Page 271 of 2100
WHEEL AND TIRE SYSTEM3E±9
Localized tread wear.
480RW004
1. Once spotty wear develops in tread due to hard
braking or abrupt starting, localized wear tends to be
promoted.
Shoulder wear (generally wear develops in outer shoul-
der):
480RW005
1. Camber or toe-in incorrect.
2. Shoulder wear caused by repeated hard-cornering.Wear in shoulders at points opposed to each other.
480RW006
1. Tire or wheel out of round or distorted.
2. Play in bearings or ball joint.
Premature wear in shoulders.
480RW007
1. Flexing of tire excessive due to under-inflation.
Page 272 of 2100
3E±10WHEEL AND TIRE SYSTEM
One sided feather edging.
480RW008
1. Wear caused by repeated hard cornering.
2. Camber or toe-in incorrect.
Page 273 of 2100
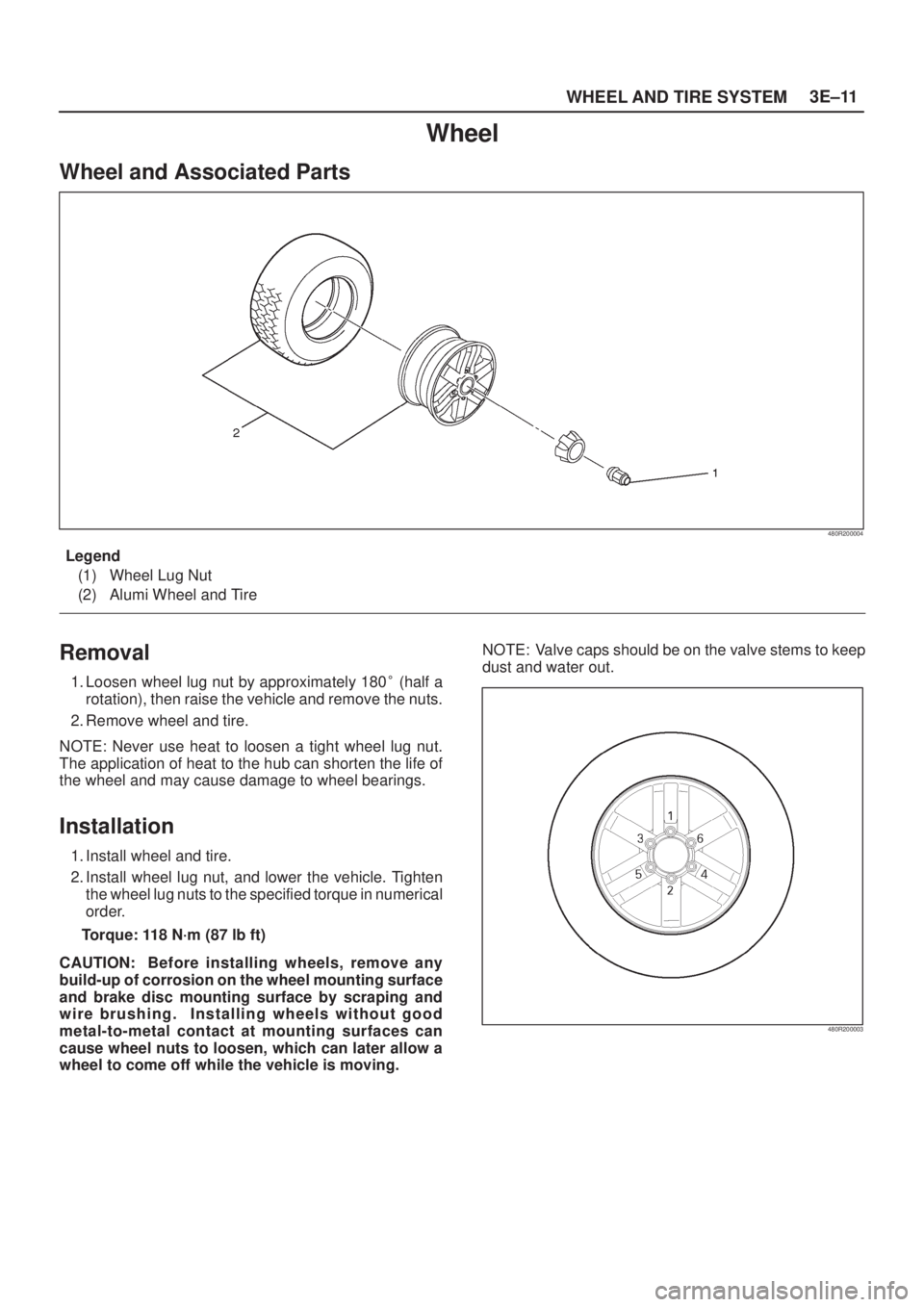
WHEEL AND TIRE SYSTEM3E±11
Wheel
Wheel and Associated Parts
480R200004
Legend
(1) Wheel Lug Nut
(2) Alumi Wheel and Tire
Removal
1. Loosen wheel lug nut by approximately 180� (half a
rotation), then raise the vehicle and remove the nuts.
2. Remove wheel and tire.
NOTE: Never use heat to loosen a tight wheel lug nut.
The application of heat to the hub can shorten the life of
the wheel and may cause damage to wheel bearings.
Installation
1. Install wheel and tire.
2. Install wheel lug nut, and lower the vehicle. Tighten
the wheel lug nuts to the specified torque in numerical
order.
Torque: 118 N´m (87 lb ft)
CAUTION: Before installing wheels, remove any
build-up of corrosion on the wheel mounting surface
and brake disc mounting surface by scraping and
wire brushing. Installing wheels without good
metal-to-metal contact at mounting surfaces can
cause wheel nuts to loosen, which can later allow a
wheel to come off while the vehicle is moving.NOTE: Valve caps should be on the valve stems to keep
dust and water out.
480R200003
Page 274 of 2100

3E±12WHEEL AND TIRE SYSTEM
Tire
Tire Replacement
When replacement is necessary, the original metric tire
size should be used. Most metric tire sizes do not have
exact corresponding alphanumeric tire sizes. It is
recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on the
same axle. If necessary to replace only one tire, it should
be paired with tire having the most tread, to equalize
braking traction.
CAUTION: Do not mix different types of tires such
as radial, bias and bias-belted tires except in
emergencies, because vehicle handling may be
seriously affected and may result in loss of control.
Tire Dismounting
Remove valve cap on valve step and deflate the tire. Then
use a tire changing machine to mount or dismount tires.
Follow the equipment manufacturer's instruction. Do not
use hand tools or tire lever alone to change tires as they
may damage the tire beads or wheel rim.
Tire Mounting
Rim bead seats should be cleaned with a wire brush or
coarse steel wool to remove lubricants, and light rust.
Before mounting a tire, the bead area should be well
lubricated with an approved tire lubricant.
After mounting, inflate the tire to 196kPa (28 psi) so that
beads are completely seated. Inflate the air to specified
pressure and install valve cap to the stem.
WARNING: NEVER STAND OVER TIRE WHEN
INFLATING. BEAD MAY BREAK WHEN BEAD SNAPS
OVER RIM'S SAFETY HUMP AND CAUSE SERIOUS
PERSONAL INJURY.
NEVER EXCEED 240 KPA (35 PSI) PRESSURE WHEN
INFLATING. IF 240 KPA (35 PSI) PRESSURE WILL
NOT SEAT BEADS, DEFLATE, RE-LUBRICATE AND
RE-INFLATE. OVER INFLATION MAY CAUSE THE
BEAD TO BREAK AND CAUSE SERIOUS PERSONAL
INJURY.
Tire Repair
There are many different materials on the market used to
repair tires.
Manufacturers have published detailed instructions on
how and when to repair tires. These instructions can be
obtained from the tire manufacturer if they are not
included with the repair kit.
Wheel Inspection
Damaged wheels and wheels with excessive run-out
must be replaced.
Wheel run out at rim (Base on hub Bore):
Aluminum
1± Vertical play: Less than 0.55 mm (0.022 in)
2± Horizontal play: Less than 0.55 mm (0.022 in)
480RS012
General Balance Procedure
Deposits of mud, etc. must be cleaned from the inside of
the rim.
The tire should be inspected for the following: match
mount paint marks, bent rims, bulges, irregular tire wear,
proper wheel size and inflation pressure. Then balance
according to the equipment manufacturer's
recommendations.
There are two types of wheel and tire balance.
Static balance is the equal distribution of weight around
the wheel.
Assemblies that are statically unbalanced cause a
bouncing action called tramp. This condition will
eventually cause uneven tire wear.
Page 275 of 2100

WHEEL AND TIRE SYSTEM3E±13
480RS013
Legend
(1) Heavy Spot Wheel Shimmy
(2) Add Balance Weights Here
Dynamic balance is the equal distribution of weight on
each side of the wheel center-line so that when the tire
spins there is no tendency for the assembly to move from
side to side. Assemblies that are dynamically unbalanced
may cause shimmy.
480RS014
Legend
(1) Heavy Spot Wheel Hop
(2) Add Balance Weights Here
WARNING: STONES SHOULD BE REMOVED FROM
THE TREAD TO AVOID OPERATOR INJURY DURING
SPIN BALANCING AND TO OBTAIN A GOOD
BALANCE.
Balancing Wheel and Tire
On-vehicle Balancing
On-Vehicle balancing methods vary with equipment and
tool manufacturers. Be sure to follow each
manufacturer's instructions during balancing operation.
Off-vehicle Balancing
Most electronic off-vehicle balancers are more accurate
than the on-vehicle spin balancers. They are easy to use
and give a dynamic balance. Although they do not correct
for drum or disc unbalance (as on- vehicle spin balancing
does), they are very accurate.
480RS015
Page 276 of 2100
3E±14WHEEL AND TIRE SYSTEM
Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
WheelsSize17 y 7JJ
Offset38.0 mm (1.50 in)
P.C.D., wheel studs139.7 mm (5.50 in)
Standard tireSizeP235/65R17
Pressure(Front)180 kPa (26 psi)
Pressure(Rear)180 kPa (26 psi)
Torque Specifications
480R200005
Page 281 of 2100

INTELLIGENT SUSPENSION3F±5
Vertical G-Sensor
Front G-sensors installed inside front actuators and the
rear G-sensor installed on the rear left frame side detect
the vehicle vertical gravity and send a signal to the Control
Unit.
Lateral G-Sensor
The G-sensor installed inside the Control Unit detects the
vehicle turning speed and sends a signal to the Control
Unit.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Several acronyms and abbreviations are commonly used
throughout this section:
BATT
Battery
DLC
Data Link Connector
DTC
Diagnostic Trouble Code
FL
Front Left
FR
Front Right
GND
Ground
HARN
Harness
IG
Ignition
PCM
Powertrain Control Module
RL
Rear Left
RR
Rear Right
SW
Switch
W/L
Warning Lamp
Vout
Voltage output
General Diagnosis
General Information
Intelligent Suspension Control troubles can be classified
into two types, those which can be detected by the
warning lamp and those which can be detected as a
vehicle abnormality by the driver.
In either case, locate the fault in accordance with
theªBASIC DIAGNOSTIC FLOWCHARTº and repair.
Please refer to
Section 3 for the diagnosis of mechanical
troubles such as abnormal noise, vehicle pulls, excessive
tire wear, wheel hop and shimmy, shake or vibration.
Service Precautions
Required Tools and Items:
�Box Wrench
�Special Tool
Some diagnosis procedures in this section require the
installation of a special tool.
J-39200 High Impedance Multimeter
When circuit measurements are requested, use a
circuit tester with high impedance.
Computer System Service Precautions
The Intelligent Suspension Control interfaces directly
with the Control Unit which is a control computer that is
similar in some regards to the Powertrain Control Module.
These modules are designed to withstand normal current
draws associated with vehicle operation. However care
must be taken to avoid overloading any of the Control Unit
circuits. In testing for opens or shorts, do not ground or
apply voltage to any of the circuits unless instructed to do
so by the appropriate diagnostic procedure. These
circuits should only be tested with a high impedance
multimeter (J-39200) or special tools as described in this
section. Power should never be removed or applied to
any control module with the ignition in the ªONº
position.Before removing or connecting battery cables,
fuses or connectors, always turn the ignition switch to
theªOFFº position.
General Service Precautions
The following are general precautions which should be
observed when servicing and diagnosing the Intelligent
Suspension Control and/or other vehicle systems. Failure
to observe these precautions may result in Intelligent
Suspension Control damage.
�If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle using
an electric arc welder, the Control Unit connectors
should be disconnected before the welding operation
begins.
�The Control Unit connectors should never be
connected or disconnected with the ignitionªONº.
Parts Handling
Be careful when handling the actuator, control unit, or
G-sensor. They should not be dropped or thrown,
because the semi-conductor G-sensor tip damage may
result.
Page 299 of 2100

INTELLIGENT SUSPENSION3F±23
DTC5 Vehicle Speed Sensor Open Circuit or Short
Circuit Description
Output speed information is provided to the control unit by
the vehicle speed sensor. The vehicle speed sensor
produces a pulsing AC voltage. The AC voltage level and
number of pulses increases as the speed of the vehicle
increases. The control unit then converts the pulsing
voltage to vehicle speed.
Diagnostic Aids
�Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections
between the control unit 48 way connector and the
speed sensor connectors. Look for possible bent,
backed out, deformed, or damaged terminals. Check
for weak terminal tension as well.
Also check for a chafed wire that could short to bare
metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire inside
the insulation.
�When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
DTC5 Vehicle Speed Sensor Open Circuit or Short
StepActionValue(s)Ye sNo
11. Jack up and support the rear axle on the stand.
2. Change the transfer mode to 2WD, using TOD
switch on instrument panel.
3. Shift the transmission lever in a forward position
and rotate the rear wheels.
Does the speedo-meter operate?
ÐGo to Step 2Go to Step 3
21. Open the throttle and rev up engine speed.
2. Using a volt meter, measure the voltage between
the meter B connector I±23 terminals 7 and 16
(GND).
Does the voltage change alternately at the specified
values?
0V and 12VGo to Step 7Go to Step 5
31. Turn off the starter switch and disconnect the
control connectors C±46 and C±44.
2. Check the continuity between the vehicle speed
sensor connector terminal 3 and meter B connector
I±23 terminal 7.
Is there continuity?
ÐGo to Step 4Go to Step 6
41. Check the continuity between the control unit
connector C±46 terminal 1 and control unit
connector C±44 terminal 48.
Is there continuity?
ÐGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Repair or replace the vehicle speed sensor.
ÐGo to Step 8Ð
6Repair the circuit between the vehicle speed sensor
connector terminal 3 and the meter B connector I±23
terminal 7 or the circuit between the control unit
connector C±44 terminal 48 and the speed sensor
connector terminal 3.
ÐGo to Step 8Ð