2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Front drive shaft
[x] Cancel search: Front drive shaftPage 1787 of 2199
OPERATION
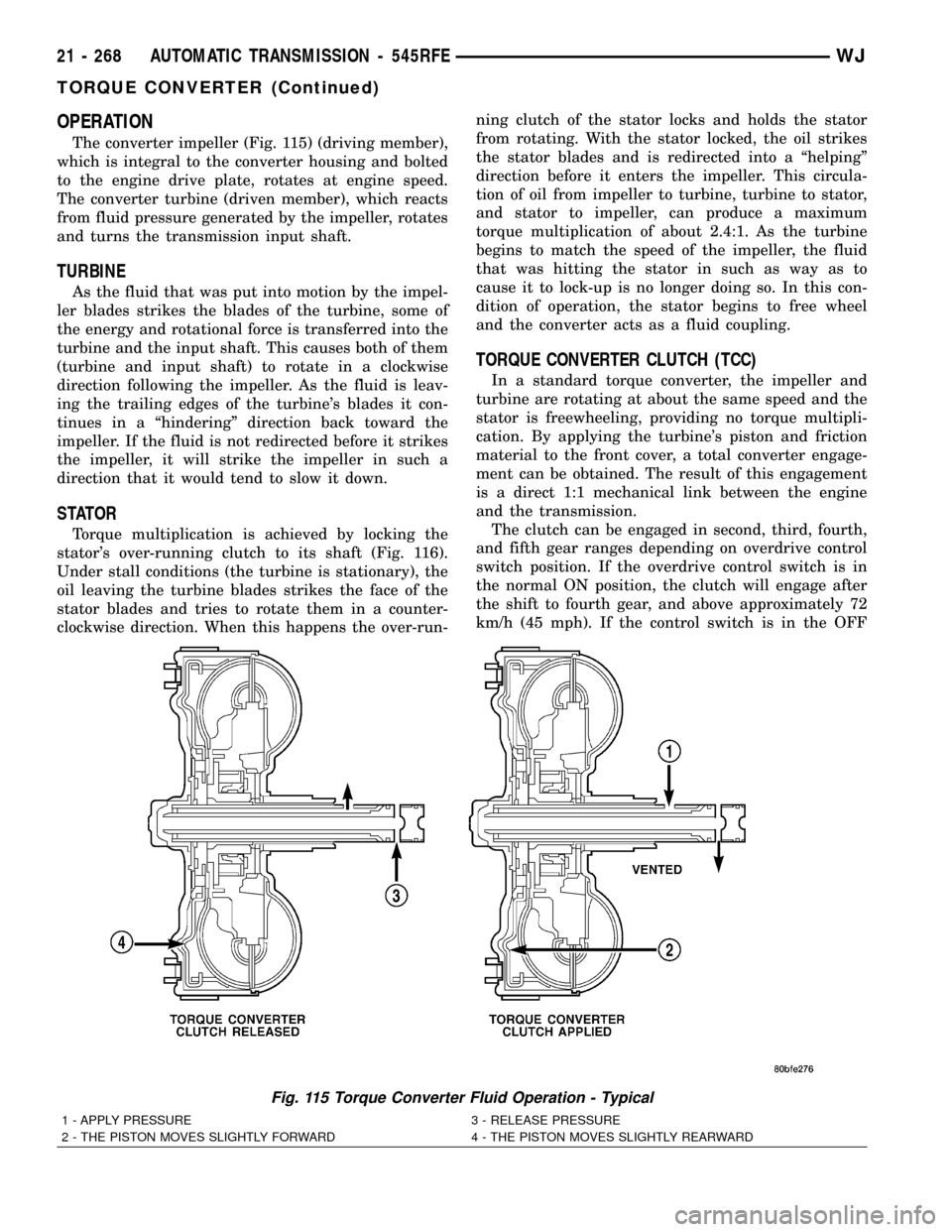
The converter impeller (Fig. 115) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 116).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over-run-ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston and friction
material to the front cover, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The clutch can be engaged in second, third, fourth,
and fifth gear ranges depending on overdrive control
switch position. If the overdrive control switch is in
the normal ON position, the clutch will engage after
the shift to fourth gear, and above approximately 72
km/h (45 mph). If the control switch is in the OFF
Fig. 115 Torque Converter Fluid Operation - Typical
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
21 - 268 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1799 of 2199
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION........................280
OPERATION..........................281
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV242.......................281
REMOVAL............................282
DISASSEMBLY........................282
CLEANING...........................292
INSPECTION.........................293
ASSEMBLY...........................295
INSTALLATION........................307
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN/
REFILL............................310FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................310
INSTALLATION........................310
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................311
OPERATION..........................311
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
REAR RETAINER BUSHING AND SEAL -
NV242HD
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................313
INSTALLATION........................313
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION
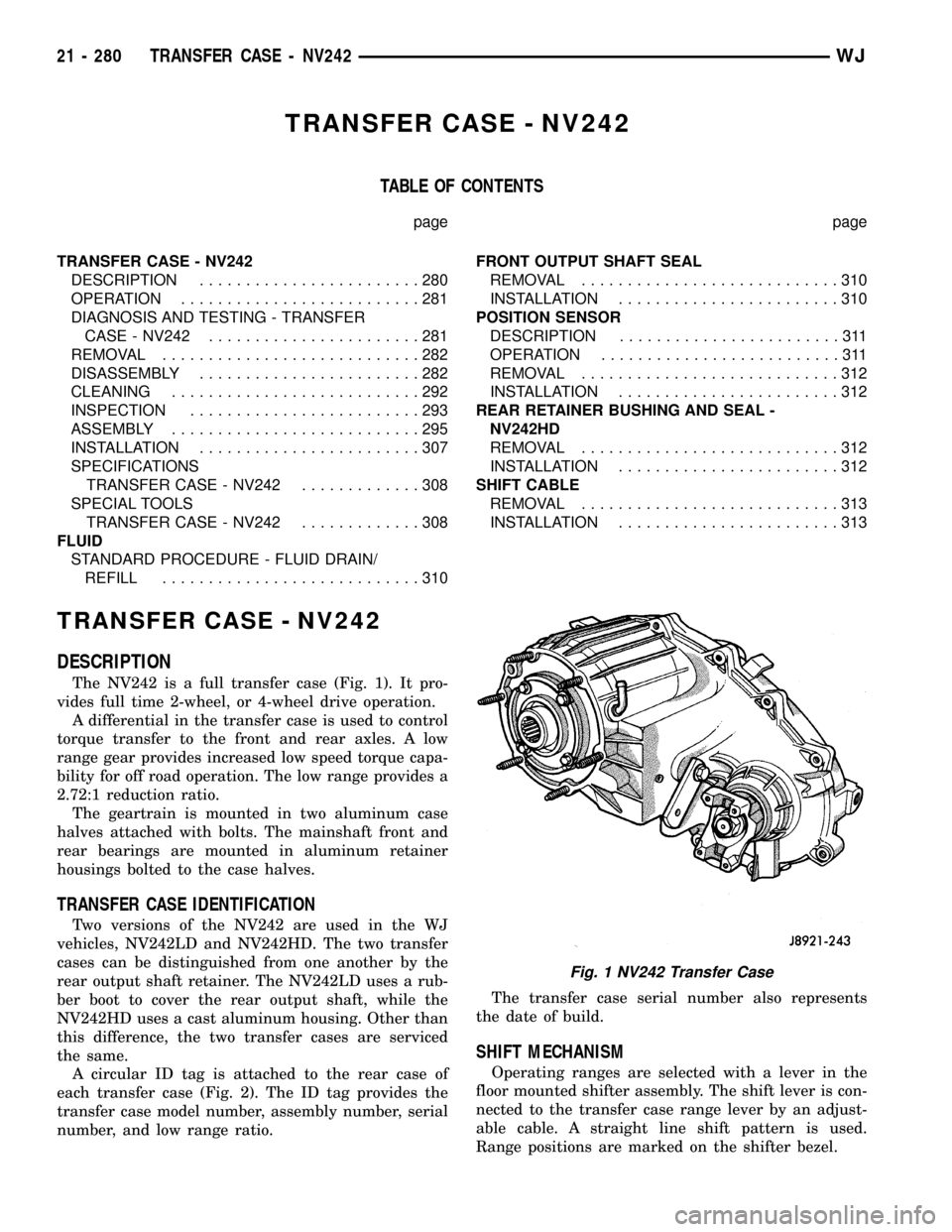
The NV242 is a full transfer case (Fig. 1). It pro-
vides full time 2-wheel, or 4-wheel drive operation.
A differential in the transfer case is used to control
torque transfer to the front and rear axles. A low
range gear provides increased low speed torque capa-
bility for off road operation. The low range provides a
2.72:1 reduction ratio.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case
halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and
rear bearings are mounted in aluminum retainer
housings bolted to the case halves.
TRANSFER CASE IDENTIFICATION
Two versions of the NV242 are used in the WJ
vehicles, NV242LD and NV242HD. The two transfer
cases can be distinguished from one another by the
rear output shaft retainer. The NV242LD uses a rub-
ber boot to cover the rear output shaft, while the
NV242HD uses a cast aluminum housing. Other than
this difference, the two transfer cases are serviced
the same.
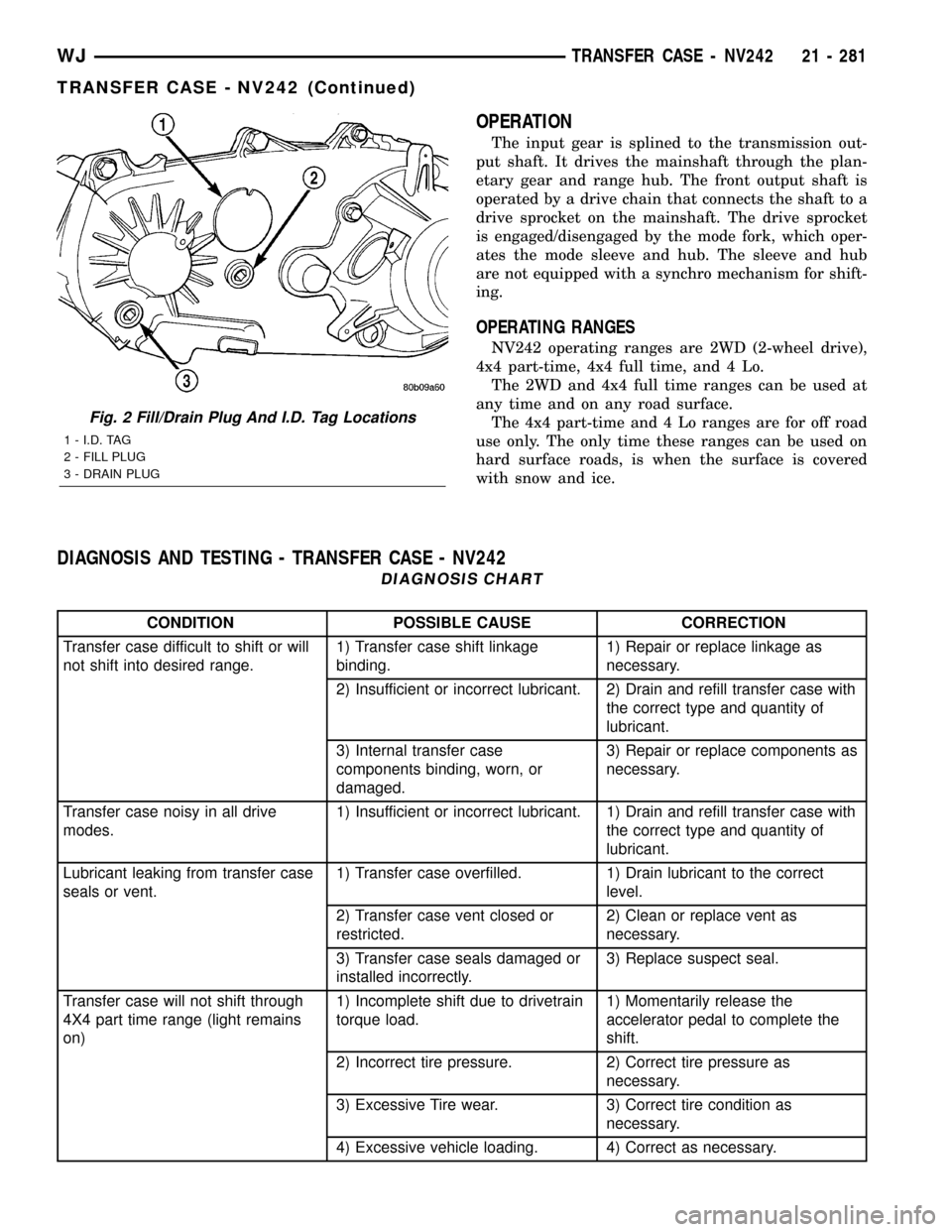
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case (Fig. 2). The ID tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a lever in the
floor mounted shifter assembly. The shift lever is con-
nected to the transfer case range lever by an adjust-
able cable. A straight line shift pattern is used.
Range positions are marked on the shifter bezel.
Fig. 1 NV242 Transfer Case
21 - 280 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
Page 1800 of 2199
OPERATION
The input gear is splined to the transmission out-
put shaft. It drives the mainshaft through the plan-
etary gear and range hub. The front output shaft is
operated by a drive chain that connects the shaft to a
drive sprocket on the mainshaft. The drive sprocket
is engaged/disengaged by the mode fork, which oper-
ates the mode sleeve and hub. The sleeve and hub
are not equipped with a synchro mechanism for shift-
ing.
OPERATING RANGES
NV242 operating ranges are 2WD (2-wheel drive),
4x4 part-time, 4x4 full time, and 4 Lo.
The 2WD and 4x4 full time ranges can be used at
any time and on any road surface.
The 4x4 part-time and 4 Lo ranges are for off road
use only. The only time these ranges can be used on
hard surface roads, is when the surface is covered
with snow and ice.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Transfer case difficult to shift or will
not shift into desired range.1) Transfer case shift linkage
binding.1) Repair or replace linkage as
necessary.
2) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 2) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct type and quantity of
lubricant.
3) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.3) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy in all drive
modes.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct type and quantity of
lubricant.
Lubricant leaking from transfer case
seals or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Transfer case vent closed or
restricted.2) Clean or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Transfer case seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace suspect seal.
Transfer case will not shift through
4X4 part time range (light remains
on)1) Incomplete shift due to drivetrain
torque load.1) Momentarily release the
accelerator pedal to complete the
shift.
2) Incorrect tire pressure. 2) Correct tire pressure as
necessary.
3) Excessive Tire wear. 3) Correct tire condition as
necessary.
4) Excessive vehicle loading. 4) Correct as necessary.
Fig. 2 Fill/Drain Plug And I.D. Tag Locations
1 - I.D. TAG
2 - FILL PLUG
3 - DRAIN PLUG
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 281
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1803 of 2199

REAR RETAINER - NV242HD
(1) Remove extension housing bolts.
(2) Tap extension housing with plastic or rawhide
mallet to loosen sealer (Fig. 10).
(3) Separate extension housing from rear retainer.
(4) Remove rear bearing snap-ring (Fig. 11).
(5) Remove bolts holding rear retainer to rear case
half.
(6) Loosen rear retainer with pry tool to break
sealer bead. Pry only against retainer boss as shown
(Fig. 12).
(7) Slide retainer off case and output shaft (Fig.
13).
OIL PUMP AND REAR CASE HALF
(1) Remove rear bearing O.D. retaining ring with
snap ring pliers. Then tilt pump and slide it off out-
put shaft (Fig. 14)
(2) Remove pickup tube O-ring from pump (Fig.
15) but do not disassemble pump; it is not a repair-
able part.
(3) Remove seal from oil pump with pry tool.
(4) Remove bolts attaching rear case to front case
(Fig. 16). Note position of the two black finish bolts
at each end of the case. These bolts go through the
case dowels and require a washer under the bolt
head.
Fig. 10 Remove Extension Housing
1 - EXTENSION HOUSING
2 - PLASTIC HAMMER
3 - REAR RETAINER
Fig. 11 Remove the Output Bearing Snap-ring
1 - REAR RETAINER
2 - SNAP-RING
3 - REAR BEARING
Fig. 12 Loosening Rear Retainer
1 - REAR RETAINER
2-TAB(2)
3 - SCREWDRIVER
4-TAB
Fig. 13 Rear Retainer Removal
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - REAR RETAINER
21 - 284 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1804 of 2199

(5) Remove rear case from front case (Fig. 17).
Insert screwdrivers into slots cast into each end of
case. Then pry upward to break sealer bead and
remove rear case.
CAUTION: Do not pry on the sealing surface of
either case half as the surfaces will become dam-
aged.
(6) Remove oil pickup tube and screen from rear
case (Fig. 18).
Fig. 14 Oil Pump Removal
1 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 15 Pickup Tube O-Ring Location
1 - OIL PUMP
2 - O-RING
Fig. 16 Spline And Dowel Bolt Locations
1 - DOWEL BOLT AND WASHER (2)
2 - CASE BOLTS
3 - SPLINE HEAD BOLT (1)
Fig. 17 Loosening/Removing Rear Case
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - FRONT CASE
4 - SCREWDRIVER
5 - REAR CASE
Fig. 18 Oil Pickup Screen, Hose And Tube Removal
1 - CONNECTING HOSE
2 - PICKUP SCREEN
3 - PICKUP TUBE
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 285
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1806 of 2199

FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT AND DRIVE CHAIN
(1) Remove drive sprocket snap-ring (Fig. 23).
(2) Remove drive sprocket and chain (Fig. 24).
(3) Remove front output shaft (Fig. 25).
SHIFT FORKS AND MAINSHAFT
(1) Remove shift detent plug, spring and pin (Fig.
26).
Fig. 23 Drive Sprocket Snap-Ring Removal
1 - DRIVE SPROCKET
2 - DRIVE SPROCKET SNAP-RING
Fig. 24 Drive Sprocket And Chain Removal
1 - DRIVE SPROCKET
2 - DRIVE CHAIN
Fig. 25 Removing Front Output Shaft
1 - FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT
Fig. 26 Detent Component Removal
1 - PLUNGER
2 - O-RING
3 - PLUG
4 - SPRING
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 287
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1809 of 2199

(13) Slide low range fork pin out of shift sector
slot.
(14) Remove low range fork and sleeve (Fig. 35).
(15) Remove shift sector.(16) Remove the shift sector shaft bushing and
o-ring (Fig. 36).
INPUT GEAR/LOW RANGE ASSEMBLY
(1) Remove front bearing retainer bolts.
(2) Remove front bearing retainer. Carefully pry
retainer loose with screwdriver (Fig. 37). Position
screwdriver in slots cast into retainer.
(3) Remove input gear snap-ring (Fig. 38).
Fig. 34 Differential Removal
1 - DIFFERENTIAL
2 - MAINSHAFT
Fig. 35 Low Range Fork And Hub Removal
1 - LOW RANGE FORK
2 - FORK HUB
Fig. 36 Remove the Shift Sector O-Ring
1 - TRANSFER CASE FRONT HOUSING
2 - SHIFT SECTOR O-RING
Fig. 37 Front Bearing Retainer Removal
1 - FRONT BEARING RETAINER
2 - RETAINER SLOT
21 - 290 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1814 of 2199

REAR OUTPUT SHAFT/YOKE/DRIVE CHAIN
Check condition of the seal contact surfaces of the
yoke slinger (Fig. 49). This surface must be clean and
smooth to ensure proper seal life. Replace the yoke
nut and seal washer as neither part should be
reused.
Inspect the shaft threads, sprocket teeth, and bear-
ing surfaces. Minor nicks on the teeth can be
smoothed with an oilstone. Use 320-400 grit emery to
smooth minor scratches on the shaft bearing sur-
faces. Rough threads on the shaft can be chased if
necessary. Replace the shaft if the threads are dam-
aged, bearing surfaces are scored, or if any sprocket
teeth are cracked or broken.
Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
Replace the chain and both sprockets if the chain is
stretched, distorted, or if any of the links bind.
Replace the bearings if rough, or noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 50)
FRONT-REAR CASES AND FRONT RETAINER
Inspect the cases and retainer for wear and dam-
age. Clean the sealing surfaces with a scraper and
3M all purpose cleaner. This will ensure proper
sealer adhesion at assembly. Replace the input
retainer seal; do not reuse it.Check case condition. If leaks were a problem, look
for gouges and severe scoring of case sealing sur-
faces. Also make sure the front case mounting studs
are in good condition.
Check the front case mounting studs and vent
tube. The tube can be secured with LoctiteŸ 271 or
680 if loose. The stud threads can be cleaned up with
a die if necessary. Also check condition of the fill/
drain plug threads in the rear case. The threads can
be repaired with a thread chaser or tap if necessary.
Or the threads can be repaired with HelicoilŸ stain-
less steel inserts if required.
OIL PUMP/OIL PICKUP
Examine the oil pump pickup parts. Replace the
pump if any part appears to be worn or damaged. Do
not disassemble the pump as individual parts are not
available. The pump is only available as a complete
assembly. The pickup screen, hose, and tube are the
only serviceable parts and are available separately.
ASSEMBLY
Lubricate transfer case components with automatic
transmission fluid or petroleum jelly (where indi-
cated) during assembly.
CAUTION: The bearing bores in various transfer
case components contain oil feed holes. Make sure
replacement bearings do not block the holes.
Fig. 49 Seal Contact Surface Of Yoke Slinger
1 - FRONT SLINGER (PART OF YOKE)
2 - SEAL CONTACT SURFACE MUST BE CLEAN AND SMOOTH
Fig. 50 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 295
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)