2002 CHRYSLER CARAVAN automatic transmission
[x] Cancel search: automatic transmissionPage 1639 of 2399

CLUTCH - FRONT
DESCRIPTION
The front clutch assembly (Fig. 119) is composed of
the front clutch retainer, pressure plate, clutch
plates, driving discs, piston, piston return spring,
return spring retainer, and snap-rings. The front
clutch is the forward-most component in the trans-
mission geartrain and is directly behind the oil
pump. It is considered a driving component.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the clutch retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through the hub of the reaction shaft support.
With pressure applied between the clutch retainer
and piston, the piston moves away from the clutch
retainer and compresses the clutch pack. This action
applies the clutch pack, allowing torque to flow
through the input shaft into the driving discs, and
into the clutch plates and pressure plate that are
lugged to the clutch retainer. The waved snap-ring is
used to cushion the application of the clutch pack. In
some transmissions, the snap-ring is selective and
used to adjust clutch pack clearance.
When pressure is released from the piston, the
spring returns the piston to its fully released position
and disengages the clutch. The release spring also
helps to cushion the application of the clutch assem-
bly. When the clutch is in the process of being
released by the release spring, fluid flows through a
vent and one-way ball-check-valve located in the
clutch retainer. The check-valve is needed to elimi-
nate the possibility of plate drag caused by centrifu-
gal force acting on the residual fluid trapped in the
clutch piston retainer.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove front clutch waved snap ring using a
suitable screwdriver (Fig. 114).
(2) Remove waved snap ring and reaction plate
(Fig. 115).
Fig. 114 Front Clutch Waved Snap Ring
1 - WAVED SNAP RING
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - FRONT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 115 Thick Steel Plate and Waved Snap Ring
1 - WAVED SNAP RING
2 - THICK STEEL PLATE
3 - FRONT CLUTCH RETAINER
21 - 82 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1643 of 2399

(5) Using feeler gauge, measure front clutch clear-
ance (Fig. 125).Front clutch clearance should be
within 1.27-2.79 mm (0.050-0.110 in.) and is not
adjustable.
CLUTCH - REAR
DESCRIPTION
The rear clutch assembly (Fig. 132) is composed of
the input shaft, rear clutch retainer, pressure plate,
clutch plates, driving discs, piston, Belleville spring,
and snap-rings. The Belleville spring acts as a lever
to multiply the force applied on to it by the apply pis-
ton. The increased apply force on the rear clutch
pack, in comparison to the front clutch pack, is
needed to hold against the greater torque load
imposed onto the rear pack. The rear clutch is
directly behind the front clutch and is considered a
driving component.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the clutch retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through the hub of the reaction shaft support.
With pressure applied between the clutch retainer
and piston, the piston moves away from the clutch
retainer and compresses the clutch pack. This action
applies the clutch pack, allowing torque to flow
through the input shaft into the driving discs, and
into the clutch plates and pressure plate that are
lugged to the clutch retainer. The waved snap-ring is
used to cushion the application of the clutch pack. In
some transmissions, the snap-ring is selective and
used to adjust clutch pack clearance.
When pressure is released from the piston, the
spring returns the piston to its fully released position
and disengages the clutch. The release spring also
helps to cushion the application of the clutch assem-
bly. When the clutch is in the process of being
released by the release spring, fluid flows through a
vent and one-way ball-check-valve located in the
clutch retainer. The check-valve is needed to elimi-
nate the possibility of plate drag caused by centrifu-
gal force acting on the residual fluid trapped in the
clutch piston retainer.
Fig. 124 Front Clutch Waved Snap Ring
1 - WAVED SNAP RING
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - FRONT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 125 Measuring Front Clutch Plate Clearance
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - FRONT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
21 - 86 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
CLUTCH - FRONT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1648 of 2399

(3) Install rear clutch pack (Fig. 137).
(4) Install snap ring using a suitable screwdriver
(Fig. 138).
(5) Using feeler gauges, measure rear clutch clear-
ance (Fig. 139).Rear clutch clearance should be
within 0.71-1.10 mm (0.028-0.043 in.).
FINAL DRIVE
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: The differential is serviced as an assembly.
Service is limited to bearing cups and cones. Any
other failure must be repaired by differential assem-
bly and transfer shaft replacement.
(1) Remove transfer shaft.
(2) Measure differential bearing turning torque.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/BEARINGS - ADJUSTMENTS)
(3) Remove adapter plate seal.
(4) Remove differential cover-to-transaxle case
bolts (Fig. 140).
Fig. 137 Rear Clutch (4-Disc Shown)
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - CLUTCH PLATES
3 - THICK STEEL PLATE
4 - SNAP RING (SELECTIVE)
5 - DRIVING DISCS
6 - PRESSURE PLATE
Fig. 138 Rear Clutch Outer Snap Ring
1 - SCREWDRIVER
2 - SNAP RING
3 - REAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 139 Measuring Rear Clutch Plate Clearance
1 - REAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
2 - FEELER GAUGE
3 - SELECTIVE SNAP RING
Fig. 140 Differential Cover Bolts
1 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER
2 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER BOLT
RS31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-91
CLUTCH - REAR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1654 of 2399
(11) Install adapter plate axle seal using Tool
L-4520 (inverted), and driver handle C-4171.
(12) Check differential turning torque. (Refer to 21
- TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
31TH/BEARINGS - ADJUSTMENTS)
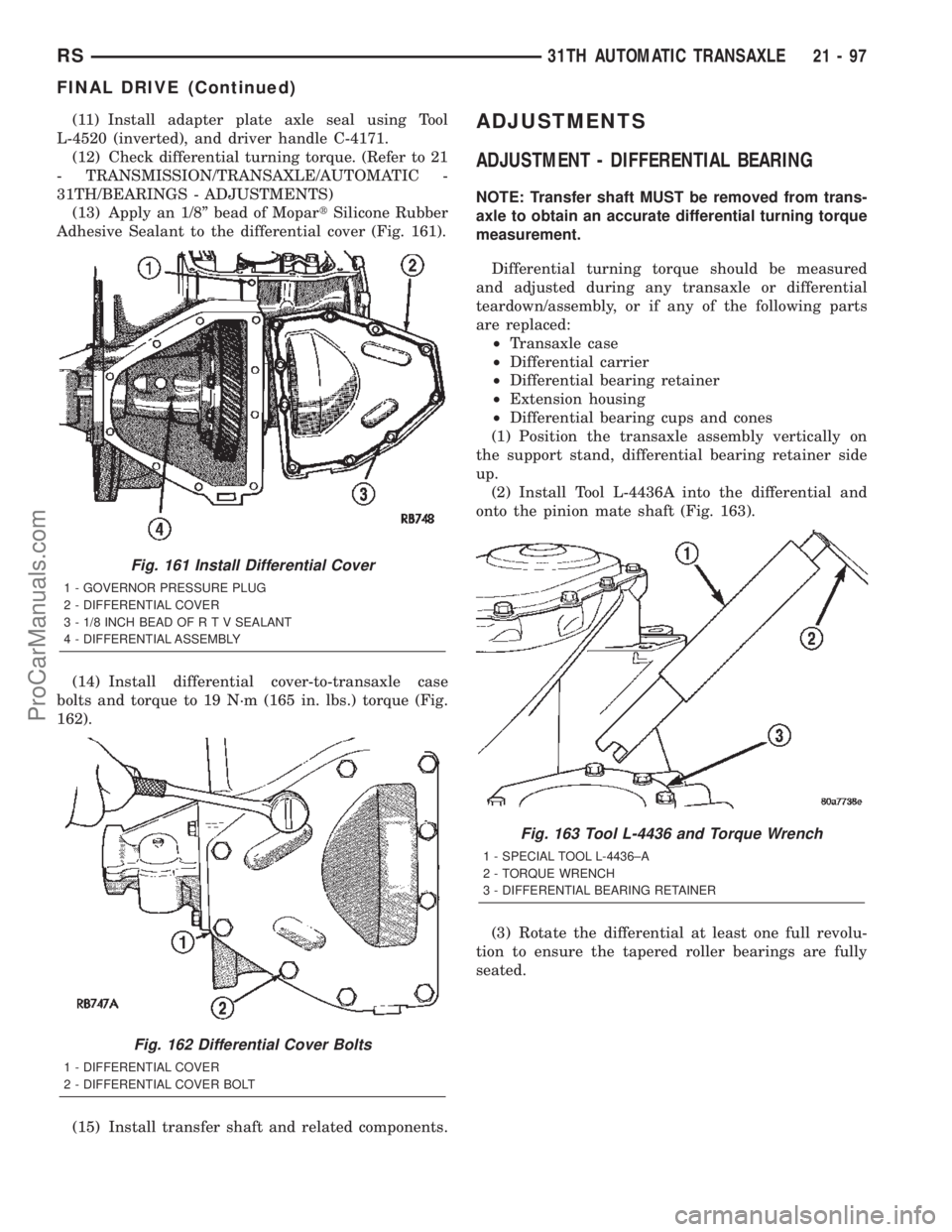
(13) Apply an 1/8º bead of MopartSilicone Rubber
Adhesive Sealant to the differential cover (Fig. 161).
(14) Install differential cover-to-transaxle case
bolts and torque to 19 N´m (165 in. lbs.) torque (Fig.
162).
(15) Install transfer shaft and related components.ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING
NOTE: Transfer shaft MUST be removed from trans-
axle to obtain an accurate differential turning torque
measurement.
Differential turning torque should be measured
and adjusted during any transaxle or differential
teardown/assembly, or if any of the following parts
are replaced:
²Transaxle case
²Differential carrier
²Differential bearing retainer
²Extension housing
²Differential bearing cups and cones
(1) Position the transaxle assembly vertically on
the support stand, differential bearing retainer side
up.
(2) Install Tool L-4436A into the differential and
onto the pinion mate shaft (Fig. 163).
(3) Rotate the differential at least one full revolu-
tion to ensure the tapered roller bearings are fully
seated.
Fig. 161 Install Differential Cover
1 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE PLUG
2 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER
3 - 1/8 INCH BEAD OF R T V SEALANT
4 - DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
Fig. 162 Differential Cover Bolts
1 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER
2 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER BOLT
Fig. 163 Tool L-4436 and Torque Wrench
1 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4436±A
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
3 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING RETAINER
RS31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-97
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1656 of 2399

FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL AND
CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: The transmission and differential sump have
a common oil sump with a communicating opening
between the two.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground. This will assure complete oil level sta-
bilization between differential and transmis-
sion.The fluid should be at normal operating
temperature (approximately 82 C. or 180 F.). The
fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT region (cross-
hatched area) on the fluid level indicator (Fig. 165).
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, the air bubbles can cause overheat-
ing, fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can inter-
fere with normal valve, clutch, and servo operation.
Foaming can also result in fluid escaping from thetransaxle dipstick where it may be mistaken for a
leak.
FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid-Type 9602) when new is red in
color. The ATF is dyed red so it can be identified from
other fluids used in the vehicle such as engine oil or
antifreeze. The red color is not permanent and is not
an indicator of fluid condition. As the vehicle is
driven, the ATF will begin to look darker in color and
may eventually become brown.This is normal.
ATF+4 also has a unique odor that may change with
age. Consequently,odor and color cannot be used
to indicate the fluid condition, or the need for a
fluid change.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
CHANGE
NOTE: For the recommended maintenance (fluid/fil-
ter change) intervals for this transaxle, (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
NOTE: Only fluids of the type labeled MoparTATF+4
(Automatic Transmission Fluid) Type 9602 should
be used. A filter change should be made at the time
of the transmission oil change. The magnet (on the
inside of the oil pan) should also be cleaned with a
clean, dry cloth.
NOTE: If the transaxle is disassembled for any rea-
son, the fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID/FILTER SERVICE (RECOMMENDED)
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Place a drain con-
tainer with a large opening, under transaxle oil pan.
(2) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner
to break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove
the oil pan.
(3) Remove oil filter-to-valve body screws (Fig.
166).
(4) Remove oil filter and gasket (Fig. 167).
(5) Install a new filter and gasket (Fig. 167).
(6) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant.
Torque oil pan bolts to 19 N´m (165 in. lbs.).
(7) Pour four quarts of MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid-Type 9602) through the dipstick
opening.
Fig. 165 Fluid Level Indicator Markings
1 - TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
RS31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-99
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1657 of 2399

(8) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(9) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the ªADDº mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 168).
(10) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.).
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)(11) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
DIPSTICK TUBE FLUID SUCTION METHOD
(ALTERNATIVE)
(1) When performing the fluid suction method,
make sure the transaxle is at full operating temper-
ature.
(2) To perform the dipstick tube fluid suction
method, use a suitable fluid suction device (VaculaŸ
or equivalent).
(3) Insert the fluid suction line into the dipstick
tube.
NOTE: Verify that the suction line is inserted to the
lowest point of the transaxle oil pan. This will
ensure complete evacuation of the fluid in the pan.
(4) Follow the manufacturers recommended proce-
dure and evacuate the fluid from the transaxle.
(5) Remove the suction line from the dipstick tube.
(6) Pour four quarts of MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission FluidÐType 9602) through the dipstick
opening.
(7) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(8) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the ªADDº mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 168).
(9) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.).
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(10) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
Fig. 166 Oil Filter Screws
1 - SCREWDRIVER HANDLE
2 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4553
3 - OIL FILTER SCREWS (2)
4 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 167 Oil Filter and Gasket
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - GASKET
3 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 168 Dipstick Markings
1 - TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
21 - 100 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FLUID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1661 of 2399

ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT
Lift and rotate the gearshift hand lever into the
park (P) gate position and remove the ignition key.
This confirms the shift lever is in the gated park (P)
position.
After confirming the park gate position, turn the
ignition switch . If the starter will operate, the park
gate position is correct. Move the shift lever into the
neutral (N) position. If the starter will operate in this
position, the linkage is properly adjusted. If the
starter fails to operate in either position, linkage
adjustment is required.
(1) Park the vehicle on level ground and set the
parking brake.
(2) Place the gearshift lever in park (P) gate posi-
tion and remove key.
(3) Loosen the cable adjustment screw at the
transaxle operating lever (Fig. 181).
(4) Pull the transaxle operating lever fully forward
to the park detent position.
(5) Release the park brake, then rock the vehicle
to assure it is in park lock. Reset the park brake.
(6) Tighten the cable adjustment screw to 8 N´m
(70 in. lbs.). Gearshift cable should now be properly
adjusted.
(7) Verify PRNDL indicator still displays the corre-
sponding gear completely. If not, readjustment of
PRNDL may be required.
(8) Check adjustment by using the preceding pro-
cedure.
GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION
The governor assembly is fastened to the transaxle
transfer shaft. It consists of a governor body, weight,
valve, and shaft.
OPERATION
The governor meters hydraulic pressure, and this
metered pressure is used to signal the transmission
when it is time for a shift to occur. It does this by
balancing governor pressure on one side of a shift
valve, and throttle pressure on the other. When gov-
ernor pressure increases far enough to overcome the
throttle pressure on the valve, a shift occurs.
With the gearshift selector in a forward driving
range, line pressure flows from the manual valve and
down to the governor valve. When the output shaft
starts to rotate with vehicle motion, the governor
weight assembly will start to move outward due to
centrifugal force. As the weight is moved outward, it
will pull the valve with it until the land of the valve
uncovers the line pressure port. As the port begins to
become uncovered, governor pressure is metered. As
the vehicle's speed continues to increase, the weight
assembly will be at a point at which governor pres-
sure is acting on the left side of the reaction area of
the valve. This produces sufficient force to compress
the spring and allow the outer weight to move out
against the outer governor body retaining ring. At a
very high speed, the governor valve will be opened as
far as possible. In this condition, it is possible for
governor pressure to meet, but not to exceed, line
pressure. Generally governor pressure ranges from
0-100 psi from idle to maximum speed, and rises pro-
portionally with the increase in output shaft speed.
Governor pressure and throttle pressure are acting
upon the shift valves to determine when a shift will
occur. Governor pressure is a direct indication of road
speed, and throttle pressure is an indication of
engine load. When both parameters have been met
by the throttle and governor pressures, an upshift or
downshift will occur.
CLEANING
Thoroughly clean all the governor parts in a suit-
able cleaning solution but do not use any type of
caustic cleaning agents.
The governor weight components and the governor
valve, must slide freely in their bores when clean and
dry. Minor surface scratches and burrs can be
smoothed with crocus cloth.
INSPECTION
The aluminum governor valve and outer weight
have a hard coating on them. Check condition of this
Fig. 181 Gearshift Cable Adjustment
1 - SHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT
2 - SHIFT CABLE
21 - 104 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1662 of 2399
coating carefully. Do not reuse either part if the coat-
ing is damaged.
Inspect the governor weight spring for distortion.
Replace the spring, if distorted, collapsed, or broken.
Clean the filter in solvent and dry it with compressed
air. Replace the filter, if damaged. Inspect the park
gear for chipped or worn gear teeth or damaged ring
grooves. Replace the gear, if damaged.
Check the teeth on the park gear for wear or dam-
age. Replace the gear if necessary. Inspect the metal
seal rings on the park gear hub. Replace the rings
only if severely worn, or broken.
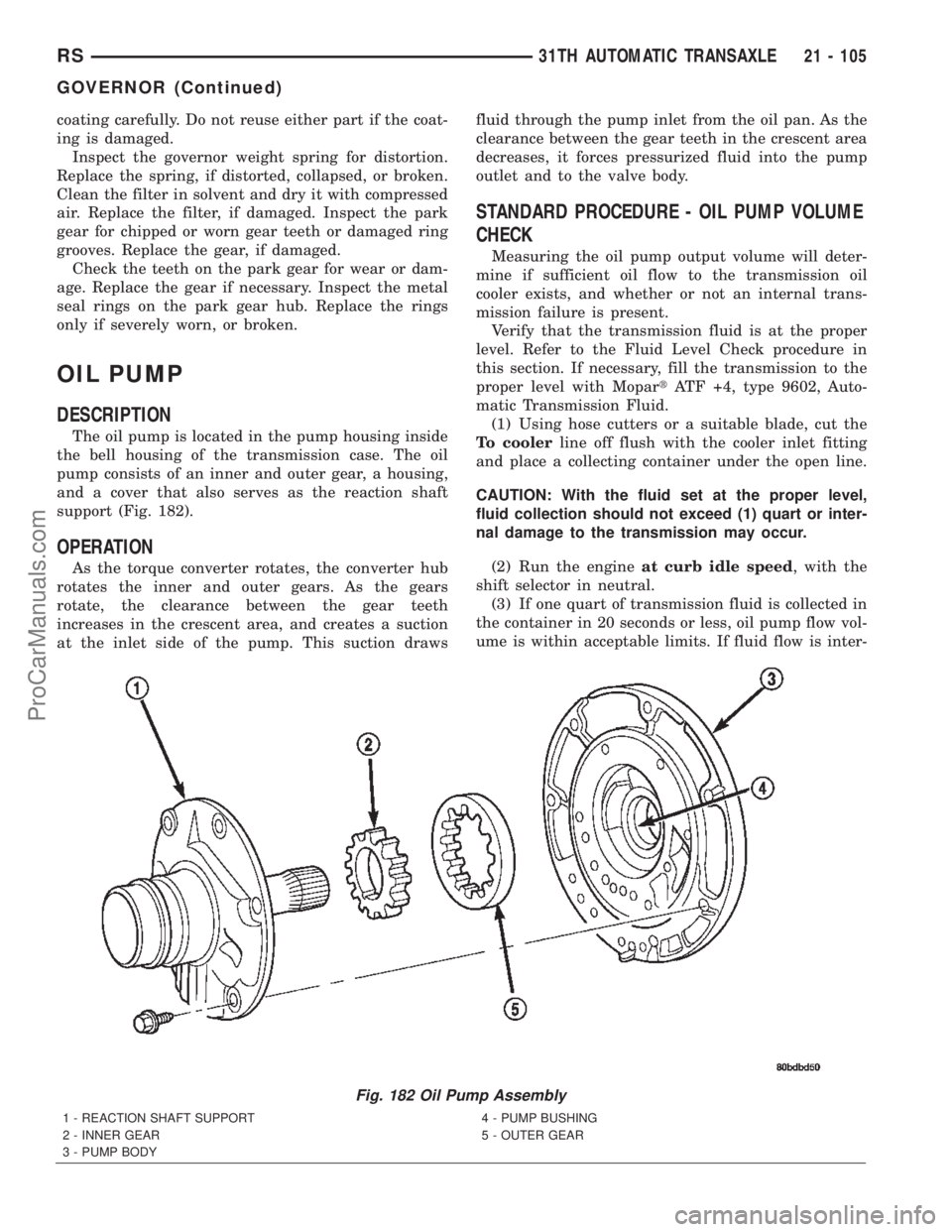
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump is located in the pump housing inside
the bell housing of the transmission case. The oil
pump consists of an inner and outer gear, a housing,
and a cover that also serves as the reaction shaft
support (Fig. 182).
OPERATION
As the torque converter rotates, the converter hub
rotates the inner and outer gears. As the gears
rotate, the clearance between the gear teeth
increases in the crescent area, and creates a suction
at the inlet side of the pump. This suction drawsfluid through the pump inlet from the oil pan. As the
clearance between the gear teeth in the crescent area
decreases, it forces pressurized fluid into the pump
outlet and to the valve body.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP VOLUME
CHECK
Measuring the oil pump output volume will deter-
mine if sufficient oil flow to the transmission oil
cooler exists, and whether or not an internal trans-
mission failure is present.
Verify that the transmission fluid is at the proper
level. Refer to the Fluid Level Check procedure in
this section. If necessary, fill the transmission to the
proper level with MopartATF +4, type 9602, Auto-
matic Transmission Fluid.
(1) Using hose cutters or a suitable blade, cut the
To coolerline off flush with the cooler inlet fitting
and place a collecting container under the open line.
CAUTION: With the fluid set at the proper level,
fluid collection should not exceed (1) quart or inter-
nal damage to the transmission may occur.
(2) Run the engineat curb idle speed, with the
shift selector in neutral.
(3) If one quart of transmission fluid is collected in
the container in 20 seconds or less, oil pump flow vol-
ume is within acceptable limits. If fluid flow is inter-
Fig. 182 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
2 - INNER GEAR
3 - PUMP BODY4 - PUMP BUSHING
5 - OUTER GEAR
RS31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 105
GOVERNOR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com