2002 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 489 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-32 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) (C0641)
The IACV is located on the side of the air inlet pipe on top of the engine. The IACV is used to maintain good quality
idle speed under all operating conditions.
When an engine is running at idle it is subject to a combination of internal and external loads that can affect idle speed.
These loads include engine friction, water pump, alternator operation, and air conditioning.
The IACV acts as an air bypass valve. The ECM uses the IACV to enable the closed loop idle speed calculation to be
made by the ECM. This calculation regulates the amount of air flow into the engine at idle, therefore compensating
for any internal or external loads that may affect idle speed.
The IACV utilises two coils that use opposing PWM signals to control the position of opening/closing of a rotary valve.
If one of the circuits that supply the PWM signal fails, the ECM closes down the remaining signal preventing the IACV
from working at its maximum/ minimum setting. If this should occur, the IACV automatically resumes a default idle
position. In this condition, the engine idle speed is raised and maintained at 1200 rev/min with no load placed on the
engine.
The idle speed in cold start condition is held at 1200 rev/min in neutral for 20 seconds and ignition timing is retarded
as a catalyst heating strategy. The cold start idle speed and the default idle position give the same engine speed 1200
rev/min, and although they are the same figure they must not be confused with each other as they are set separately
by the ECM.
Note that the rotary valve must not be forced to move by mechanical means. The actuator can not be
serviced; if defective, the entire IACV must be replaced.
Input/Output
The input to the IACV is a 12 volt signal from fuse 2 located in the engine compartment fuse box. The output earth
signal to open and close the actuator is controlled by the ECM as follows:
lIACV (open signal) - via pin 42 of connector C0636 of the ECM
lIACV (closed signal) - via pin 43 of connector C0636 of the ECM
The IACV can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lActuator faulty.
lRotary valve seized.
lWiring loom fault.
lConnector fault.
lIntake system air leak.
lBlocked actuator port or hoses.
lRestricted or crimped actuator port or hoses.
Page 490 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-33
In the event of an IACV signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEither low or high idle speed.
lEngine stalls.
lDifficult starting.
lIdle speed in default condition.
There are eight IACV diagnostic checks performed by the ECM:
lOutput short circuit to earth – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to battery supply – opening coil
lOutput open circuit – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to earth – closing coil
lOutput short circuit to battery voltage – closing coil
lOutput open circuit – closing coil
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error low (engine speed must be 100 rev/min less than the target speed, engine load
less than 2.5 and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h less than the expected air flow for a fault condition to
be flagged).
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error high (the engine speed must be more than 180 rev/min greater than the target
speed and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h greater than the expected air flow for a fault condition to be
flagged).
Should a malfunction of the component occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Fuel pump relay
The fuel pump relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It is a 4 pin normally open relay. Input from the
ECM allows the fuel pump relay to control the electrical input to the fuel pump, regulating the fuel supply to the fuel
injectors. When the ignition is switched on and the engine is cranked, the fuel pump relay is activated by the ECM,
allowing the fuel system to be pressurised to 3.5 bar (52 lbf.in
2). The ECM then deactivates the relay until the engine
has started.
If the fuel pump runs, but the fuel pressure is out of limits, adaptive fuel faults will be stored.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1510 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - opening winding
P1513 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - opening winding
P1514 IACV opening coil malfunction Open circuit - opening winding
P1553 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - closing winding
P1552 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - closing winding
P1551 IACV closing coil malfunction Open circuit - closing winding
P0505 Idle control system malfunction Blocked IACV - high or low rev/min error
Page 502 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-45
Ignition timing
The ignition timing is an important part of the ECM adaptive strategy. Ignition is controlled by a direct ignition system
using two four-ended coils operating on the wasted spark principle.
When the ECM triggers an ignition coil to spark, current from the coil travels to one spark plug, then jumps the gap at
the spark plug electrodes, igniting the mixture in the cylinder in the process. Current continues to travel along the earth
path (via the cylinder head) to the spark plug negative electrode at the cylinder that is on the exhaust stroke. The
current jumps across the spark plug electrodes and back to the coil completing the circuit. Since it has simultaneously
sparked in a cylinder that is on the exhaust stroke, it has not provided an ignition source there and is consequently
termed 'wasted'.
Conditions
The ECM calculates ignition timing using input from the following:
lCKP sensor.
lKnock sensors (KS).
lMAF sensor.
lTP sensor (idle only).
lECT sensor.
Function
At engine start up, the ECM sets ignition timing dependent on ECT information and starting rev/min from the CKP. As
the running characteristics of the engine change, the ignition timing changes. The ECM compares the CKP signal to
stored values in its memory, and if necessary advances or retards the spark via the ignition coils.
Ignition timing is used by the ECM for knock control.
Knock control
The ECM uses active knock control to prevent possible engine damage due to pre-ignition. This is achieved by
converting engine block noise into a suitable electrical signal that can be processed by the ECM. A major contributing
factor to engine 'knock' is fuel quality, the ECM can function satisfactorily on 91 RON fuel as well as the 95 RON fuel
that it is calibrated for.
Conditions
The ECM knock control system operates as follows:
lHot running engine.
l91 or 95 RON fuel.
Function
The ECM knock control uses two sensors located one between the centre two cylinders of each bank. The knock
sensors consist of piezo ceramic crystals that oscillate to create a voltage signal. During pre-ignition, the frequency
of crystal oscillation increases which alters the signal output to the ECM.
If the knock sensors detect pre-ignition in any of the cylinders, the ECM retards the ignition timing by 3
° for that
particular cylinder. If this action stops the engine knock, the ignition timing is restored to its previous figure in
increments of 0.75
°. If this action does not stop engine knock then the ECM retards the ignition timing a further 3° up
to a maximum of -15
° and then restores it by 0.75° and so on until the engine knock is eliminated.
The ECM also counteracts engine knock at high intake air temperatures by retarding the ignition as above. The ECM
uses the IAT signal to determine air temperature.
Page 513 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-56 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Cruise control block diagram
1SLABS ECU
2BCU
3Cruise control master switch
4SET+ switch
5RES switch
6Brake pedal switch7Clutch pedal switch
8Cruise control ECU
9Vacuum pump assembly incorporating
pneumatic actuator
10Automatic gear selector lever
Page 520 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-63
Body control unit
On manual gearbox vehicles, the BCU provides cruise control lockout or suspend function as described under brake
pedal switch.
On vehicles with automatic gearbox, the BCU monitors the status of the brake pedal switch as well as the status of
the automatic gearbox gear selector lever. The BCU monitors the gear selector lever to determine which gearbox
position the driver has selected. If the BCU detects that the driver has selected park, reverse or neutral, it sends a
signal to the cruise control ECU which inhibits cruise operation or deactivates cruise control if it is activated.
Input/Output
If the BCU receives a brake pedal switch signal or an automatic gearbox gear selector lever position signal, the BCU
sends a HIGH signal to the cruise control ECU. The cruise control ECU cancels or inhibits cruise control functions.
Page 526 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
ADJUSTMENTS 18-2-69
ADJUST ME NTS
Cable - throttle
$% 19.20.05
Adjust
1.Loosen outer cable locknuts.
2.Adjust the rear locknut until it is in contact with
the back of the abutment bracket and the
throttle lever is in contact with the inner driven
lever.
3.Ensure that the driven lever remains in contact
with the throttle stop screw, (throttle closed).
4.Tighten cable front nut to lock cable to
abutment bracket.
Cable - cruise control
$% 19.75.11
Adjust
1.Ensure that the throttle cable is correctly
adjusted.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
V8, ADJUSTMENTS, Cable - throttle.
2.Loosen outer cable locknuts.
3.Adjust the rear locknut to obtain a 0.5 to 1.5
mm (0.019 to 0.060 in) gap, dimension 'A',
between the cruise control cable lever and the
throttle cable driven lever.
4.Tighten cable front locknut.
Page 533 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-76 REPAIRS
Sensor - camshaft position (CMP)
$% 18.30.24
Remove
1.Release fixings and remove battery cover.
2.Disconnect battery earth lead.
3.Raise front of vehicle.
WARNING: Do not work on or under a
vehicle supported only by a jack. Always
support the vehicle on safety stands.
4.Release fixings and remove underbelly panel.
5.Remove engine oil filter.
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Filter - oil.
6.Disconnect engine harness from CMP sensor
and release CMP sensor multiplug from
bracket.
7.Remove bolt from clamp securing CMP sensor
to timing gear cover.
8.Remove clamp and CMP sensor. Discard 'O'
ring from CMP sensor.
Refit
1.Ensure CMP sensor is clean, fit new 'O' ring
and sensor to cover.
2.Fit clamp to CMP sensor and tighten bolt to 8
Nm (6 lbf.ft).
3.Fit sensor multiplug to bracket and connect
engine harness to multiplug.
4.Fit engine oil filter.
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Filter - oil.
5.Fit underbelly panel and secure with fixings.
6.Lower vehicle and connect battery earth lead.
7.Fit battery cover and secure with fixings.
Knock sensor (KS)
$% 18.30.28
Remove
1.Release fixings and remove battery cover.
2.Disconnect battery earth lead.
3.Raise front of vehicle.
WARNING: Do not work on or under a
vehicle supported only by a jack. Always
support the vehicle on safety stands.
4.Remove fixings securing underbelly panel and
remove panel.
5.Disconnect multiplug from KS.
6.Remove nut securing KS to cylinder block and
remove KS.
Refit
1.Clean mating faces of KS and cylinder block.
2.Fit KS to cylinder block and tighten nut to 22
Nm (16 lbf.ft).
3.Connect multiplug to KS.
4.Fit underbelly panel and secure with fixings.
5.Remove stand(s) and lower vehicle.
6.Connect battery earth lead.
7.Fit battery cover and secure the fixings.
Page 536 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
REPAIRS 18-2-79
4.Release outer cable from clip, loosen lock nuts
and remove outer cable from abutment
bracket.
5.Release inner cable from operating lever and
remove cable.
Refit
1.Position cable, secure to bulkhead and
connect inner cable to throttle pedal.
2.Position inner cable to operating lever and
connect outer cable to abutment bracket and
retaining clip.
3.Position closing panel and secure fasteners.
4.Adjust throttle cable.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
V8, ADJUSTMENTS, Cable - throttle.
Sensor - Mass Air Flow (MAF)
$% 19.22.25
Remove
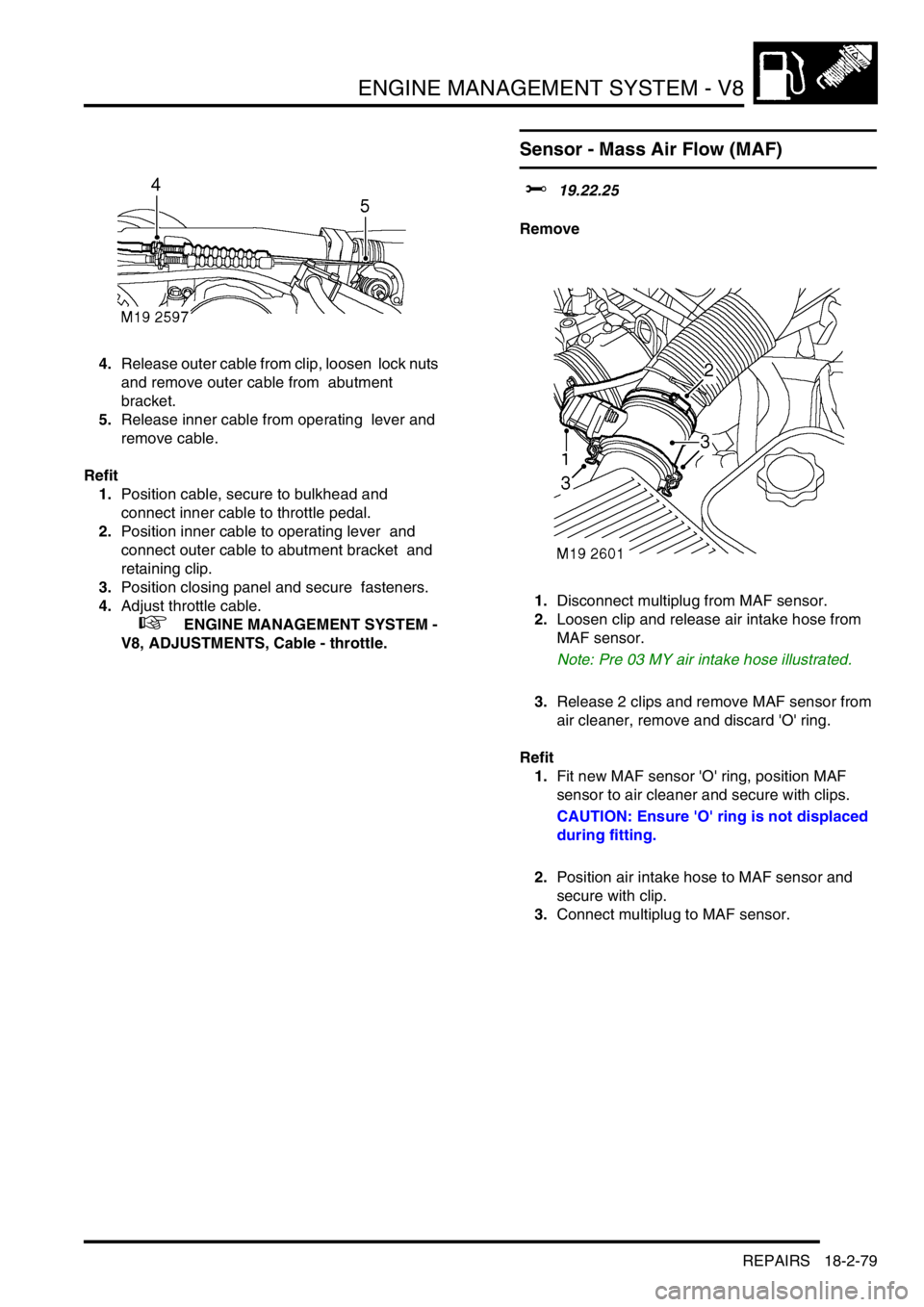
1.Disconnect multiplug from MAF sensor.
2.Loosen clip and release air intake hose from
MAF sensor.
Note: Pre 03 MY air intake hose illustrated.
3.Release 2 clips and remove MAF sensor from
air cleaner, remove and discard 'O' ring.
Refit
1.Fit new MAF sensor 'O' ring, position MAF
sensor to air cleaner and secure with clips.
CAUTION: Ensure 'O' ring is not displaced
during fitting.
2.Position air intake hose to MAF sensor and
secure with clip.
3.Connect multiplug to MAF sensor.