2002 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 476 of 1672
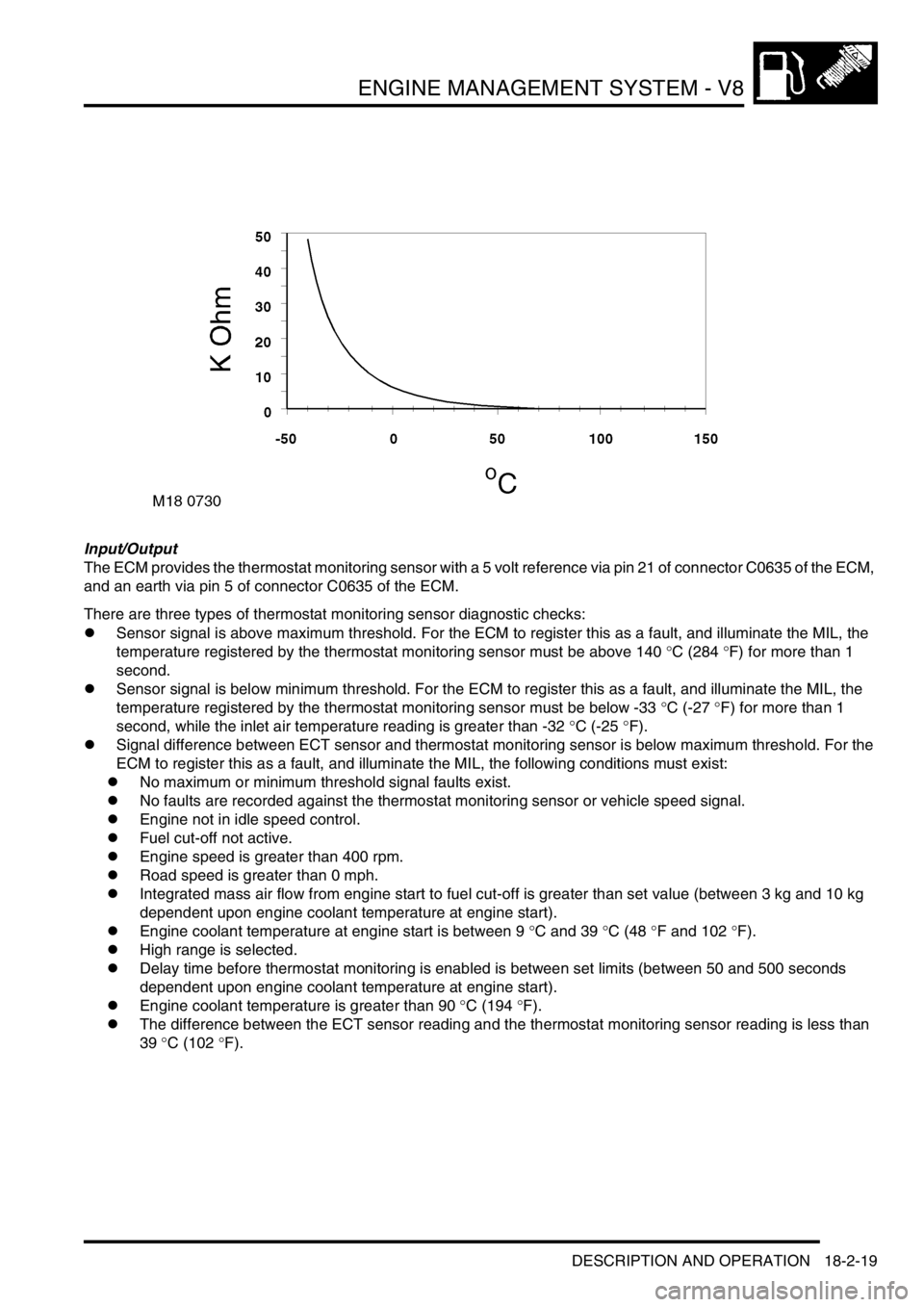
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-19
Input/Output
The ECM provides the thermostat monitoring sensor with a 5 volt reference via pin 21 of connector C0635 of the ECM,
and an earth via pin 5 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
There are three types of thermostat monitoring sensor diagnostic checks:
lSensor signal is above maximum threshold. For the ECM to register this as a fault, and illuminate the MIL, the
temperature registered by the thermostat monitoring sensor must be above 140
°C (284 °F) for more than 1
second.
lSensor signal is below minimum threshold. For the ECM to register this as a fault, and illuminate the MIL, the
temperature registered by the thermostat monitoring sensor must be below -33
°C (-27 °F) for more than 1
second, while the inlet air temperature reading is greater than -32
°C (-25 °F).
lSignal difference between ECT sensor and thermostat monitoring sensor is below maximum threshold. For the
ECM to register this as a fault, and illuminate the MIL, the following conditions must exist:
lNo maximum or minimum threshold signal faults exist.
lNo faults are recorded against the thermostat monitoring sensor or vehicle speed signal.
lEngine not in idle speed control.
lFuel cut-off not active.
lEngine speed is greater than 400 rpm.
lRoad speed is greater than 0 mph.
lIntegrated mass air flow from engine start to fuel cut-off is greater than set value (between 3 kg and 10 kg
dependent upon engine coolant temperature at engine start).
lEngine coolant temperature at engine start is between 9
°C and 39 °C (48 °F and 102 °F).
lHigh range is selected.
lDelay time before thermostat monitoring is enabled is between set limits (between 50 and 500 seconds
dependent upon engine coolant temperature at engine start).
lEngine coolant temperature is greater than 90
°C (194 °F).
lThe difference between the ECT sensor reading and the thermostat monitoring sensor reading is less than
39
°C (102 °F).
Page 477 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Should a malfunction occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by TestBook:
Mass Air Flow (MAF)/ Inlet Air Temperature (IAT) sensor (C0149)
The MAF/ IAT sensors are combined into a single unit and located between the air filter housing and the inlet manifold.
The ECM receives input signals from the MAF/ IAT sensor to calculate the mass of air flowing into the engine inlet
manifold.
Input/Output
The MAF sensor has both electrical input and output. Input to the MAF sensor comes from two different sources.
Battery voltage is supplied to the MAF sensor via fuse 2 of the engine compartment fuse box. The MAF sensor also
utilises a 5 volt reference input via pin 7 of connector C0636 of the ECM. The MAF sensor output voltage is measured
via pin 23 of connector C0636 of the ECM.
The IAT sensor has only electrical output. Output from the IAT sensor is measured at pin 34 of connector C0636 of
the ECM, this is a variable voltage/ resistance measured by the sensor to provide air temperature information to the
ECM.
The MAF/ IAT sensor share the same sensor earth. Sensor earth is via pin 9 of connector C0636 of the ECM.
The MAF/ IAT sensor and its connector has silver plated terminals for its low current signals to protect against
corrosion. DO NOT apply 12V to the 5V supply, as this will destroy the internal circuitry. The MAF/IAT sensor should
not be dropped or roughly handled and should be kept free from contamination.
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P1117 Radiator outlet temperature
thermister lowThermostat reading below -33 °C (-
27 °F)
P1118 Radiator outlet temperature
thermister highThermostat reading above 140 °C
(284 °F)
P0126 Engine thermostat defective Difference in radiator and engine
coolant temperatures too small
Page 478 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-21
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
The MAF sensor utilises a “hot film” element contained in the air intake duct to monitor the mass of the air flow being
drawn into the engine. The MAF sensor contains two sensing elements, one element is controlled at ambient
temperature (e.g. 25
°C (77°F)), while the other is heated to 200°C (360°F) above the ambient temperature (e.g. 225°C
(437
°F)).
When the intake air passes the heated element, it cools it down, so lowering the resistance of the hot film element. In
order to maintain the same temperature, the circuit to the heated element has to supply more current. The change in
current causes a corresponding change in potential difference to be detected in the monitoring circuit. This change is
supplied to the ECM as a voltage between 0 and 5V, where it is processed by the ECM's internal mapping to interpret
the data as a measure of the mass of air flow.
The measured air mass flow is used by the ECM to determine the fuel quantity to be injected in order to maintain the
stoiciometric air:fuel mixture for optimum engine performance and low emissions.
Normal operating parameters of the MAF sensor are as follows:
MAF output
If the MAF sensor fails, the ECM implements a back up strategy which is based on throttle angle. Poor throttle
response and reduced performance will result.
The MAF sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lContaminated sensor element.
lDamaged sensor element.
lAir leak after the MAF sensor.
lInlet air restriction.
lResistance in wiring harness causing signal offset.
Page 479 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-22 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
In the event of a MAF sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lDuring driving engine rev/min may dip, before recovering.
lDifficult starting.
lEngine stalls after starting.
lDelayed throttle response.
lEmissions control inoperative.
lIdle speed control inoperative.
lReduced engine performance.
lMAF sensor signal offset.
There are two types of MAF sensor diagnostic check:
lThe MAF sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold for specific speed range – the engine must have
exceeded 200 rev/min for longer than 300 ms and remain above 400 rev/min. The signal must be less than the
threshold mapped against engine speed for longer than 500 ms.
lThe MAF sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold for specific speed range – the engine must have
exceeded 200 rev/min for longer than 10 ms. The signal must be greater than the threshold mapped against
engine speed for longer than 300 ms.
If the MAF sensor fails the following fault codes will be produced and can be retrieved by TestBook:
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor utilises a thermistor with a negative temperature coefficient (NTC); as
temperature rises, the thermistor resistance decreases. The change in resistance causes a change in input voltage
at the ECM. The ECM converts the voltage value it receives to provide an indication of the temperature of the inlet air.
Normal operating parameters of the IAT sensor are as follows:
IAT output
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0102 Mass or volume air flow low input MAF signal < minimum threshold, which is speed
dependent
P0103 Mass or volume air flow circuit high input MAF signal > maximum threshold, which is speed
dependent
Page 480 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-23
Should the IAT sensor fail, the ECM defaults to an assumed air temperature of 45 °C (113 °F).
The IAT sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle battery supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lIncreased sensor resistance.
lDamaged sensor element.
In the event of an IAT sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lAdaptive fuelling disabled.
lIdle speed adaption disabled.
lCatalyst monitoring affected due to exhaust temperature model.
lIdle speed actuator test disabled.
lWarm up ignition angle affected.
lCondenser fan hot restart inhibited.
There are two types of IAT sensor diagnostic checks:
lThe IAT sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold – the engine has to have been running for longer than
180 seconds, and idle speed control must have been operational for longer than 10 seconds. No fuel cut off is
active. The IAT sensor signal must be less than -35
°C (-31°F) for longer than 200 ms.
lThe IAT sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold – the ECM has to be powered up (engine does not
need to be running), and the signal must be greater than 140
°C (284°F) for longer than 200 ms.
If the IAT sensor fails the following fault codes will be produced and can be retrieved by TestBook:
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0112 Intake air temperature circuit low input Intake air temperature signal less than minimum
threshold, after time for exhaust to warm up
P0113 Intake air temperature circuit high input Intake air temperature signal greater than maximum
threshold
Page 481 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-24 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Air intake duct – Gulf models from 2000MY
1Heat reflective insulation
2Supplementary air intake duct
The density of the intake air is partly dependent on altitude and temperature. Hot air has a lower density than cold air;
consequently in hot climates, the low air density can result in low power due to low volumetric efficiency.
In order to improve engine performance, Gulf specification models from 2000MY have a secondary air intake duct
which is located under the front left inner wing of the vehicle. Cooler air from the side of the vehicle is routed through
the duct to the air cleaner, where it combines with air entering via the front grille.
In addition to the secondary air duct, the vehicles are fitted with a larger front grille and have larger cooling and
condenser fans.
The MAF/IAT sensor, air cleaner and air cleaner duct are encased in insulation bags to help keep the intake air cool
and so increase the mass of air entering the engine intake manifold.
The air cleaner includes a cyclone filter and also a dump valve in the bottom of the unit. Sand and dust particles which
are carried into the air cleaner with the air flow are automatically expunged via the dump valve.
M180452
1
2
Page 482 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-25
Throttle Position (TP) sensor (C0175)
The TP sensor is located on the throttle body assembly in the engine compartment. The ECM is able to determine the
position of the throttle plate and the rate of change of its angle. The ECM processes the signal received from the TP
sensor.
The TP sensor consists of a resistance track and a sliding contact connected to the throttle plate assembly. As the
throttle is opened and closed the sliding contact moves along the resistance track to change the output voltage of the
sensor. The ECM determines throttle plate position by processing this output voltage. The connection of the sensor
to the throttle plate assembly is via a shaft.
The ECM is able to determine the closed throttle position, this enables the TP sensor to be fitted without the need for
prior adjustment. The TP sensor signal has input into the ECM's fuelling strategy and also to determine closed throttle
position for idle speed control. The TP sensor also supplies the ECM with information to enable the overrun fuel cut
off strategy to be implemented. When the ECM receives closed throttle information from the TP sensor it closes the
injectors for the duration of the closed throttle time.
The TP sensor signal is also used by the Electronic Automatic Transmission (EAT) ECU to determine the correct point
for gear shifts and acceleration kickdown. The ECM also supplies the SLABS ECU with this TP sensor information as
a PWM signal.
Input/Output
The TP sensor has electrical input and output. Input is a 5 volt supply via pin 10 of connector C0636 of the ECM. The
signal output is via pin 24 of connector C0636 and is a varying voltage, less than 0.5V (closed throttle) and greater
than 4.5V (wide open throttle) depending on throttle plate position. The TP sensor earth is via pin 25 of connector
C0636 of the ECM, this acts as a screen to protect the integrity of the TP sensor signal.
The connector and sensor terminals are gold plated for corrosion and temperature resistance, care must be exercised
while probing the connector and sensor terminals.
If the TP sensor signal fails, the ECM uses a default value derived from engine load and speed.
The TP sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lSignal out of parameters.
lBlocked air filter (load monitoring, ratio of the TP sensor to air flow).
lRestriction in air inlet (load monitoring, ratio of the TP sensor to air flow).
lVacuum leak
Page 483 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-26 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
In the event of a TP sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEngine performance concern.
lDelayed throttle response.
lFailure of emission control.
lClosed loop idle speed control inoperative.
lAutomatic gearbox kickdown inoperative.
lIncorrect altitude adaptation.
lMIL illuminated (NAS only).
There are three throttle position sensor diagnostic checks:
lTP sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold value – the engine speed must be greater than 400 rev/
min for longer than 2 seconds and the signal must be greater than 96% for longer than 50 ms.
lTP sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold – the engine speed must be greater than 400 rev/min for
longer than 2 seconds and the signal must be less than 4% for longer than 50 ms.
lRatio of throttle position to mass of air flow – the calculated throttle angle must be outside limits when the engine
speed is between 800 rev/min and 4000 rev/min, the engine load is between 2 and 6.5 and the coolant
temperature is above -10
°C (14°F).
Should a malfunction of the TP sensor occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Heated Oxygen Sensors (HO
2S) (C0642)
The market requirement dictates how many HO
2S are fitted to the vehicle.
l4 sensors are fitted to all NAS and EU-3 vehicles.
l2 sensors fitted to all UK, European, Australia and Japanese pre EU-3 specification vehicles.
lNo sensors fitted to ROW vehicles.
The HO
2S monitor the oxygen content of the exhaust gases. By positioning the sensors one for each bank upstream
of the catalytic converter in the exhaust pipe, the ECM can control fuelling on each bank independently of the other.
This allows greater control of the air:fuel ratio and maintains optimum catalyst efficiency. On NAS vehicles the ECM
also uses two HO
2S positioned downstream of the catalytic converters in the exhaust pipe to monitor catalytic
converter efficiency. The ECM is able to achieve this by comparing the values of the upstream HO
2S and the down
stream sensor for the same bank. These comparative values form part of the ECM OBD strategy.
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0101 Mass or volume air flow circuit range/
performance problemLoad monitoring, the ratio of throttle position to air flow
P0122 TPS a circuit low input Signal < minimum threshold
P0123 TPS a circuit high input Signal > maximum threshold