2002 JEEP LIBERTY torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 1716 of 1803
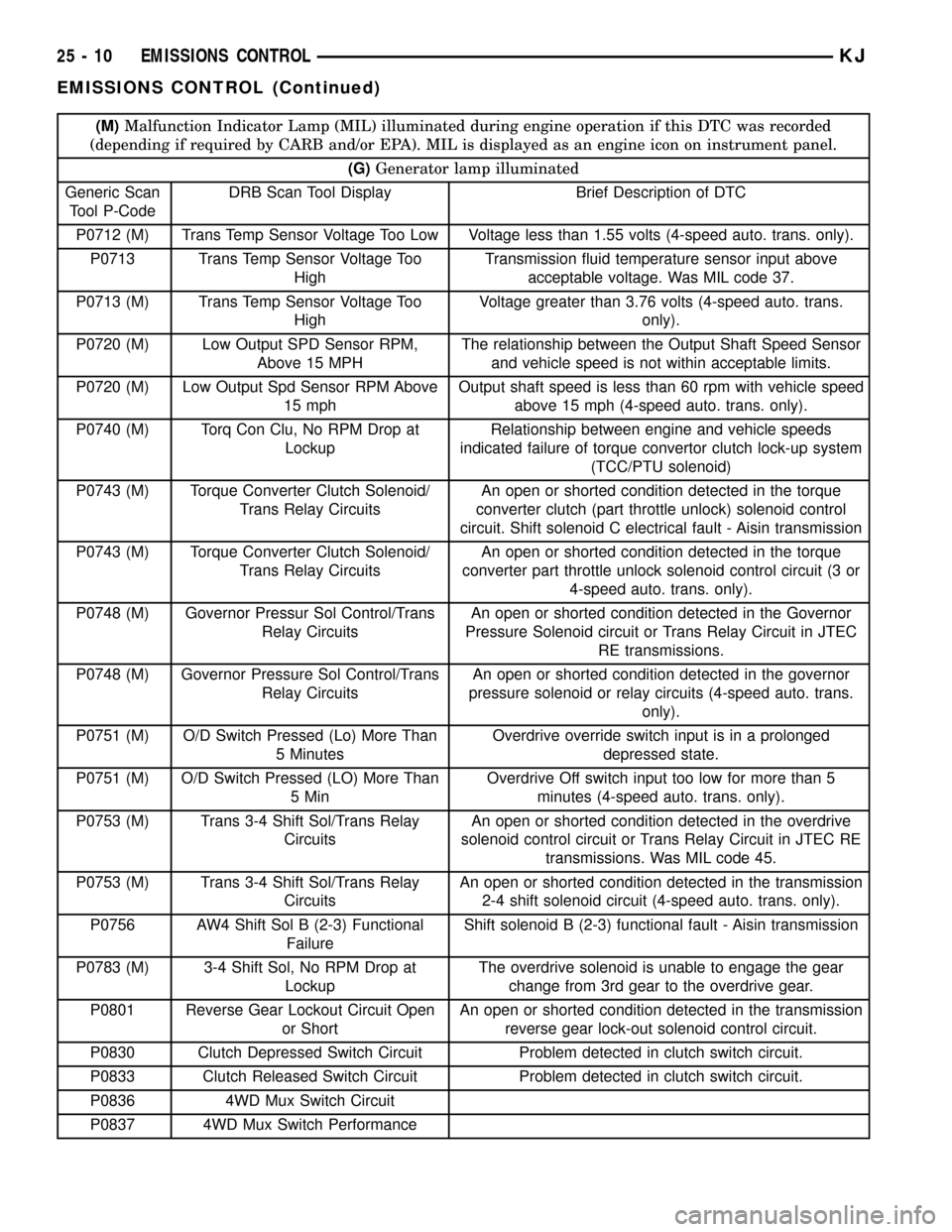
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0712 (M) Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too Low Voltage less than 1.55 volts (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P0713 Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too
HighTransmission fluid temperature sensor input above
acceptable voltage. Was MIL code 37.
P0713 (M) Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too
HighVoltage greater than 3.76 volts (4-speed auto. trans.
only).
P0720 (M) Low Output SPD Sensor RPM,
Above 15 MPHThe relationship between the Output Shaft Speed Sensor
and vehicle speed is not within acceptable limits.
P0720 (M) Low Output Spd Sensor RPM Above
15 mphOutput shaft speed is less than 60 rpm with vehicle speed
above 15 mph (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P0740 (M) Torq Con Clu, No RPM Drop at
LockupRelationship between engine and vehicle speeds
indicated failure of torque convertor clutch lock-up system
(TCC/PTU solenoid)
P0743 (M) Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid/
Trans Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the torque
converter clutch (part throttle unlock) solenoid control
circuit. Shift solenoid C electrical fault - Aisin transmission
P0743 (M) Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid/
Trans Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the torque
converter part throttle unlock solenoid control circuit (3 or
4-speed auto. trans. only).
P0748 (M) Governor Pressur Sol Control/Trans
Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Governor
Pressure Solenoid circuit or Trans Relay Circuit in JTEC
RE transmissions.
P0748 (M) Governor Pressure Sol Control/Trans
Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the governor
pressure solenoid or relay circuits (4-speed auto. trans.
only).
P0751 (M) O/D Switch Pressed (Lo) More Than
5 MinutesOverdrive override switch input is in a prolonged
depressed state.
P0751 (M) O/D Switch Pressed (LO) More Than
5 MinOverdrive Off switch input too low for more than 5
minutes (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P0753 (M) Trans 3-4 Shift Sol/Trans Relay
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the overdrive
solenoid control circuit or Trans Relay Circuit in JTEC RE
transmissions. Was MIL code 45.
P0753 (M) Trans 3-4 Shift Sol/Trans Relay
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the transmission
2-4 shift solenoid circuit (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P0756 AW4 Shift Sol B (2-3) Functional
FailureShift solenoid B (2-3) functional fault - Aisin transmission
P0783 (M) 3-4 Shift Sol, No RPM Drop at
LockupThe overdrive solenoid is unable to engage the gear
change from 3rd gear to the overdrive gear.
P0801 Reverse Gear Lockout Circuit Open
or ShortAn open or shorted condition detected in the transmission
reverse gear lock-out solenoid control circuit.
P0830 Clutch Depressed Switch Circuit Problem detected in clutch switch circuit.
P0833 Clutch Released Switch Circuit Problem detected in clutch switch circuit.
P0836 4WD Mux Switch Circuit
P0837 4WD Mux Switch Performance
25 - 10 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1724 of 1803

LEAK DETECTION PUMP MONITOR (IF EQUIPPED)
The leak detection assembly incorporates two pri-
mary functions: it must detect a leak in the evapora-
tive system and seal the evaporative system so the
leak detection test can be run.
The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode:The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º
water. The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid
as the system begins to pump up to this pressure. As
the pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop
off. If there is no leak in the system, the pump would
eventually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .040º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases dueto the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
MISFIRE MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
FUEL SYSTEM MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the Air Fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. This is done by making
short term corrections in the fuel injector pulse width
based on the O2S sensor output. The programmed
memory acts as a self calibration tool that the engine
controller uses to compensate for variations in engine
specifications, sensor tolerances and engine fatigue
over the life span of the engine. By monitoring the
actual fuel-air ratio with the O2S sensor (short term)
and multiplying that with the program long-term
(adaptive) memory and comparing that to the limit,
it can be determined whether it will pass an emis-
sions test. If a malfunction occurs such that the PCM
cannot maintain the optimum A/F ratio, then the
MIL will be illuminated.
CATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.
25 - 18 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1730 of 1803

EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM............................24
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE............................26
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................27
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................27
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................27
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................28
REMOVAL.............................28INSTALLATION.........................28
ORVR
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
P C V VA LV E
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................31
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE.....31
REMOVAL.............................32
INSTALLATION.........................32
VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION.........................33
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION.........................33
OPERATION...........................33
REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................33
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM
The evaporation control system prevents the emis-
sion of fuel tank vapors into the atmosphere. When
fuel evaporates in the fuel tank, the vapors pass
through the control valve located in the top section of
the fuel pump module, through the fuel management
valve, and through vent hoses and tubes to a char-
coal filled evaporative canister. The canister tempo-
rarily holds the vapors. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) allows intake manifold vacuum to
draw vapors into the combustion chambers during
certain operating conditions.
Gas powered engines use a duty cycle purge sys-
tem. The PCM controls vapor flow by operating theduty cycle EVAP purge solenoid. Refer to Duty Cycle
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid.
When equipped with certain emissions packages, a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) will be used as part of
the evaporative system for OBD II requirements.
Also refer to Leak Detection Pump.
Vehicles powered with gasoline engines are also
equipped with ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor
Recovery). Refer to ORVR for additional information.
NOTE: The evaporative system uses specially man-
ufactured lines/hoses. If replacement becomes nec-
essary, only use fuel resistant, low permeation
hose.
Certain components can be found in (Fig. 1).
25 - 24 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSKJ
Page 1732 of 1803
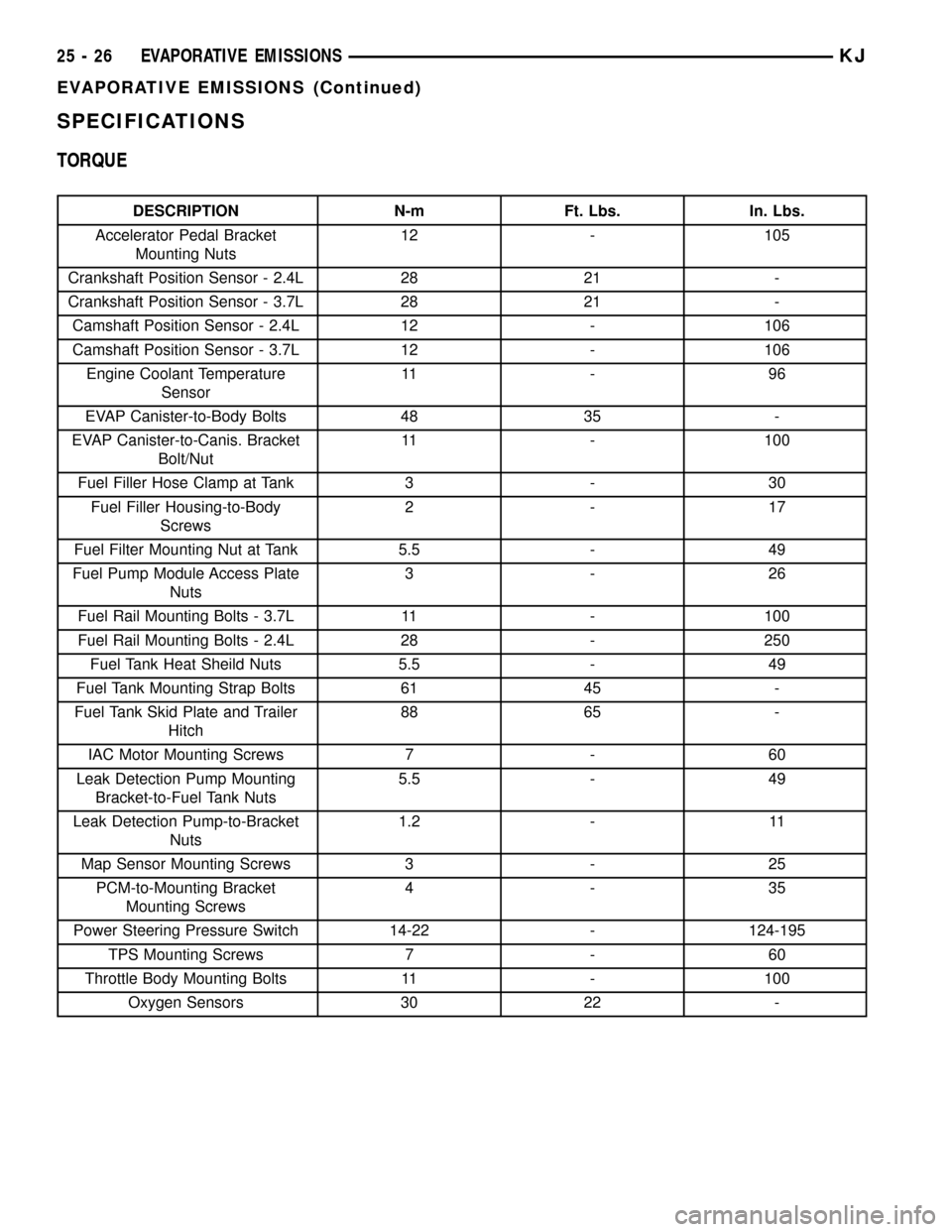
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Accelerator Pedal Bracket
Mounting Nuts12 - 105
Crankshaft Position Sensor - 2.4L 28 21 -
Crankshaft Position Sensor - 3.7L 28 21 -
Camshaft Position Sensor - 2.4L 12 - 106
Camshaft Position Sensor - 3.7L 12 - 106
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor11 - 9 6
EVAP Canister-to-Body Bolts 48 35 -
EVAP Canister-to-Canis. Bracket
Bolt/Nut11 - 100
Fuel Filler Hose Clamp at Tank 3 - 30
Fuel Filler Housing-to-Body
Screws2-17
Fuel Filter Mounting Nut at Tank 5.5 - 49
Fuel Pump Module Access Plate
Nuts3-26
Fuel Rail Mounting Bolts - 3.7L 11 - 100
Fuel Rail Mounting Bolts - 2.4L 28 - 250
Fuel Tank Heat Sheild Nuts 5.5 - 49
Fuel Tank Mounting Strap Bolts 61 45 -
Fuel Tank Skid Plate and Trailer
Hitch88 65 -
IAC Motor Mounting Screws 7 - 60
Leak Detection Pump Mounting
Bracket-to-Fuel Tank Nuts5.5 - 49
Leak Detection Pump-to-Bracket
Nuts1.2 - 11
Map Sensor Mounting Screws 3 - 25
PCM-to-Mounting Bracket
Mounting Screws4-35
Power Steering Pressure Switch 14-22 - 124-195
TPS Mounting Screws 7 - 60
Throttle Body Mounting Bolts 11 - 100
Oxygen Sensors 30 22 -
25 - 26 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSKJ
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)
Page 1734 of 1803

The pump contains a 3 port solenoid, a pump that
contains a switch, a spring loaded canister vent valve
seal, 2 check valves and a spring/diaphragm.
OPERATION
Immediately after a cold start, engine temperature
between 40ÉF and 86ÉF, the 3 port solenoid is briefly
energized. This initializes the pump by drawing air
into the pump cavity and also closes the vent seal.
During non-test test conditions, the vent seal is held
open by the pump diaphragm assembly which pushes
it open at the full travel position. The vent seal will
remain closed while the pump is cycling. This is due
to the operation of the 3 port solenoid which prevents
the diaphragm assembly from reaching full travel.
After the brief initialization period, the solenoid is
de-energized, allowing atmospheric pressure to enter
the pump cavity. This permits the spring to drive the
diaphragm which forces air out of the pump cavity
and into the vent system. When the solenoid is ener-
gized and de-energized, the cycle is repeated creating
flow in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump
is controlled in 2 modes:
PUMP MODE:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate
to achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten
the overall test time.
TEST MODE:The solenoid is energized with a
fixed duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur
when the diaphragm reaches the switch closure
point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5 inches
of water.
When the pump starts, the cycle rate is quite high.
As the system becomes pressurized pump rate drops.
If there is no leak the pump will quit. If there is a
leak, the test is terminated at the end of the test
mode.
If there is no leak, the purge monitor is run. If the
cycle rate increases due to the flow through the
purge system, the test is passed and the diagnostic is
complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is attached (bolt-
ed) to the front of the fuel tank (Fig. 3). The LDP
fresh air filter is located on the end of a hose. This
hose is attached to the fuel fill tube assembly below
and near the fuel fill opening (Fig. 1). The LDP and
LDP filter are typically replaced (serviced) as one
unit.
(1) Raise vehicle.(2) Carefully remove two 3/4º vent hoses at sides
of LDP.
(3) Carefully remove other vapor/vacuum hoses
from LDP.
(4) Place a hydraulic jack under fuel tank.
(5) Loosen 2 fuel tank strap mounting bolts at
front of tank about 10 turns.
(6) Lower front of fuel tank about 1/2º.
(7) Remove 2 LDP mounting nuts (Fig. 3) and
lower LDP slightly to gain access to electrical connec-
tor (Fig. 4).
(8) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP. To dis-
connect: Slide red colored tab upward. Push on black
colored tab while removing connector.
(9) Remove LDP from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is attached (bolt-
ed) to the front of the fuel tank. The LDP filter is
located on the end of a hose. This hose is attached to
the fuel fill tube assembly below and near the fuel
fill opening. The LDP and LDP filter are replaced
(serviced) as one unit.
(1) Install electrical connector to LDP. Push red
colored tab downward to lock connector to LDP.
(2) Position LDP and LDP bracket to fuel tank
mounting studs and install 2 nuts. Tighten nuts to 1
N´m (11 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Raise fuel tank to body and tighten 2 strap
bolts to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 3 LDP LOCATION / MOUNTING
1 - LDP
2 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
3 - MOUNTING NUTS
4 - FRONT OF FUEL TANK
25 - 28 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSKJ
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1738 of 1803

(13) If vacuum is not present, disconnect each PCV
system hose at top of each crankcase breather (Fig.
8). Check for obstructions or restrictions.
(14) If vacuum is still not present, remove each
PCV system crankcase breather (Fig. 8) from each
cylinder head. Check for obstructions or restrictions.
If plugged, replace breather. Tighten breather to 12
N´m (106 in. lbs.) torque. Do not attempt to clean
breather
(15) If vacuum is still not present, disconnect each
PCV system hose at each fitting and check for
obstructions or restrictions.
REMOVAL
2.4L
The PCV valve is attached to the left/front side of
the valve cover (Fig. 5). It is secured with 1 bolt. An
o-ring is used to seal valve to valve cover (Fig. 6).
(1) Remove hose from valve (Fig. 5). Check condi-
tion of hose.
(2) Remove 1 bolt.
(3) Remove PCV valve from valve cover.
(4) Check condition of valve o-ring.
3.7L
The PCV valve is located on the oil filler tube (Fig.
12). Two locating tabs are located on the side of the
valve (Fig. 12). These 2 tabs fit into a cam lock in the
oil filler tube. An o-ring seals the valve to the filler
tube.
(1) Disconnect PCV line/hose (Fig. 12) by discon-
necting rubber hose at PCV valve fitting.
(2) Remove PCV valve at oil filler tube by rotating
PCV valve downward (counter-clockwise) until locat-
ing tabs have been freed at cam lock (Fig. 12). After
tabs have cleared, pull valve straight out from filler
tube.To prevent damage to PCV valve locating
tabs, valve must be pointed downward for
removal. Do not force valve from oil filler tube.
(3) After valve is removed, check condition of valve
o-ring (Fig. 12).
INSTALLATION
2.4L
(1) Check condition of PCV valve o-ring.
(2) Install PCV valve into valve cover.
(3) Install PCV valve mounting bolt.
(4) Install hose to valve.3.7L
The PCV valve is located on the oil filler tube. Two
locating tabs are located on the side of the valve.
These 2 tabs fit into a cam lock in the oil filler tube.
An o-ring seals the valve to the filler tube.
(1) Return PCV valve back to oil filler tube by
placing valve locating tabs into cam lock. Press PCV
valve in and rotate valve upward. A slight click will
be felt when tabs have engaged cam lock. Valve
should be pointed towards rear of vehicle.
(2) Connect PCV line/hose and rubber hose to PCV
valve.
Fig. 12 PCV Valve/Oil Filler Tube Location
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
25 - 32 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSKJ
PCV VALVE (Continued)
Page 1739 of 1803

VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION
A vacuum schematic for emission related items can
be found on the VECI label. Refer to Vehicle Emis-
sion Control Information (VECI) Label for label loca-
tion.
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION
A maintenance free, EVAP canister is used on all
gasoline powered models. The EVAP canister is
located near the left/front corner of the fuel tank.
OPERATION
The EVAP canister is filled with granules of an
activated carbon mixture. Fuel vapors entering the
EVAP canister are absorbed by the charcoal granules.
The canister serves two functions: as a temporary
fuel vapor storage point while refueling the vehicle
for the ORVR system, as a temporary vapor storage
point while the engine is running.
Fuel tank pressure vents into the EVAP canister.
Fuel vapors are temporarily held in the canister until
they can be drawn into the intake manifold. The duty
cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid allows the EVAP
canister to be purged at predetermined times and at
certain engine operating conditions.
Refer to ORVR for additional information.
REMOVAL
The EVAP canister is located near front of fuel
tank and next to left/rear spring. (Fig. 13).
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Disconnect vacuum hoses/lines at EVAP canis-
ter. Note location of lines before removal.
(3) Remove EVAP canister and mounting bracket
assembly from body (2 bolts).
(4) Remove canister-to-mounting bracket bolt.
(5) Slide 2 canister mounting pins from mounting
bracket (Fig. 14).
INSTALLATION
(1) Slide 2 canister mounting pins into mounting
bracket (Fig. 14).
(2) Install canister-to-mounting bracket bolt.
(3) Position canister and bracket assembly to body.
(4) Install 2 mounting bracket bolts. Tighten to 47
N´m (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect vacuum hoses/lines at EVAP canister.
(6) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 13 EVAP CANISTER LOCATION
1 - LEFT/REAR SPRING
2 - EVAP CANISTER
3 - MOUNTING BRACKET
4 - BRACKET BOLTS
5 - VACUUM LINES
Fig. 14 EVAP CANISTER MOUNTING PINS
1 - MOUNTING PINS
2 - MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - EVAP CANISTER
KJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 33
Page 1744 of 1803
CASE BEARINGS - REMOVAL,
DIFFERENTIAL...............3-110,3-43,3-79
CASE, NV231 - TRANSFER............21-206
CASE, NV242 - TRANSFER............21-244
CASE SKID PLATE - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER...........................13-7
CASE SKID PLATE - REMOVAL,
TRANSFER...........................13-7
CASE, SPECIFICATIONS - NV242
TRANSFER.........................21-244
CASTER ADJUSTMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, CAMBER..................2-5
CASTER AND TOE ADJUSTMENT -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, CAMBER........2-5
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - DESCRIPTION . . . 11-2
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - INSPECTION....11-3
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - INSTALLATION . . . 11-3
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - REMOVAL......11-2
CAUSES OF BURNT FLUID - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING......................21-125
CAUTION - SERVICE CAUTIONS.........24-39
CAUTION, HALF SHAFT.................3-10
CAUTION, REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/
TUBES PRECAUTIONS.................24-40
CAUTIONS, CAUTION - SERVICE.........24-39
CD CHANGER - DESCRIPTION...........8A-7
CD CHANGER - INSTALLATION...........8A-7
CD CHANGER - OPERATION.............8A-7
CD CHANGER - REMOVAL..............8A-7
CENTER - DESCRIPTION, POWER
DISTRIBUTION....................8W-97-6
CENTER - OPERATION, POWER
DISTRIBUTION....................8W-97-7
CENTER - REMOVAL, POWER
DISTRIBUTION....................8W-97-7
CENTER ASSEMBLY, ASSEMBLY -
POWER DISTRIBUTION.............8W-97-10
CENTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION,
INSTRUMENT PANEL.................23-154
CENTER BEZEL - REMOVAL,
INSTRUMENT PANEL.................23-154
CENTER DISASSEMBLY, DISASSEMBLY -
POWER DISTRIBUTION..............8W-97-7
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
BULB - INSTALLATION................8L-19
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
BULB - REMOVAL....................8L-18
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
UNIT - INSTALLATION.................8L-19
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
UNIT - REMOVAL....................8L-19
CENTER SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
INSTALLATION, REAR.................8O-33
CENTER SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
REMOVAL, REAR....................8O-32
CENTERING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
CLOCKSPRING......................8O-14
CERTIFICATION LABEL - DESCRIPTION,
VEHICLE SAFETY...................Intro.-9
CHAIN COVER(S) - INSTALLATION,
TIMING BELT.........................9-76
CHAIN COVER(S) - REMOVAL, TIMING
BELT ...............................9-74
CHAIN WEAR, STANDARD PROCEDURE -
MEASURING TIMING...................9-71
CHANGER - DESCRIPTION, CD...........8A-7
CHANGER - INSTALLATION, CD..........8A-7
CHANGER - OPERATION, CD.............8A-7
CHANGER - REMOVAL, CD..............8A-7
CHANNEL - INSTALLATION, GLASS RUN . 23-123,
23-130
CHANNEL - REMOVAL, GLASS RUN....23-123,
23-130
CHARGE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM...............24-41
CHARGE CAPACITY - SPECIFICATIONS....24-42
CHARGING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
BATTERY............................8F-8
CHARGING INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION . . . 8J-15
CHARGING INDICATOR - OPERATION.....8J-15
CHARGING SYSTEM - DESCRIPTION
.....8F-22
CHARGING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING
...........................8F-22
CHARGING SYSTEM - OPERATION
.......8F-22
CHART - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
............7-6
CHART, SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
.....19-15,
19-19,19-8CHART, SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE....2-17,2-8
CHECK - STANDARD PROCEDURE, FLUID
LEVEL............................21-126
CHECK - STANDARD PROCEDURE, OIL
PUMP VOLUME.....................21-148
CHECK STRAP - INSTALLATION . . 23-121,23-128,
23-135
CHECK STRAP - REMOVAL.....23-121,23-128,
23-135
CHECK VALVE - DESCRIPTION, FRONT....8R-8
CHECK VALVE - DESCRIPTION, FUEL
TANK ..............................14-28
CHECK VALVE - DESCRIPTION, REAR....8R-34
CHECK VALVE - DESCRIPTION, VACUUM . . 24-28
CHECK VALVE - INSTALLATION, FRONT....8R-9
CHECK VALVE - INSTALLATION, FUEL
TANK ..............................14-28
CHECK VALVE - INSTALLATION, REAR....8R-35
CHECK VALVE - INSTALLATION, VACUUM . 24-28
CHECK VALVE - OPERATION, FRONT......8R-9
CHECK VALVE - OPERATION, FUEL TANK . . 14-28
CHECK VALVE - OPERATION, REAR......8R-34
CHECK VALVE - OPERATION, VACUUM....24-28
CHECK VALVE - REMOVAL, FRONT.......8R-9
CHECK VALVE - REMOVAL, FUEL TANK . . . 14-28
CHECK VALVE - REMOVAL, REAR.......8R-34
CHECK VALVE - REMOVAL, VACUUM.....24-28
CHECKING TRANSMISSION CLUTCH
OPERATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, AIR.......................21-80
CHECKS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
PRELIMINARY.........................7-3
CHILD TETHER ANCHOR - DESCRIPTION . . 8O-13
CHILD TETHER ANCHOR - OPERATION . . . 8O-13
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM -
DESCRIPTION........................8B-1
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING........................8B-6
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM - OPERATION . . . 8B-2
CHOKE AND RELAY - DESCRIPTION,
AMPLIFIER..........................8A-3
CHOKE AND RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, AMPLIFIER..................8A-4
CHOKE AND RELAY - INSTALLATION,
AMPLIFIER..........................8A-4
CHOKE AND RELAY - OPERATION,
AMPLIFIER..........................8A-3
CHOKE AND RELAY - REMOVAL,
AMPLIFIER..........................8A-4
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET -
DESCRIPTION.....................8W-97-2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING.....................8W-97-2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET - OPERATION . 8W-97-2
CLEVIS BRACKET - INSTALLATION........2-13
CLEVIS BRACKET - REMOVAL...........2-13
CLOCKSPRING - DESCRIPTION.........8O-13
CLOCKSPRING - INSTALLATION.........8O-16
CLOCKSPRING - OPERATION...........8O-14
CLOCKSPRING - REMOVAL............8O-15
CLOCKSPRING CENTERING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE........................8O-14
CLUSTER - ASSEMBLY, INSTRUMENT....8J-10
CLUSTER - DESCRIPTION, INSTRUMENT . . . 8J-2
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
INSTRUMENT........................8J-7
CLUSTER - DISASSEMBLY, INSTRUMENT . . . 8J-9
CLUSTER - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT . 8J-11
CLUSTER - OPERATION, INSTRUMENT.....8J-4
CLUSTER - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT......8J-9
CLUSTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION.......23-147
CLUSTER BEZEL - REMOVAL..........23-147
CLUTCH - ASSEMBLY, LOW/REVERSE
. . . 21-146
CLUTCH - CLEANING, LOW/REVERSE
....21-146
CLUTCH - DESCRIPTION
.................6-1
CLUTCH - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
.......6-2
CLUTCH - DISASSEMBLY, LOW/REVERSE
. 21-145
CLUTCH - INSPECTION, A/C
COMPRESSOR
.......................24-14
CLUTCH - INSPECTION, LOW/REVERSE
. . 21-146
CLUTCH - INSTALLATION, A/C
COMPRESSOR
.......................24-14
CLUTCH - OPERATION
..................6-1
CLUTCH - REMOVAL, A/C COMPRESSOR
. . 24-13
CLUTCH - SPECIFICATIONS
...............6-5
CLUTCH - WARNING
....................6-2
CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - ASSEMBLY, INPUT
. 21-138CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - DESCRIPTION,
INPUT............................21-133
CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - DISASSEMBLY,
INPUT............................21-135
CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - OPERATION,
INPUT............................21-135
CLUTCH BREAK-IN - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, A/C COMPRESSOR........24-12
CLUTCH COIL - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, A/C COMPRESSOR...........24-12
CLUTCH DISC - INSTALLATION............6-6
CLUTCH DISC - REMOVAL...............6-6
CLUTCH OPERATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION......................21-80
CLUTCH PEDAL - INSTALLATION.........6-10
CLUTCH PEDAL - REMOVAL.............6-10
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION........................6-11
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..............6-11
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH -
OPERATION..........................6-11
CLUTCH RELAY - DESCRIPTION, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-15
CLUTCH RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, COMPRESSOR...............24-15
CLUTCH RELAY - INSTALLATION, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-16
CLUTCH RELAY - OPERATION, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-15
CLUTCH RELAY - REMOVAL, A/C
COMPRESSOR........................24-16
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING -
INSTALLATION.........................6-6
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING - REMOVAL....6-6
CLUTCH SWITCH OVERRIDE RELAY -
DESCRIPTION........................6-10
CLUTCH SWITCH OVERRIDE RELAY -
INSTALLATION........................6-10
CLUTCH SWITCH OVERRIDE RELAY -
OPERATION..........................6-10
CLUTCH SWITCH OVERRIDE RELAY -
REMOVAL...........................6-10
CLUTCHES - DESCRIPTION, HOLDING . . . 21-131
CLUTCHES - OPERATION, HOLDING.....21-132
CMTC LAMP REPLACEMENT -
STANDARD PROCEDURE...............8M-2
COAT FINISH - DESCRIPTION, BASE
COAT/CLEAR.......................23-162
COAT/CLEAR COAT FINISH -
DESCRIPTION, BASE.................23-162
CODE - DESCRIPTION, PAINT..........23-162
CODES - DESCRIPTION, DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE............................25-2
CODES - SPECIFICATIONS, PAINT.......23-162
CODES - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
ERASING TRANSMITTER...............8M-8
CODES - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
SETTING TRANSMITTER...............8M-9
COIL - DESCRIPTION, IGNITION..........8I-9
COIL - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, A/C
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH...............24-12
COIL - INSTALLATION, IGNITION.........8I-10
COIL - OPERATION, IGNITION............8I-9
COIL - REMOVAL, IGNITION............8I-10
COIL CAPACITOR - DESCRIPTION,
IGNITION...........................8I-16
COIL CAPACITOR - INSTALLATION,
IGNITION...........................8I-16
COIL CAPACITOR - OPERATION,
IGNITION...........................8I-16
COIL CAPACITOR - REMOVAL, IGNITION . . . 8I-16
COIL RESISTANCE, 2.4L - IGNITION
.......8I-2
COIL RESISTANCE, 3.7L V-6 - IGNITION
....8I-3
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER - INSTALLATION
....3-70
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER - REMOVAL
.......3-70
COLUMN - DESCRIPTION
...............19-5
COLUMN - INSTALLATION
...............19-7
COLUMN - REMOVAL
..................19-5
COLUMN, SPECIAL TOOLS - STEERING
....19-8
COMBINATION FLASHER - DESCRIPTION
. . 8L-19
COMBINATION FLASHER - OPERATION
. . . 8L-19
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, CYLINDER
......9-8
COMMUNICATION - DESCRIPTION
........8E-8
COMMUNICATION - OPERATION
..........8E-8
KJINDEX 5
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page