2002 DODGE RAM wheel bolt torque
[x] Cancel search: wheel bolt torquePage 243 of 2255

(3) Transfer slave cylinder, release fork and boot,
fork pivot stud and wire/hose brackets to new hous-
ing.
(4) Lubricate release fork and pivot contact sur-
faces with Mopar High Temperature wheel bearing
grease or equivalent before installation.
(5) Align and install clutch housing on transmis-
sion (Fig. 19). Tighten housing bolts closest to align-
ment dowels first and to the following torque values:
²1/4in. diameter ªAº bolts - 4.5 N´m (40 in.lb.).
²3/8in. diameter ªAº bolts - 47.5 N´m (35 ft.lb.).
²7/16in. diameter ªAº bolts - 68 N´m (50 ft.lb.).
²ªBº bolts for 5.2L/5.9L applications - 41 N´m (30
ft.lb.).
²ªBº bolts for 5.9L TD/8.0L applications - 47.5
N´m (35 ft.lb.).
²ªCº bolts for 5.2/5.9L applications - 68 N´m (50
ft.lb.).
²ªCº bolts for 5.9L TD applications - 47.5 N´m (35
ft.lb.).
²ªCº bolts for 8.0L applications - 74.5 N´m (55
ft.lb.).
(6) Install transmission-to-engine strut after
installing clutch housing. Tighten bolt attaching
strut to clutch housing first and engine bolt last.
(7) Install the starter to the clutch housing.
(8) Install the clutch housing dust shield to the
clutch housing. Tighten the bolts to
(9) Install transmission and transfer case, if
equipped. Refer to 21Transmission and Transfer Case
for proper procedures.
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and transfer case, if
equipped. Refer to 21 Transmission and Transfer
Case forprocedures.
(2) Remove clutch housing, for NV4500 equipped
vehicles.
(3) Disconnect release bearing from release fork
and remove bearing (Fig. 20).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Inspect bearing slide surface on transmis-
sion front bearing retainer. Replace retainer if slide
surface is scored, worn or cracked. Inspect release
lever and pivot stud. Be sure stud is secure and in
good condition. Be sure fork is not distorted or
worn. Replace fork spring clips if bent or damaged.
(1) Lubricate input shaft splines, bearing retainer
slide surface, lever pivot ball stud and release lever
pivot surface with Mopar high temperature bearing
grease or equilvalent.
Fig. 18 Transmission/Clutch Housing - NV4500
1 - CLUTCH HOUSING
2 - TRANSMISSION
Fig. 19 Clutch Housing Installation - NV4500
1 - ENGINE BLOCK
2 - CLUTCH DISC AND COVER
3 - CLUTCH HOUSING
4 - DUST COVER
6 - 12 CLUTCHBR/BE
CLUTCH HOUSING (Continued)
Page 244 of 2255

(2) Install release fork and release bearing (Fig.
21) and verify fork and bearing are secured by spring
clips. Also be sure that the release fork is installed
properly.
NOTE: The rear side of the release lever has one
end with a raised area. This raised area goes
toward the slave cylinder side of the transmission.
(3) Install clutch housing, if removed.(4) Install transmission and transfer case, if
equipped. Refer to 21 Transmission and Transfer
Case for procedures.
FLYWHEEL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLYWHEEL
Check flywheel runout whenever misalignment is
suspected. Flywheel runout should not exceed 0.08
mm (0.003 in.). Measure runout at the outer edge of
the flywheel face with a dial indicator. Mount the
indicator on a stud installed in place of one of the fly-
wheel bolts.
Common causes of runout are:
²heat warpage
²improper machining
²incorrect bolt tightening
²improper seating on crankshaft flange shoulder
²foreign material on crankshaft flange
Flywheel machining is not recommended. The fly-
wheel clutch surface is machined to a unique contour
and machining will negate this feature. Minor fly-
wheel scoring can be cleaned up by hand with 180
grit emery or with surface grinding equipment.
Remove only enough material to reduce scoring
(approximately 0.001 - 0.003 in.). Heavy stock
removal isnot recommended.Replace the flywheel
if scoring is severe and deeper than 0.076 mm (0.003
in.). Excessive stock removal can result in flywheel
cracking or warpage after installation; it can also
weaken the flywheel and interfere with proper clutch
release.
Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
flywheel. Dirt and grease on the flange surface may
cock the flywheel causing excessive runout. Use new
bolts when remounting a flywheel and secure the
bolts with Mopar Lock And Seal or equivalent.
Tighten flywheel bolts to specified torque only. Over-
tightening can distort the flywheel hub causing
runout.
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: If the teeth are worn or damaged, the fly-
wheel should be replaced as an assembly. This is
the recommended repair. In cases where a new fly-
wheel is not readily available, (V10/Diesel Engine
only) a replacement ring gear can be installed. The
following procedure must be observed to avoid
damaging the flywheel and replacement gear.
WARNING: WEAR PROTECTIVE GOGGLES OR
SAFETY GLASSES WHILE CUTTING RING GEAR.
Fig. 20 Clutch Release Components
1 - CONED WASHER
2 - CLUTCH HOUSING
3 - RELEASE FORK
4 - RELEASE BEARING AND SLEEVE
5 - PIVOT 23 N´m (200 IN. LBS.)
6 - SPRING
Fig. 21 Clutch Release Fork
1 - PIVOT BALL
2 - FORK
3 - SLAVE CYLINDER OPENING
4 - BEARING
BR/BECLUTCH 6 - 13
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING (Continued)
Page 426 of 2255
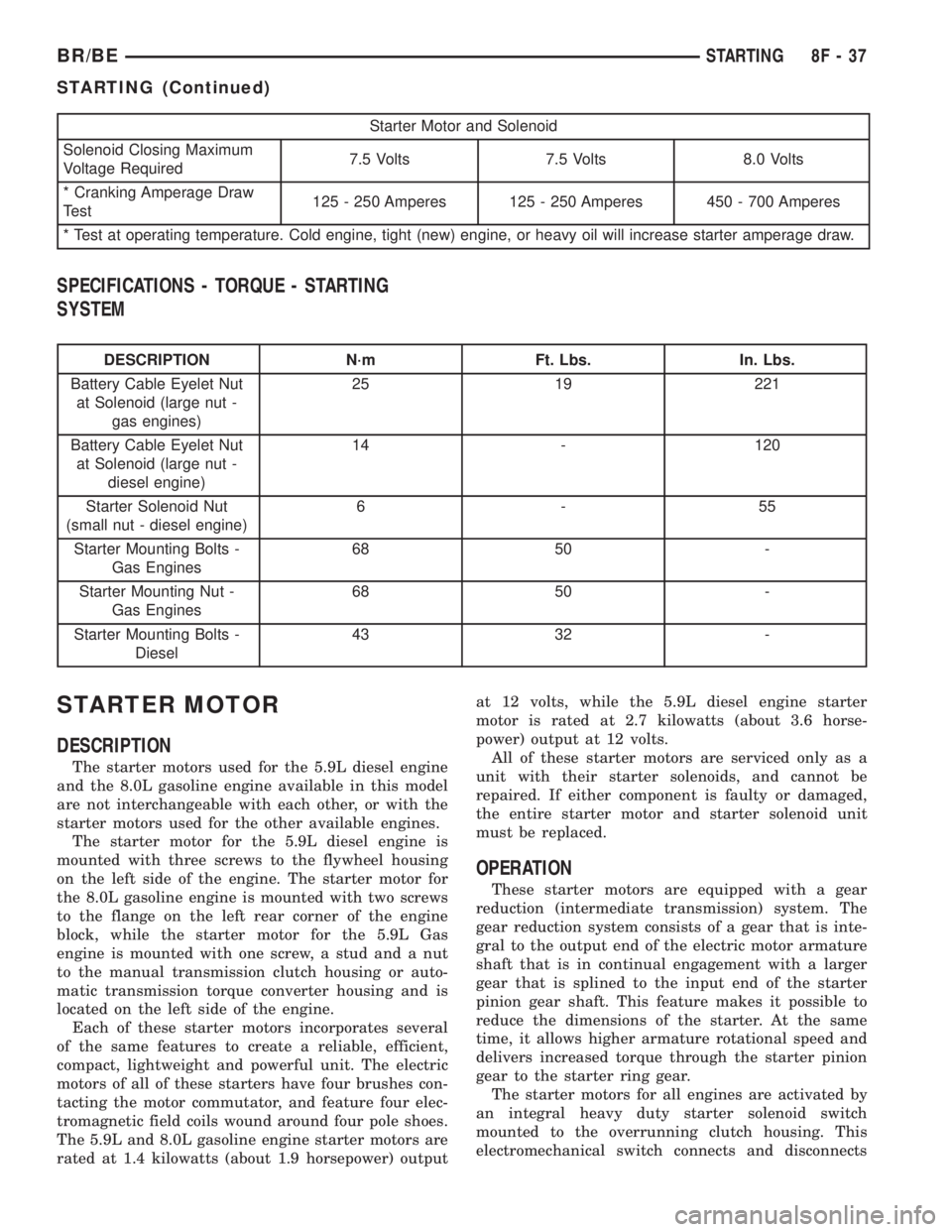
Starter Motor and Solenoid
Solenoid Closing Maximum
Voltage Required7.5 Volts 7.5 Volts 8.0 Volts
* Cranking Amperage Draw
Test125 - 250 Amperes 125 - 250 Amperes 450 - 700 Amperes
* Test at operating temperature. Cold engine, tight (new) engine, or heavy oil will increase starter amperage draw.
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - STARTING
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Battery Cable Eyelet Nut
at Solenoid (large nut -
gas engines)25 19 221
Battery Cable Eyelet Nut
at Solenoid (large nut -
diesel engine)14 - 120
Starter Solenoid Nut
(small nut - diesel engine)6-55
Starter Mounting Bolts -
Gas Engines68 50 -
Starter Mounting Nut -
Gas Engines68 50 -
Starter Mounting Bolts -
Diesel43 32 -
STARTER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The starter motors used for the 5.9L diesel engine
and the 8.0L gasoline engine available in this model
are not interchangeable with each other, or with the
starter motors used for the other available engines.
The starter motor for the 5.9L diesel engine is
mounted with three screws to the flywheel housing
on the left side of the engine. The starter motor for
the 8.0L gasoline engine is mounted with two screws
to the flange on the left rear corner of the engine
block, while the starter motor for the 5.9L Gas
engine is mounted with one screw, a stud and a nut
to the manual transmission clutch housing or auto-
matic transmission torque converter housing and is
located on the left side of the engine.
Each of these starter motors incorporates several
of the same features to create a reliable, efficient,
compact, lightweight and powerful unit. The electric
motors of all of these starters have four brushes con-
tacting the motor commutator, and feature four elec-
tromagnetic field coils wound around four pole shoes.
The 5.9L and 8.0L gasoline engine starter motors are
rated at 1.4 kilowatts (about 1.9 horsepower) outputat 12 volts, while the 5.9L diesel engine starter
motor is rated at 2.7 kilowatts (about 3.6 horse-
power) output at 12 volts.
All of these starter motors are serviced only as a
unit with their starter solenoids, and cannot be
repaired. If either component is faulty or damaged,
the entire starter motor and starter solenoid unit
must be replaced.
OPERATION
These starter motors are equipped with a gear
reduction (intermediate transmission) system. The
gear reduction system consists of a gear that is inte-
gral to the output end of the electric motor armature
shaft that is in continual engagement with a larger
gear that is splined to the input end of the starter
pinion gear shaft. This feature makes it possible to
reduce the dimensions of the starter. At the same
time, it allows higher armature rotational speed and
delivers increased torque through the starter pinion
gear to the starter ring gear.
The starter motors for all engines are activated by
an integral heavy duty starter solenoid switch
mounted to the overrunning clutch housing. This
electromechanical switch connects and disconnects
BR/BESTARTING 8F - 37
STARTING (Continued)
Page 427 of 2255

the feed of battery voltage to the starter motor, also
engaging and disengaging the starter pinion gear
with the starter ring gear.
All starter motors use an overrunning clutch and
starter pinion gear unit to engage and drive a starter
ring gear that is integral to the flywheel (manual
transmission), torque converter or torque converter
drive plate (automatic transmission) mounted on the
rear crankshaft flange.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER MOTOR
Correct starter motor operation can be confirmed
by performing the following free running bench test.
This test can only be performed with starter motor
removed from vehicle. Refer to Starter Specifications
for starter motor specifications.
(1) Remove starter motor from vehicle. Refer to
Starter MotorRemoval and Installation.
(2) Mount starter motor securely in a soft-jawed
bench vise. The vise jaws should be clamped on
mounting flange of starter motor. Never clamp on
starter motor by field frame.
(3) Connect suitable volt-ampere tester and 12-volt
battery to starter motor in series, and set ammeter to
100 ampere scale (250 ampere scale for diesel engine
starters). See instructions provided by manufacturer
of volt-ampere tester being used.
(4) Install jumper wire from solenoid terminal to
solenoid battery terminal. The starter motor should
operate. If starter motor fails to operate, replace
faulty starter motor assembly.
(5) Adjust carbon pile load of tester to obtain free
running test voltage. Refer to Specifications for the
starter motor free running test voltage specifications.
(6) Note reading on ammeter and compare this
reading to free running test maximum amperage
draw. Refer to Specifications for starter motor free
running test maximum amperage draw specifica-
tions.
(7) If ammeter reading exceeds maximum amper-
age draw specification, replace faulty starter motor
assembly.
STARTER MOTOR SOLENOID
This test can only be performed with starter motor
removed from vehicle.
(1) Remove starter motor. Refer toStarter Motor
Removal and Installation.
(2) Disconnect wire from solenoid field coil termi-
nal.
(3) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and solenoid field coil terminal with continuity tester
(Fig. 7). There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace faulty starter motor assembly.(4) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and solenoid case (Fig. 8). There should be continuity.
If not OK, replace faulty starter motor assembly.
REMOVAL
5.9L GASOLINE ENGINE
(1) Disconnect and isolate negative battery cable.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Remove nut and lock washer securing starter
motor to mounting stud (Fig. 9).
(4) While supporting starter motor, remove upper
mounting bolt from starter motor.
(5) If equipped with automatic transmission, slide
cooler tube bracket forward on tubes far enough for
starter motor mounting flange to be removed from
lower mounting stud.
(6) Move starter motor towards front of vehicle far
enough for nose of starter pinion housing to clear
housing. Always support starter motor during this
process, do not let starter motor hang from wire har-
ness.
(7) Tilt nose downwards and lower starter motor
far enough to access and remove nut that secures
battery positive cable wire harness connector eyelet
Fig. 7 Continuity Test Between Solenoid Terminal
and Field Coil Terminal - Typical
1 - OHMMETER
2 - SOLENOID TERMINAL
3 - FIELD COIL TERMINAL
Fig. 8 Continuity Test Between Solenoid Terminal
and Solenoid Case - Typical
1 - SOLENOID TERMINAL
2 - OHMMETER
3 - SOLENOID
8F - 38 STARTINGBR/BE
STARTER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 635 of 2255

(4) Insert servo studs through holes in servo cable
sleeve.
(5) Install servo mounting nuts and tighten to 8.5
N´m (75 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect vacuum line to servo.
(7) Connect electrical connector to servo terminals.
(8) Connect servo cable to throttle body. Refer to
Servo Cable Removal/Installation in this group.
(9) Install battery tray. Tighten all battery tray
mounting hardware to 16 N´m (140 in. lbs.) torque.
(10) Position battery into battery tray.
(11) If equipped, install battery heat shield.
(12) Install battery holddown clamp. Tighten bolt
to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Connect positive battery cable to battery.
(14) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(15) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
INSTALLATION - DIESEL WITH AUTO. TRANS.
(1) Position servo to mounting bracket.
(2) Align hole in cable connector with hole in servo
pin. Install cable-to-servo retaining clip.
(3) Insert servo studs through holes in servo
mounting bracket.
(4) Insert servo studs through holes in servo cable
sleeve.
(5) Install servo mounting nuts and tighten to 8.5
N´m (75 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect vacuum line to servo.
(7) Connect electrical connector to servo terminals.
(8) Connect servo cable to throttle lever by push-
ing cable connector rearward onto lever pin while
holding lever forward.
(9) Install battery tray. Tighten all battery tray
mounting hardware to 16 N´m (140 in. lbs.) torque.
(10) Position battery into battery tray.
(11) If equipped, install battery heat shield.
(12) Install battery holddown clamp. Tighten bolt
to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Connect positive battery cable to battery.
(14) Connect negative battery cables to both bat-
teries.
(15) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
(16) Install cable/lever cover.
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
Gas Engines and Diesel With Auto. Trans.
There are two separate switch pods that operate
the speed control system. The steering-wheel-
mounted switches use multiplexed circuits to provideinputs to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) for
ON, OFF, RESUME, ACCELERATE, SET, DECEL
and CANCEL modes. Refer to the owner's manual for
more information on speed control switch functions
and setting procedures.
The individual switches cannot be repaired. If one
switch fails, the entire switch module must be
replaced.
Diesel With Manual Trans.
There are two separate switch pods that operate
the speed control system. The steering-wheel-
mounted switches use multiplexed circuits to provide
inputs to the Engine Control Module (ECM) for ON,
OFF, RESUME, ACCELERATE, SET, DECEL and
CANCEL modes. Refer to the owner's manual for
more information on speed control switch functions
and setting procedures.
The individual switches cannot be repaired. If one
switch fails, the entire switch module must be
replaced.
OPERATION
Gas Engines and Diesel With Auto. Trans.
When speed control is selected by depressing the
ON, OFF switch, the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) allows a set speed to be stored in its RAM for
speed control. To store a set speed, depress the SET
switch while the vehicle is moving at a speed
between approximately 35 and 85 mph. In order for
the speed control to engage, the brakes cannot be
applied, nor can the gear selector be indicating the
transmission is in Park or Neutral.
The speed control can be disengaged manually by:
²Stepping on the brake pedal.
²Depressing the OFF switch.
²Depressing the CANCEL switch.
The speed control can be disengaged also by any of
the following conditions:
²An indication of Park or Neutral.
²The vehicle speed signal increases at a rate of
10 mph per second (indicates that the co-efficient of
friction between the road surface and tires is
extremely low).
²Depressing the clutch pedal.
²Excessive engine rpm (indicates that the trans-
mission may be in a low gear).
²The vehicle speed signal decreases at a rate of
10 mph per second (indicates that the vehicle may
have decelerated at an extremely high rate).
²If the actual speed is not within 20 mph of the
set speed.
The previous disengagement conditions are pro-
grammed for added safety.
8P - 12 SPEED CONTROLBR/BE
SPEED CONTROL SERVO (Continued)
Page 1082 of 2255
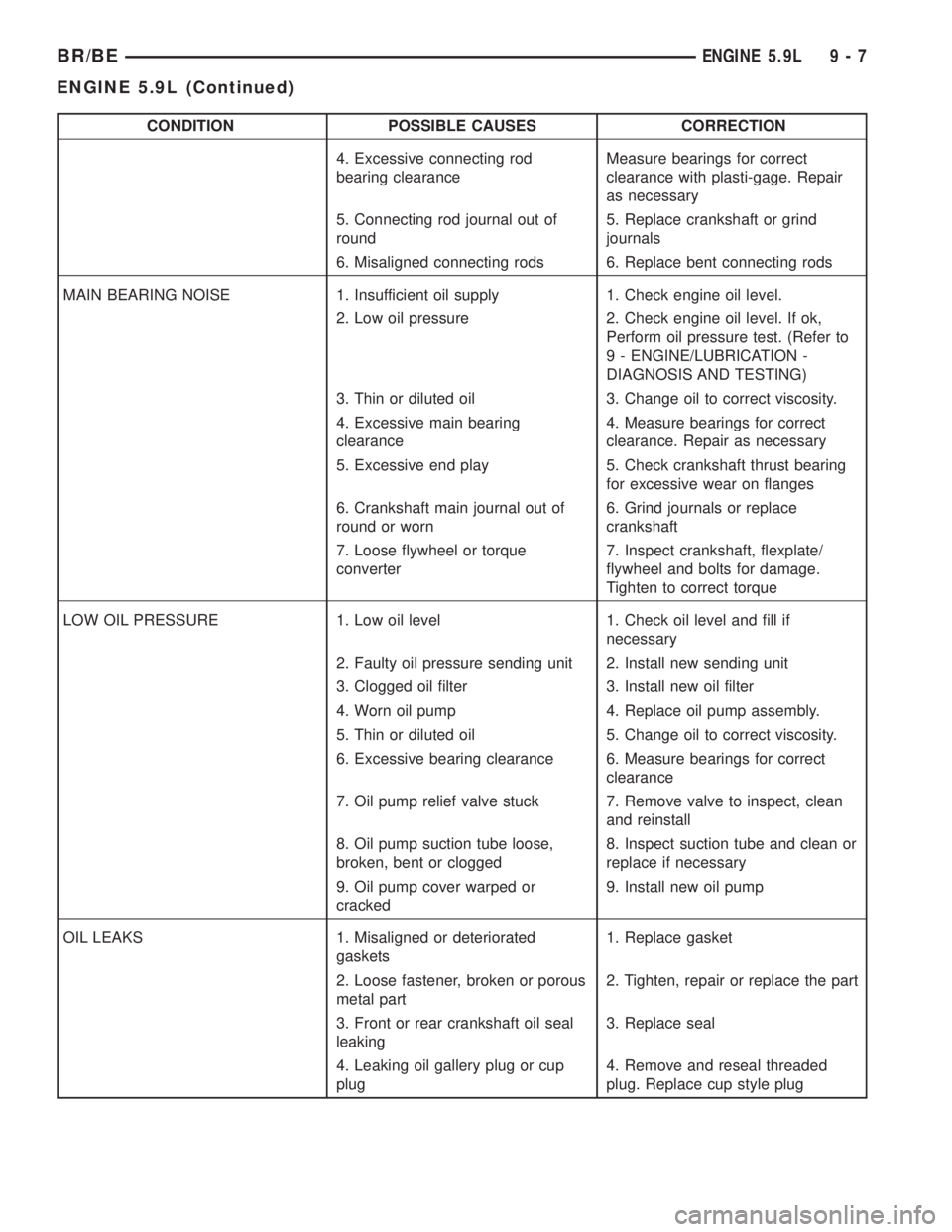
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
4. Excessive connecting rod
bearing clearanceMeasure bearings for correct
clearance with plasti-gage. Repair
as necessary
5. Connecting rod journal out of
round5. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals
6. Misaligned connecting rods 6. Replace bent connecting rods
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure 2. Check engine oil level. If ok,
Perform oil pressure test. (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
3. Thin or diluted oil 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Excessive main bearing
clearance4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary
5. Excessive end play 5. Check crankshaft thrust bearing
for excessive wear on flanges
6. Crankshaft main journal out of
round or worn6. Grind journals or replace
crankshaft
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter7. Inspect crankshaft, flexplate/
flywheel and bolts for damage.
Tighten to correct torque
LOW OIL PRESSURE 1. Low oil level 1. Check oil level and fill if
necessary
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit 2. Install new sending unit
3. Clogged oil filter 3. Install new oil filter
4. Worn oil pump 4. Replace oil pump assembly.
5. Thin or diluted oil 5. Change oil to correct viscosity.
6. Excessive bearing clearance 6. Measure bearings for correct
clearance
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck 7. Remove valve to inspect, clean
and reinstall
8. Oil pump suction tube loose,
broken, bent or clogged8. Inspect suction tube and clean or
replace if necessary
9. Oil pump cover warped or
cracked9. Install new oil pump
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated
gaskets1. Replace gasket
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part2. Tighten, repair or replace the part
3. Front or rear crankshaft oil seal
leaking3. Replace seal
4. Leaking oil gallery plug or cup
plug4. Remove and reseal threaded
plug. Replace cup style plug
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 7
ENGINE 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1092 of 2255
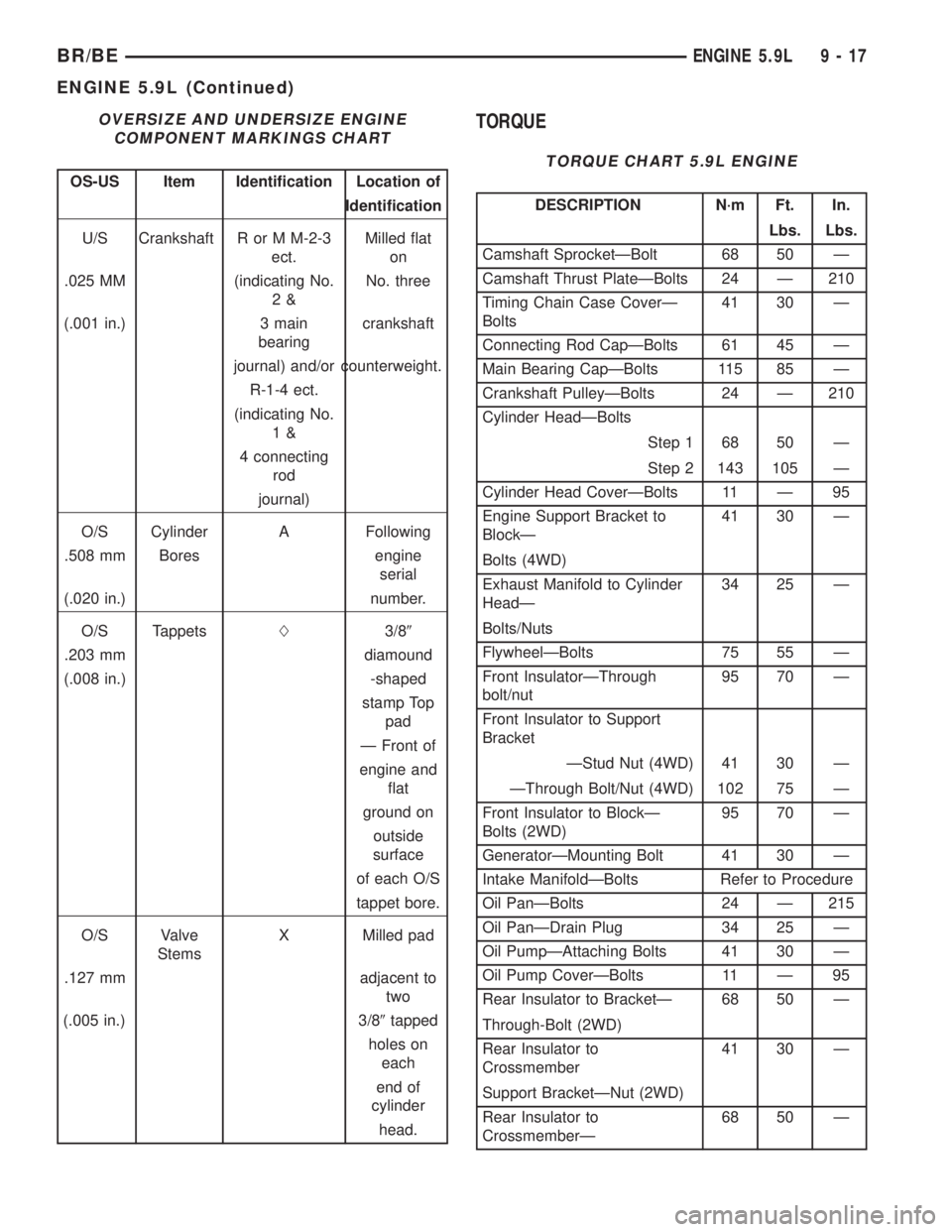
OVERSIZE AND UNDERSIZE ENGINE
COMPONENT MARKINGS CHART
OS-US Item Identification Location of
Identification
U/S Crankshaft R or M M-2-3
ect.Milled flat
on
.025 MM (indicating No.
2&No. three
(.001 in.) 3 main
bearingcrankshaft
journal) and/or counterweight.
R-1-4 ect.
(indicating No.
1&
4 connecting
rod
journal)
O/S Cylinder A Following
.508 mm Bores engine
serial
(.020 in.) number.
O/S TappetsL3/89
.203 mm diamound
(.008 in.) -shaped
stamp Top
pad
Ð Front of
engine and
flat
ground on
outside
surface
of each O/S
tappet bore.
O/S Valve
StemsX Milled pad
.127 mm adjacent to
two
(.005 in.) 3/89tapped
holes on
each
end of
cylinder
head.
TORQUE
TORQUE CHART 5.9L ENGINE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 68 50 Ð
Camshaft Thrust PlateÐBolts 24 Ð 210
Timing Chain Case CoverÐ
Bolts41 30 Ð
Connecting Rod CapÐBolts 61 45 Ð
Main Bearing CapÐBolts 115 85 Ð
Crankshaft PulleyÐBolts 24 Ð 210
Cylinder HeadÐBolts
Step 1 68 50 Ð
Step 2 143 105 Ð
Cylinder Head CoverÐBolts 11 Ð 95
Engine Support Bracket to
BlockÐ41 30 Ð
Bolts (4WD)
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder
HeadÐ34 25 Ð
Bolts/Nuts
FlywheelÐBolts 75 55 Ð
Front InsulatorÐThrough
bolt/nut95 70 Ð
Front Insulator to Support
Bracket
ÐStud Nut (4WD) 41 30 Ð
ÐThrough Bolt/Nut (4WD) 102 75 Ð
Front Insulator to BlockÐ
Bolts (2WD)95 70 Ð
GeneratorÐMounting Bolt 41 30 Ð
Intake ManifoldÐBolts Refer to Procedure
Oil PanÐBolts 24 Ð 215
Oil PanÐDrain Plug 34 25 Ð
Oil PumpÐAttaching Bolts 41 30 Ð
Oil Pump CoverÐBolts 11 Ð 95
Rear Insulator to BracketÐ 68 50 Ð
Through-Bolt (2WD)
Rear Insulator to
Crossmember41 30 Ð
Support BracketÐNut (2WD)
Rear Insulator to
CrossmemberÐ68 50 Ð
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 17
ENGINE 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1104 of 2255

INSTALLATIONÐCAMSHAFT
(1) Lubricate camshaft lobes and camshaft bearing
journals and insert the camshaft to within 51 mm (2
inches) of its final position in cylinder block.
(2) Install Camshaft Holder Tool C-3509 with
tongue back of distributor drive gear (Fig. 21).
(3) Hold tool in position with a distributor lock-
plate bolt. This tool will restrict camshaft from being
pushed in too far and prevent knocking out the welch
plug in rear of cylinder block.Tool should remain
installed until the camshaft and crankshaft
sprockets and timing chain have been installed.
(4) Install camshaft thrust plate and chain oil tab.
Make sure tang enters lower right hole in
thrust plate.Tighten bolts to 24 N´m (210 in. lbs.)
torque. Top edge of tab should be flat against thrust
plate in order to catch oil for chain lubrication.
(5) Install timing chain and gears (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN
AND SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(6) Measure camshaft end play (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). If not within limits
install a new thrust plate.
(7) Each tappet reused must be installed in the
same position from which it was removed.When
camshaft is replaced, all of the tappets must be
replaced.
(8) Install distributor and distributor drive shaft.
(9) Install push rods and tappets.
(10) Install rocker arms.
(11) Install timing case cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(12) Install cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).(13) Install intake manifold (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - INSTALLA-
TION).
(14) Install the engine cover.
(15) Install the A/C Condenser (if equipped)
(16) Install the radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR - INSTALLATION).
(17) Start engine check for leaks.
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CONNECTING ROD
BEARING FITTING
Fit all rods on a bank until completed. DO NOT
alternate from one bank to another, because connect-
ing rods and pistons are not interchangeable from
one bank to another.
The bearing caps are not interchangeable and
should be marked at removal to ensure correct
assembly.
Each bearing cap has a small V-groove across the
parting face. When installing the lower bearing shell,
be certain that the V-groove in the shell is in line
with the V-groove in the cap. This provides lubrica-
tion of the cylinder wall in the opposite bank.
The bearing shells must be installed so that the
tangs are in the machined grooves in the rods and
caps.
Limits of taper or out-of-round on any crankshaft
journals should be held to 0.025 mm (0.001 in.).
Bearings are available in 0.025 mm (0.001 in.), 0.051
mm (0.002 in.), 0.076 mm (0.003 in.), 0.254 mm
(0.010 in.) and 0.305 mm (0.012 in.) undersize.
Install the bearings in pairs. DO NOT use a new
bearing half with an old bearing half. DO NOT
file the rods or bearing caps.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft (Fig. 22) is of a cast nodular steel
splayed type design, with five main bearing journal-
s.The crankshaft is located at the bottom of the
engine block and is held in place with five main bear-
ing caps. The number 3 counterweight is the location
for journal size identification.
OPERATION
The crankshaft transfers force generated by com-
bustion within the cylinder bores to the flywheel or
flexplate.
Fig. 21 Camshaft Holding Tool C-3509 (Installed
Position)
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3509
2 - DRIVE GEAR
3 - DISTRIBUTOR LOCK BOLT
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 29
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) (Continued)