2002 DODGE RAM tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 1841 of 2255
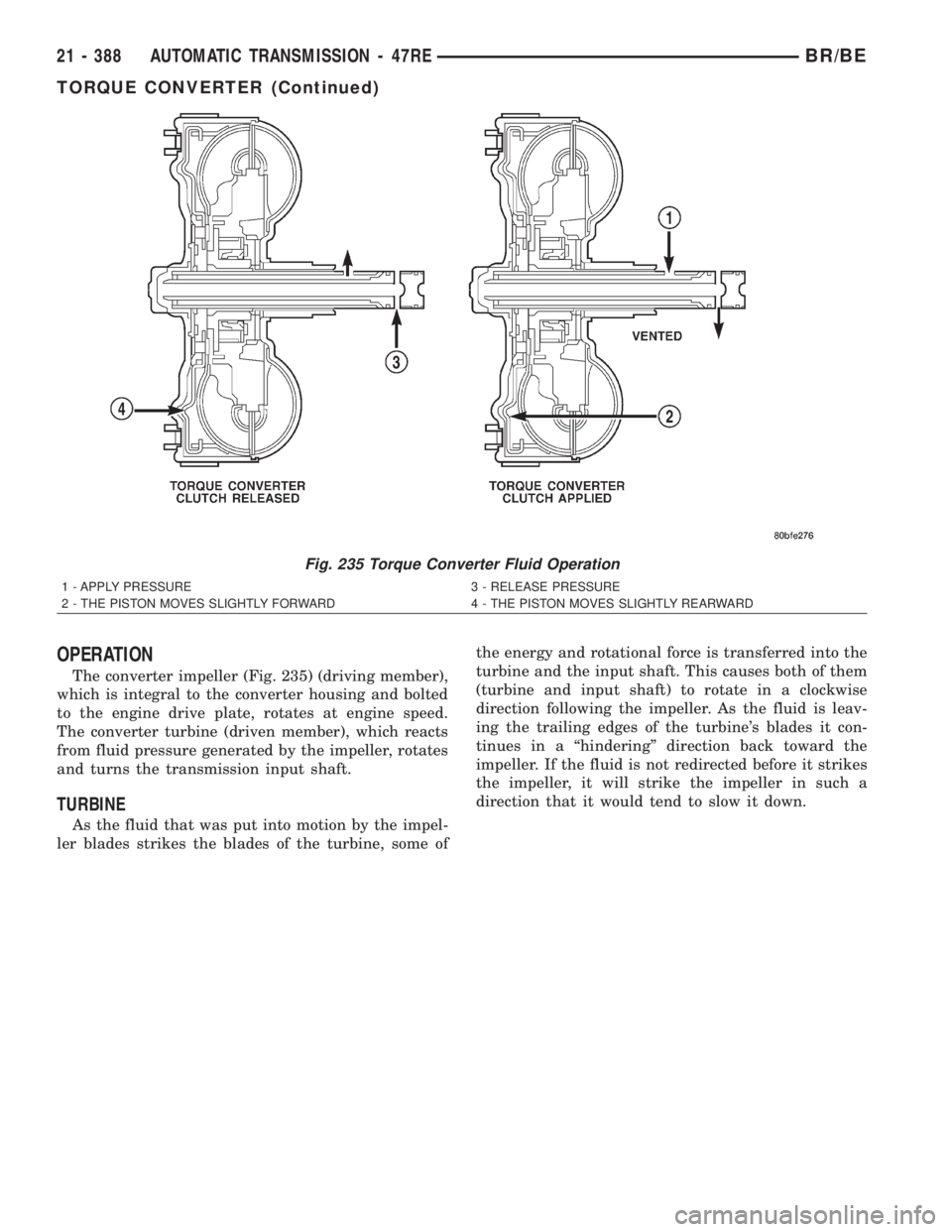
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 235) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some ofthe energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
Fig. 235 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
21 - 388 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1851 of 2255
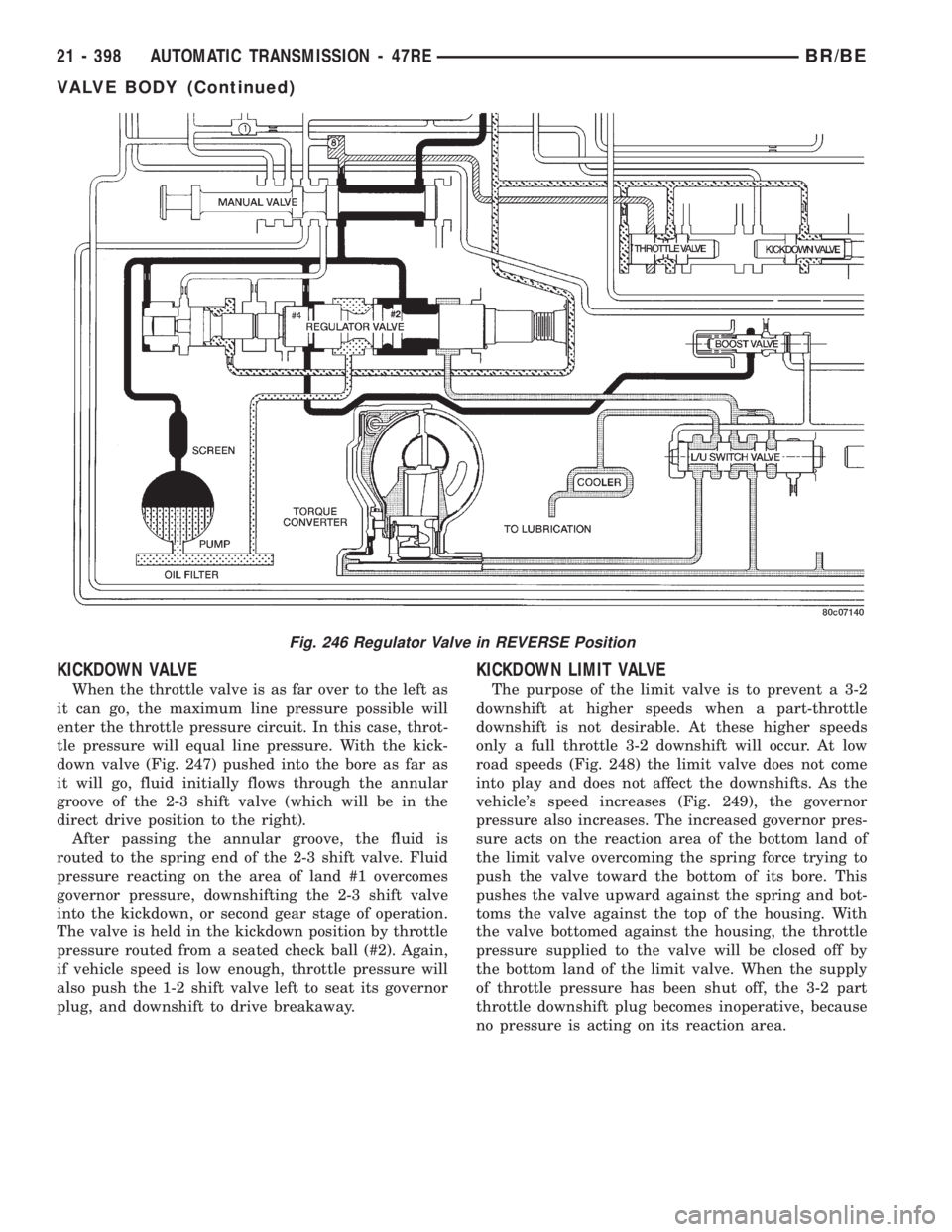
KICKDOWN VALVE
When the throttle valve is as far over to the left as
it can go, the maximum line pressure possible will
enter the throttle pressure circuit. In this case, throt-
tle pressure will equal line pressure. With the kick-
down valve (Fig. 247) pushed into the bore as far as
it will go, fluid initially flows through the annular
groove of the 2-3 shift valve (which will be in the
direct drive position to the right).
After passing the annular groove, the fluid is
routed to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve. Fluid
pressure reacting on the area of land #1 overcomes
governor pressure, downshifting the 2-3 shift valve
into the kickdown, or second gear stage of operation.
The valve is held in the kickdown position by throttle
pressure routed from a seated check ball (#2). Again,
if vehicle speed is low enough, throttle pressure will
also push the 1-2 shift valve left to seat its governor
plug, and downshift to drive breakaway.
KICKDOWN LIMIT VALVE
The purpose of the limit valve is to prevent a 3-2
downshift at higher speeds when a part-throttle
downshift is not desirable. At these higher speeds
only a full throttle 3-2 downshift will occur. At low
road speeds (Fig. 248) the limit valve does not come
into play and does not affect the downshifts. As the
vehicle's speed increases (Fig. 249), the governor
pressure also increases. The increased governor pres-
sure acts on the reaction area of the bottom land of
the limit valve overcoming the spring force trying to
push the valve toward the bottom of its bore. This
pushes the valve upward against the spring and bot-
toms the valve against the top of the housing. With
the valve bottomed against the housing, the throttle
pressure supplied to the valve will be closed off by
the bottom land of the limit valve. When the supply
of throttle pressure has been shut off, the 3-2 part
throttle downshift plug becomes inoperative, because
no pressure is acting on its reaction area.
Fig. 246 Regulator Valve in REVERSE Position
21 - 398 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1858 of 2255

The higher engine speed and line pressure would
open the vent too far and reduce line pressure too
much. Throttle pressure, which increases with engine
speed (throttle opening), is used to oppose the move-
ment of the pressure valve to help control the meter-
ing passage at the vent. The throttle pressure is
combined with spring pressure to reduce the force of
the throttle pressure plug on the pressure valve. The
larger spring at the right closes the regulator valve
passage and maintains or increases line pressure.
The increased line pressure works against the reac-
tion area of the line pressure plug and the reaction
area left of land #3 simultaneously moves the regu-
lator valve train to the right and controls the meter-
ing passage.
The kickdown valve, along with the throttle valve,
serve to delay upshifts until the correct vehicle speed
has been reached. It also controls downshifts upon
driver demand, or increased engine load. If these
valves were not in place, the shift points would be at
the same speed for all throttle positions. The kick-
down valve is actuated by a cam connected to the
throttle. This is accomplished through either a link-
age or a cable. The cam forces the kickdown valve
toward the throttle valve compressing the spring
between them and moving the throttle valve. As the
throttle valve land starts to uncover its port, line
pressure is ªmeteredº out into the circuits and viewed
as throttle pressure. This increased throttle pressure
is metered out into the circuits it is applied to: the
1-2 and 2-3 shift valves. When the throttle pressure
is high enough, a 3-2 downshift will occur. If the
vehicle speed is low enough, a 2-1 downshift will
occur.
SWITCH VALVE
When the transmission is in Drive Second before
the TCC application occurs (Fig. 258), the pressure
regulator valve is supplying torque converter pres-
sure to the switch valve. The switch valve directs
this pressure through the transmission input shaft,
into the converter, through the converter, back out
between the input shaft and the reaction shaft, and
back up to the switch valve. From the switch valve,
the fluid pressure is directed to the transmission
cooler, and lubrication pressure returns from the
cooler to lubricate different portions of the transmis-
sion.Once the TCC control valve has moved to the right
(Fig. 259), line pressure is directed to the tip of the
switch valve, forcing the valve to the right. The
switch valve now vents oil from the front of the pis-
ton in the torque converter, and supplies line pres-
sure to the (rear) apply side of the torque converter
piston. This pressure differential causes the piston to
apply against the friction material, cutting off any
further flow of line pressure oil. After the switch
valve is shuttled right allowing line pressure to
engage the TCC, torque converter pressure is
directed past the switch valve into the transmission
cooler and lubrication circuits.
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve (Fig. 260) is a relay valve. The
purpose of the manual valve is to direct fluid to the
correct circuit needed for a specific gear or driving
range. The manual valve, as the name implies, is
manually operated by the driver with a lever located
on the side of the valve body. The valve is connected
mechanically by either a cable or linkage to the gear-
shift mechanism. The valve is held in each of its
positions by a spring-loaded roller or ball that
engages the ªroostercombº of the manual valve lever.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up valve
controls the back (ON) side of the torque converter
clutch. When the PCM energizes the TCC solenoid to
engage the converter clutch piston, pressure is
applied to the TCC lock-up valve which moves to the
right and applies pressure to the torque converter
clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP TIMING VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up timing
valve is there to block any 4-3 downshift until the
TCC is completely unlocked and the clutch is disen-
gaged.
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 405
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1871 of 2255

VALVE BODY LOWER HOUSING
(1) Remove timing valve cover.
(2) Remove 3-4 timing valve and spring.
(3) Remove 3-4 quick fill valve, spring and plug.
(4) Remove 3-4 shift valve and spring.
(5) Remove converter clutch valve, spring and plug
(Fig. 293).
(6) Remove converter clutch timing valve, retainer
and valve spring.
3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
(1) Remove end plate from housing.
(2) Remove piston spring.
(3) Remove piston. Remove and discard piston
seals (Fig. 294).
CLEANING
Clean the valve housings, valves, plugs, springs,
and separator plates with a standard parts cleaningsolution only. Do not use gasoline, kerosene, or any
type of caustic solution.
Do not immerse any of the electrical components in
cleaning solution. Clean the governor solenoid and
sensor and the dual solenoid and harness assembly
by wiping them off with dry shop towels only.
Dry all except the electrical parts with compressed
air. Make sure all passages are clean and free from
obstructions.Do not use rags or shop towels to
dry or wipe off valve body components. Lint
from these materials can stick to valve body
parts, interfere with valve operation, and clog
filters and fluid passages.
Wipe the governor pressure sensor and solenoid
valve with dry, lint free shop towels only. The O-rings
on the sensor and solenoid valve are the only service-
able components. Be sure the vent ports in the sole-
noid valve are open and not blocked by dirt or debris.
Replace the valve and/or sensor only when DRB scan
tool diagnosis indicates this is necessary. Or, if either
Fig. 292 Upper Housing Shift Valve and Pressure Plug Locations
1 - UPPER HOUSING 8 - RETAINER
2 - 1-2 SHIFT VALVE AND SPRING 9 - 1-2 SHIFT CONTROL VALVE AND SPRING
3 - 2-3 SHIFT VALVE AND SPRING 10 - PRESSURE PLUG COVER
4 - 2-3 THROTTLE PLUG 11 - LINE PRESSURE PLUG
5 - LIMIT VALVE HOUSING 12 - PLUG SLEEVE
6 - LIMIT VALVE COVER 13 - THROTTLE PRESSURE SPRING AND PLUG
7 - LIMIT VALVE AND SPRING
21 - 418 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1898 of 2255
Or the threads can be repaired with HelicoilŸ stain-
less steel inserts if required.
OIL PUMP/OIL PICKUP
Examine the oil pump pickup parts. Replace the
pump if any part appears to be worn or damaged. Do
not disassemble the pump as individual parts are not
available. The pump is only available as a complete
assembly. The pickup screen, hose, and tube are the
only serviceable parts and are available separately.
ASSEMBLY
BEARINGS AND SEALS
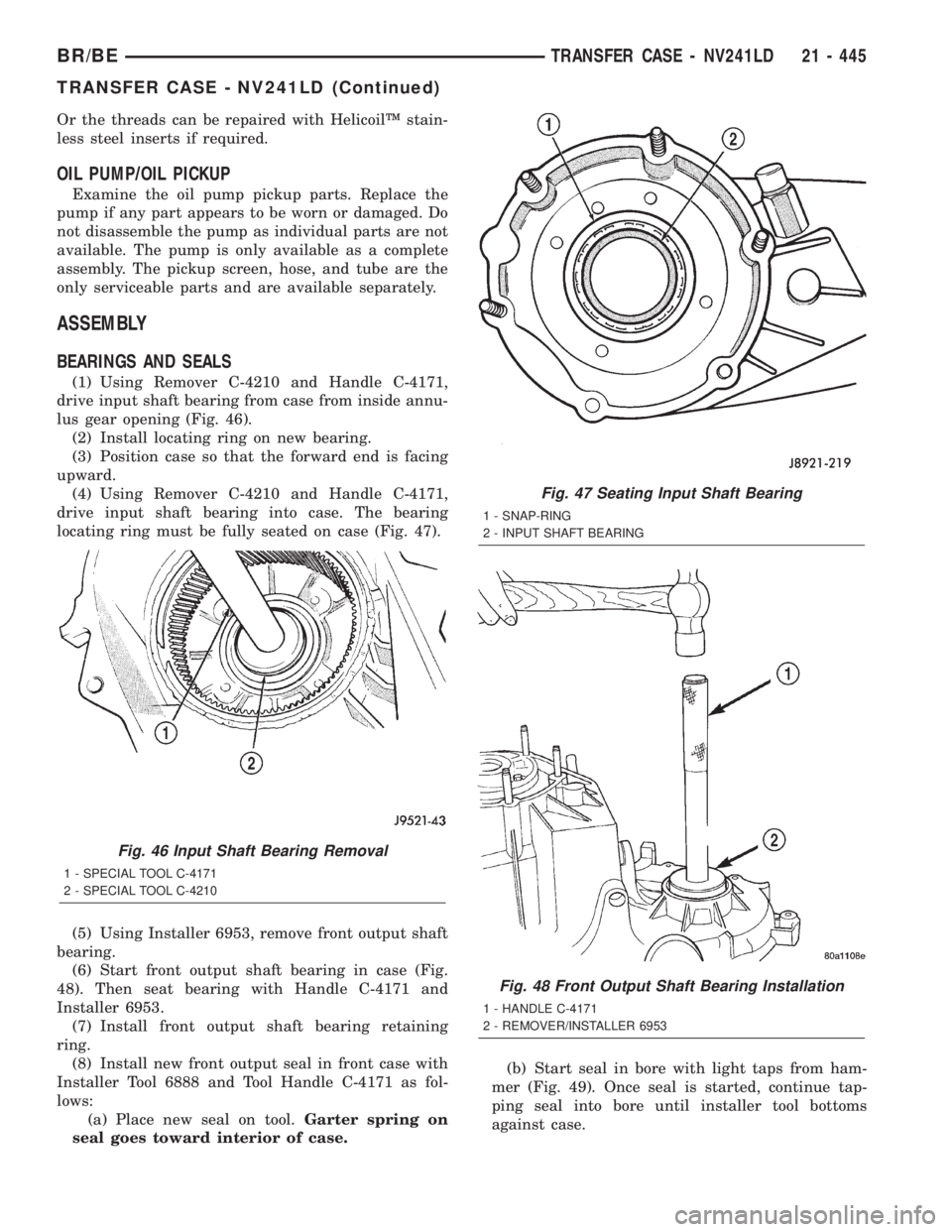
(1) Using Remover C-4210 and Handle C-4171,
drive input shaft bearing from case from inside annu-
lus gear opening (Fig. 46).
(2) Install locating ring on new bearing.
(3) Position case so that the forward end is facing
upward.
(4) Using Remover C-4210 and Handle C-4171,
drive input shaft bearing into case. The bearing
locating ring must be fully seated on case (Fig. 47).
(5) Using Installer 6953, remove front output shaft
bearing.
(6) Start front output shaft bearing in case (Fig.
48). Then seat bearing with Handle C-4171 and
Installer 6953.
(7) Install front output shaft bearing retaining
ring.
(8) Install new front output seal in front case with
Installer Tool 6888 and Tool Handle C-4171 as fol-
lows:
(a) Place new seal on tool.Garter spring on
seal goes toward interior of case.(b) Start seal in bore with light taps from ham-
mer (Fig. 49). Once seal is started, continue tap-
ping seal into bore until installer tool bottoms
against case.
Fig. 46 Input Shaft Bearing Removal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4210
Fig. 47 Seating Input Shaft Bearing
1 - SNAP-RING
2 - INPUT SHAFT BEARING
Fig. 48 Front Output Shaft Bearing Installation
1 - HANDLE C-4171
2 - REMOVER/INSTALLER 6953
BR/BETRANSFER CASE - NV241LD 21 - 445
TRANSFER CASE - NV241LD (Continued)
Page 1903 of 2255
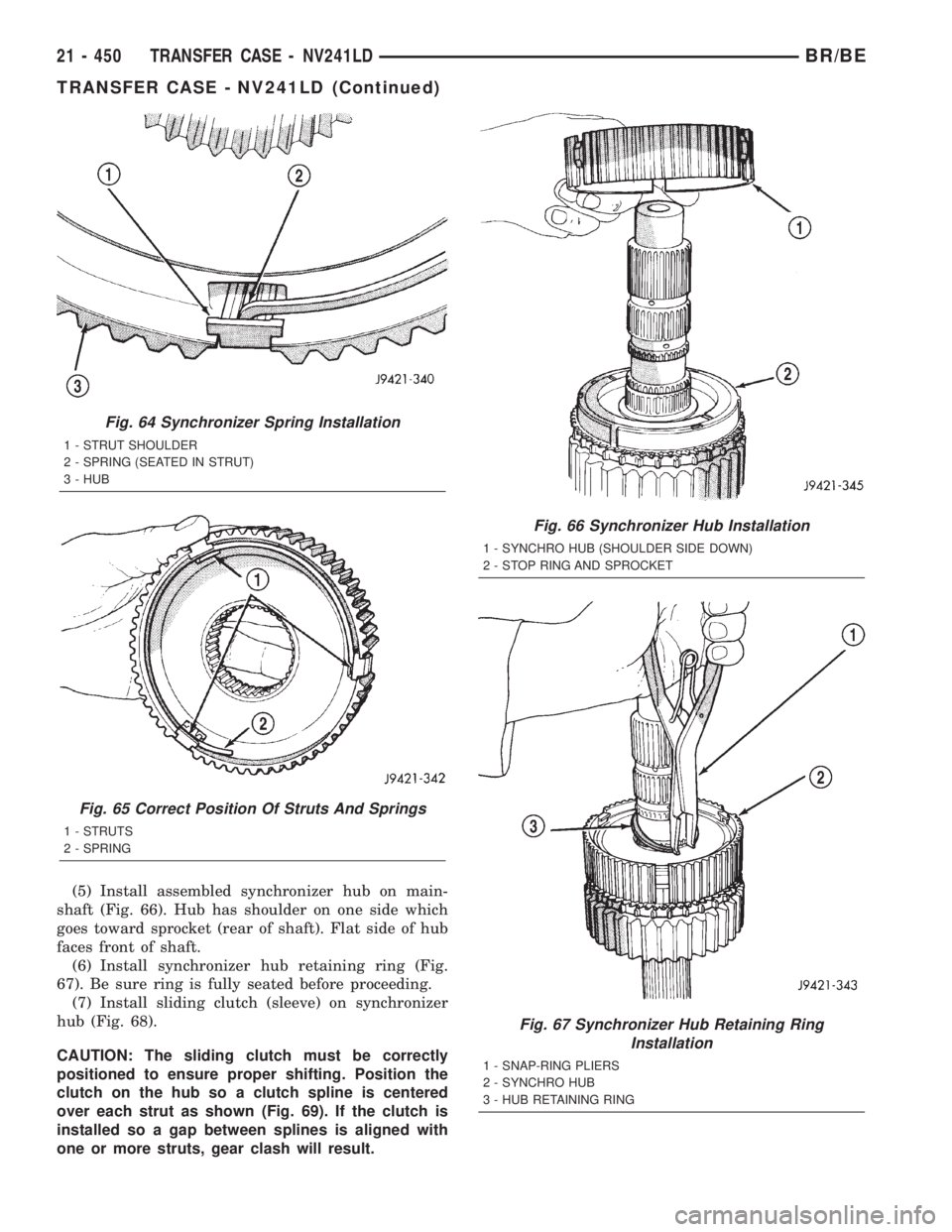
(5) Install assembled synchronizer hub on main-
shaft (Fig. 66). Hub has shoulder on one side which
goes toward sprocket (rear of shaft). Flat side of hub
faces front of shaft.
(6) Install synchronizer hub retaining ring (Fig.
67). Be sure ring is fully seated before proceeding.
(7) Install sliding clutch (sleeve) on synchronizer
hub (Fig. 68).
CAUTION: The sliding clutch must be correctly
positioned to ensure proper shifting. Position the
clutch on the hub so a clutch spline is centered
over each strut as shown (Fig. 69). If the clutch is
installed so a gap between splines is aligned with
one or more struts, gear clash will result.
Fig. 64 Synchronizer Spring Installation
1 - STRUT SHOULDER
2 - SPRING (SEATED IN STRUT)
3 - HUB
Fig. 65 Correct Position Of Struts And Springs
1 - STRUTS
2 - SPRING
Fig. 66 Synchronizer Hub Installation
1 - SYNCHRO HUB (SHOULDER SIDE DOWN)
2 - STOP RING AND SPROCKET
Fig. 67 Synchronizer Hub Retaining Ring
Installation
1 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
2 - SYNCHRO HUB
3 - HUB RETAINING RING
21 - 450 TRANSFER CASE - NV241LDBR/BE
TRANSFER CASE - NV241LD (Continued)
Page 1914 of 2255

FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transfer case into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove front propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIF-
FERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/
PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(4) Remove companion flange nut (Fig. 98). Dis-
card nut after removal. It is not reusable.
(5) Remove companion flange from output shaft.
Use a suitable puller if flange can not be removed by
hand.
(6) Remove companion flange rubber seal from
front output shaft (Fig. 99).(7) Remove front output shaft seal with suitable
pry tool, or a slide hammer mounted screw.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new front output seal in front case with
Installer Tool 6888 and Tool Handle C-4171 (Fig.
100) as follows:
(a) Place new seal on tool. Garter spring on seal
goes toward interior of case.
(b) Start seal in bore. Once seal is started, con-
tinue tapping seal into bore until installer tool bot-
toms against case.
(c) Remove installer and verify that seal is
recessed the proper amount. Seal should be 2.03 to
2.5 mm (0.080 to 0.100 in.) below top edge of seal
bore in front case (Fig. 101). This is correct final
seal position.
CAUTION: Be sure the front output seal is seated
below the top edge of the case bore as shown. The
seal could loosen, or become cocked if not seated
to recommended depth.
Fig. 97 Fill/Drain Plug and I.D. Tag Location -
Typical
1 - I.D. TAG
2 - FILL PLUG
3 - DRAIN PLUG
Fig. 98 Removing Companion Flange Nut
1 - COMPANION FLANGE
2 - 1-1/8º SOCKET
Fig. 99 Companion Flange Seal Removal
1 - FLANGE SEAL
Fig. 100 Front Output Seal Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6888
BR/BETRANSFER CASE - NV241LD 21 - 461
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1933 of 2255
ASSEMBLY
BEARINGS AND SEALS
(1) Using Remover C-4210 and Handle C-4171,
drive input shaft bearing from case from inside annu-
lus gear opening (Fig. 42).
(2) Install locating ring on new bearing.
(3) Position case so that the forward end is facing
upward.
(4) Using Remover C-4210 and Handle C-4171,
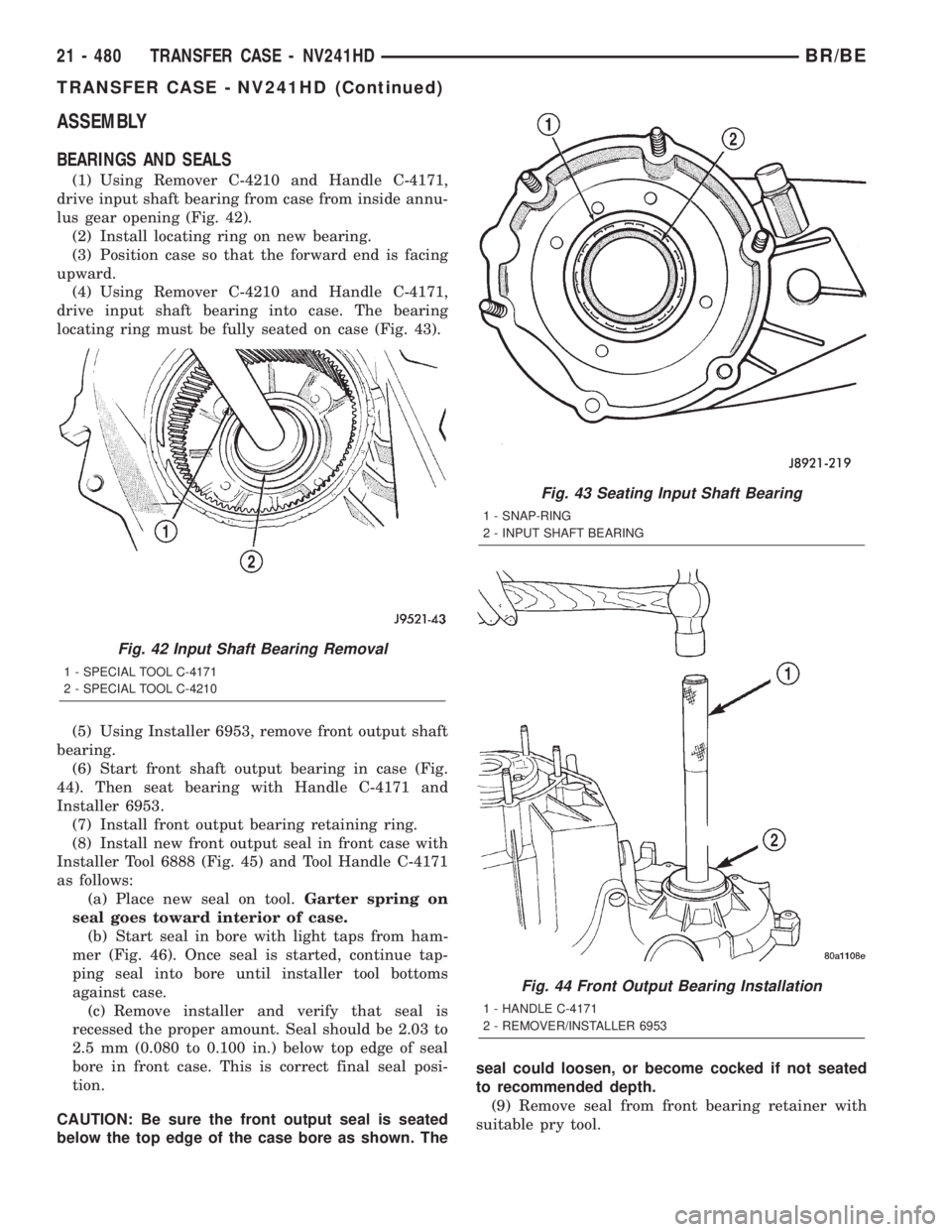
drive input shaft bearing into case. The bearing
locating ring must be fully seated on case (Fig. 43).
(5) Using Installer 6953, remove front output shaft
bearing.
(6) Start front shaft output bearing in case (Fig.
44). Then seat bearing with Handle C-4171 and
Installer 6953.
(7) Install front output bearing retaining ring.
(8) Install new front output seal in front case with
Installer Tool 6888 (Fig. 45) and Tool Handle C-4171
as follows:
(a) Place new seal on tool.Garter spring on
seal goes toward interior of case.
(b) Start seal in bore with light taps from ham-
mer (Fig. 46). Once seal is started, continue tap-
ping seal into bore until installer tool bottoms
against case.
(c) Remove installer and verify that seal is
recessed the proper amount. Seal should be 2.03 to
2.5 mm (0.080 to 0.100 in.) below top edge of seal
bore in front case. This is correct final seal posi-
tion.
CAUTION: Be sure the front output seal is seated
below the top edge of the case bore as shown. Theseal could loosen, or become cocked if not seated
to recommended depth.
(9) Remove seal from front bearing retainer with
suitable pry tool.
Fig. 42 Input Shaft Bearing Removal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4210
Fig. 43 Seating Input Shaft Bearing
1 - SNAP-RING
2 - INPUT SHAFT BEARING
Fig. 44 Front Output Bearing Installation
1 - HANDLE C-4171
2 - REMOVER/INSTALLER 6953
21 - 480 TRANSFER CASE - NV241HDBR/BE
TRANSFER CASE - NV241HD (Continued)