2002 DODGE RAM ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 1206 of 2255

(9) Disconnect turbocharger oil supply line at the
turbocharger end. Cap off open ports to prevent
intrusion of dirt or foreign material.
(10) Remove exhaust manifold-to-cylinder head
bolts and spacers. Remove exhaust manifold and tur-
bocharger from the vehicle as an assembly.
(11) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(12) Remove generator upper bracket.
(13) Disconnect radiator upper hose from the ther-
mostat housing.
(14) Disconnect the coolant temperature sensor
connector.
(15) Remove the engine harness to cylinder head
attaching bolt at front of head.
(16) Remove the engine harness ground fastener
at front of head below the thermostat housing.(17) Remove the throttle linkage cover (Fig. 15).
(18) Remove the six (6) accelerator pedal position
sensor assembly-to-cylinder head bracket bolts (Fig.
16) and secure the entire assembly out of the way.
Disconnect the APPS connector (Fig. 17).It is not
necessary to disconnect the cables from the
throttle control assembly.
(19) Remove the intake air grid heater wires from
the grid heater.
(20) Remove engine oil level indicator tube attach-
ing bolt from the air inlet housing.
Fig. 13 Cylinder Head and Gasket
1 - THERMOSTAT BORE
2 - INTAKE RUNNER
3 - CYLINDER HEAD
4 - CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
5 - CYLINDER BLOCK
Fig. 14 Exhaust Pipe-to-Turbocharger Elbow
1 - EXHAUST PIPE
2 - TURBOCHARGER EXHAUST PIPE
Fig. 15 Throttle Linkage Cover
1 - CABLE/LEVER/LINKAGE COVER
2 - PUSH UP LOWER TAB
3 - SCREWS/CLIPS (2)
4 - TAB PUSH HERE
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 131
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1230 of 2255

clearance.Press firmly to ensure that it is seated
in the tappet.
(b) Raise the dowel rod to bring the tappet to
the top of its travel, and wrap a rubber band
around the dowel rods (Fig. 88) to prevent the tap-
pets from dropping into the crankcase.
(c) Repeat this procedure for the remaining cyl-
inders.
(27) Verify that the camshaft timing marks are
aligned with the crankshaft and injection pump
marks (Fig. 89).
(28) Remove the bolts from the thrust plate (Fig.
90).
CAUTION: When removing the camshaft and thrust
plate, grab the thrust plate to prevent it from falling
into the crankcase.
(29) Remove the camshaft (Fig. 91) and thrust
plate.
INSPECTION
Camshaft
(1) Inspect the valve lobes and bearing journals for
cracks, pitting, scoring, or generally excessive wear.
Replace any camshaft that exceeds the allowable lim-
its.
(2) Measure the bearing journals and lobes (Fig.
92).
CAUTION: If Camshaft lobes are worn, requiring
camshaft replacement, it is necessary to replace the
tappets also. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
SOLID LIFTERS - REMOVAL).
Fig. 87 Push Rod Removal/Installation
Fig. 88 Use Wooden Dowel Rods to Secure Tappets
in Place
Fig. 89 Timing Mark Alignment
Fig. 90 Thrust Plate Bolt Location
1 - CAMSHAFT GEAR
2 - THRUST PLATE
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 155
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 1240 of 2255

INSPECTION
(1) Visually inspect the tappet the tappet socket,
stem, and face for excessive wear, cracks, or obvious
damage (Fig. 118).
(2) Measure the tappet stem diameter. Replace the
tappet if it falls below the minimum size (Fig. 118).
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert the trough the full length of the cam-
shaft bore (Fig. 115). Again, make sure the cap end
goes in first and the open side faces up (towards tap-
pets).
(2) Lower the tappet installation tool through the
push rod hole (Fig. 119) and into the trough.
(3) Retrieve the tappet installation tool using the
hooked rod provided with the tool kit (Fig. 120).
(4) Lubricate the tappet with clean engine oil or
suitable equivalent and install the tappet to the
installation tool (Fig. 121).
(5) Pull the tappet up and into position (Fig. 121).
If difficulty is experienced getting the tappet to make
the turn into the tappet bore, wiggle the trough
whilegentlypulling up on the tappet.(6) With the tappet in place, rotate the trough one
half turn so the open side is down (toward crank-
shaft) (Fig. 122).
(7) Remove the tappet installation tool from the
tappet.
(8) Re-install a dowel rod and secure the rod with
a rubber band.
(9) Rotate the trough one half turn and repeat the
procedure for the remaining tappets.
(10) Install the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - INSTALLATION).
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The piston (Fig. 123) is constructed of aluminum
and is gravity cast, free floating design. The piston
Fig. 116 Secure Dowel/Tappet to Adjacent Cylinder
Fig. 117 Lift Dowel Rod to Disengage from Tappet
Fig. 118 Tappet Inspection
TAPPET STEM DIAMETER
15.925 mm (0.627 in.) MIN.
15.977 mm (0.629 in.) MAX.
Fig. 119 Insert Installation Tool through Push Rod
Hole
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 165
SOLID LIFTERS/TAPPETS (Continued)
Page 1289 of 2255
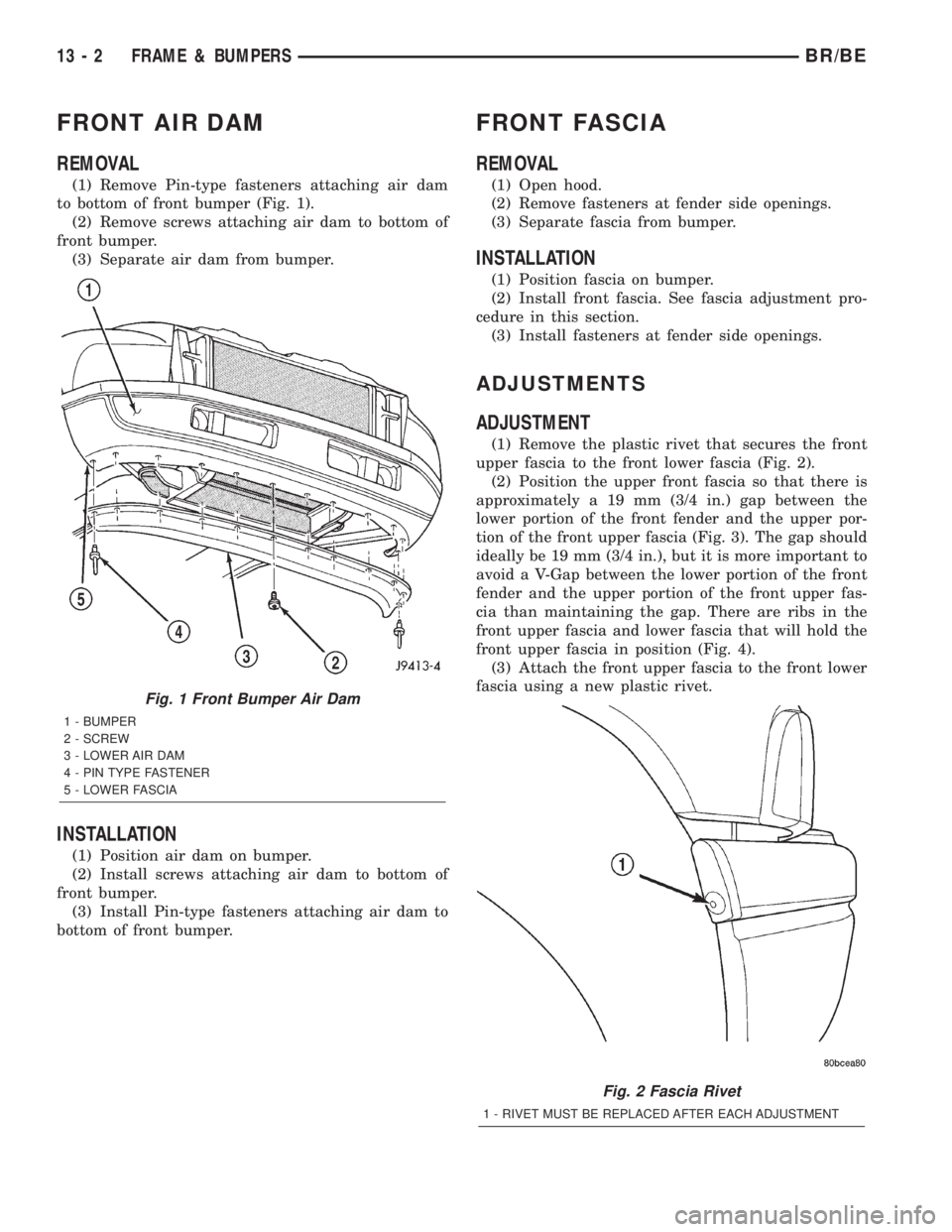
FRONT AIR DAM
REMOVAL
(1) Remove Pin-type fasteners attaching air dam
to bottom of front bumper (Fig. 1).
(2) Remove screws attaching air dam to bottom of
front bumper.
(3) Separate air dam from bumper.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position air dam on bumper.
(2) Install screws attaching air dam to bottom of
front bumper.
(3) Install Pin-type fasteners attaching air dam to
bottom of front bumper.
FRONT FASCIA
REMOVAL
(1) Open hood.
(2) Remove fasteners at fender side openings.
(3) Separate fascia from bumper.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fascia on bumper.
(2) Install front fascia. See fascia adjustment pro-
cedure in this section.
(3) Install fasteners at fender side openings.
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Remove the plastic rivet that secures the front
upper fascia to the front lower fascia (Fig. 2).
(2) Position the upper front fascia so that there is
approximately a 19 mm (3/4 in.) gap between the
lower portion of the front fender and the upper por-
tion of the front upper fascia (Fig. 3). The gap should
ideally be 19 mm (3/4 in.), but it is more important to
avoid a V-Gap between the lower portion of the front
fender and the upper portion of the front upper fas-
cia than maintaining the gap. There are ribs in the
front upper fascia and lower fascia that will hold the
front upper fascia in position (Fig. 4).
(3) Attach the front upper fascia to the front lower
fascia using a new plastic rivet.
Fig. 1 Front Bumper Air Dam
1 - BUMPER
2 - SCREW
3 - LOWER AIR DAM
4 - PIN TYPE FASTENER
5 - LOWER FASCIA
Fig. 2 Fascia Rivet
1 - RIVET MUST BE REPLACED AFTER EACH ADJUSTMENT
13 - 2 FRAME & BUMPERSBR/BE
Page 1307 of 2255
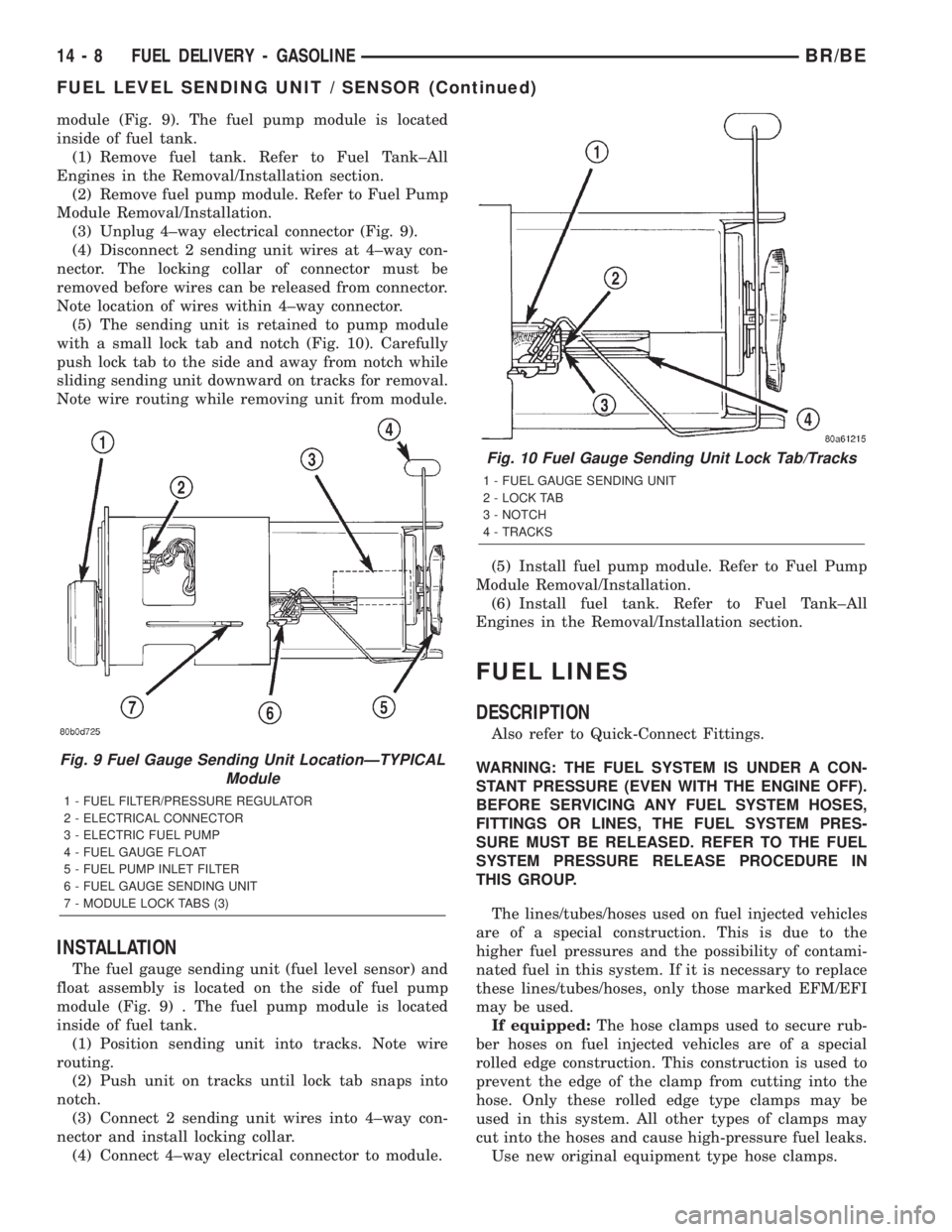
module (Fig. 9). The fuel pump module is located
inside of fuel tank.
(1) Remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank±All
Engines in the Removal/Installation section.
(2) Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
(3) Unplug 4±way electrical connector (Fig. 9).
(4) Disconnect 2 sending unit wires at 4±way con-
nector. The locking collar of connector must be
removed before wires can be released from connector.
Note location of wires within 4±way connector.
(5) The sending unit is retained to pump module
with a small lock tab and notch (Fig. 10). Carefully
push lock tab to the side and away from notch while
sliding sending unit downward on tracks for removal.
Note wire routing while removing unit from module.
INSTALLATION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) and
float assembly is located on the side of fuel pump
module (Fig. 9) . The fuel pump module is located
inside of fuel tank.
(1) Position sending unit into tracks. Note wire
routing.
(2) Push unit on tracks until lock tab snaps into
notch.
(3) Connect 2 sending unit wires into 4±way con-
nector and install locking collar.
(4) Connect 4±way electrical connector to module.(5) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
(6) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank±All
Engines in the Removal/Installation section.
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION
Also refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP.
The lines/tubes/hoses used on fuel injected vehicles
are of a special construction. This is due to the
higher fuel pressures and the possibility of contami-
nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, only those marked EFM/EFI
may be used.
If equipped:The hose clamps used to secure rub-
ber hoses on fuel injected vehicles are of a special
rolled edge construction. This construction is used to
prevent the edge of the clamp from cutting into the
hose. Only these rolled edge type clamps may be
used in this system. All other types of clamps may
cut into the hoses and cause high-pressure fuel leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
Fig. 9 Fuel Gauge Sending Unit LocationÐTYPICAL
Module
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP
4 - FUEL GAUGE FLOAT
5 - FUEL PUMP INLET FILTER
6 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
7 - MODULE LOCK TABS (3)
Fig. 10 Fuel Gauge Sending Unit Lock Tab/Tracks
1 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
2 - LOCK TAB
3 - NOTCH
4 - TRACKS
14 - 8 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1338 of 2255

REMOVAL - 8.0L
The crankshaft position sensor is located on the
right-lower side of the cylinder block, forward of the
right engine mount, just above the oil pan rail (Fig.
27).
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Disconnect sensor pigtail harness from main
engine wiring harness.
(3) Remove sensor mounting bolt (Fig. 28).
(4) Cut plastic tie strap (Fig. 27) securing sensor
pigtail harness to side of engine block.
(5) Carefully pry sensor from cylinder block in a
rocking action with two small screwdrivers.
(6) Remove sensor from vehicle.
(7) Check condition of sensor o-ring (Fig. 29).
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L
(1) Position crankshaft position sensor to engine.
(2) Install mounting bolts and tighten to 8 N´m (70
in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect main harness electrical connector to
sensor.
(4) Install air cleaner tube.
INSTALLATION - 8.0L
The crankshaft position sensor is located on the
right-lower side of the cylinder block, forward of the
right engine mount, just above the oil pan rail (Fig.
27).
(1) Apply a small amount of engine oil to sensor
o-ring (Fig. 29).
(2) Install sensor into cylinder block with a slight
rocking action. Do not twist sensor into position as
damage to o-ring may result.
Fig. 27 Crankshaft Position Sensor LocationÐ8.0L
V-10 Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - HOLE
3 - OIL FILTER
4 - PLASTIC TIE STRAP
5 - PIGTAIL HARNESS
Fig. 28 Sensor Removal/InstallationÐ8.0L V-10
Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLT
3 - SENSOR POSITIONED FLUSH TO CYLINDER BLOCK
Fig. 29 Sensor O-RingÐ8.0L V-10 Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR O-RING
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - PIGTAIL HARNESS
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 39
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1339 of 2255

CAUTION: Before tightening sensor mounting bolt,
be sure sensor is completely flush to cylinder block
(Fig. 28). If sensor is not flush, damage to sensor
mounting tang may result.
(3) Install mounting bolt and tighten to 8 N´m (70
in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect sensor pigtail harness to main engine
wiring harness
(5) Install new plastic tie strap (Fig. 27) to secure
sensor pigtail harness to side of engine block. Thread
tie strap through casting hole on cylinder block.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The 5±pin, 12±volt, fuel pump relay is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the
label on the PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) energizes
the electric fuel pump through the fuel pump relay.
The fuel pump relay is energized by first applying
battery voltage to it when the ignition key is turned
ON, and then applying a ground signal to the relay
from the PCM.
Whenever the ignition key is turned ON, the elec-
tric fuel pump will operate. But, the PCM will shut-
down the ground circuit to the fuel pump relay in
approximately 1±3 seconds unless the engine is oper-
ating or the starter motor is engaged.
REMOVAL
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC) (Fig. 30). Refer to label on PDC
cover for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC) (Fig. 30) . Refer to label on PDC
cover for relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The IAC stepper motor is mounted to the throttle
body, and regulates the amount of air bypassing the
control of the throttle plate. As engine loads and
ambient temperatures change, engine rpm changes.
A pintle on the IAC stepper motor protrudes into a
passage in the throttle body, controlling air flow
through the passage. The IAC is controlled by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to maintain the
target engine idle speed.
OPERATION
At idle, engine speed can be increased by retract-
ing the IAC motor pintle and allowing more air to
pass through the port, or it can be decreased by
restricting the passage with the pintle and diminish-
ing the amount of air bypassing the throttle plate.
The IAC is called a stepper motor because it is
moved (rotated) in steps, or increments. Opening the
IAC opens an air passage around the throttle blade
which increases RPM.
The PCM uses the IAC motor to control idle speed
(along with timing) and to reach a desired MAP dur-
ing decel (keep engine from stalling).
The IAC motor has 4 wires with 4 circuits. Two of
the wires are for 12 volts and ground to supply elec-
trical current to the motor windings to operate the
stepper motor in one direction. The other 2 wires are
also for 12 volts and ground to supply electrical cur-
rent to operate the stepper motor in the opposite
direction.
Fig. 30 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
14 - 40 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1356 of 2255

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL SYSTEM AIR
LEAK VACUUM TEST
The proceeding test will determine if a fuel system
air leak exists at the engine. Air leaks will cause
hard starting and/or poor performance.
A hand-operated vacuum pump/gauge equipped
with a remote or built-on fluid container will be used.
A typical hand-operated pump is shown in (Fig. 2).
The use of a hand-operated pumpwitha fluid con-
tainer will prevent fuel oil from entering and possibly
damaging pump. Two rubber caps (one 5/16º and one
3/8º) will also be used to temporarily plug / seal fuel
system.
Vacuum Test Set-Up, Specifications and
Conditions
²Examine all engine fuel system components, fit-
tings, lines and hoses for visual evidence of fuel leak-
age. Repair as necessary before proceeding.
²Be sure gauge on your hand-operated pump is
accurate and pump does not leak. Perform a simple
test on pump. Add a 3 foot section (minimum) of
clear plastic hose to the pump.
²Apply maximum 15-20 inches of vacuum for
tests.
²System should hold 15-20 inches of vacuum for 5
continuous minutes. After 5 minutes, vacuum should
not drop more than 0.1 inch Hg for 1 minute.²Disconnect fuel supply and return lines (quick-
connects) at rear of engine (Fig. 3).
²Drain as much fuel as possible from engine fuel
lines. Also, completely drain fuel filter/water separa-
tor housing. Refer to Fuel Filter/Water Separator
Removal and Installation for fuel draining proce-
dures. This step must be done to prevent liquid fuel
from entering and possibly damaging your hand-op-
erated pump.
Testing All Engine Fuel System Components Together
This test will indicate an air leak is present some-
where on the engine.
(1) Be sure water drain valve is securely closed.
(2) Examine all engine fuel system components,
fittings, lines and hoses for visual evidence of fuel
leakage. Repair as necessary.
(3) Install 5/16º rubber cap to fuel return line on
engine (Fig. 4).
(4) Install hand-operated vacuum pump to fuel
supply line on engine (Fig. 4).
(5) Perform vacuum test. Be careful not to allow
liquid fuel to get into your hand-operated vacuum
pump.
(6) Vacuum holds ? End of test; no leaks found on
engine.
(7) Vacuum leak ? Proceed. The following tests will
isolate the component that is leaking.
Fig. 2 HAND-OPERATED VACUUM PUMP (TYPICAL)
1 - PUMP
2 - CONTAINER
Fig. 3 QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS LOCATION
1 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE
2 - SUPPORT BRACKET BOLT
3 - FUEL RETURN LINE
4 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS (2)
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 57