2002 DODGE RAM oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 180 of 2255
(12) Install wheel and tire assemblies and lower
the vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove fill hole plug from the differential
housing cover.
(3) Remove differential housing cover and drain
lubricant from the housing.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Do not use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove axle shafts.
(6) Note the orientation of the installation refer-
ence letters stamped on the bearing caps and hous-
ing machined sealing surface (Fig. 26).
(7) Remove the differential bearing caps.
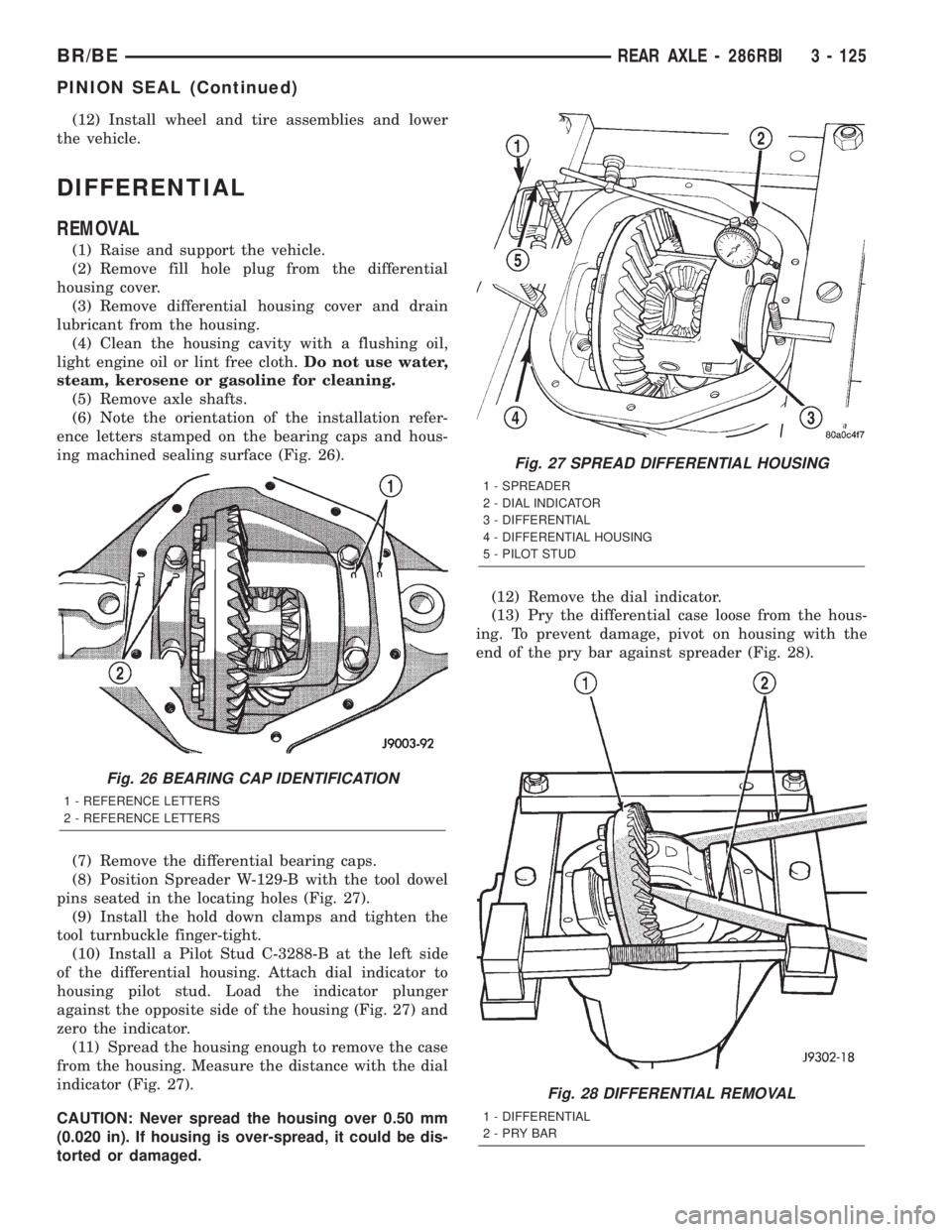
(8) Position Spreader W-129-B with the tool dowel
pins seated in the locating holes (Fig. 27).
(9) Install the hold down clamps and tighten the
tool turnbuckle finger-tight.
(10) Install a Pilot Stud C-3288-B at the left side
of the differential housing. Attach dial indicator to
housing pilot stud. Load the indicator plunger
against the opposite side of the housing (Fig. 27) and
zero the indicator.
(11) Spread the housing enough to remove the case
from the housing. Measure the distance with the dial
indicator (Fig. 27).
CAUTION: Never spread the housing over 0.50 mm
(0.020 in). If housing is over-spread, it could be dis-
torted or damaged.(12) Remove the dial indicator.
(13) Pry the differential case loose from the hous-
ing. To prevent damage, pivot on housing with the
end of the pry bar against spreader (Fig. 28).
Fig. 26 BEARING CAP IDENTIFICATION
1 - REFERENCE LETTERS
2 - REFERENCE LETTERS
Fig. 27 SPREAD DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
1 - SPREADER
2 - DIAL INDICATOR
3 - DIFFERENTIAL
4 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
5 - PILOT STUD
Fig. 28 DIFFERENTIAL REMOVAL
1 - DIFFERENTIAL
2-PRYBAR
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 286RBI 3 - 125
PINION SEAL (Continued)
Page 186 of 2255
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR/
TONE RING
REMOVAL
NOTE: The ring and pinion gears are service as a
matched set. Never replace the ring gear without
replacing the matched pinion gear.
(1) Remove differential from the housing.
(2) Place differential case in a vise with soft metal
jaw protectors. (Fig. 43)
(3) Remove the ring gear bolts.
(4) Drive ring gear from differential case with a
soft hammer (Fig. 43).
(5) Remove the exciter ring from the differential
case by tapping it off with a brass drift.
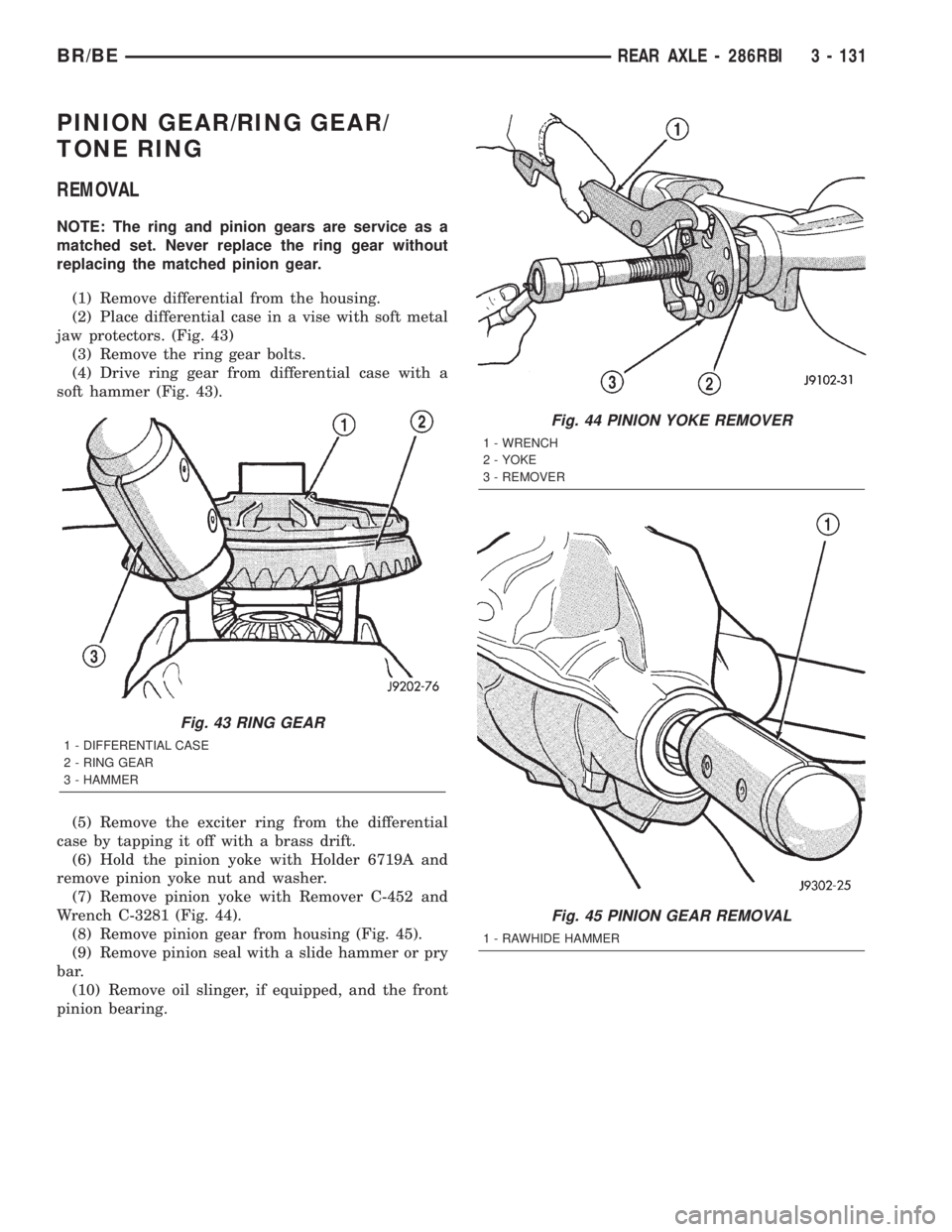
(6) Hold the pinion yoke with Holder 6719A and
remove pinion yoke nut and washer.
(7) Remove pinion yoke with Remover C-452 and
Wrench C-3281 (Fig. 44).
(8) Remove pinion gear from housing (Fig. 45).
(9) Remove pinion seal with a slide hammer or pry
bar.
(10) Remove oil slinger, if equipped, and the front
pinion bearing.
Fig. 43 RING GEAR
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
2 - RING GEAR
3 - HAMMER
Fig. 44 PINION YOKE REMOVER
1 - WRENCH
2 - YOKE
3 - REMOVER
Fig. 45 PINION GEAR REMOVAL
1 - RAWHIDE HAMMER
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 286RBI 3 - 131
Page 188 of 2255
(4) Install pinion front bearing and oil slinger, if
equipped. Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on
the lip of pinion seal.
(5) Installnewpinion seal with an appropriate
installer (Fig. 51).
NOTE: Pinion depth shims are placed between the
rear pinion bearing cone and pinion gear to achieve
proper ring and pinion gear mesh. If ring and piniongears are reused, the pinion depth shim should not
require replacement or adjustment. If the ring and
pinion gears are replaced refer to Adjustments to
select the proper thickness shim.
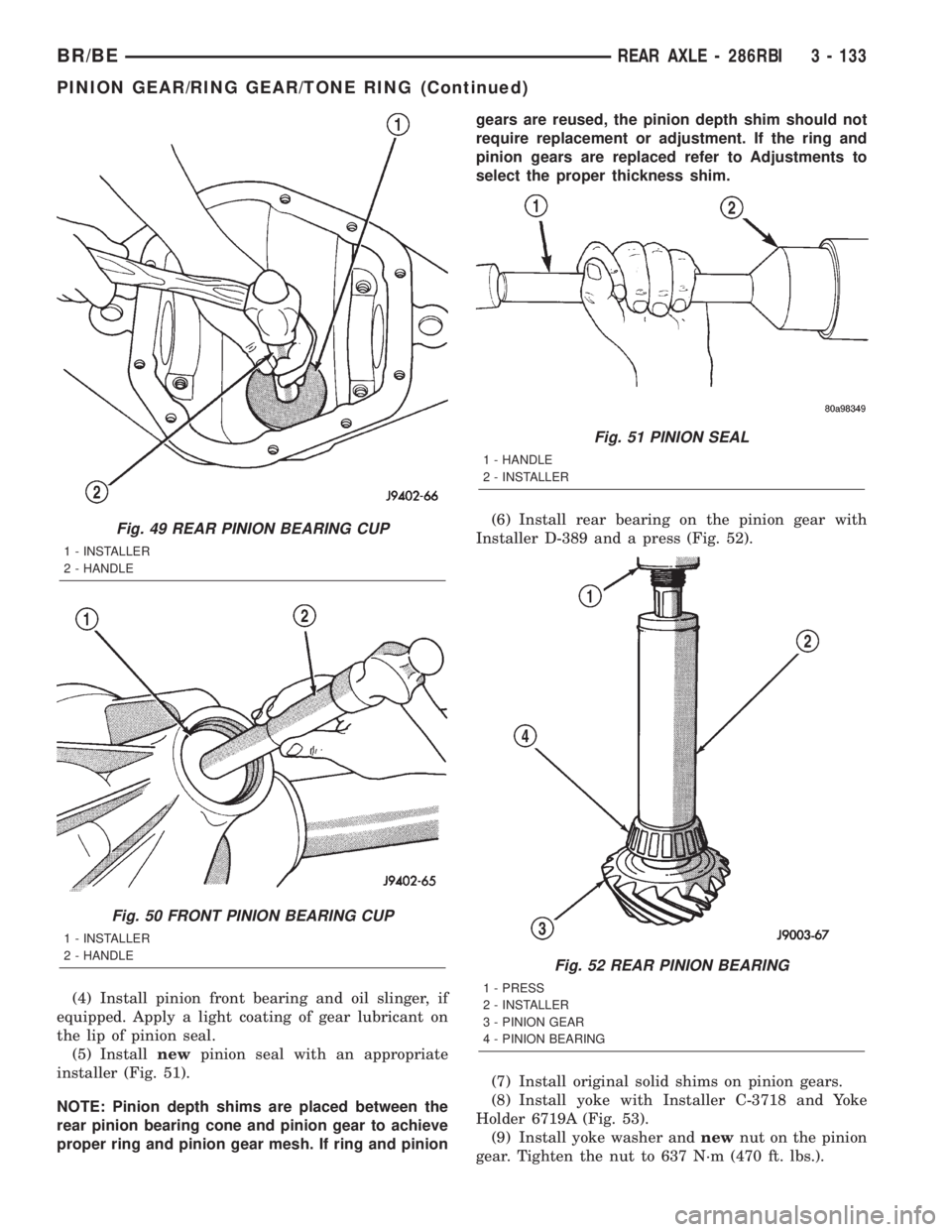
(6) Install rear bearing on the pinion gear with
Installer D-389 and a press (Fig. 52).
(7) Install original solid shims on pinion gears.
(8) Install yoke with Installer C-3718 and Yoke
Holder 6719A (Fig. 53).
(9) Install yoke washer andnewnut on the pinion
gear. Tighten the nut to 637 N´m (470 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 49 REAR PINION BEARING CUP
1 - INSTALLER
2 - HANDLE
Fig. 50 FRONT PINION BEARING CUP
1 - INSTALLER
2 - HANDLE
Fig. 51 PINION SEAL
1 - HANDLE
2 - INSTALLER
Fig. 52 REAR PINION BEARING
1 - PRESS
2 - INSTALLER
3 - PINION GEAR
4 - PINION BEARING
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 286RBI 3 - 133
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR/TONE RING (Continued)
Page 194 of 2255

CAUTION: Never use gasoline, kerosene, alcohol,
motor oil, transmission fluid, or any fluid containing
mineral oil to clean the system components. These
fluids damage rubber cups and seals. Use only
fresh brake fluid or Mopar brake cleaner to clean or
flush brake system components. These are the only
cleaning materials recommended. If system contam-
ination is suspected, check the fluid for dirt, discol-
oration, or separation into distinct layers. Also
check the reservoir cap seal for distortion. Drain
and flush the system with new brake fluid if con-
tamination is suspected.
CAUTION: Use Mopar brake fluid, or an equivalent
quality fluid meeting SAE/DOT standards J1703 and
DOT 3. Brake fluid must be clean and free of con-
taminants. Use fresh fluid from sealed containers
only to ensure proper antilock component opera-
tion.
CAUTION: Use Mopar multi-mileage or high temper-
ature grease to lubricate caliper slide surfaces,
drum brake pivot pins, and shoe contact points on
the backing plates. Use multi-mileage grease or GE
661 or Dow 111 silicone grease on caliper slide pins
to ensure proper operation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM
Base brake components consist of the brake shoes,
calipers, wheel cylinders, brake drums, rotors, brake
lines, master cylinder, booster, and parking brake
components.
Brake diagnosis involves determining if the prob-
lem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic, or vacuum
operated component.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary check.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) Check condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, vibration, and a condition
similar to grab.
(2) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rear
of vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(3) Inspect brake fluid level and condition. Note
that the brake reservoir fluid level will decrease in
proportion to normal lining wear.Also note that
brake fluid tends to darken over time. This is
normal and should not be mistaken for contam-
ination.(a) If fluid level is abnormally low, look for evi-
dence of leaks at calipers, wheel cylinders, brake
lines, and master cylinder.
(b) If fluid appears contaminated, drain out a
sample to examine. System will have to be flushed
if fluid is separated into layers, or contains a sub-
stance other than brake fluid. The system seals
and cups will also have to be replaced after flush-
ing. Use clean brake fluid to flush the system.
(4) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and pedal. Also
note if vehicle was being operated with parking
brake partially applied.
(5) Check brake pedal operation. Verify that pedal
does not bind and has adequate free play. If pedal
lacks free play, check pedal and power booster for
being loose or for bind condition. Do not road test
until condition is corrected.
(6) Check booster vacuum check valve and hose.
(7) If components checked appear OK, road test
the vehicle.
ROAD TESTING
(1) If complaint involved low brake pedal, pump
pedal and note if it comes back up to normal height.
(2) Check brake pedal response with transmission
in Neutral and engine running. Pedal should remain
firm under constant foot pressure.
(3) During road test, make normal and firm brake
stops in 25-40 mph range. Note faulty brake opera-
tion such as low pedal, hard pedal, fade, pedal pulsa-
tion, pull, grab, drag, noise, etc.
(4) Attempt to stop the vehicle with the parking
brake only and note grab, drag, noise, etc.
PEDAL FALLS AWAY
A brake pedal that falls away under steady foot
pressure is generally the result of a system leak. The
leak point could be at a brake line, fitting, hose, or
caliper/wheel cylinder. If leakage is severe, fluid will
be evident at or around the leaking component.
Internal leakage (seal by-pass) in the master cylin-
der caused by worn or damaged piston cups, may
also be the problem cause.
An internal leak in the ABS or RWAL system may
also be the problem with no physical evidence.
LOW PEDAL
If a low pedal is experienced, pump the pedal sev-
eral times. If the pedal comes back up, worn linings,
rotors, drums, or rear brakes out of adjustment are
the most likely causes. The proper course of action is
to inspect and replace all worn component and make
the proper adjustments.
BR/BEBRAKES - BASE 5 - 5
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 196 of 2255

mile or two. However, if the lining is both soaked and
dirt contaminated, cleaning and/or replacement will
be necessary.
BRAKE LINING CONTAMINATION
Brake lining contamination is mostly a product of
leaking calipers or wheel cylinders, worn seals, driv-
ing through deep water puddles, or lining that has
become covered with grease and grit during repair.
Contaminated lining should be replaced to avoid fur-
ther brake problems.
WHEEL AND TIRE PROBLEMS
Some conditions attributed to brake components
may actually be caused by a wheel or tire problem.
A damaged wheel can cause shudder, vibration and
pull. A worn or damaged tire can also cause pull.
Severely worn tires with very little tread left can
produce a grab-like condition as the tire loses and
recovers traction. Flat-spotted tires can cause vibra-
tion and generate shudder during brake operation. A
tire with internal damage such as a severe bruise,
cut, or ply separation can cause pull and vibration.
BRAKE NOISES
Some brake noise is common with rear drum
brakes and on some disc brakes during the first few
stops after a vehicle has been parked overnight or
stored. This is primarily due to the formation of trace
corrosion (light rust) on metal surfaces. This light
corrosion is typically cleared from the metal surfaces
after a few brake applications causing the noise to
subside.
BRAKE SQUEAK/SQUEAL
Brake squeak or squeal may be due to linings that
are wet or contaminated with brake fluid, grease, or
oil. Glazed linings and rotors with hard spots can
also contribute to squeak. Dirt and foreign material
embedded in the brake lining will also cause squeak/
squeal.
A very loud squeak or squeal is frequently a sign of
severely worn brake lining. If the lining has worn
through to the brake shoes in spots, metal-to-metal
contact occurs. If the condition is allowed to continue,
rotors and drums can become so scored that replace-
ment is necessary.
BRAKE CHATTER
Brake chatter is usually caused by loose or worn
components, or glazed/burnt lining. Rotors with hard
spots can also contribute to chatter. Additional causes
of chatter are out-of-tolerance rotors, brake lining not
securely attached to the shoes, loose wheel bearings
and contaminated brake lining.THUMP/CLUNK NOISE
Thumping or clunk noises during braking are fre-
quentlynotcaused by brake components. In many
cases, such noises are caused by loose or damaged
steering, suspension, or engine components. However,
calipers that bind on the slide surfaces can generate
a thump or clunk noise. In addition, worn out,
improperly adjusted, or improperly assembled rear
brake shoes can also produce a thump noise.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANUAL BLEEDING
Use Mopar brake fluid, or an equivalent quality
fluid meeting SAE J1703-F and DOT 3 standards
only. Use fresh, clean fluid from a sealed container at
all times.
(1) Remove reservoir filler caps and fill reservoir.
(2) If calipers, or wheel cylinders were overhauled,
open all caliper and wheel cylinder bleed screws.
Then close each bleed screw as fluid starts to drip
from it. Top off master cylinder reservoir once more
before proceeding.
(3) Attach one end of bleed hose to bleed screw
and insert opposite end in glass container partially
filled with brake fluid (Fig. 1). Be sure end of bleed
hose is immersed in fluid.
(4)
Open up bleeder, then have a helper press down
the brake pedal. Once the pedal is down close the
bleeder. Repeat bleeding until fluid stream is clear and
free of bubbles. Then move to the next wheel.
Fig. 1 Bleed Hose Setup
1 - BLEED HOSE
2 - FLUID CONTAINER PARTIALLY FILLED WITH FLUID
BR/BEBRAKES - BASE 5 - 7
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 202 of 2255
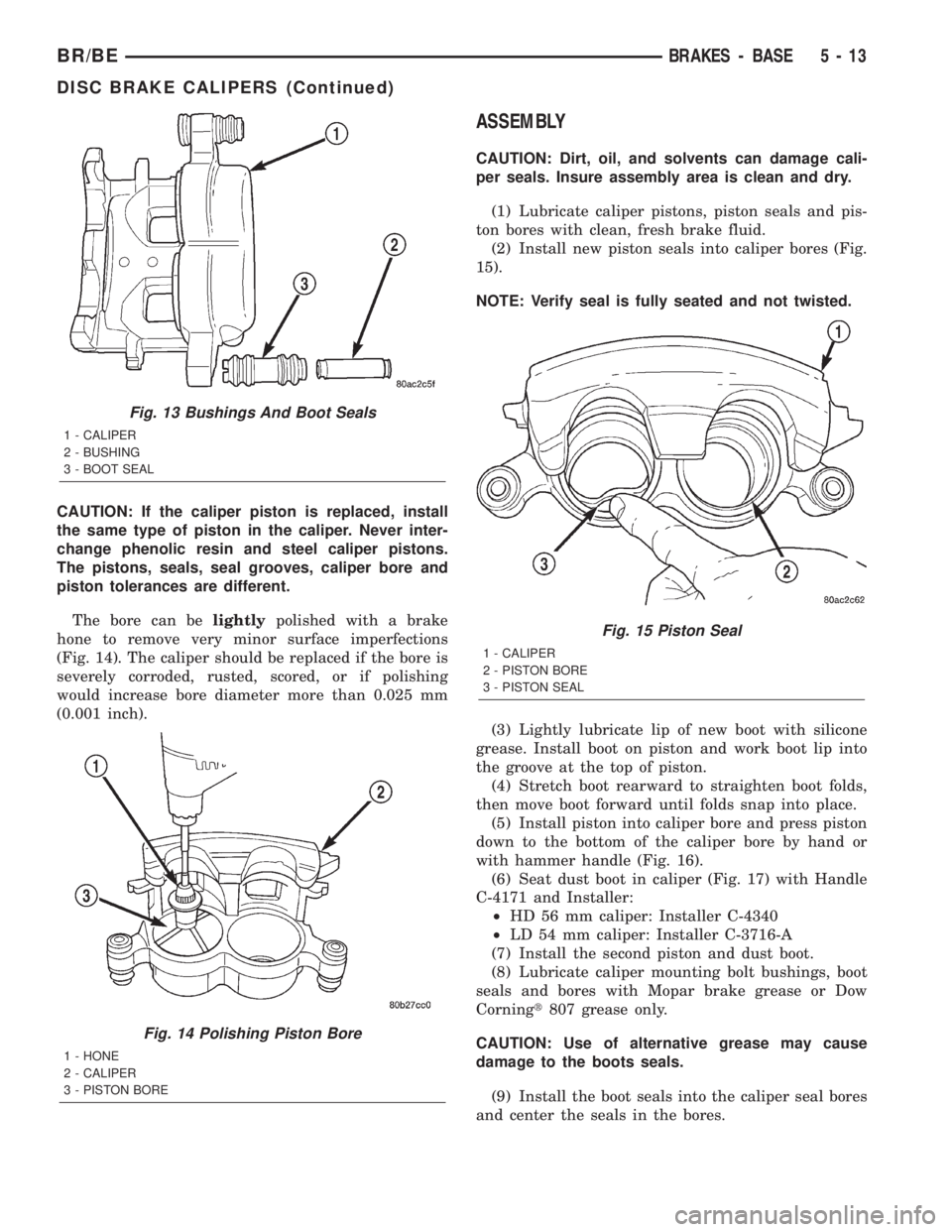
CAUTION: If the caliper piston is replaced, install
the same type of piston in the caliper. Never inter-
change phenolic resin and steel caliper pistons.
The pistons, seals, seal grooves, caliper bore and
piston tolerances are different.
The bore can belightlypolished with a brake
hone to remove very minor surface imperfections
(Fig. 14). The caliper should be replaced if the bore is
severely corroded, rusted, scored, or if polishing
would increase bore diameter more than 0.025 mm
(0.001 inch).
ASSEMBLY
CAUTION: Dirt, oil, and solvents can damage cali-
per seals. Insure assembly area is clean and dry.
(1) Lubricate caliper pistons, piston seals and pis-
ton bores with clean, fresh brake fluid.
(2) Install new piston seals into caliper bores (Fig.
15).
NOTE: Verify seal is fully seated and not twisted.
(3) Lightly lubricate lip of new boot with silicone
grease. Install boot on piston and work boot lip into
the groove at the top of piston.
(4) Stretch boot rearward to straighten boot folds,
then move boot forward until folds snap into place.
(5) Install piston into caliper bore and press piston
down to the bottom of the caliper bore by hand or
with hammer handle (Fig. 16).
(6) Seat dust boot in caliper (Fig. 17) with Handle
C-4171 and Installer:
²HD 56 mm caliper: Installer C-4340
²LD 54 mm caliper: Installer C-3716-A
(7) Install the second piston and dust boot.
(8) Lubricate caliper mounting bolt bushings, boot
seals and bores with Mopar brake grease or Dow
Corningt807 grease only.
CAUTION: Use of alternative grease may cause
damage to the boots seals.
(9) Install the boot seals into the caliper seal bores
and center the seals in the bores.
Fig. 13 Bushings And Boot Seals
1 - CALIPER
2 - BUSHING
3 - BOOT SEAL
Fig. 14 Polishing Piston Bore
1 - HONE
2 - CALIPER
3 - PISTON BORE
Fig. 15 Piston Seal
1 - CALIPER
2 - PISTON BORE
3 - PISTON SEAL
BR/BEBRAKES - BASE 5 - 13
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS (Continued)
Page 204 of 2255

(8) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(9) Verify a firm pedal before moving the vehicle.
FLUID
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts.
Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of
petroleum in the brake fluid.
To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush system. Replace master cylinder, propor-
tioning valve, caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals,
Antilock Brakes hydraulic unit and all hydraulic
fluid hoses.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL
Always clean the master cylinder reservoir and
caps before checking fluid level. If not cleaned, dirt
could enter the fluid.
The fluid fill level is indicated on the side of the
master cylinder reservoir (Fig. 19).
The correct fluid level is to the FULL indicator on
the side of the reservoir. If necessary, add fluid to the
proper level.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications and SAE J1703 standards.
No other type of brake fluid is recommended or
approved for usage in the vehicle brake system. Use
only Mopar brake fluid or an equivalent from a
tightly sealed container.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container of brake fluid will absorb moisture
from the air and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-based
fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of such
type fluids will result in seal damage of the vehicle
brake hydraulic system causing a failure of the
vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids would
be items such as engine oil, transmission fluid,
power steering fluid, etc.
FLUID RESERVOIR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove reservoir cap and empty fluid into
drain container.
(2) Clamp cylinder body in vise with brass protec-
tive jaws.
(3) Remove pins that retain reservoir to master
cylinder. Use hammer and pin punch to remove pins
(Fig. 20).
(4) Loosen reservoir from grommets with pry tool
(Fig. 21).
(5) Remove reservoir by rocking it to one side and
pulling free of grommets (Fig. 22).
(6) Remove old grommets from cylinder body (Fig.
23).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Do not use any type of tool to install the
grommets. Tools may cut, or tear the grommets cre-
ating a leak problem after installation. Install the
grommets using finger pressure only.
(1) Lubricate new grommets with clean brake fluid
and Install new grommets in cylinder body (Fig. 24).
Use finger pressure to install and seat grommets.
(2) Start reservoir in grommets. Then rock reser-
voir back and forth while pressing downward to seat
it in grommets.
Fig. 19 Master Cylinder Fluid Level - Typical
1 - INDICATOR
2 - RESERVOIR
BR/BEBRAKES - BASE 5 - 15
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS (Continued)
Page 227 of 2255

FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The ABS brake system uses 3 wheel speed sensors.
A sensor is mounted to each front steering knuckles.
The third sensor is mounted on top of the rear axle
differential housing.
OPERATION
The Wheel Speed Sensor consists of a magnet sur-
rounded by windings from a single strand of wire.
The sensor sends a small AC signal to the CAB. This
signal is generated by magnetic induction. The mag-
netic induction is created when a toothed sensor ring
(exciter ring or tone wheel) passes the stationary
magnetic WSS.
When the ring gear is rotated, the exciter ring
passes the tip of the WSS. As the exciter ring tooth
approaches the tip of the WSS, the magnetic lines of
force expand, causing the magnetic field to cut across
the sensor's windings. This, in turn causes current to
flow through the WSS circuit (Fig. 2) in one direc-
tion. When the exciter ring tooth moves away from
the sensor tip, the magnetic lines of force collapse
cutting the winding in the opposite direction. This
causes the current to flow in the opposite direction.
Every time a tooth of the exciter ring passes the tip
of the WSS, an AC signal is generated. Each AC sig-
nal (positive to negative signal or sinewave) is inter-
preted by the CAB. It then compares the frequency of
the sinewave to a time value to calculate vehicle
speed. The CAB continues to monitor the frequency
to determine a deceleration rate that would indicate
a possible wheel-locking tendency.
The signal strength of any magnetic induction sen-
sor is directly affected by:
²Magnetic field strength; the stronger the mag-
netic field, the stronger the signal
²Number of windings in the sensor; more wind-
ings provide a stronger signal
²Exciter ring speed; the faster the exciter ring/
tone wheel rotates, the stronger the signal will be
²Distance between the exciter ring teeth and
WSS; the closer the WSS is to the exciter ring/tone
wheel, the stronger the signal will be
The rear WSS is not adjustable. A clearance speci-
fication has been established for manufacturing toler-
ances. If the clearance is not within these
specifications, then either the WSS or other compo-
nents may be damaged. The clearance between the
WSS and the exciter ring is 0.005 ± 0.050 in.
The assembly plant performs a ªRolls Testº on
every vehicle that leaves the assembly plant. One of
the test performed is a test of the WSS. To properlytest the sensor, the assembly plant connects test
equipment to the Data Link Connector (DLC). This
connector is located to the right of the steering col-
umn and attached to the lower portion of the instru-
ment panel (Fig. 3). The rolls test terminal is spliced
to the WSS circuit. The vehicle is then driven on a
set of rollers and the WSS output is monitored for
proper operation.
Fig. 2 Operation of the Wheel Speed Sensor
1 - MAGNETIC CORE
2 - CAB
3 - AIR GAP
4 - EXCITER RING
5 - COIL
Fig. 3 Data Link Connector - Typical
1 - 16±WAY DATA LINK CONNECTOR
5 - 38 BRAKES - ABSBR/BE