2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE oil filter
[x] Cancel search: oil filterPage 1589 of 2199

(1) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to reverse flush cooler and lines after
repair
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The transmission cooler and lines should be
reverse flushed whenever a malfunction generates
sludge and/or debris. The torque converter should
also be replaced at the same time.
Failure to flush the cooler and lines will result in
recontamination. Flushing applies to auxiliary coolers
as well. The torque converter should also be replaced
whenever a failure generates sludge and debris. This
is necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in NEUTRAL and
the transmission fluid at normal operating tempera-
ture.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.
The transmission fluid level can be checked two
ways.
PROCEDURE ONE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operat-
ing temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive
vehicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).
(2) Position vehicle on level surface.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to NEUTRAL.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep
dirt from entering tube.
(7) Remove dipstick (Fig. 87) and check fluid level
as follows:
(a) Correct acceptable level is in crosshatch area.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN line.
(d) If fluid is low, add only enough MopartAT F
+4, type 9602, to restore correct level. Do not over-
fill.
21 - 70 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1590 of 2199

PROCEDURE TWO
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select engine.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
figure. (Fig. 88)
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the figure.NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION). The service fluid fill after a
filter change is approximately 3.8 liters (4.0 quarts).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission (Fig. 89).
(4) Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmis-
sion.
(5) Slowly separate front of pan and gasket away
from transmission allowing the fluid to drain into
drain pan.
(6) Hold up pan and remove remaining bolt hold-
ing pan to transmission.
Fig. 88 42/44RE Fluid Fill Graph
Fig. 87 Dipstick Fluid Level Marks - Typical
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - MAXIMUM CORRECT FLUID LEVEL
3 - ACCEPTABLE FLUID LEVEL
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 71
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1591 of 2199

(7) While holding pan level, lower pan and gasket
away from transmission.
(8) Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
(9) Remove screws holding filter to valve body
(Fig. 90).
(10) Separate filter from valve body and pour fluid
in filter into drain pan.
(11) Dispose of used trans fluid and filter properly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position a new transmission oil filter onto the
valve body.
(2) Install the screws to hold the filter to the valve
body. Tighten the screws to 4 N´m (35 in.lbs.).
(3) Clean the gasket surfaces of the transmission
oil pan and transmission pan rail.NOTE: The transmission pan oil gasket is reusable.
Inspect the sealing surfaces of the gasket. If the
sealing ribs on both surfaces appear to be in good
condition, clean the gasket of any foreign material
and reinstall.
(4) Position the oil pan gasket onto the oil pan.
(5) Position the oil pan and gasket onto the trans-
mission and install several bolts to hold the pan and
gasket to the transmission.
(6) Install the remainder of the oil pan bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 13.6 N´m (125 in.lbs.).
(7) Lower vehicle and fill transmission. (Refer to
21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC/
FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL
To avoid overfilling transmission after a fluid
change or overhaul, perform the following procedure:
(1) Remove dipstick and insert clean funnel in
transmission fill tube.
(2) Add following initial quantity of MopartAT F
+4, type 9602, to transmission:
(a) If only fluid and filter were changed, add3
pints (1-1/2 quarts)of ATF +4 to transmission.
(b) If transmission was completely overhauled,
torque converter was replaced or drained, and
cooler was flushed, add12 pints (6 quarts)of ATF
+4 to transmission.
(3) Apply parking brakes.
(4)
Start and run engine at normal curb idle speed.
(5) Apply service brakes, shift transmission
through all gear ranges then back to NEUTRAL, set
parking brake, and leave engine running at curb idle
speed.
(6) Remove funnel, insert dipstick and check fluid
level. If level is low,add fluid to bring level to
MIN mark on dipstick.Check to see if the oil level
is equal on both sides of the dipstick. If one side is
noticably higher than the other, the dipstick has
picked up some oil from the dipstick tube. Allow the
oil to drain down the dipstick tube and re-check.
(7) Drive vehicle until transmission fluid is at nor-
mal operating temperature.
(8) With the engine running at curb idle speed, the
gear selector in NEUTRAL, and the parking brake
applied, check the transmission fluid level.
CAUTION: Do not overfill transmission, fluid foam-
ing and shifting problems can result.
(9) Add fluid to bring level up to MAX arrow
mark.
When fluid level is correct, shut engine off, release
park brake, remove funnel, and install dipstick in fill
tube.
Fig. 89 Transmission Pan
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - GASKET
3-PAN
Fig. 90 Transmission Filter
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - FILTER
21 - 72 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1673 of 2199
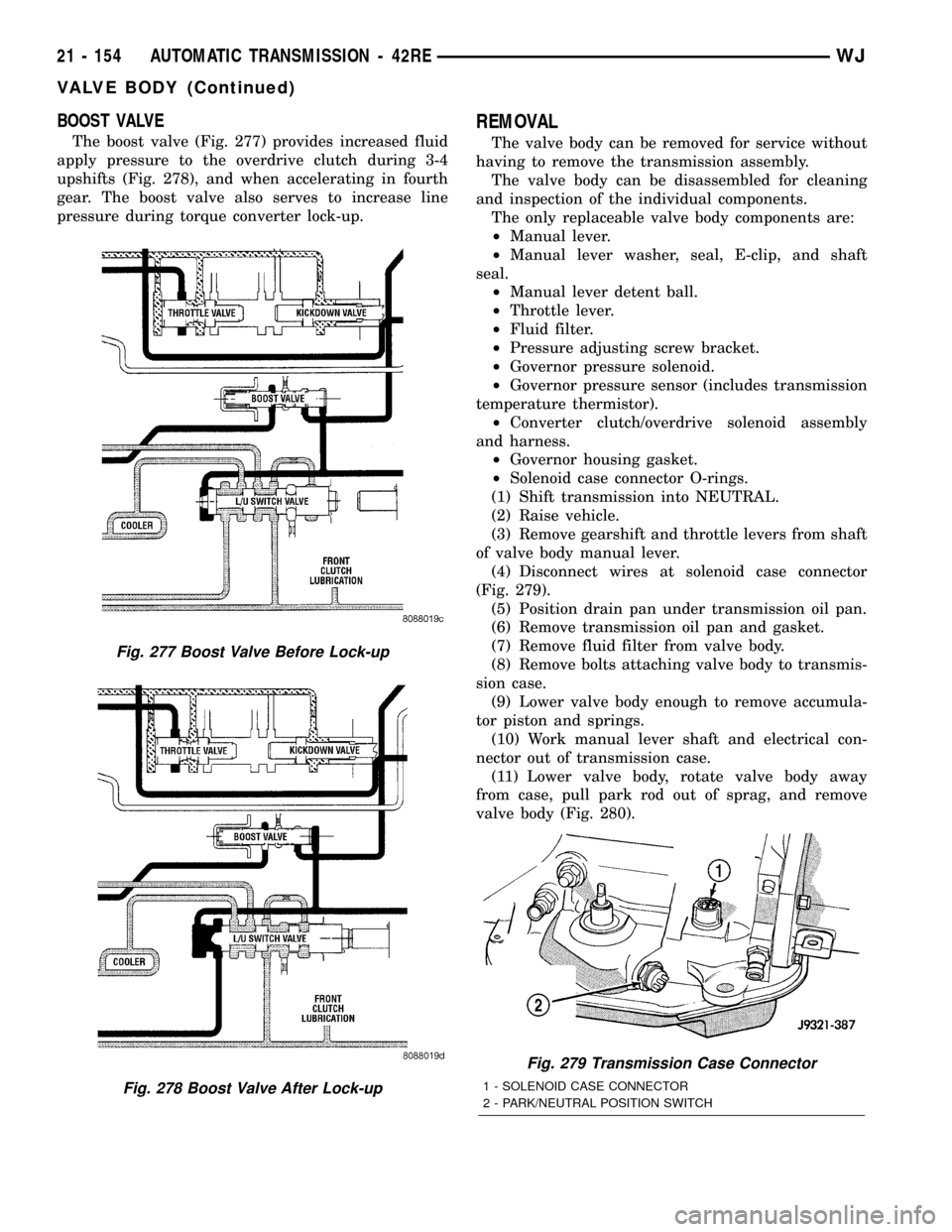
BOOST VALVE
The boost valve (Fig. 277) provides increased fluid
apply pressure to the overdrive clutch during 3-4
upshifts (Fig. 278), and when accelerating in fourth
gear. The boost valve also serves to increase line
pressure during torque converter lock-up.
REMOVAL
The valve body can be removed for service without
having to remove the transmission assembly.
The valve body can be disassembled for cleaning
and inspection of the individual components.
The only replaceable valve body components are:
²Manual lever.
²Manual lever washer, seal, E-clip, and shaft
seal.
²Manual lever detent ball.
²Throttle lever.
²Fluid filter.
²Pressure adjusting screw bracket.
²Governor pressure solenoid.
²Governor pressure sensor (includes transmission
temperature thermistor).
²Converter clutch/overdrive solenoid assembly
and harness.
²Governor housing gasket.
²Solenoid case connector O-rings.
(1) Shift transmission into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove gearshift and throttle levers from shaft
of valve body manual lever.
(4) Disconnect wires at solenoid case connector
(Fig. 279).
(5) Position drain pan under transmission oil pan.
(6) Remove transmission oil pan and gasket.
(7) Remove fluid filter from valve body.
(8) Remove bolts attaching valve body to transmis-
sion case.
(9) Lower valve body enough to remove accumula-
tor piston and springs.
(10) Work manual lever shaft and electrical con-
nector out of transmission case.
(11) Lower valve body, rotate valve body away
from case, pull park rod out of sprag, and remove
valve body (Fig. 280).
Fig. 277 Boost Valve Before Lock-up
Fig. 278 Boost Valve After Lock-up
Fig. 279 Transmission Case Connector
1 - SOLENOID CASE CONNECTOR
2 - PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH
21 - 154 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1685 of 2199

Wipe the governor pressure sensor and solenoid
valve with dry, lint free shop towels only. The O-rings
on the sensor and solenoid valve are the only service-
able components. Be sure the vent ports in the sole-
noid valve are open and not blocked by dirt or debris.
Replace the valve and/or sensor only when DRB scan
tool diagnosis indicates this is necessary. Or, if either
part has sustained physical damage (dented,
deformed, broken, etc.).
CAUTION: Do not turn the small screw at the end of
the solenoid valve for any reason. Turning the
screw in either direction will ruin solenoid calibra-
tion and result in solenoid failure. In addition, the
filter on the solenoid valve is NOT serviceable. Do
not try to remove the filter as this will damage the
valve housing.
INSPECTION
Inspect the throttle and manual valve levers and
shafts. Do not attempt to straighten a bent shaft or
correct a loose lever. Replace these components if
worn, bent, loose or damaged in any way.
Inspect all of the valve body mating surfaces for
scratches, nicks, burrs, or distortion. Use a straight-
edge to check surface flatness. Minor scratches may
be removed with crocus cloth using only very light
pressure.Minor distortion of a valve body mating surface
may be corrected by smoothing the surface with a
sheet of crocus cloth. Position the crocus cloth on a
surface plate, sheet of plate glass or equally flat sur-
face. If distortion is severe or any surfaces are
heavily scored, the valve body will have to be
replaced.
CAUTION: Many of the valves and plugs, such as
the throttle valve, shuttle valve plug, 1-2 shift valve
and 1-2 governor plug, are made of coated alumi-
num. Aluminum components are identified by the
dark color of the special coating applied to the sur-
face (or by testing with a magnet). Do not sand alu-
minum valves or plugs under any circumstances.
This practice could damage the special coating
causing the valves/plugs to stick and bind.
Inspect the valves and plugs for scratches, burrs,
nicks, or scores. Minor surface scratches on steel
valves and plugs can be removed with crocus cloth
butdo not round off the edges of the valve or
plug lands.Maintaining sharpness of these edges is
vitally important. The edges prevent foreign matter
from lodging between the valves and plugs and the
bore.
Inspect all the valve and plug bores in the valve
body. Use a penlight to view the bore interiors.
Replace the valve body if any bores are distorted or
scored. Inspect all of the valve body springs. The
springs must be free of distortion, warpage or broken
coils.
Check the two separator plates for distortion or
damage of any kind. Inspect the upper housing,
lower housing, 3-4 accumulator housing, and transfer
plate carefully. Be sure all fluid passages are clean
and clear. Check condition of the upper housing and
transfer plate check balls as well. The check balls
and ball seats must not be worn or damaged.
Trial fit each valve and plug in its bore to check
freedom of operation. When clean and dry, the valves
and plugs should drop freely into the bores.
Valve body bores do not change dimensionally with
use. If the valve body functioned correctly when new,
it will continue to operate properly after cleaning and
inspection. It should not be necessary to replace a
valve body assembly unless it is damaged in han-
dling.
The only serviceable valve body components are
listed below. The remaining valve body components
are serviced only as part of a complete valve body
assembly. Serviceable parts are:
²dual solenoid and harness assembly
²solenoid gasket
²solenoid case connector O-rings and shoulder
bolt
²switch valve and spring
Fig. 310 Accumulator Housing Components
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
3 - TEFLON SEALS
4 - PISTON SPRING
5 - COVER PLATE AND SCREWS
21 - 166 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1694 of 2199

GOVERNOR BODY, SENSOR AND SOLENOID
(1) Turn valve body assembly over so accumulator
side of transfer plate is facing down.
(2) Install new O-rings on governor pressure sole-
noid and sensor.
(3) Lubricate solenoid and sensor O-rings with
clean transmission fluid.
(4) Install governor pressure sensor in governor
body.
(5) Install governor pressure solenoid in governor
body. Push solenoid in until it snaps into place in
body.
(6) Position governor body gasket on transfer
plate.
(7) Install retainer plate on governor body and
around solenoid. Be sure solenoid connector is posi-
tioned in retainer cutout.
(8) Align screw holes in governor body and trans-
fer plate. Then install and tighten governor body
screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Connect harness wires to governor pressure
solenoid and governor pressure sensor.
(10) Install fluid filter and pan.
(11) Lower vehicle.
(12) Fill transmission with recommended fluid and
road test vehicle to verify repair.
INSTALLATION
(1) Check condition of O-ring seals on valve body
harness connector (Fig. 330). Replace seals on con-
nector body if cut or worn.
(2) Check condition of manual lever shaft seal in
transmission case. Replace seal if lip is cut or worn.
Install new seal with 15/16 deep well socket (Fig.
331).
(3) Check condition of seals on accumulator piston
(Fig. 332). Install new piston seals, if necessary.
(4) Place valve body manual lever in low (1 posi-
tion) so ball on park lock rod will be easier to install
in sprag.
(5) Lubricate shaft of manual lever with petroleum
jelly. This will ease inserting shaft through seal in
case.
(6) Lubricate seal rings on valve body harness con-
nector with petroleum jelly.
(7) Position valve body in case and work end of
park lock rod into and through pawl sprag. Turn pro-
peller shaft to align sprag and park lock teeth if nec-
essary. The rod will click as it enters pawl. Move rod
to check engagement.
CAUTION: It is possible for the park rod to displace
into a cavity just above the pawl sprag during
installation. Make sure the rod is actually engaged
in the pawl and has not displaced into this cavity.(8) Install accumulator springs and piston into
case. Then swing valve body over piston and outer
spring to hold it in place.
(9) Align accumulator piston and outer spring,
manual lever shaft and electrical connector in case.
(10) Then seat valve body in case and install one
or two bolts to hold valve body in place.
(11) Tighten valve body bolts alternately and
evenly to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.) torque.
(12) Install new fluid filter on valve body. Tighten
filter screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install throttle and gearshift levers on valve
body manual lever shaft.
(14) Check and adjust front and rear bands if nec-
essary.
(15) Connect solenoid case connector wires.
(16) Install oil pan and new gasket. Tighten pan
bolts to 13.6 N´m (125 in. lbs.) torque.
(17) Lower vehicle and fill transmission with
MopartATF +4, type 9602, fluid.
(18) Check and adjust gearshift and throttle valve
cables, if necessary.
ADJUSTMENTS - VALVE BODY
CONTROL PRESSURE ADJUSTMENTS
There are two control pressure adjustments on the
valve body;
²Line Pressure
²Throttle Pressure
Line and throttle pressures are interdependent
because each affects shift quality and timing. As a
result, both adjustments must be performed properly
and in the correct sequence. Adjust line pressure first
and throttle pressure last.
Fig. 330 Valve Body Harness Connector O-Ring Seal
1 - CONNECTOR O-RINGS
2 - VALVE BODY HARNESS CONNECTOR
3 - HARNESS
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 175
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1696 of 2199

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE
DESCRIPTION........................178
OPERATION..........................179
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.....................179
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY . 180
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD
TESTING...........................180
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST....................181
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH OPERATION....182
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK................182
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR.....................183
REMOVAL............................183
DISASSEMBLY........................185
CLEANING...........................190
INSPECTION.........................190
ASSEMBLY...........................190
INSTALLATION........................197
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS.............199
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION.....................220
SPECIAL TOOLS
RFE TRANSMISSION.................221
4C RETAINER/BULKHEAD
DISASSEMBLY........................224
ASSEMBLY...........................224
ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL............................225
INSTALLATION........................225
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION........................226
OPERATION..........................226
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK......226
ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK...................227
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL.............228
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID.......................228DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION....................228
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK............................229
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER REPLACEMENT...............230
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL...............................230
GEARSHIFT CABLE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GEARSHIFT
CABLE.............................231
REMOVAL............................231
INSTALLATION........................231
ADJUSTMENTS - GEARSHIFT CABLE......232
HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................233
OPERATION..........................234
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION........................235
OPERATION..........................235
DISASSEMBLY........................237
ASSEMBLY...........................238
INPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................244
OPERATION..........................244
REMOVAL............................244
INSTALLATION........................244
LINE PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................245
OPERATION..........................245
REMOVAL............................245
INSTALLATION........................245
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
DISASSEMBLY........................246
CLEANING...........................247
INSPECTION.........................247
ASSEMBLY...........................247
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................248
OPERATION..........................248
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP
VOLUME CHECK.....................249
DISASSEMBLY........................250
CLEANING...........................252
INSPECTION.........................252
ASSEMBLY...........................253
OIL PUMP FRONT SEAL
REMOVAL............................253
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 177
Page 1698 of 2199
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan
sealing surface (Fig. 1). Refer to this information
when ordering replacement parts. A label is attached
to the transmission case above the stamped numbers.
The label gives additional information which may
also be necessary for identification purposes.
GEAR RATIOS The 545RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime............................1.50:1
3rd .................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
5th .................................0.67:1
Reverse..............................3.00:1
OPERATION
The 545RFE offers full electronic control of all auto-
matic up and downshifts, and features real-time adap-
tive closed-loop shift and pressure control. Electronic
shift and torque converter clutch controls help protect
the transmission from damage due to high tempera-
tures, which can occur under severe operating condi-
tions. By altering shift schedules, line pressure, and
converter clutch control, these controls reduce heat gen-
eration and increase transmission cooling.
To help reduce efficiency-robbing parasitic losses,
the transmission includes a dual-stage transmission
fluid pump with electronic output pressure control.
Under most driving conditions, pump output pres-
sure greatly exceeds that which is needed to keep the
clutches applied. The 545RFE pump-pressure controlsystem monitors input torque and adjusts the pump
pressure accordingly. The primary stage of the pump
works continuously; the second stage is bypassed
when demand is low. The control system also moni-
tors input and output speed and, if incipient clutch
slip is observed, the pressure control solenoid duty
cycle is varied, increasing pressure in proportion to
demand.
A high-travel torque converter damper assembly
allows earlier torque converter clutch engagement to
reduce slippage. Needle-type thrust bearings reduce
internal friction. The 545RFE is packaged in a one-
piece die-cast aluminum case. To reduce NVH, the
case has high lateral, vertical and torsional stiffness.
It is also designed to maximize the benefit of the
structural dust cover that connects the bottom of the
bell housing to the engine bedplate, enhancing over-
all power train stiffness. Dual filters protect the
pump and other components. A pump return filter is
added to the customary main sump filter. Indepen-
dent lubrication and cooler circuits assure ample
pressure for normal transmission operation even if
the cooler is obstructed or the fluid cannot flow due
to extremely low temperatures.
The hydraulic control system design (without elec-
tronic assist) provides the transmission with PARK,
REVERSE, NEUTRAL, SECOND, and THIRD gears,
based solely on driver shift lever selection. This
design allows the vehicle to be driven (in ªlimp-inº
mode) in the event of a electronic control system fail-
ure, or a situation that the Transmission Control
Module (TCM) recognizes as potentially damaging to
the transmission.
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic
functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a
545RFE automatic transmission, check for Diagnos-
tic Trouble Codes with the DRBTscan tool.
Transmission malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Fig. 1 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 179
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)