2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE belt
[x] Cancel search: beltPage 5 of 2199
FASTENER USAGE
DESCRIPTION - FASTENER USAGE
WARNING: USE OF AN INCORRECT FASTENER
MAY RESULT IN COMPONENT DAMAGE OR PER-
SONAL INJURY.
Fasteners and torque specifications references in
this Service Manual are identified in metric and SAE
format.
During any maintenance or repair procedures, it is
important to salvage all fasteners (nuts, bolts, etc.)
for reassembly. If the fastener is not salvageable, a
fastener of equivalent specification must be used.
THREADED HOLE REPAIR
DESCRIPTION - THREADED HOLE REPAIR
Most stripped threaded holes can be repaired using
a Helicoilt. Follow the vehicle or Helicoiltrecommen-
dations for application and repair procedures.
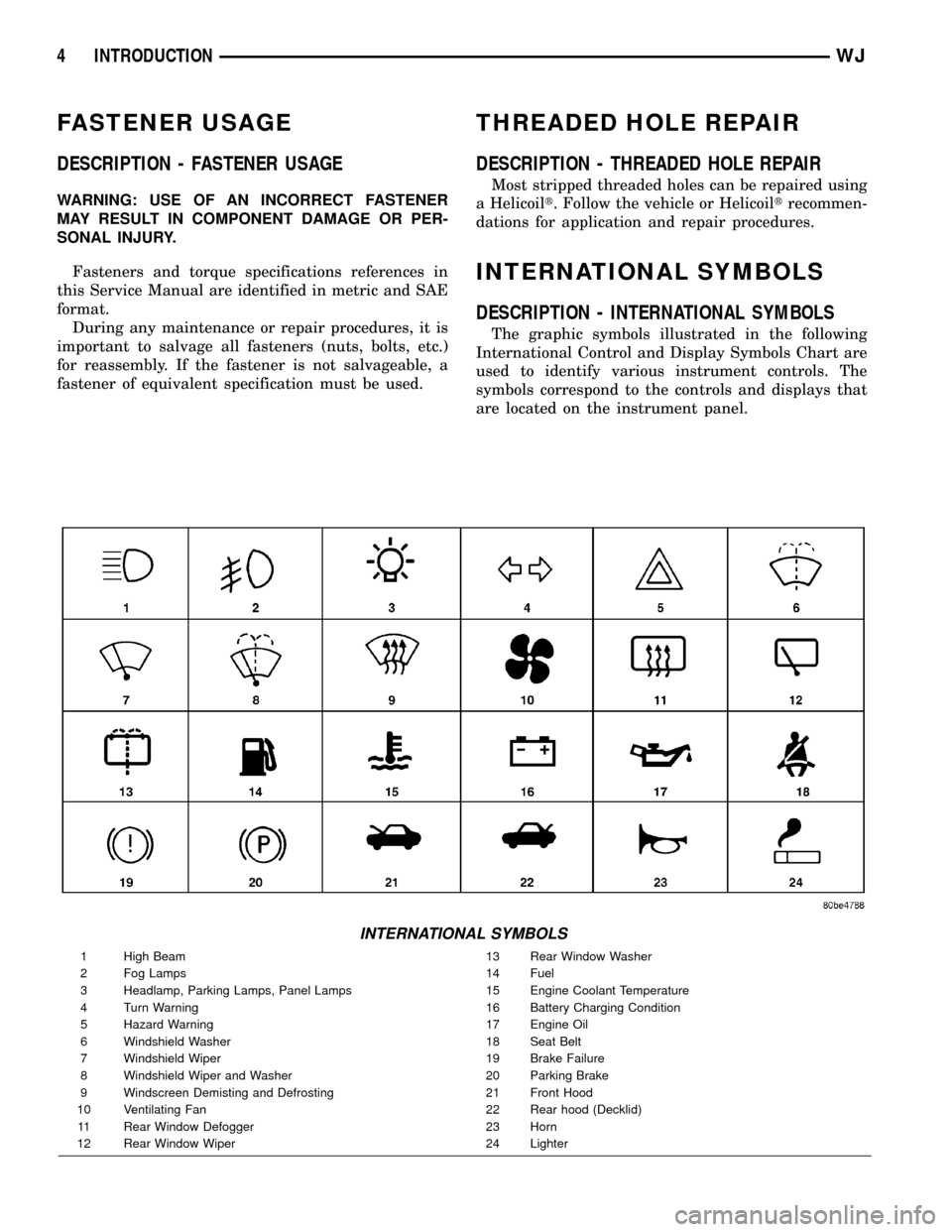
INTERNATIONAL SYMBOLS
DESCRIPTION - INTERNATIONAL SYMBOLS
The graphic symbols illustrated in the following
International Control and Display Symbols Chart are
used to identify various instrument controls. The
symbols correspond to the controls and displays that
are located on the instrument panel.
INTERNATIONAL SYMBOLS
1 High Beam 13 Rear Window Washer
2 Fog Lamps 14 Fuel
3 Headlamp, Parking Lamps, Panel Lamps 15 Engine Coolant Temperature
4 Turn Warning 16 Battery Charging Condition
5 Hazard Warning 17 Engine Oil
6 Windshield Washer 18 Seat Belt
7 Windshield Wiper 19 Brake Failure
8 Windshield Wiper and Washer 20 Parking Brake
9 Windscreen Demisting and Defrosting 21 Front Hood
10 Ventilating Fan 22 Rear hood (Decklid)
11 Rear Window Defogger 23 Horn
12 Rear Window Wiper 24 Lighter
4 INTRODUCTIONWJ
Page 18 of 2199
JUMP STARTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - JUMP STARTING
WARNING: REVIEW ALL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND WARNINGS IN GROUP 8A, BATTERY/START-
ING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS. DO NOT
JUMP START A FROZEN BATTERY, PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT. DO NOT JUMP START WHEN
MAINTENANCE FREE BATTERY INDICATOR DOT IS
YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR. DO NOT JUMP
START A VEHICLE WHEN THE BATTERY FLUID IS
BELOW THE TOP OF LEAD PLATES. DO NOT
ALLOW JUMPER CABLE CLAMPS TO TOUCH
EACH OTHER WHEN CONNECTED TO A BOOSTER
SOURCE. DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BAT-
TERY. REMOVE METALLIC JEWELRY WORN ON
HANDS OR WRISTS TO AVOID INJURY BY ACCI-
DENTAL ARCING OF BATTERY CURRENT. WHEN
USING A HIGH OUTPUT BOOSTING DEVICE, DO
NOT ALLOW BATTERY VOLTAGE TO EXCEED 16
VOLTS. REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED
WITH DEVICE BEING USED.
CAUTION: When using another vehicle as a
booster, do not allow vehicles to touch. Electrical
systems can be damaged on either vehicle.
TO JUMP START A DISABLED VEHICLE:
(1) Raise hood on disabled vehicle and visually
inspect engine compartment for:
²Battery cable clamp condition, clean if necessary.
²Frozen battery.
²Yellow or bright color test indicator, if equipped.
²Low battery fluid level.
²Generator drive belt condition and tension.
²Fuel fumes or leakage, correct if necessary.
CAUTION: If the cause of starting problem on dis-
abled vehicle is severe, damage to booster vehicle
charging system can result.
(2) When using another vehicle as a booster
source, park the booster vehicle within cable reach.
Turn off all accessories, set the parking brake, place
the automatic transmission in PARK or the manual
transmission in NEUTRAL and turn the ignition
OFF.
(3) On disabled vehicle, place gear selector in park
or neutral and set park brake. Turn off all accesso-
ries.
(4) Connect jumper cables to booster battery. RED
clamp to positive terminal (+). BLACK clamp to neg-
ative terminal (-). DO NOT allow clamps at opposite
end of cables to touch, electrical arc will result.
Review all warnings in this procedure.
(5) On disabled vehicle, connect RED jumper cable
clamp to positive (+) terminal. Connect BLACK
jumper cable clamp to engine ground as close to the
ground cable attaching point as possible (Fig. 8).
(6) Start the engine in the vehicle which has the
booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes,
then start the engine in the vehicle with the dis-
charged battery.
CAUTION: Do not crank starter motor on disabled
vehicle for more than 15 seconds, starter will over-
heat and could fail.
(7) Allow battery in disabled vehicle to charge to
at least 12.4 volts (75% charge) before attempting to
start engine. If engine does not start within 15 sec-
onds, stop cranking engine and allow starter to cool
(15 min.), before cranking again.
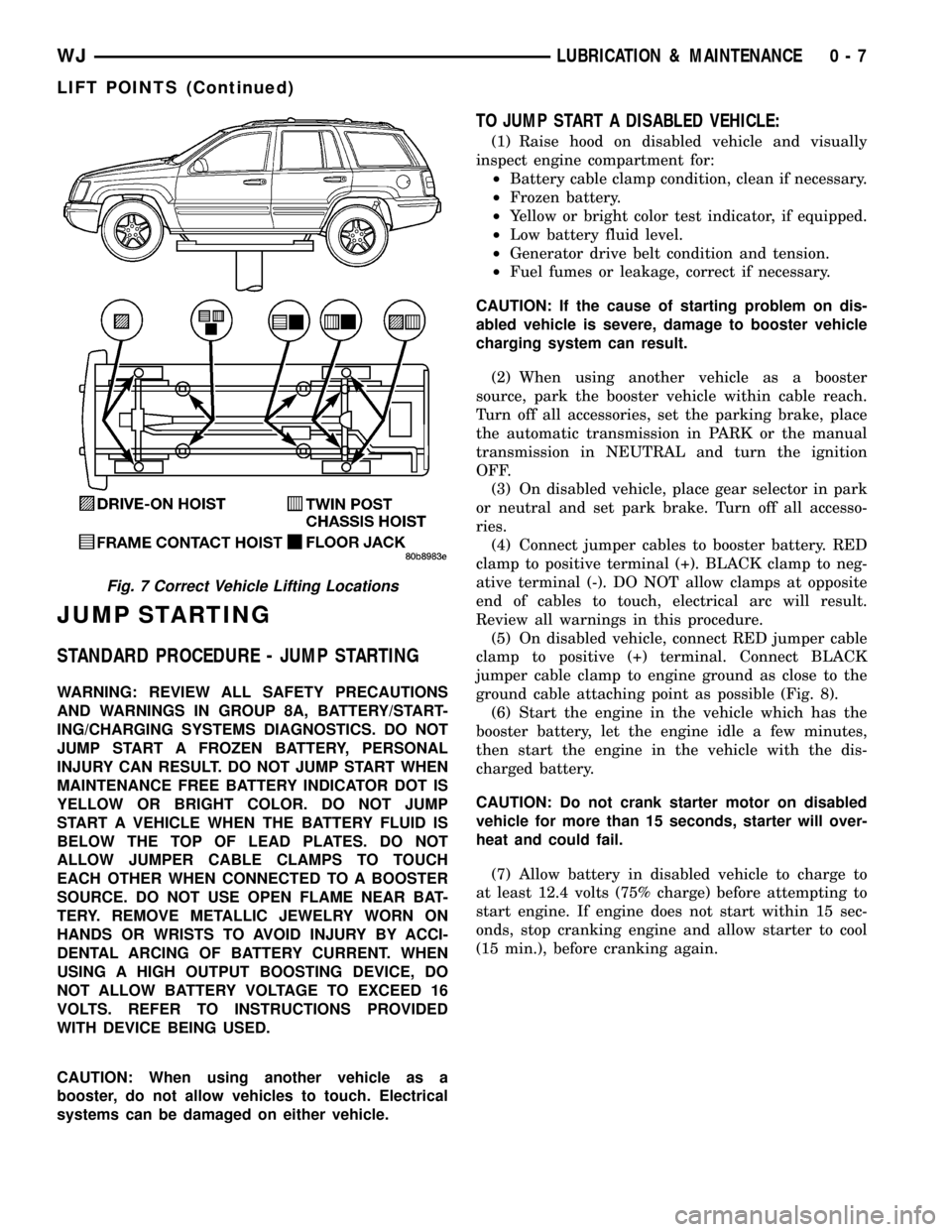
Fig. 7 Correct Vehicle Lifting Locations
WJLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 7
LIFT POINTS (Continued)
Page 62 of 2199

BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front±end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear-end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
WJFRONT AXLE - 186FBI 3 - 17
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 97 of 2199

peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
3 - 52 REAR AXLE - 198RBIWJ
REAR AXLE - 198RBI (Continued)
Page 137 of 2199

and therefore creates pressure in the pump. The tun-
ing of the front and rear axle orifices and valves
inside the gerotor pump is unique and each system
includes a torque-limiting pressure relief valve to
protect the clutch pack, which also facilitates vehicle
control under extreme side-to-side traction varia-
tions. The resulting pressure is applied to the clutch
pack and the transfer of torque is completed.
Under conditions in which opposite wheels are on
surfaces with widely different friction characteristics,
Vari-loktdelivers far more torque to the wheel on
the higher traction surface than do conventional
Trac-loktsystems. Because conventional Trac-lokt
differentials are initially pre-loaded to assure torque
transfer, normal driving (where inner and outer
wheel speeds differ during cornering, etc.) produces
torque transfer during even slight side-to-side speed
variations. Since these devices rely on friction from
this preload to transfer torque, normal use tends to
cause wear that reduces the ability of the differential
to transfer torque over time. By design, the Vari-lokt
system is less subject to wear, remaining more con-
sistent over time in its ability to transfer torque. The
coupling assembly is serviced as a unit. From a ser-
vice standpoint the coupling also benefits from using
the same lubricant supply as the ring and pinion
gears.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, tooth contact, worn/damaged
gears, or the carrier housing not having the proper
offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
3 - 92 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 224 of 2199

COOLING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L
ENGINE..............................1
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
ROUTING 4.7L ENGINE..................1
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM 4.0L
ENGINE..............................1
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM
ROUTING 4.0L ENGINE..................1
DESCRIPTIONÐHOSE CLAMPS...........1
OPERATION
OPERATIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM.........2
OPERATIONÐHOSE CLAMPS............2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)...................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐPRELIMINARY
CHECKS.............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART.............5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM LEAKS......................10DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM DEAERATION.................12
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐDRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L ENGINE.........12
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L ENGINE.........12
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM - 4.0L ENGINE........13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM - 4.0L ENGINE........13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT.................13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM - REVERSE FLUSHING..........14
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE............................14
SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING...........................15
ACCESSORY DRIVE......................16
ENGINE...............................24
TRANSMISSION.........................55
COOLING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L
ENGINE
The cooling system consists of the following items:
²Hydraulic cooling fan and fan drive assembly
²Radiator
²Power steering oil cooler
²Radiator pressure cap
²Thermostat
²Coolant reserve/overflow system
²Transmission oil cooler (if equipped with an
automatic transmission)
²Coolant
²Water pump
²Hoses and hose clamps
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM ROUTING
4.7L ENGINE
For cooling system routing refer to (Fig. 1).
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM 4.0L
ENGINE
The cooling system consists of:
²A radiator
²Mechanical Cooling Fan
²Thermal viscous fan drive-Low disengaged
²Fan shroud (Fig. 2)
²Radiator pressure cap
²Thermostat
²Coolant reserve/overflow system
²Transmission oil cooler (if equipped with an
automatic transmission)
²Coolant
²Water pump
²Hoses and hose clamps
²Accessory drive belt
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM ROUTING
4.0L ENGINE
For cooling system routing refer to (Fig. 3).
DESCRIPTIONÐHOSE CLAMPS
The cooling system utilizes both worm drive and
spring type hose clamps. If a spring type clamp
WJCOOLING 7 - 1
Page 227 of 2199

²SLIGHT TAIL WIND AT IDLE
²SLOW TRAFFIC
²TRAFFIC JAMS
²HIGH SPEED
²STEEP GRADES
Driving techniques that avoid overheating are:
²Idle with A/C off when temperature gauge is at
end of normal range.
²Increase engine speed for more air flow is recom-
mended.(1) TRAILER TOWING:
Consult Trailer Towing section of owners manual.
Do not exceed limits.
(2) AIR CONDITIONING; ADD-ON OR AFTER
MARKET:
A maximum cooling package should have been
ordered with vehicle if add-on or after market A/C is
installed. If not, maximum cooling system compo-
nents should be installed for model involved per
manufacturer's specifications.
(3) RECENT SERVICE OR ACCIDENT REPAIR:
Determine if any recent service has been per-
formed on vehicle that may effect cooling system.
This may be:
²Engine adjustments (incorrect timing)
²Slipping engine accessory drive belt(s)
²Brakes (possibly dragging)
²Changed parts. Incorrect water pump, or pump
rotating in wrong direction due to belt not correctly
routed
²Reconditioned radiator or cooling system refill-
ing (possibly under filled or air trapped in system).
NOTE: If investigation reveals none of the previous
items as a cause for an engine overheating com-
plaint, refer to following Cooling System Diagnosis
charts.
These charts are to be used as a quick-reference
only. Refer to the group text for information.
Fig. 4 Spring Clamp Size Location
1 - SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
7 - 4 COOLINGWJ
COOLING (Continued)
Page 231 of 2199
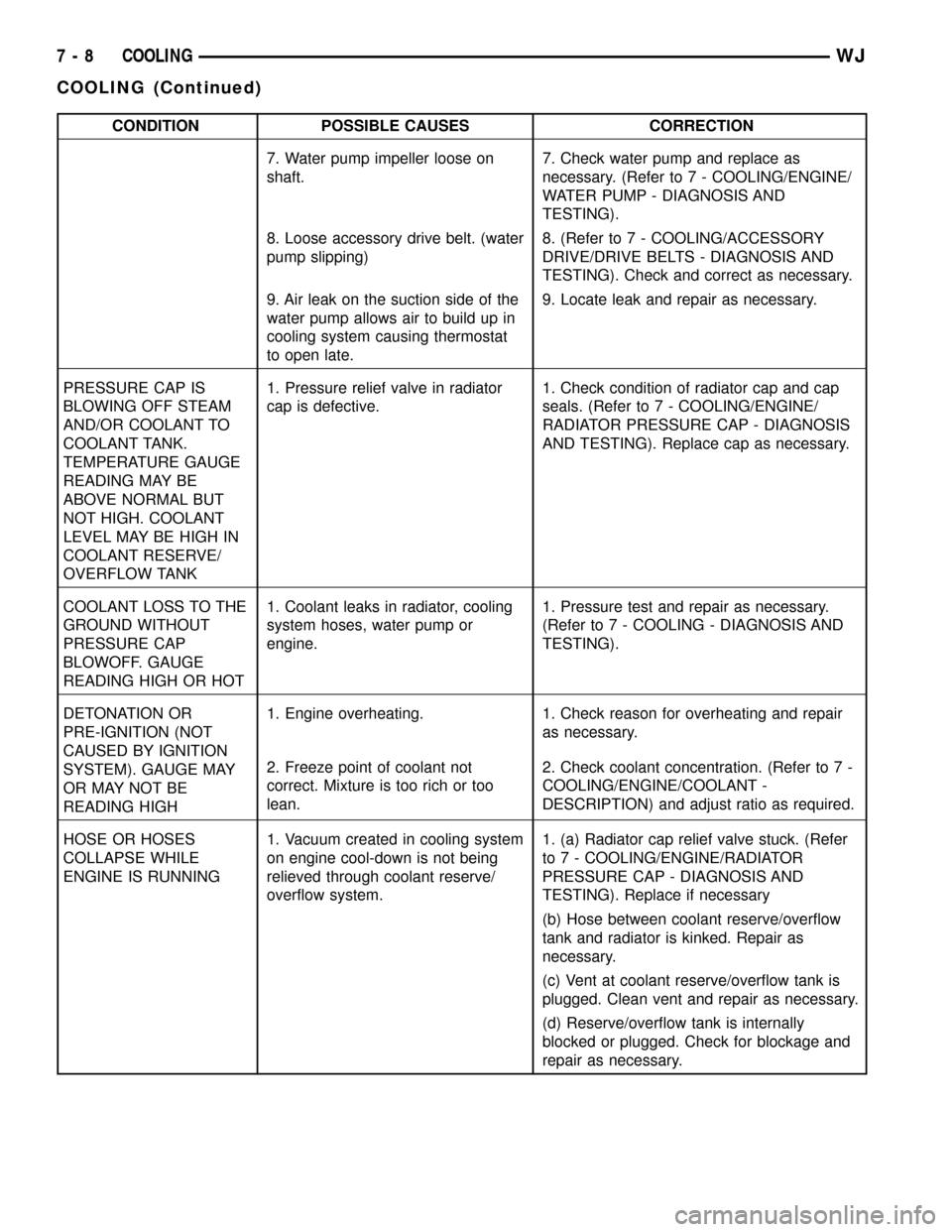
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
7. Water pump impeller loose on
shaft.7. Check water pump and replace as
necessary. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
WATER PUMP - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
8. Loose accessory drive belt. (water
pump slipping)8. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY
DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). Check and correct as necessary.
9. Air leak on the suction side of the
water pump allows air to build up in
cooling system causing thermostat
to open late.9. Locate leak and repair as necessary.
PRESSURE CAP IS
BLOWING OFF STEAM
AND/OR COOLANT TO
COOLANT TANK.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READING MAY BE
ABOVE NORMAL BUT
NOT HIGH. COOLANT
LEVEL MAY BE HIGH IN
COOLANT RESERVE/
OVERFLOW TANK1. Pressure relief valve in radiator
cap is defective.1. Check condition of radiator cap and cap
seals. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING). Replace cap as necessary.
COOLANT LOSS TO THE
GROUND WITHOUT
PRESSURE CAP
BLOWOFF. GAUGE
READING HIGH OR HOT1. Coolant leaks in radiator, cooling
system hoses, water pump or
engine.1. Pressure test and repair as necessary.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
DETONATION OR
PRE-IGNITION (NOT
CAUSED BY IGNITION
SYSTEM). GAUGE MAY
OR MAY NOT BE
READING HIGH1. Engine overheating. 1. Check reason for overheating and repair
as necessary.
2. Freeze point of coolant not
correct. Mixture is too rich or too
lean.2. Check coolant concentration. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/COOLANT -
DESCRIPTION) and adjust ratio as required.
HOSE OR HOSES
COLLAPSE WHILE
ENGINE IS RUNNING1. Vacuum created in cooling system
on engine cool-down is not being
relieved through coolant reserve/
overflow system.1. (a) Radiator cap relief valve stuck. (Refer
to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
PRESSURE CAP - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). Replace if necessary
(b) Hose between coolant reserve/overflow
tank and radiator is kinked. Repair as
necessary.
(c) Vent at coolant reserve/overflow tank is
plugged. Clean vent and repair as necessary.
(d) Reserve/overflow tank is internally
blocked or plugged. Check for blockage and
repair as necessary.
7 - 8 COOLINGWJ
COOLING (Continued)