2002 JEEP LIBERTY evi c
[x] Cancel search: evi cPage 1706 of 1803
oils are not compatible with PAG oils, and should
never be introduced to an R-134a refrigerant system.
There are different PAG oils available, and each
contains a different additive package. The PXF±18
compressor used in this vehicle is designed to use an
SP±10 PAG refrigerant oil. Use only refrigerant oil of
this same type to service the refrigerant system.
OPERATION
After performing any refrigerant recovery or recy-
cling operation, always replenish the refrigerant sys-
tem with the same amount of the recommended
refrigerant oil as was removed. Too little refrigerant
oil can cause compressor damage, and too much can
reduce air conditioning system performance.
PAG refrigerant oil is much more hygroscopic than
mineral oil, and will absorb any moisture it comes
into contact with, even moisture in the air. The PAG
oil container should always be kept tightly capped
until it is ready to be used. After use, recap the oil
container immediately to prevent moisture contami-
nation.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT OIL
LEVEL
When an air conditioning system is assembled at
the factory, all components except the compressor are
refrigerant oil free. After the refrigerant system has
been charged and operated, the refrigerant oil in the
compressor is dispersed throughout the refrigerant
system. The accumulator, evaporator, condenser, and
compressor will each retain a significant amount of
the needed refrigerant oil.
It is important to have the correct amount of oil in
the refrigerant system. This ensures proper lubrica-tion of the compressor. Too little oil will result in
damage to the compressor. Too much oil will reduce
the cooling capacity of the air conditioning system.
It will not be necessary to check the oil level in the
compressor or to add oil, unless there has been an oil
loss. An oil loss may occur due to a rupture or leak
from a refrigerant line, a connector fitting, a compo-
nent, or a component seal. If a leak occurs, add 30
milliliters (1 fluid ounce) of refrigerant oil to the
refrigerant system after the repair has been made.
Refrigerant oil loss will be evident at the leak point
by the presence of a wet, shiny surface around the
leak.
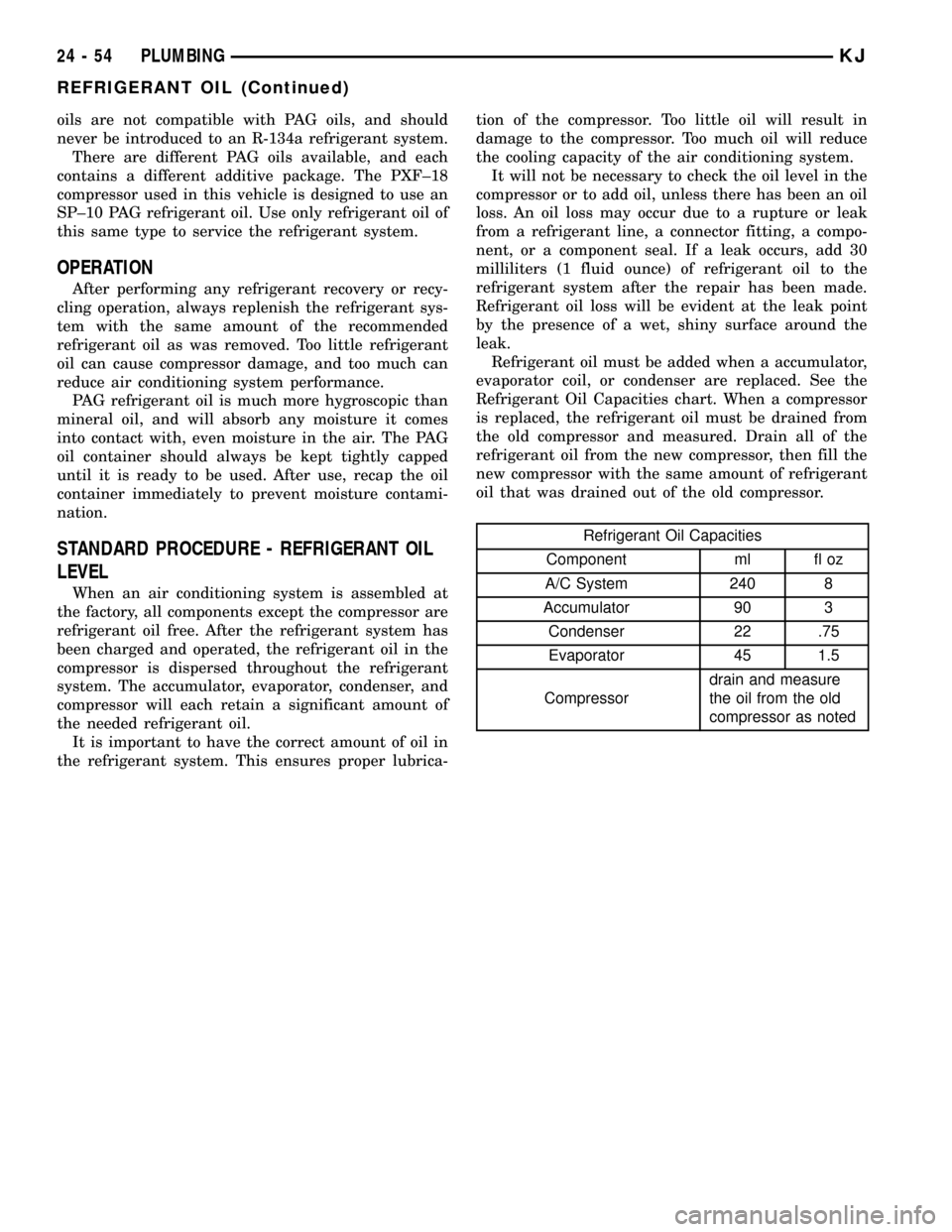
Refrigerant oil must be added when a accumulator,
evaporator coil, or condenser are replaced. See the
Refrigerant Oil Capacities chart. When a compressor
is replaced, the refrigerant oil must be drained from
the old compressor and measured. Drain all of the
refrigerant oil from the new compressor, then fill the
new compressor with the same amount of refrigerant
oil that was drained out of the old compressor.
Refrigerant Oil Capacities
Component ml fl oz
A/C System 240 8
Accumulator 90 3
Condenser 22 .75
Evaporator 45 1.5
Compressordrain and measure
the oil from the old
compressor as noted
24 - 54 PLUMBINGKJ
REFRIGERANT OIL (Continued)
Page 1708 of 1803

DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connect
the DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0030 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0031 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0032 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0036 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0037 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0038 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0043 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0044 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0051 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0052 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1725 of 1803

Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. This can increase vehicle emissions
and deteriorate engine performance, driveability and
fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S's sensor strategy is based on the fact that
as a catalyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity
and its efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring
the oxygen storage capacity of a catalyst, its effi-
ciency can be indirectly calculated. The upstream
O2S is used to detect the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gas before the gas enters the catalytic con-
verter. The PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the
output of the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxy-
gen content (lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a
low content of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL will be illu-
minated.
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION
The term ªTripº has different meanings depending
on what the circumstances are. If the MIL (Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp) is OFF, a Trip is defined as
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst
Monitor have been completed in the same drive cycle.
When any Emission DTC is set, the MIL on the
dash is turned ON. When the MIL is ON, it takes 3good trips to turn the MIL OFF. In this case, it
depends on what type of DTC is set to know what a
ªTripº is.
For the Fuel Monitor or Mis-Fire Monitor (contin-
uous monitor), the vehicle must be operated in the
ªSimilar Condition Windowº for a specified amount of
time to be considered a Good Trip.
If a Non-Contiuous OBDII Monitor fails twice in a
row and turns ON the MIL, re-running that monitor
which previously failed, on the next start-up and
passing the monitor, is considered to be a Good Trip.
These will include the following:
²Oxygen Sensor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Purge Flow Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
²EGR Monitor (if equipped)
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
If any other Emission DTC is set (not an OBDII
Monitor), a Good Trip is considered to be when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Monitor have
been completed; or 2 Minutes of engine run time if
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor or Catalyst Monitor have
been stopped from running.
It can take up to 2 Failures in a row to turn on the
MIL. After the MIL is ON, it takes 3 Good Trips to
turn the MIL OFF. After the MIL is OFF, the PCM
will self-erase the DTC after 40 Warm-up cycles. A
Warm-up cycle is counted when the ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor) has crossed 160ÉF and
has risen by at least 40ÉF since the engine has been
started.
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum if
the TPS indicates a small throttle opening.
All open/short circuit checks or any component that
has an associated limp in will set a fault after 1 trip
with the malfunction present. Components without
KJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 19
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1726 of 1803

an associated limp in will take two trips to illumi-
nate the MIL.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
DESCRIPTION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
causing driveability problems. The PCM might not
store diagnostic trouble codes for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause the
PCM to store diagnostic trouble codes for other sys-
tems or components. For example, a fuel pressure
problem will not register a fault directly, but could
cause a rich/lean condition or misfire. This could
cause the PCM to store an oxygen sensor or misfire
diagnostic trouble code
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor or fuel system diag-
nostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system, although it may set a fuel
system fault.
FUEL INJECTOR MECHANICAL MALFUNCTIONS
The PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is
clogged, the needle is sticking or if the wrong injectoris installed. However, these could result in a rich or
lean condition causing the PCM to store a diagnostic
trouble code for either misfire, an oxygen sensor, or
the fuel system.
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
Although the PCM monitors engine exhaust oxygen
content when the system is in closed loop, it cannot
determine excessive oil consumption.
THROTTLE BODY AIRFLOW
The PCM cannot detect a clogged or restricted air
cleaner inlet or filter element.
VACUUM ASSIST
The PCM cannot detect leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices. However, these could cause the PCM
to store a MAP sensor diagnostic trouble code and
cause a high idle condition.
PCM SYSTEM GROUND
The PCM cannot determine a poor system ground.
However, one or more diagnostic trouble codes may
be generated as a result of this condition. The mod-
ule should be mounted to the body at all times, also
during diagnostic.
PCM CONNECTOR ENGAGEMENT
The PCM may not be able to determine spread or
damaged connector pins. However, it might store
diagnostic trouble codes as a result of spread connec-
tor pins.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The PCM compares input signal voltages from each
input device with established high and low limits for
the device. If the input voltage is not within limits
and other criteria are met, the PCM stores a diagnos-
tic trouble code in memory. Other diagnostic trouble
code criteria might include engine RPM limits or
input voltages from other sensors or switches that
must be present before verifying a diagnostic trouble
code condition.
DESCRIPTION - LOAD VALUE
ENGINE IDLE/NEUTRAL 2500 RPM/NEUTRAL
All Engines 2% to 8% of Maximum Load 9% to 17% of Maximum Load
25 - 20 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1728 of 1803

²Priority4ÐTwotrip failure or matured fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) and misfire or one trip cat-
alyst damaging misfire.
Non-emissions related failures have no priority.
One trip failures of two trip faults have low priority.
Two trip failures or matured faults have higher pri-
ority. One and two trip failures of fuel system and
misfire monitor take precedence over non-fuel system
and non-misfire failures.
DTC Self Erasure
With one trip components or systems, the MIL is
illuminated upon test failure and DTCs are stored.
Two trip monitors are components requiring failure
in two consecutive trips for MIL illumination. Upon
failure of the first test, the Task Manager enters a
maturing code. If the component fails the test for a
second time the code matures and a DTC is set.
After three good trips the MIL is extinguished and
the Task Manager automatically switches the trip
counter to a warm-up cycle counter. DTCs are auto-
matically erased following 40 warm-up cycles if the
component does not fail again.
For misfire and fuel system monitors, the compo-
nent must pass the test under a Similar Conditions
Window in order to record a good trip. A Similar Con-
ditions Window is when engine RPM is within 375
RPM and load is within 10% of when the fault
occurred.
NOTE: It is important to understand that a compo-
nent does not have to fail under a similar window of
operation to mature. It must pass the test under a
Similar Conditions Window when it failed to record
a Good Trip for DTC erasure for misfire and fuel
system monitors.
DTCs can be erased anytime with a DRB III. Eras-
ing the DTC with the DRB III erases all OBD II
information. The DRB III automatically displays a
warning that erasing the DTC will also erase all
OBD II monitor data. This includes all counter infor-
mation for warm-up cycles, trips and Freeze Frame.
Trip Indicator
TheTripis essential for running monitors and
extinguishing the MIL. In OBD II terms, a trip is a
set of vehicle operating conditions that must be met
for a specific monitor to run. All trips begin with a
key cycle.
Good Trip
The Good Trip counters are as follows:
²Specific Good Trip
²Fuel System Good Trip
²Misfire Good Trip
²Alternate Good Trip (appears as a Global Good
Trip on DRB III)²Comprehensive Components
²Major Monitor
²Warm-Up Cycles
Specific Good Trip
The term Good Trip has different meanings
depending on the circumstances:
²If the MIL is OFF, a trip is defined as when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst Monitor
have been completed in the same drive cycle.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by the Fuel
Monitor or Misfire Monitor (both continuous moni-
tors), the vehicle must be operated in the Similar
Condition Window for a specified amount of time.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by a Task
Manager commanded once-per-trip monitor (such as
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Catalyst Monitor, Purge
Flow Monitor, Leak Detection Pump Monitor, EGR
Monitor or Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor), a good
trip is when the monitor is passed on the next start-
up.
²If the MIL is ON and any other emissions DTC
was set (not an OBD II monitor), a good trip occurs
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Mon-
itor have been completed, or two minutes of engine
run time if the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst
Monitor have been stopped from running.
Fuel System Good Trip
To count a good trip (three required) and turn off
the MIL, the following conditions must occur:
²Engine in closed loop
²Operating in Similar Conditions Window
²Short Term multiplied by Long Term less than
threshold
²Less than threshold for a predetermined time
If all of the previous criteria are met, the PCM will
count a good trip (three required) and turn off the
MIL.
Misfire Good Trip
If the following conditions are met the PCM will
count one good trip (three required) in order to turn
off the MIL:
²Operating in Similar Condition Window
²1000 engine revolutions with no misfire
Warm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRB III. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
25 - 22 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1733 of 1803

EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
is located in the engine compartment. It is attached
to a bracket located between the battery and the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). The EVAP system
test port is located near the solenoid.
OPERATION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
regulates the rate of vapor flow from the EVAP can-
ister to the intake manifold. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) operates the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop oper-
ation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM cycles
(energizes and de-energizes) the solenoid 5 or 10
times per second, depending upon operating condi-
tions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by chang-
ing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the amount
of time that the solenoid is energized. The PCM
adjusts solenoid pulse width based on engine operat-
ing condition.
REMOVAL
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
is located in the engine compartment (Fig. 2). It is
attached to a bracket located between the battery
and the Power Distribution Center (PDC). The EVAP
system test port is located near the solenoid (Fig. 2).
(1) Disconnect electrical wiring connector at sole-
noid.
(2) Disconnect vacuum harness at solenoid.
(3) Remove solenoid and its support bracket (pull
straight up).
INSTALLATION
(1) Slip EVAP canister purge solenoid onto its
mounting bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum harness to solenoid.
(3) Connect electrical connector to solenoid.
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION
The plastic fuel tank filler tube cap is threaded
onto the end of the fuel fill tube. All models are
equipped with a 1/4 turn cap.
OPERATION
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of fuel filler tube
is prevented by the use of a pressure-vacuum fuel fill
cap. Relief valves inside the cap will release fuel tank
pressure at predetermined pressures. Fuel tank vac-
uum will also be released at predetermined values.
This cap must be replaced by a similar unit if
replacement is necessary. This is in order for the sys-
tem to remain effective.
CAUTION: Remove fill cap before servicing any fuel
system component to relieve tank pressure. If
equipped with an ORVR system and a Leak Detec-
tion Pump (LDP), the cap must be tightened
securely. If cap is left loose, a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) may be set.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is bolted to the
front of the fuel tank (Fig. 1).
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is used only with
certain emission packages.
The LDP is a device used to detect a leak in the
evaporative system.
Fig. 2 EVAP / PURGE SOLENOID LOCATION
1 - BATTERY
2 - EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID LOCATION
3 - MOUNTING BRACKET
4 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
5 - SOLENOID ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
6 - EVAP SYSTEM TEST PORT
KJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 27
Page 1742 of 1803

BATTERY TRAY - OPERATION...........8F-21
BATTERY TRAY - REMOVAL............8F-21
BEAM INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, HIGH . . 8J-22
BEAM INDICATOR - OPERATION, HIGH....8J-22
BEAM RELAY - DESCRIPTION,
HEADLAMP HIGH....................8L-33
BEAM RELAY - DESCRIPTION,
HEADLAMP LOW.....................8L-39
BEAM RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, HEADLAMP HIGH............8L-34
BEAM RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, HEADLAMP LOW.............8L-40
BEAM RELAY - INSTALLATION,
HEADLAMP HIGH....................8L-35
BEAM RELAY - INSTALLATION,
HEADLAMP LOW.....................8L-41
BEAM RELAY - OPERATION, HEADLAMP
HIGH..............................8L-33
BEAM RELAY - OPERATION, HEADLAMP
LOW ..............................8L-39
BEAM RELAY - REMOVAL, HEADLAMP
HIGH..............................8L-34
BEAM RELAY - REMOVAL, HEADLAMP
LOW ..............................8L-40
BEARING - FITTING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, CONNECTING ROD.........9-40
BEARING - INSTALLATION, CLUTCH
RELEASE.............................6-6
BEARING - INSTALLATION, HUB...........2-9
BEARING - INSTALLATION, PILOT.........6-8
BEARING - REMOVAL, CLUTCH RELEASE . . . 6-6
BEARING - REMOVAL, HUB..............2-9
BEARING - REMOVAL, PILOT.............6-8
BEARING, FITTING - CONNECTING ROD....9-49
BEARING, FITTING - MAIN..............9-45
BEARINGS - INSTALLATION, AXLE . . . 3-102,3-38
BEARINGS - INSTALLATION,
DIFFERENTIAL CASE..........3-110,3-44,3-79
BEARINGS - REMOVAL, AXLE.......3-102,3-38
BEARINGS - REMOVAL, DIFFERENTIAL
CASE......................3-110,3-43,3-79
BEARING/SEAL - INSTALLATION, AXLE....3-67
BEARING/SEAL - REMOVAL, AXLE........3-66
BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) -
INSTALLATION, TIMING.................9-76
BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - REMOVAL,
TIMING.............................9-74
BELT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
SERPENTINE DRIVE...................7-15
BELT & RETRACTOR - INSTALLATION,
FRONT SEAT........................8O-24
BELT & RETRACTOR - INSTALLATION,
REAR CENTER SEAT..................8O-33
BELT & RETRACTOR - INSTALLATION,
REAR OUTBOARD SEAT...............8O-34
BELT & RETRACTOR - REMOVAL, FRONT
SEAT ..............................8O-23
BELT & RETRACTOR - REMOVAL, REAR
CENTER SEAT.......................8O-32
BELT & RETRACTOR - REMOVAL, REAR
OUTBOARD SEAT....................8O-33
BELT BUCKLE - INSTALLATION, FRONT
SEAT ..............................8O-26
BELT BUCKLE - INSTALLATION, REAR
SEAT ..............................8O-35
BELT BUCKLE - REMOVAL, FRONT SEAT . . 8O-25
BELT BUCKLE - REMOVAL, REAR SEAT . . . 8O-34
BELT MOLDING - INSTALLATION, FRONT
DOOR OUTER......................23-186
BELT MOLDING - INSTALLATION, REAR
DOOR OUTER......................23-186
BELT MOLDING - REMOVAL, FRONT
DOOR OUTER......................23-186
BELT MOLDING - REMOVAL, REAR
DOOR OUTER......................23-186
BELT SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, SEAT.....8O-35
BELT SWITCH - OPERATION, SEAT.......8O-36
BELT TENSIONER - DESCRIPTION, SEAT . . 8O-36
BELT TENSIONER - OPERATION, SEAT....8O-36
BELT TURNING LOOP ADJUSTER -
INSTALLATION, SEAT
.................8O-38
BELT TURNING LOOP ADJUSTER -
REMOVAL, SEAT
.....................8O-37
BELTLINE WEATHERSTRIP -
INSTALLATION, SWING GATE
..........23-186
BELTLINE WEATHERSTRIP - REMOVAL,
SWING GATE
.......................23-186
BEZEL - INSTALLATION, CLUSTER
......23-147BEZEL - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT
PANEL CENTER.....................23-154
BEZEL - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT
PANEL PASSENGER SIDE.............23-154
BEZEL - INSTALLATION, SHIFT.........23-158
BEZEL - REMOVAL, CLUSTER..........23-147
BEZEL - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT PANEL
CENTER...........................23-154
BEZEL - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT PANEL
PASSENGER SIDE...................23-154
BEZEL - REMOVAL, SHIFT.............23-158
BEZELS - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT
PANEL DRIVER SIDE.................23-154
BEZELS - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT
PANEL DRIVER SIDE.................23-153
BLADE - DESCRIPTION, FRONT WIPER . . . 8R-13
BLADE - DESCRIPTION, REAR WIPER....8R-39
BLADE - INSTALLATION, FRONT WIPER . . . 8R-14
BLADE - INSTALLATION, REAR WIPER....8R-40
BLADE - OPERATION, FRONT WIPER.....8R-14
BLADE - OPERATION, REAR WIPER......8R-39
BLADE - REMOVAL, FRONT WIPER......8R-14
BLADE - REMOVAL, REAR WIPER.......8R-40
BLEEDING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
ABS BRAKE..........................5-33
BLEEDING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
MANUAL.............................5-6
BLEEDING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
MASTER CYLINDER...................5-24
BLEEDING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
PRESSURE...........................5-5
BLEND DOOR - INSTALLATION..........24-35
BLEND DOOR - REMOVAL.............24-35
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR -
INSTALLATION.......................24-20
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR - REMOVAL....24-20
BLOCK - CLEANING, ENGINE............9-39
BLOCK - DESCRIPTION, ENGINE..........9-39
BLOCK - DESCRIPTION, JUNCTION....8W-97-4
BLOCK - DESCRIPTION, JUNCTION.......5-20
BLOCK - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
JUNCTION........................8W-97-4
BLOCK - INSPECTION, ENGINE...........9-40
BLOCK - INSTALLATION, JUNCTION.......5-20
BLOCK - OPERATION, JUNCTION......8W-97-4
BLOCK - OPERATION, JUNCTION.........5-20
BLOCK - REMOVAL, JUNCTION...........5-20
BLOCKER - INSTALLATION, KNEE.......23-155
BLOCKER - REMOVAL, KNEE..........23-155
BLOWER MOTOR - DESCRIPTION.......24-30
BLOWER MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................24-30
BLOWER MOTOR - INSTALLATION.......24-31
BLOWER MOTOR - OPERATION.........24-30
BLOWER MOTOR - REMOVAL...........24-30
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY - DESCRIPTION . . 24-20
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING.......................24-21
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY -
INSTALLATION.......................24-22
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY - OPERATION . . . 24-20
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY - REMOVAL.....24-21
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR -
DESCRIPTION.......................24-22
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.............24-22
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR -
INSTALLATION.......................24-22
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR -
OPERATION.........................24-22
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR - REMOVAL . . 24-22
BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION.......................24-23
BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING.......................24-23
BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH -
INSTALLATION.......................24-23
BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH - OPERATION . . 24-23
BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH - REMOVAL . . . 24-23
BODY - ASSEMBLY, VALVE............21-176
BODY & CABLE - DESCRIPTION,
ANTENNA...........................8A-4
BODY & CABLE - INSTALLATION,
ANTENNA
...........................8A-6
BODY & CABLE - OPERATION, ANTENNA
. . . 8A-5
BODY & CABLE - REMOVAL, ANTENNA
....8A-6
BODY - CLEANING, VALVE
............21-175
BODY - DESCRIPTION, THROTTLE
.......14-43BODY - DESCRIPTION, VALVE..........21-171
BODY - DISASSEMBLY, VALVE.........21-173
BODY - INSPECTION, VALVE...........21-175
BODY - INSTALLATION, THROTTLE.......14-44
BODY - INSTALLATION, VALVE.........21-177
BODY - OPERATION, THROTTLE.........14-43
BODY - OPERATION, VALVE...........21-171
BODY - REMOVAL, THROTTLE..........14-43
BODY - REMOVAL, VALVE.............21-172
BODY AND CABLE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, ANTENNA...................8A-5
BODY CONTROL MODULE -
DESCRIPTION........................8E-2
BODY CONTROL MODULE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING........................8E-7
BODY CONTROL MODULE -
INSTALLATION........................8E-7
BODY CONTROL MODULE - OPERATION . . . 8E-5
BODY CONTROL MODULE - REMOVAL.....8E-7
BODY LUBRICATION - STANDARD
PROCEDURE.........................23-3
BODY SIDE MOLDINGS - INSTALLATION . 23-140
BODY SIDE MOLDINGS - REMOVAL.....23-140
BODY, SPECIAL TOOLS.................23-5
BOOSTER - DESCRIPTION, POWER
BRAKE..............................5-21
BOOSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
MASTER CYLINDER/POWER.........5-21,5-24
BOOSTER - INSTALLATION, POWER
BRAKE..............................5-23
BOOSTER - OPERATION, POWER BRAKE . . . 5-21
BOOSTER - REMOVAL, POWER BRAKE....5-22
BOOT - INSTALLATION, 4WD FLOOR
SHIFT.............................23-156
BOOT - REMOVAL, 4WD FLOOR SHIFT . . . 23-156
BORE HONING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, CYLINDER................9-39
BOX - INSTALLATION, GLOVE..........23-148
BOX - REMOVAL, GLOVE.............23-148
BOX LATCH - INSTALLATION, GLOVE....23-148
BOX LATCH - REMOVAL, GLOVE........23-148
BOX LATCH STRIKER - INSTALLATION,
GLOVE............................23-149
BOX LATCH STRIKER - REMOVAL,
GLOVE............................23-148
B-PILLAR LOWER TRIM - INSTALLATION . 23-157
B-PILLAR LOWER TRIM - REMOVAL....23-157
B-PILLAR UPPER TRIM - INSTALLATION . 23-158
B-PILLAR UPPER TRIM - REMOVAL.....23-157
BRACKET - INSTALLATION, CLEVIS.......2-13
BRACKET - INSTALLATION, HOOD AJAR
SWITCH............................8Q-13
BRACKET - INSTALLATION, PASSENGER
AIRBAG MOUNTING..................8O-31
BRACKET - INSTALLATION, REARVIEW
MIRROR SUPPORT..................23-161
BRACKET - REMOVAL, CLEVIS...........2-13
BRACKET - REMOVAL, HOOD AJAR
SWITCH............................8Q-13
BRACKET - REMOVAL, PASSENGER
AIRBAG MOUNTING..................8O-31
BRAKE - ADJUSTMENT, REAR DRUM......5-12
BRAKE - DESCRIPTION, PARKING........5-29
BRAKE - DESCRIPTION, REAR DRUM.....5-10
BRAKE - INSTALLATION, CONTROLLER
ANTILOCK..........................8E-10
BRAKE - OPERATION, PARKING..........5-29
BRAKE - OPERATION, REAR DRUM.......5-11
BRAKE - REMOVAL, CONTROLLER
ANTILOCK..........................8E-10
BRAKE BLEEDING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, ABS.....................5-33
BRAKE BOOSTER - DESCRIPTION,
POWER.............................5-21
BRAKE BOOSTER - INSTALLATION,
POWER.............................5-23
BRAKE BOOSTER - OPERATION, POWER . . . 5-21
BRAKE BOOSTER - REMOVAL, POWER....5-22
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER -
INSTALLATION, DISC...................5-18
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER - REMOVAL,
DISC...............................5-18
BRAKE CALIPERS - ASSEMBLY, DISC......5-16
BRAKE CALIPERS - CLEANING, DISC
......5-16
BRAKE CALIPERS - DESCRIPTION, DISC
. . . 5-13
BRAKE CALIPERS - DISASSEMBLY, DISC
. . . 5-14
BRAKE CALIPERS - INSPECTION, DISC
....5-16
BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION, DISC
. . . 5-17
KJINDEX 3
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page
Page 1744 of 1803
CASE BEARINGS - REMOVAL,
DIFFERENTIAL...............3-110,3-43,3-79
CASE, NV231 - TRANSFER............21-206
CASE, NV242 - TRANSFER............21-244
CASE SKID PLATE - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER...........................13-7
CASE SKID PLATE - REMOVAL,
TRANSFER...........................13-7
CASE, SPECIFICATIONS - NV242
TRANSFER.........................21-244
CASTER ADJUSTMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, CAMBER..................2-5
CASTER AND TOE ADJUSTMENT -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, CAMBER........2-5
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - DESCRIPTION . . . 11-2
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - INSPECTION....11-3
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - INSTALLATION . . . 11-3
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - REMOVAL......11-2
CAUSES OF BURNT FLUID - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING......................21-125
CAUTION - SERVICE CAUTIONS.........24-39
CAUTION, HALF SHAFT.................3-10
CAUTION, REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/
TUBES PRECAUTIONS.................24-40
CAUTIONS, CAUTION - SERVICE.........24-39
CD CHANGER - DESCRIPTION...........8A-7
CD CHANGER - INSTALLATION...........8A-7
CD CHANGER - OPERATION.............8A-7
CD CHANGER - REMOVAL..............8A-7
CENTER - DESCRIPTION, POWER
DISTRIBUTION....................8W-97-6
CENTER - OPERATION, POWER
DISTRIBUTION....................8W-97-7
CENTER - REMOVAL, POWER
DISTRIBUTION....................8W-97-7
CENTER ASSEMBLY, ASSEMBLY -
POWER DISTRIBUTION.............8W-97-10
CENTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION,
INSTRUMENT PANEL.................23-154
CENTER BEZEL - REMOVAL,
INSTRUMENT PANEL.................23-154
CENTER DISASSEMBLY, DISASSEMBLY -
POWER DISTRIBUTION..............8W-97-7
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
BULB - INSTALLATION................8L-19
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
BULB - REMOVAL....................8L-18
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
UNIT - INSTALLATION.................8L-19
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
UNIT - REMOVAL....................8L-19
CENTER SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
INSTALLATION, REAR.................8O-33
CENTER SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
REMOVAL, REAR....................8O-32
CENTERING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
CLOCKSPRING......................8O-14
CERTIFICATION LABEL - DESCRIPTION,
VEHICLE SAFETY...................Intro.-9
CHAIN COVER(S) - INSTALLATION,
TIMING BELT.........................9-76
CHAIN COVER(S) - REMOVAL, TIMING
BELT ...............................9-74
CHAIN WEAR, STANDARD PROCEDURE -
MEASURING TIMING...................9-71
CHANGER - DESCRIPTION, CD...........8A-7
CHANGER - INSTALLATION, CD..........8A-7
CHANGER - OPERATION, CD.............8A-7
CHANGER - REMOVAL, CD..............8A-7
CHANNEL - INSTALLATION, GLASS RUN . 23-123,
23-130
CHANNEL - REMOVAL, GLASS RUN....23-123,
23-130
CHARGE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM...............24-41
CHARGE CAPACITY - SPECIFICATIONS....24-42
CHARGING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
BATTERY............................8F-8
CHARGING INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION . . . 8J-15
CHARGING INDICATOR - OPERATION.....8J-15
CHARGING SYSTEM - DESCRIPTION
.....8F-22
CHARGING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING
...........................8F-22
CHARGING SYSTEM - OPERATION
.......8F-22
CHART - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
............7-6
CHART, SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
.....19-15,
19-19,19-8CHART, SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE....2-17,2-8
CHECK - STANDARD PROCEDURE, FLUID
LEVEL............................21-126
CHECK - STANDARD PROCEDURE, OIL
PUMP VOLUME.....................21-148
CHECK STRAP - INSTALLATION . . 23-121,23-128,
23-135
CHECK STRAP - REMOVAL.....23-121,23-128,
23-135
CHECK VALVE - DESCRIPTION, FRONT....8R-8
CHECK VALVE - DESCRIPTION, FUEL
TANK ..............................14-28
CHECK VALVE - DESCRIPTION, REAR....8R-34
CHECK VALVE - DESCRIPTION, VACUUM . . 24-28
CHECK VALVE - INSTALLATION, FRONT....8R-9
CHECK VALVE - INSTALLATION, FUEL
TANK ..............................14-28
CHECK VALVE - INSTALLATION, REAR....8R-35
CHECK VALVE - INSTALLATION, VACUUM . 24-28
CHECK VALVE - OPERATION, FRONT......8R-9
CHECK VALVE - OPERATION, FUEL TANK . . 14-28
CHECK VALVE - OPERATION, REAR......8R-34
CHECK VALVE - OPERATION, VACUUM....24-28
CHECK VALVE - REMOVAL, FRONT.......8R-9
CHECK VALVE - REMOVAL, FUEL TANK . . . 14-28
CHECK VALVE - REMOVAL, REAR.......8R-34
CHECK VALVE - REMOVAL, VACUUM.....24-28
CHECKING TRANSMISSION CLUTCH
OPERATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, AIR.......................21-80
CHECKS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
PRELIMINARY.........................7-3
CHILD TETHER ANCHOR - DESCRIPTION . . 8O-13
CHILD TETHER ANCHOR - OPERATION . . . 8O-13
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM -
DESCRIPTION........................8B-1
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING........................8B-6
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM - OPERATION . . . 8B-2
CHOKE AND RELAY - DESCRIPTION,
AMPLIFIER..........................8A-3
CHOKE AND RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, AMPLIFIER..................8A-4
CHOKE AND RELAY - INSTALLATION,
AMPLIFIER..........................8A-4
CHOKE AND RELAY - OPERATION,
AMPLIFIER..........................8A-3
CHOKE AND RELAY - REMOVAL,
AMPLIFIER..........................8A-4
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET -
DESCRIPTION.....................8W-97-2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING.....................8W-97-2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET - OPERATION . 8W-97-2
CLEVIS BRACKET - INSTALLATION........2-13
CLEVIS BRACKET - REMOVAL...........2-13
CLOCKSPRING - DESCRIPTION.........8O-13
CLOCKSPRING - INSTALLATION.........8O-16
CLOCKSPRING - OPERATION...........8O-14
CLOCKSPRING - REMOVAL............8O-15
CLOCKSPRING CENTERING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE........................8O-14
CLUSTER - ASSEMBLY, INSTRUMENT....8J-10
CLUSTER - DESCRIPTION, INSTRUMENT . . . 8J-2
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
INSTRUMENT........................8J-7
CLUSTER - DISASSEMBLY, INSTRUMENT . . . 8J-9
CLUSTER - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT . 8J-11
CLUSTER - OPERATION, INSTRUMENT.....8J-4
CLUSTER - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT......8J-9
CLUSTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION.......23-147
CLUSTER BEZEL - REMOVAL..........23-147
CLUTCH - ASSEMBLY, LOW/REVERSE
. . . 21-146
CLUTCH - CLEANING, LOW/REVERSE
....21-146
CLUTCH - DESCRIPTION
.................6-1
CLUTCH - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
.......6-2
CLUTCH - DISASSEMBLY, LOW/REVERSE
. 21-145
CLUTCH - INSPECTION, A/C
COMPRESSOR
.......................24-14
CLUTCH - INSPECTION, LOW/REVERSE
. . 21-146
CLUTCH - INSTALLATION, A/C
COMPRESSOR
.......................24-14
CLUTCH - OPERATION
..................6-1
CLUTCH - REMOVAL, A/C COMPRESSOR
. . 24-13
CLUTCH - SPECIFICATIONS
...............6-5
CLUTCH - WARNING
....................6-2
CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - ASSEMBLY, INPUT
. 21-138CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - DESCRIPTION,
INPUT............................21-133
CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - DISASSEMBLY,
INPUT............................21-135
CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - OPERATION,
INPUT............................21-135
CLUTCH BREAK-IN - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, A/C COMPRESSOR........24-12
CLUTCH COIL - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, A/C COMPRESSOR...........24-12
CLUTCH DISC - INSTALLATION............6-6
CLUTCH DISC - REMOVAL...............6-6
CLUTCH OPERATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION......................21-80
CLUTCH PEDAL - INSTALLATION.........6-10
CLUTCH PEDAL - REMOVAL.............6-10
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION........................6-11
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..............6-11
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH -
OPERATION..........................6-11
CLUTCH RELAY - DESCRIPTION, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-15
CLUTCH RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, COMPRESSOR...............24-15
CLUTCH RELAY - INSTALLATION, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-16
CLUTCH RELAY - OPERATION, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-15
CLUTCH RELAY - REMOVAL, A/C
COMPRESSOR........................24-16
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING -
INSTALLATION.........................6-6
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING - REMOVAL....6-6
CLUTCH SWITCH OVERRIDE RELAY -
DESCRIPTION........................6-10
CLUTCH SWITCH OVERRIDE RELAY -
INSTALLATION........................6-10
CLUTCH SWITCH OVERRIDE RELAY -
OPERATION..........................6-10
CLUTCH SWITCH OVERRIDE RELAY -
REMOVAL...........................6-10
CLUTCHES - DESCRIPTION, HOLDING . . . 21-131
CLUTCHES - OPERATION, HOLDING.....21-132
CMTC LAMP REPLACEMENT -
STANDARD PROCEDURE...............8M-2
COAT FINISH - DESCRIPTION, BASE
COAT/CLEAR.......................23-162
COAT/CLEAR COAT FINISH -
DESCRIPTION, BASE.................23-162
CODE - DESCRIPTION, PAINT..........23-162
CODES - DESCRIPTION, DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE............................25-2
CODES - SPECIFICATIONS, PAINT.......23-162
CODES - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
ERASING TRANSMITTER...............8M-8
CODES - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
SETTING TRANSMITTER...............8M-9
COIL - DESCRIPTION, IGNITION..........8I-9
COIL - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, A/C
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH...............24-12
COIL - INSTALLATION, IGNITION.........8I-10
COIL - OPERATION, IGNITION............8I-9
COIL - REMOVAL, IGNITION............8I-10
COIL CAPACITOR - DESCRIPTION,
IGNITION...........................8I-16
COIL CAPACITOR - INSTALLATION,
IGNITION...........................8I-16
COIL CAPACITOR - OPERATION,
IGNITION...........................8I-16
COIL CAPACITOR - REMOVAL, IGNITION . . . 8I-16
COIL RESISTANCE, 2.4L - IGNITION
.......8I-2
COIL RESISTANCE, 3.7L V-6 - IGNITION
....8I-3
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER - INSTALLATION
....3-70
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER - REMOVAL
.......3-70
COLUMN - DESCRIPTION
...............19-5
COLUMN - INSTALLATION
...............19-7
COLUMN - REMOVAL
..................19-5
COLUMN, SPECIAL TOOLS - STEERING
....19-8
COMBINATION FLASHER - DESCRIPTION
. . 8L-19
COMBINATION FLASHER - OPERATION
. . . 8L-19
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, CYLINDER
......9-8
COMMUNICATION - DESCRIPTION
........8E-8
COMMUNICATION - OPERATION
..........8E-8
KJINDEX 5
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page