Page 1488 of 1672

BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-19
Operation
For IDM inputs which are also inputs for BCU functions, the delay before the BCU recognises the change in input
status is less than 250 ms. The BCU uses a debounce algorithm to ignore changes in input having a duration less
than 100 ms with the exception of automatic gearbox W, X, Y, Z inputs, which have a debounce period of 33 ms.
Transit mode
To prevent excessive battery drain during transit to overseas markets, the vehicle is placed in a transit mode.
To exit the transit mode, simultaneously hold down the heated rear window switch and the rear fog lamp switch, turn
the ignition switch from 0 to II and, after a minimum of 2 seconds, release the switches.
Transit mode can be entered using TestBook. When TestBook communicates with the BCU for diagnostics related to
BCU operation, it first checks that the vehicle is not in transit mode.
Anti-theft system
The BCU uses the driver's door key lock and unlock switches to activate and deactivate the security system. The
driver's door lock is also used for entering the EKA.
+ ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Immobilisation
For immobilisation, the BCU disables the starter motor relay. When the engine is cranking, the ECM looks for a coded
signal from the BCU. If the signal is not received within one second of cranking, the fuel supply to the engine is
stopped and the injectors are disabled. This also prevents unburnt fuel from entering the catalyst.
If the BCU is disconnected, the engine starter motor will remain isolated by the starter motor relay and the ECM will
remain immobilised. The main wiring for the system is contained within the main harness which is relatively
inaccessible, so preventing intruders from disabling the system by cutting the wires for the immobilisation system.
Once the immobiliser has been activated, destruction of the trigger device or the wiring to it will not disarm the system.
The RF transmitter communicates to the BCU via the RF receiver using a 70 bit code. Pressing the unlock button on
the transmitter will re-mobilise the vehicle. The RF transponder is integrated into the metal key assembly, inserting
the key into the ignition switch will induce a signal in the exciter coil to re-mobilise the vehicle.
Anti-theft alarm
The alarm system provides a warning of unauthorised access to the vehicle and includes perimetric and volumetric
monitoring under the control of the BCU.
The perimetric protection system detects opening of all doors, tail door and bonnet and will also detect the operation
of the ignition key switch. The following conditions must be satisfied before the BCU will operate all of the functions
of perimetric protection:
lAll doors and hinged panels are in the closed position.
lIgnition key out of the ignition switch.
lInertia switch is not tripped.
If all conditions are not satisfied the BCU will enter a mislock condition.
The volumetric sensor uses two ultrasonic sensors mounted in the headlining to detect movement within the vehicle.
The alarm will trigger when the sensor signals the BCU for 200 ms or greater. Within a single setting period the alarm
system will allow a maximum of 10 triggers as a result of any combination of sensor inputs. It is possible to lock the
vehicle without enabling the volumetric alarm by using the key. The same conditions needed to satisfy enabling of the
perimetric protection system is also needed to enable volumetric protection.
Page 1490 of 1672

BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-21
Passive coil
The passive coil is located around the ignition key barrel. When the BCU detects that the ignition key has been turned
to the crank position, the vehicle's immobilisation system is activated and a signal is sent to the passive coil at a
frequency of 125 kHz. The magnetic field generated in the coil is induced in the remote transmitter to trigger a re-
mobilisation signal.
BBUS/ alarm sounder/ vehicle horn
The BBUS is an audible warning device which operates under the control of the BCU if the anti-theft system is
activated or the vehicle battery is disconnected. The unit contains its own internal battery power source which is
charged via a feed from the passenger compartment fuse box. The BBUS will not sound if the battery is disconnected
while the security system has not been set.
Some markets utilise an alarm sounder which operates independently or in conjunction with the vehicle horn if the
anti-theft system is triggered.
Security system status LED
The LED flashes when the anti-theft system has been set. There are four different flash rates dependent on mode of
operation or other system information.
Central door locking
The doors can be locked by the following methods:
lPressing the lock button on the remote transmitter.
lLocking the vehicle from the driver's door with the key.
lPressing the lower half of the central door lock switch.
lPushing the sill button down (will only lock that particular door).
lBy driving over 7 km/h (4 mph) – ( if the speed related locking function has been enabled).
The BCU will prevent locking if the logical conditions for locking are not satisfied. Conditions which will prevent door
locking include:
lDriver's door open.
lIgnition switch on.
lInertia switch tripped.
lVehicle is already superlocked.
A mislock may occur if the logical conditions are not met.
The doors can be unlocked by the following methods:
lPressing the unlock button on the remote transmitter
lUnlocking the vehicle from the driver's door with the key.
lPressing the upper half of the central door locking switch (not operational if the vehicle is superlocked).
lPulling the interior door handles (not operational if the vehicle is superlocked).
lInertia switch being triggered while the ignition is on and the security system is de-activated.
The BCU supplies information via the serial data bus to the IDM to energise the coil of the relays for each of the door
lock actuators.
The BCU normally checks the following inputs to determine lock/ unlock requirements:
lUnlock request.
lLock request.
lSuperlock request.
lSingle point entry request.
lLock passenger and rear doors request.
Page 1510 of 1672
ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-4-1
Deze pagina werd opzettelijk niet gebruikt
Cette page est intentionnellement vierge
Questa pagina è stata lasciata in bianco di proposito Diese Seite ist leer
Esta página foi deixada intencionalmente em branco
Esta página fue dejada en blanco intencionalmente This page is intentionally left blank
ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN DESCRIPTION AND OPERAT ION
Page 1511 of 1672
ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
86-4-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Alarm system component layout
RHD shown, LHD similar
Page 1512 of 1672
ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-4-3
1Theft deterrent LED
2Receiver
3Volumetric sensors
4Central door locking switch
5Body Control Unit (BCU)
6Bonnet activated alarm switch
7Vehicle horn
8Alarm sounder
9Fuel cut off switch
10Fuel flap release switch
11Door latch switches, drivers door key lock/
unlock switches
12Battery Backed Up Sounder (BBUS)
13Passive remobilisation exciter coil
Page 1513 of 1672
ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
86-4-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Alarm system block diagram
1Body Control Unit (BCU)
2Remote handset
3Receiver
4Fuel cut off switch
5Ignition switch
6Central door locking switch
7Volumetric sensors
8Bonnet activated alarm switch
9Drivers door key lock/unlock switches
10Door latch switches 11Fuel flap release switch
12Intelligent Driver Module (IDM)
13Battery Backed Up Sounder (BBUS)
14Alarm sounder
15Vehicle horns
16Direction indicators
17Door lock actuators
18Engine Control Module (ECM)
19Starter motor
Page 1514 of 1672

ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-4-5
Description
General
The anti-theft system deters the theft of the vehicle with both active and passive systems. The active systems monitor
the vehicle perimeter and, in some markets the vehicle interior, for intrusion. If the system detects intrusion, an alarm
sounds. The passive systems include a vehicle immobiliser as well as protection against intrusion through super
locking the doors. The vehicle is immobilised whenever the ignition key is removed from the ignition switch. Super
locking prevents the interior door handles from opening the doors. In addition, there are many features and functions
that enhance system operation.
It is possible to perform the various functions associated with the anti-theft system remotely. To accomplish this, the
handset generates a radio frequency when the lock button or unlock button is depressed. This signal is transmitted
to the Body Control Unit (BCU) via a receiver located in front of rear sunroof beneath the headlining. Precise alignment
of the handset to the receiver is not necessary. The approximate operating range between the handset and the
receiver is 10 metres (33 feet).
It is important to understand the configuration of the system on each particular vehicle. There are many
different combinations of features with dedicated operating modes. System configuration for each vehicle
can be determined using TestBook.
The anti-theft system is controlled centrally by the BCU, which is located below and behind the passenger glovebox.
A serial communication link communicates between the Intelligent Driver Module (IDM) located within the fusebox,
the BCU and the LED located in the instrument panel.
The state of the alarm is stored in the BCU. If the battery is disconnected while the alarm is armed, the alarm will be
triggered when the battery is reconnected.
NOTE: Disconnecting the battery while the alarm is armed triggers the alarm. Always disarm the alarm system before
disconnecting the battery.
The BCU also receives inputs from the following components:
lIgnition key in sensor.
lIgnition switch.
lFuel cut off switch.
lFuel flap release switch.
The BCU also interacts with the following components:
lStarter relay.
lVehicle horns.
lDirection indicators.
lFuel flap release actuator.
lCourtesy lamps.
Page 1515 of 1672
ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
86-4-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
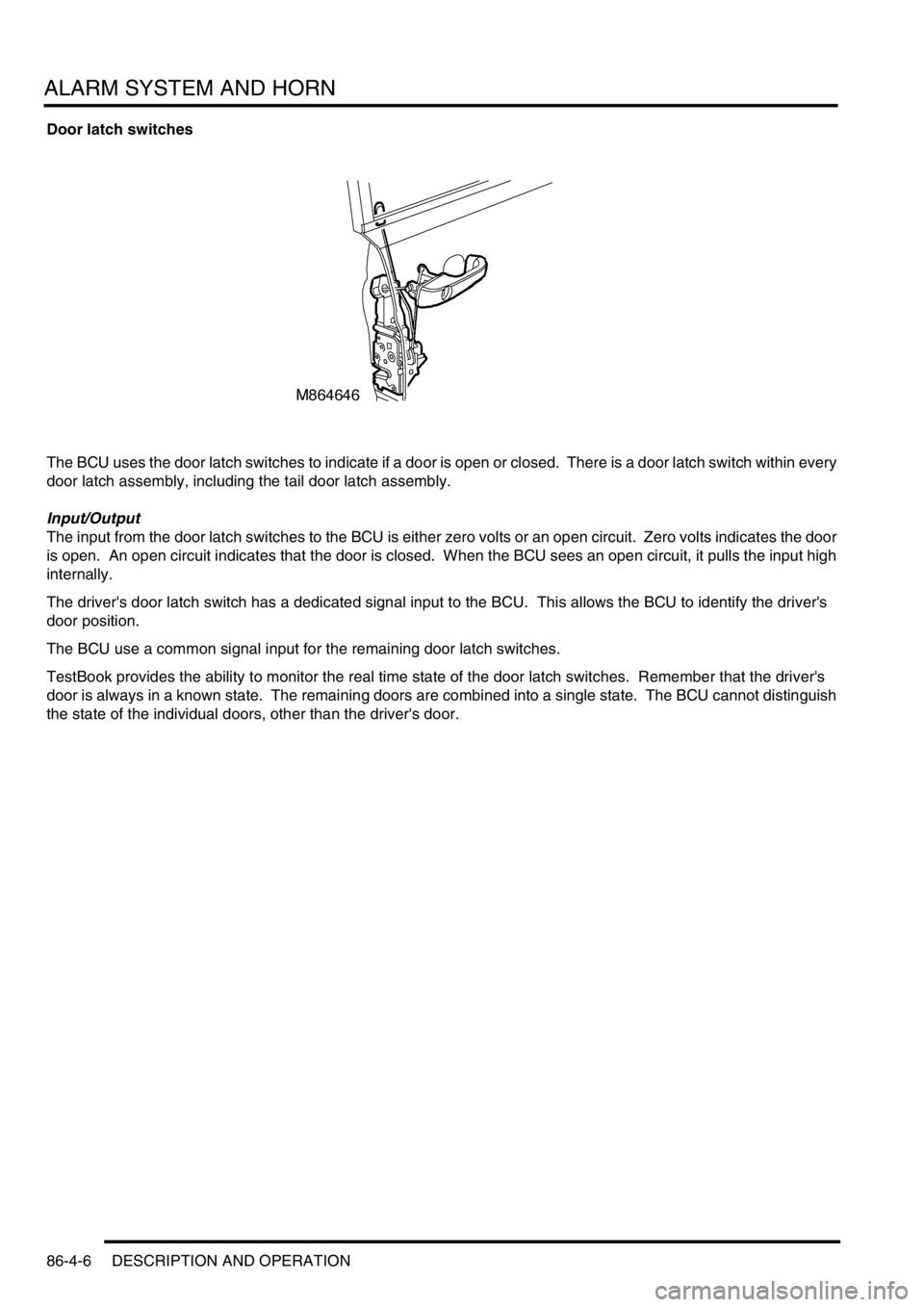
Door latch switches
The BCU uses the door latch switches to indicate if a door is open or closed. There is a door latch switch within every
door latch assembly, including the tail door latch assembly.
Input/Output
The input from the door latch switches to the BCU is either zero volts or an open circuit. Zero volts indicates the door
is open. An open circuit indicates that the door is closed. When the BCU sees an open circuit, it pulls the input high
internally.
The driver's door latch switch has a dedicated signal input to the BCU. This allows the BCU to identify the driver's
door position.
The BCU use a common signal input for the remaining door latch switches.
TestBook provides the ability to monitor the real time state of the door latch switches. Remember that the driver's
door is always in a known state. The remaining doors are combined into a single state. The BCU cannot distinguish
the state of the individual doors, other than the driver's door.