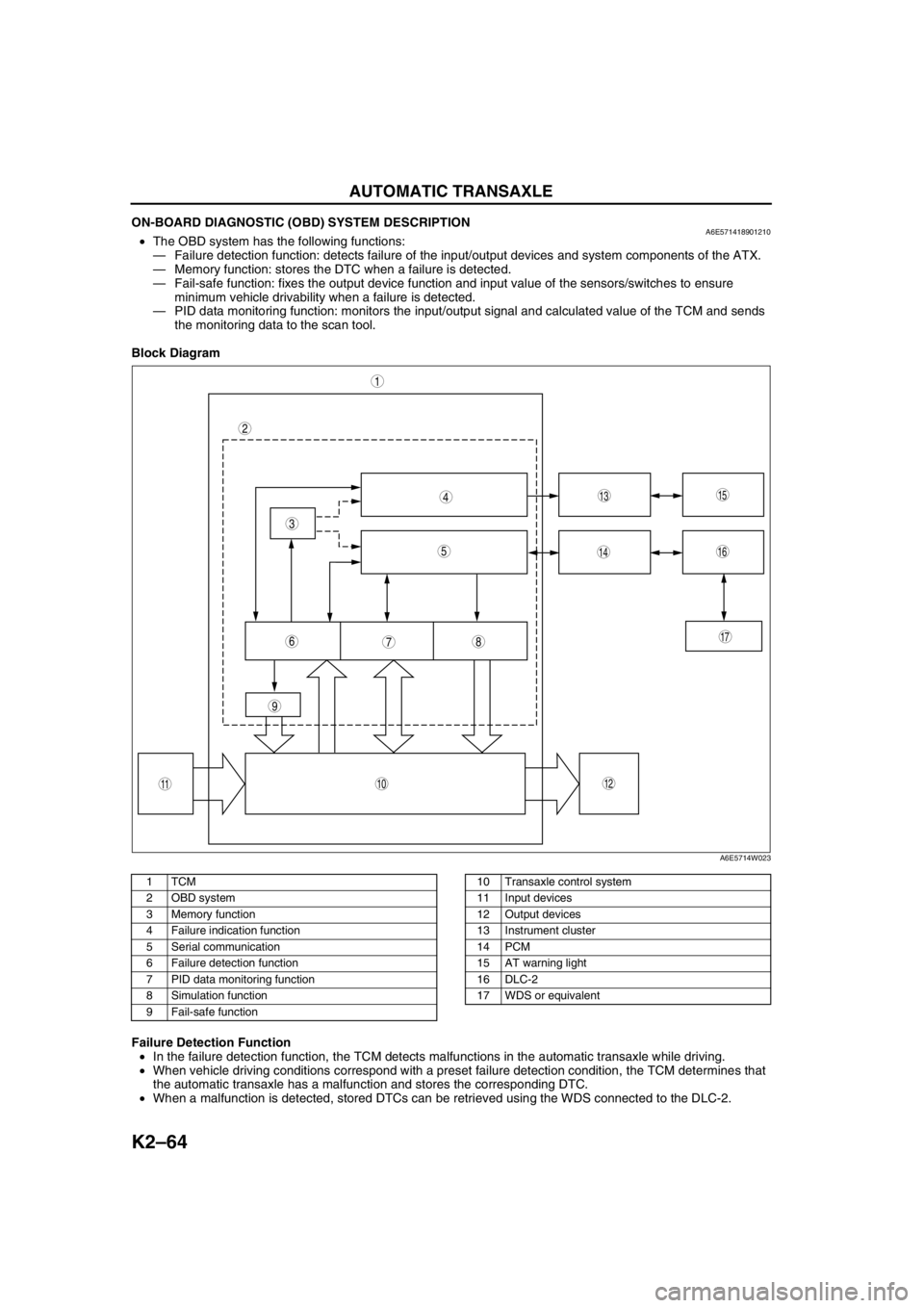
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901210•The OBD system has the following functions:
—Failure detection function: detects failure of the input/output devices and system components of the ATX.
—Memory function: stores the DTC when a failure is detected.
—Fail-safe function: fixes the output device function and input value of the sensors/switches to ensure
minimum vehicle drivability when a failure is detected.
—PID data monitoring function: monitors the input/output signal and calculated value of the TCM and sends
the monitoring data to the scan tool.
Block Diagram
.
Failure Detection Function
•In the failure detection function, the TCM detects malfunctions in the automatic transaxle while driving.
•When vehicle driving conditions correspond with a preset failure detection condition, the TCM determines that
the automatic transaxle has a malfunction and stores the corresponding DTC.
•When a malfunction is detected, stored DTCs can be retrieved using the WDS connected to the DLC-2.
9
87
5
4
3
1
2
10
17
15
1614
13
1112
6
A6E5714W023
1TCM
2 OBD system
3 Memory function
4 Failure indication function
5 Serial communication
6 Failure detection function
7 PID data monitoring function
8 Simulation function
9 Fail-safe function10 Transaxle control system
11 Input devices
12 Output devices
13 Instrument cluster
14 PCM
15 AT warning light
16 DLC-2
17 WDS or equivalent