2002 DODGE RAM weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 135 of 2255

torque supplied to the non-slipping wheel. The differ-
ential resist wheel spin on bumpy roads and provide
more pulling power when one wheel looses traction.
Pulling power is provided continuously until both
wheels loose traction. If both wheels slip due to
unequal traction, operation is normal. In extreme
cases of differences of traction, the wheel with the
least traction may spin.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AXLE
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, incorrect pinion depth, tooth
contact, worn/damaged gears, or the carrier housing
not having the proper offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion shaft can also cause a snap-
ping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
NOTE: All driveline components should be exam-
ined before starting any repair.
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
3 - 80 REAR AXLE - 267RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)
Page 136 of 2255
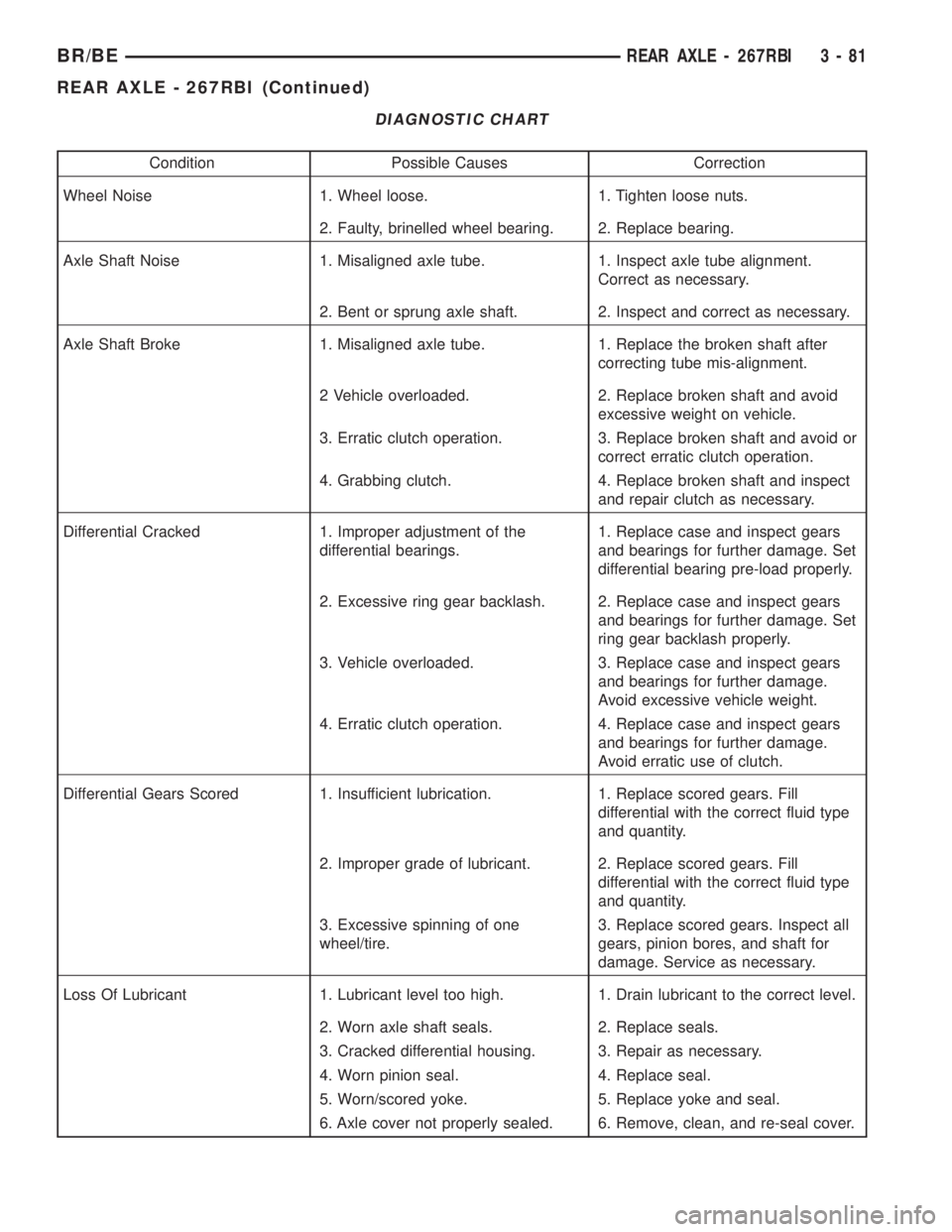
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid or
correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage. Set
differential bearing pre-load properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage. Set
ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal cover.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 267RBI 3 - 81
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)
Page 164 of 2255

noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion shaft can also cause a snap-
ping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise issimilar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
NOTE: All driveline components should be exam-
ined before starting any repair.
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
Fig. 3 TRAC-LOK LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL
1 - CASE
2 - RING GEAR
3 - DRIVE PINION
4 - PINION GEAR
5 - MATE SHAFT
6 - CLUTCH PACK
7 - SIDE GEAR
8 - CLUTCH PACK
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 286RBI 3 - 109
REAR AXLE - 286RBI (Continued)
Page 165 of 2255

DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
3 - 110 REAR AXLE - 286RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 286RBI (Continued)
Page 302 of 2255

(4) Install thermostat into recessed machined
groove on intake manifold (Fig. 25).
(5) Install thermostat housing (Fig. 25).
(6) Install housing-to-intake manifold bolts.
Tighten bolts to 25 N´m (220 in. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION: Housing bolts should be tightened
evenly to prevent damage to housing and to pre-
vent leaks.
(7) Connect the wiring to both sensors.
(8) Install the upper radiator hose and hose clamp
to thermostat housing.
(9) Install support rod.
(10) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(12) Start and warm engine. Check for leaks.
ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT - 5.9L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: Do not operate an engine without a ther-
mostat, except for servicing or testing. An engine
with the thermostat removed will operate in the
radiator bypass mode, causing an overheat condi-
tion.
The thermostat of the 5.9L diesel engine is located
in the front of the cylinder head, underneath the
water outlet connector (Fig. 26).
The same thermostat is used for winter and sum-
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with-
out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes longer engine
warmup time, unreliable warmup performance,
increased exhaust emissions and crankcase condensa-
tion that can result in sludge formation.
OPERATION
The wax pellet is located in a sealed container at
the spring end of the thermostat. When heated, the
pellet expands, overcoming closing spring tension
and water pump pressure to force the valve to open.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐTHERMOSTAT
The cooling system used with the diesel engine
provides the extra coolant capacity and extra cooling
protection needed for higher GVWR (Gross Vehicle
Weight Rating) and GCWR (Gross Combined Weight
Rating) vehicles.
This system capacity will not effect warm up or
cold weather operating characteristics if the thermo-stat is operating properly. This is because coolant
will be held in the engine until it reaches the ther-
mostat ªsetº temperature.
Diesel engines, due to their inherent efficiency are
slower to warm up than gasoline powered engines,
and will operate at lower temperatures when the
vehicle is unloaded. Because of this, lower tempera-
ture gauge readings for diesel versus gasoline
engines may, at times be normal.
Typically, complaints of low engine coolant temper-
ature are observed as low heater output when com-
bined with cool or cold outside temperatures.
To help promote faster engine warm-up, the elec-
tric engine block heater must be used with cool or
cold outside temperatures. This will help keep the
engine coolant warm when the vehicle is parked. Use
the block heater if the outside temperature is below
4ÉC (40ÉF).Do not use the block heater if the
outside temperature is above 4ÉC (40ÉF).
A ªCold Weather Coverº is available from the parts
department through the Mopar Accessories product
line. This accessory cover is designed to block airflow
entering the radiator and engine compartment to
promote faster engine warm-up. It attaches to the
front of the vehicle at the grill opening.The cover is
to be used with cool or cold temperatures only.
If used with high outside temperatures, serious
engine damage could result.Refer to the litera-
ture supplied with the cover for additional informa-
tion.
Fig. 26 ThermostatÐ5.9L DieselÐTypical
1 - WATER OUTLET CONNECTOR
2 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
3 - THERMOSTAT
BR/BEENGINE 7 - 53
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - 8.0L (Continued)
Page 400 of 2255

STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROMETER TEST
The hydrometer test reveals the battery state-of-
charge by measuring the specific gravity of the elec-
trolyte.This test cannot be performed on
maintenance-free batteries with non-removable
cell caps.If the battery has non-removable cell caps,
refer to Diagnosis and Testing for alternate methods
of determining the battery state-of-charge.
Specific gravity is a comparison of the density of
the battery electrolyte to the density of pure water.
Pure water has a specific gravity of 1.000, and sulfu-
ric acid has a specific gravity of 1.835. Sulfuric acid
makes up approximately 35% of the battery electro-
lyte by weight, or 24% by volume. In a fully-charged
battery the electrolyte will have a temperature-cor-
rected specific gravity of 1.260 to 1.290. However, a
specific gravity of 1.235 or above is satisfactory for
the battery to be load tested and/or returned to ser-
vice.
Before testing, visually inspect the battery for any
damage (a cracked case or cover, loose posts, etc.)
that would cause the battery to be faulty. Then
remove the battery cell caps and check the electrolyte
level. Add distilled water if the electrolyte level is
below the top of the battery plates. Refer to Battery
System Cleaning for the proper battery inspection
procedures.
See the instructions provided by the manufacturer
of the hydrometer for recommendations on the cor-
rect use of the hydrometer that you are using.
Remove only enough electrolyte from the battery cell
so that the float is off the bottom of the hydrometer
barrel with pressure on the bulb released. To read
the hydrometer correctly, hold it with the top surface
of the electrolyte at eye level (Fig. 8).
CAUTION: Exercise care when inserting the tip of
the hydrometer into a battery cell to avoid damag-
ing the plate separators. Damaged plate separators
can cause early battery failure.Hydrometer floats are generally calibrated to indi-
cate the specific gravity correctly only at 26.7É C.
When testing the specific gravity at any other tem-
perature, a correction factor is required. The correc-
tion factor is approximately a specific gravity value
of 0.004, which may also be identified as four points
of specific gravity. For each 5.5É C above 26.7É C, add
four points. For each 5.5É C below 26.7É C, subtract
four points. Always correct the specific gravity for
temperature variation.
EXAMPLE:A battery is tested at -12.2É C and has
a specific gravity of 1.240. Determine the actual spe-
cific gravity as follows:
(1) Determine the number of degrees above or
below 26.7É C:26.7É C + -12.2É C = 14.5É C below
the 26.7É C specification
(2) Divide the result from Step 1 by 5.5É C:14.5É
C ÷ 5.5É C = 2.64
(3) Multiply the result from Step 2 by the temper-
ature correction factor (0.004):2.64 X 0.004 = 0.01
(4) The temperature at testing was below 26.7É C;
therefore, the temperature correction factor is sub-
tracted:1.240 - 0.01 = 1.23
(5) The corrected specific gravity of the battery cell
in this example is 1.23.
Fig. 7 Built-In Indicator Sight Glass Chart
Fig. 8 Hydrometer - Typical
1 - BULB
2 - SURFACE COHESION
3 - SPECIFIC GRAVITY READING
4 - TEMPERATURE READING
5 - HYDROMETER BARREL
6 - FLOAT
BR/BEBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 11
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 426 of 2255
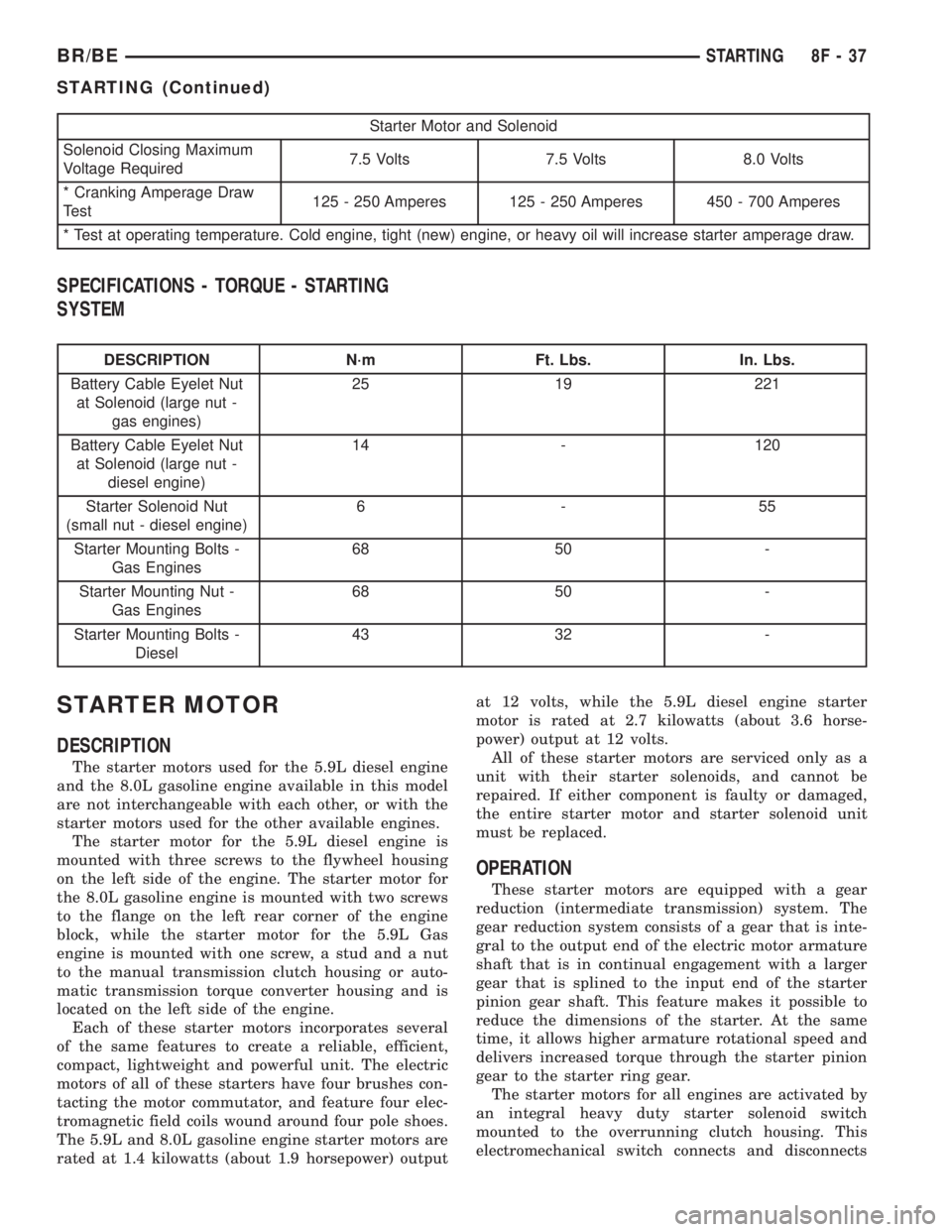
Starter Motor and Solenoid
Solenoid Closing Maximum
Voltage Required7.5 Volts 7.5 Volts 8.0 Volts
* Cranking Amperage Draw
Test125 - 250 Amperes 125 - 250 Amperes 450 - 700 Amperes
* Test at operating temperature. Cold engine, tight (new) engine, or heavy oil will increase starter amperage draw.
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - STARTING
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Battery Cable Eyelet Nut
at Solenoid (large nut -
gas engines)25 19 221
Battery Cable Eyelet Nut
at Solenoid (large nut -
diesel engine)14 - 120
Starter Solenoid Nut
(small nut - diesel engine)6-55
Starter Mounting Bolts -
Gas Engines68 50 -
Starter Mounting Nut -
Gas Engines68 50 -
Starter Mounting Bolts -
Diesel43 32 -
STARTER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The starter motors used for the 5.9L diesel engine
and the 8.0L gasoline engine available in this model
are not interchangeable with each other, or with the
starter motors used for the other available engines.
The starter motor for the 5.9L diesel engine is
mounted with three screws to the flywheel housing
on the left side of the engine. The starter motor for
the 8.0L gasoline engine is mounted with two screws
to the flange on the left rear corner of the engine
block, while the starter motor for the 5.9L Gas
engine is mounted with one screw, a stud and a nut
to the manual transmission clutch housing or auto-
matic transmission torque converter housing and is
located on the left side of the engine.
Each of these starter motors incorporates several
of the same features to create a reliable, efficient,
compact, lightweight and powerful unit. The electric
motors of all of these starters have four brushes con-
tacting the motor commutator, and feature four elec-
tromagnetic field coils wound around four pole shoes.
The 5.9L and 8.0L gasoline engine starter motors are
rated at 1.4 kilowatts (about 1.9 horsepower) outputat 12 volts, while the 5.9L diesel engine starter
motor is rated at 2.7 kilowatts (about 3.6 horse-
power) output at 12 volts.
All of these starter motors are serviced only as a
unit with their starter solenoids, and cannot be
repaired. If either component is faulty or damaged,
the entire starter motor and starter solenoid unit
must be replaced.
OPERATION
These starter motors are equipped with a gear
reduction (intermediate transmission) system. The
gear reduction system consists of a gear that is inte-
gral to the output end of the electric motor armature
shaft that is in continual engagement with a larger
gear that is splined to the input end of the starter
pinion gear shaft. This feature makes it possible to
reduce the dimensions of the starter. At the same
time, it allows higher armature rotational speed and
delivers increased torque through the starter pinion
gear to the starter ring gear.
The starter motors for all engines are activated by
an integral heavy duty starter solenoid switch
mounted to the overrunning clutch housing. This
electromechanical switch connects and disconnects
BR/BESTARTING 8F - 37
STARTING (Continued)
Page 537 of 2255

VEHICLE PREPARATION FOR HEADLAMP
ALIGNMENT
(1) Verify headlamp dimmer switch and high beam
indicator operation.
(2) Verify headlamps are set for low beam opera-
tion.
(3) Correct defective components that could hinder
proper headlamp alignment.
(4) Verify proper tire inflation.
(5) Clean headlamp lenses.
(6) Verify that luggage area is not heavily loaded.
(7) Fuel tank should be FULL. Add 2.94 kg (6.5
lbs.) of weight over the fuel tank for each estimated
gallon of missing fuel.
HEADLAMP ADJUSTMENT
Headlamps can be aligned using the screen method
provided or alignment tool C-4466±A or equivalent
can be used. refer to the instructions provided with
the tool for proper procedures.
A properly aimed low beam headlamp will project
top edge of high intensity pattern on screen from 50
mm (2 in.) above to 50 mm (2 in.) below headlamp
centerline. The side-to-side outboard edge of high
intensity pattern should be from 50 mm (2 in.) left to
50 mm (2 in.) right of headlamp centerline. (Fig. 20)
The preferred headlamp alignment is 1º down
for the up/down adjustment and 0 for the left/
right adjustment.The high beam pattern should be
correct when the low beams are aligned properly.
To adjust headlamp aim, rotate alignment screws
(Fig. 21) to achieve the specified high intensity pat-
tern.
LICENSE PLATE LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove license plate lamp lens.
(3) Pull bulb from license plate lamp.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install bulb in license plate lamp.
(2) Install license plate lamp lens.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
LICENSE PLATE LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove screws attaching license plate panel to
cargo box.
(3) Disengage license plate lamp wire connector
from body wire harness (Fig. 22).
(4) Separate license plate lamp from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position license plate lamp in vehicle.
Fig. 21 Aero Headlamp Alignment
1 - LEFT AND RIGHT ADJUSTMENT SCREW
2 - UP AND DOWN ADJUSTMENT SCREW
Fig. 22 License Plate Lamp Panel
1 - LIGHTING HARNESS
2 - BUMPER
3 - LICENSE PLATE LAMP
4 - SCREW
5 - LAMP PANEL
8L - 22 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORBR/BE
HEADLAMP UNIT (Continued)