2001 NISSAN X-TRAIL relay
[x] Cancel search: relayPage 18 of 3833
GI-16
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
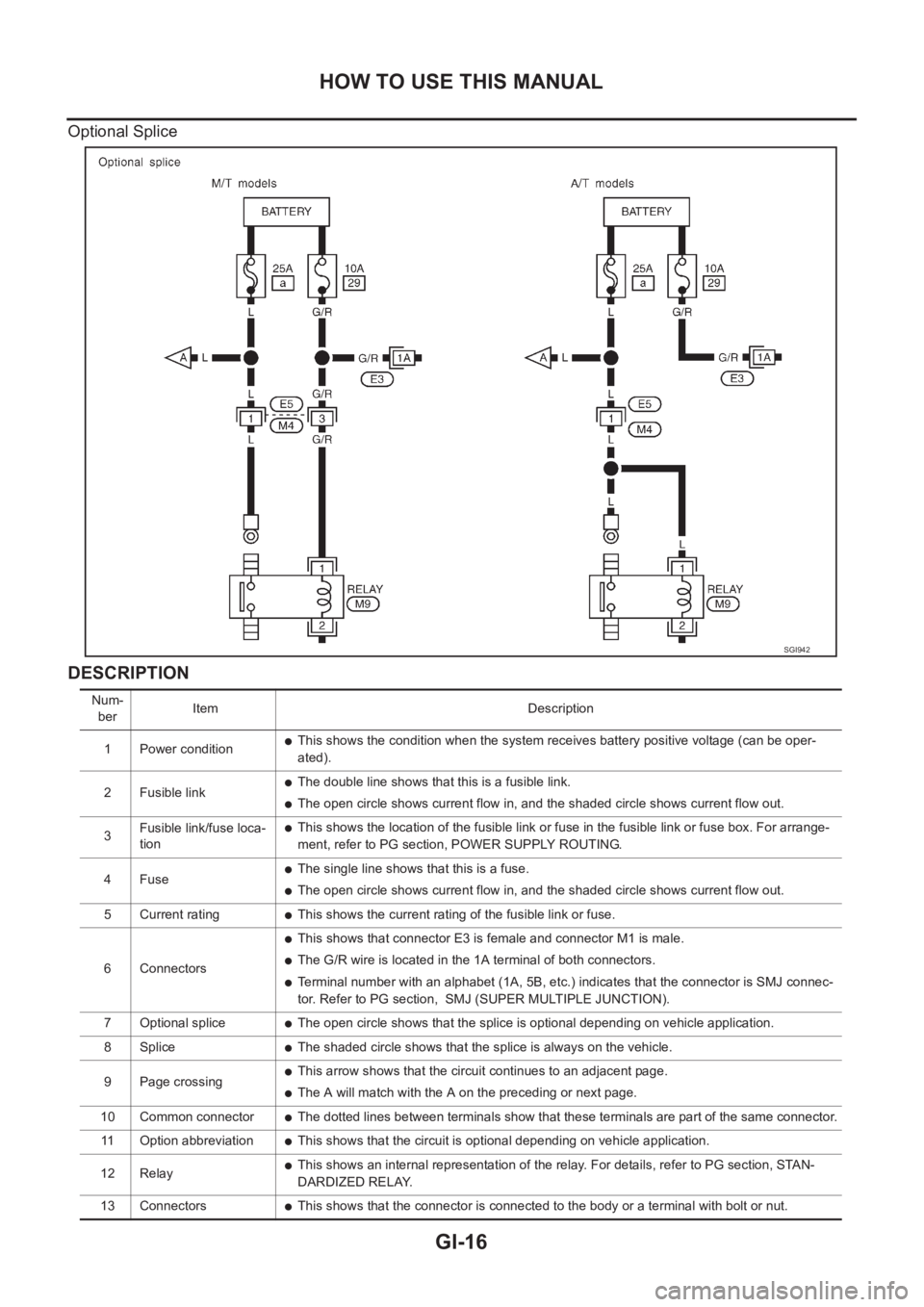
Optional Splice
DESCRIPTION
SGI942
Num-
berItem Description
1 Power condition
●This shows the condition when the system receives battery positive voltage (can be oper-
ated).
2 Fusible link
●The double line shows that this is a fusible link.
●The open circle shows current flow in, and the shaded circle shows current flow out.
3Fusible link/fuse loca-
tion
●This shows the location of the fusible link or fuse in the fusible link or fuse box. For arrange-
ment, refer to PG section, POWER SUPPLY ROUTING.
4Fuse
●The single line shows that this is a fuse.
●The open circle shows current flow in, and the shaded circle shows current flow out.
5 Current rating
●This shows the current rating of the fusible link or fuse.
6 Connectors
●This shows that connector E3 is female and connector M1 is male.
●The G/R wire is located in the 1A terminal of both connectors.
●Terminal number with an alphabet (1A, 5B, etc.) indicates that the connector is SMJ connec-
tor. Refer to PG section, SMJ (SUPER MULTIPLE JUNCTION).
7 Optional splice
●The open circle shows that the splice is optional depending on vehicle application.
8 Splice
●The shaded circle shows that the splice is always on the vehicle.
9 Page crossing
●This arrow shows that the circuit continues to an adjacent page.
●The A will match with the A on the preceding or next page.
10 Common connector
●The dotted lines between terminals show that these terminals are part of the same connector.
11 Option abbreviation
●This shows that the circuit is optional depending on vehicle application.
12 Relay
●This shows an internal representation of the relay. For details, refer to PG section, STAN-
DARDIZED RELAY.
13 Connectors
●This shows that the connector is connected to the body or a terminal with bolt or nut.
Page 26 of 3833
GI-24
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
●Heat sensitive
●Freezing
●Water intrusion
●Electrical load
●Cold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is important for simulating the conditions of the
problem.
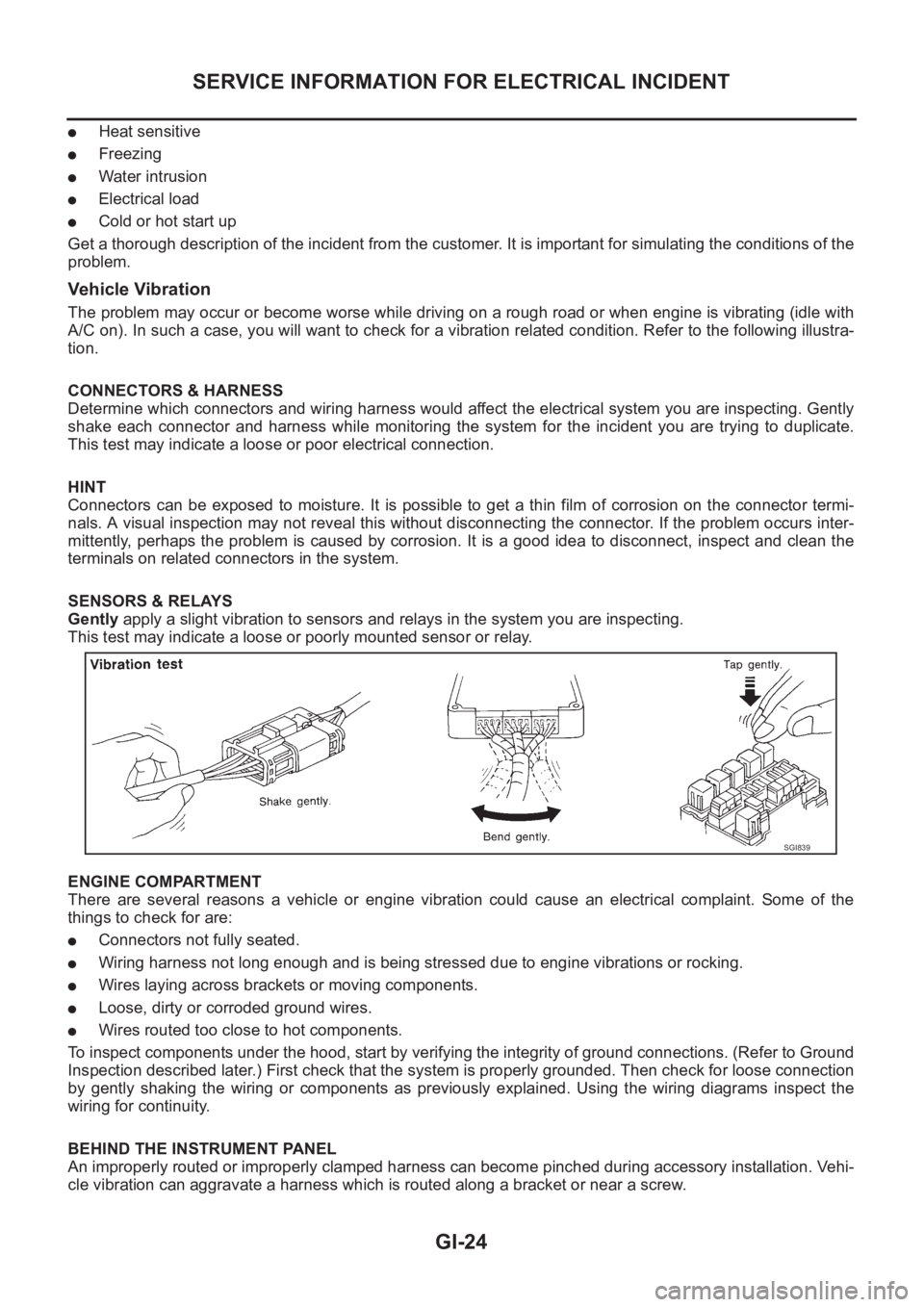
Vehicle Vibration
The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough road or when engine is vibrating (idle with
A/C on). In such a case, you will want to check for a vibration related condition. Refer to the following illustra-
tion.
CONNECTORS & HARNESS
Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the electrical system you are inspecting. Gently
shake each connector and harness while monitoring the system for the incident you are trying to duplicate.
This test may indicate a loose or poor electrical connection.
HINT
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible to get a thin film of corrosion on the connector termi-
nals. A visual inspection may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the problem occurs inter-
mittently, perhaps the problem is caused by corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean the
terminals on related connectors in the system.
SENSORS & RELAYS
Gently apply a slight vibration to sensors and relays in the system you are inspecting.
This test may indicate a loose or poorly mounted sensor or relay.
ENGINE COMPARTMENT
There are several reasons a vehicle or engine vibration could cause an electrical complaint. Some of the
things to check for are:
●Connectors not fully seated.
●Wiring harness not long enough and is being stressed due to engine vibrations or rocking.
●Wires laying across brackets or moving components.
●Loose, dirty or corroded ground wires.
●Wires routed too close to hot components.
To inspect components under the hood, start by verifying the integrity of ground connections. (Refer to Ground
Inspection described later.) First check that the system is properly grounded. Then check for loose connection
by gently shaking the wiring or components as previously explained. Using the wiring diagrams inspect the
wiring for continuity.
BEHIND THE INSTRUMENT PANEL
An improperly routed or improperly clamped harness can become pinched during accessory installation. Vehi-
cle vibration can aggravate a harness which is routed along a bracket or near a screw.
SGI839
Page 28 of 3833
GI-26
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Cold or Hot Start Up
On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the car is started cold, or it may occur when
the car is restarted hot shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep the car overnight to
make a proper diagnosis.
CIRCUIT INSPECTION
Introduction
In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy task if it is approached in a logical and organized method.
Before beginning it is important to have all available information on the system to be tested. Also, get a thor-
ough understanding of system operation. Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while testing electrical components. Gently shake the wiring har-
ness or electrical component to do this.
NOTE:
Refer to “How to Check Terminal” to probe or check terminal.
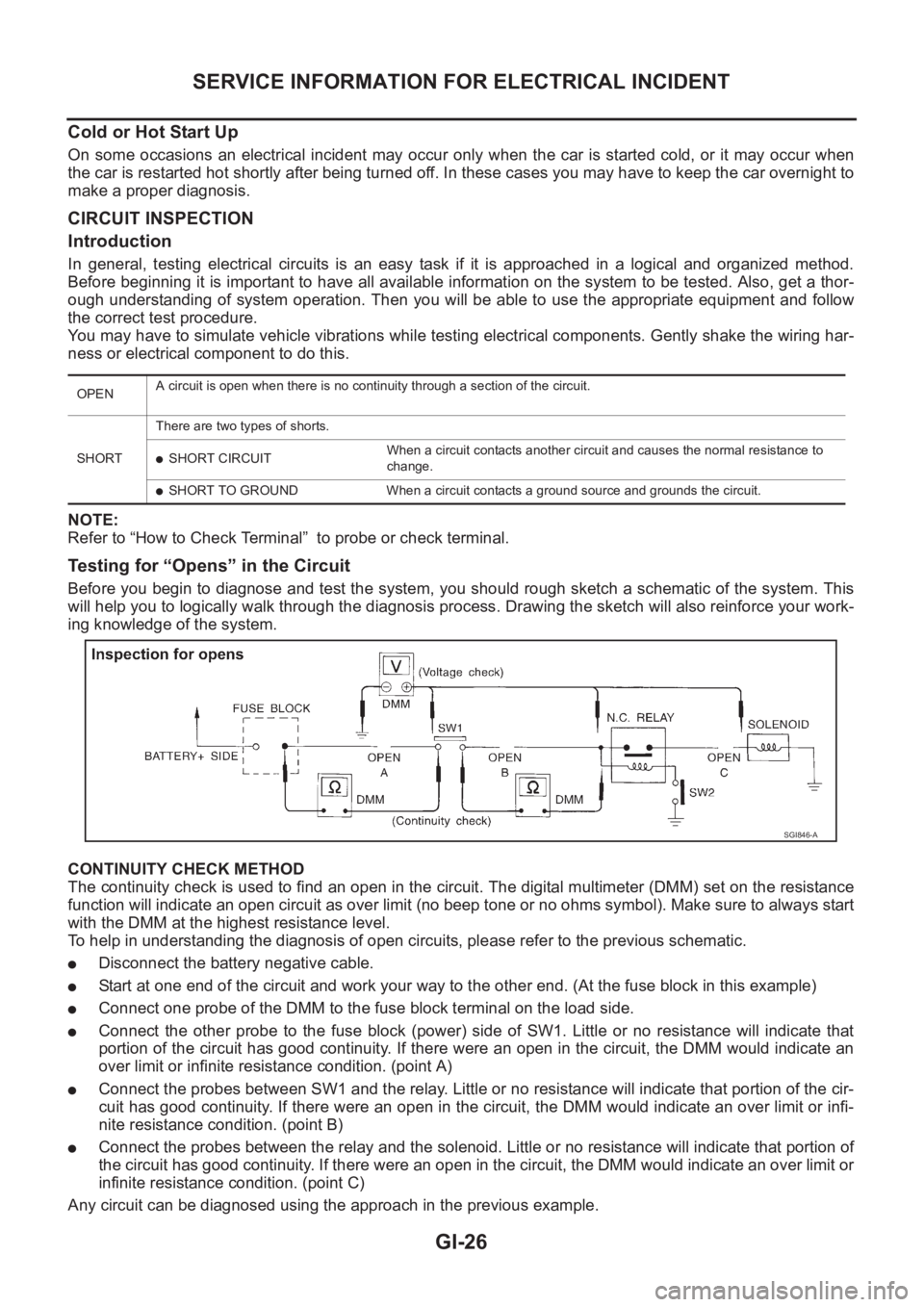
Testing for “Opens” in the Circuit
Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should rough sketch a schematic of the system. This
will help you to logically walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will also reinforce your work-
ing knowledge of the system.
CONTINUITY CHECK METHOD
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circuit. The digital multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance
function will indicate an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbol). Make sure to always start
with the DMM at the highest resistance level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits, please refer to the previous schematic.
●Disconnect the battery negative cable.
●Start at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end. (At the fuse block in this example)
●Connect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on the load side.
●Connect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1. Little or no resistance will indicate that
portion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an
over limit or infinite resistance condition. (point A)
●Connect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the cir-
cuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or infi-
nite resistance condition. (point B)
●Connect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of
the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or
infinite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
OPENA circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of the circuit.
SHORTThere are two types of shorts.
●SHORT CIRCUITWhen a circuit contacts another circuit and causes the normal resistance to
change.
●SHORT TO GROUND When a circuit contacts a ground source and grounds the circuit.
SGI846-A
Page 29 of 3833
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-27
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
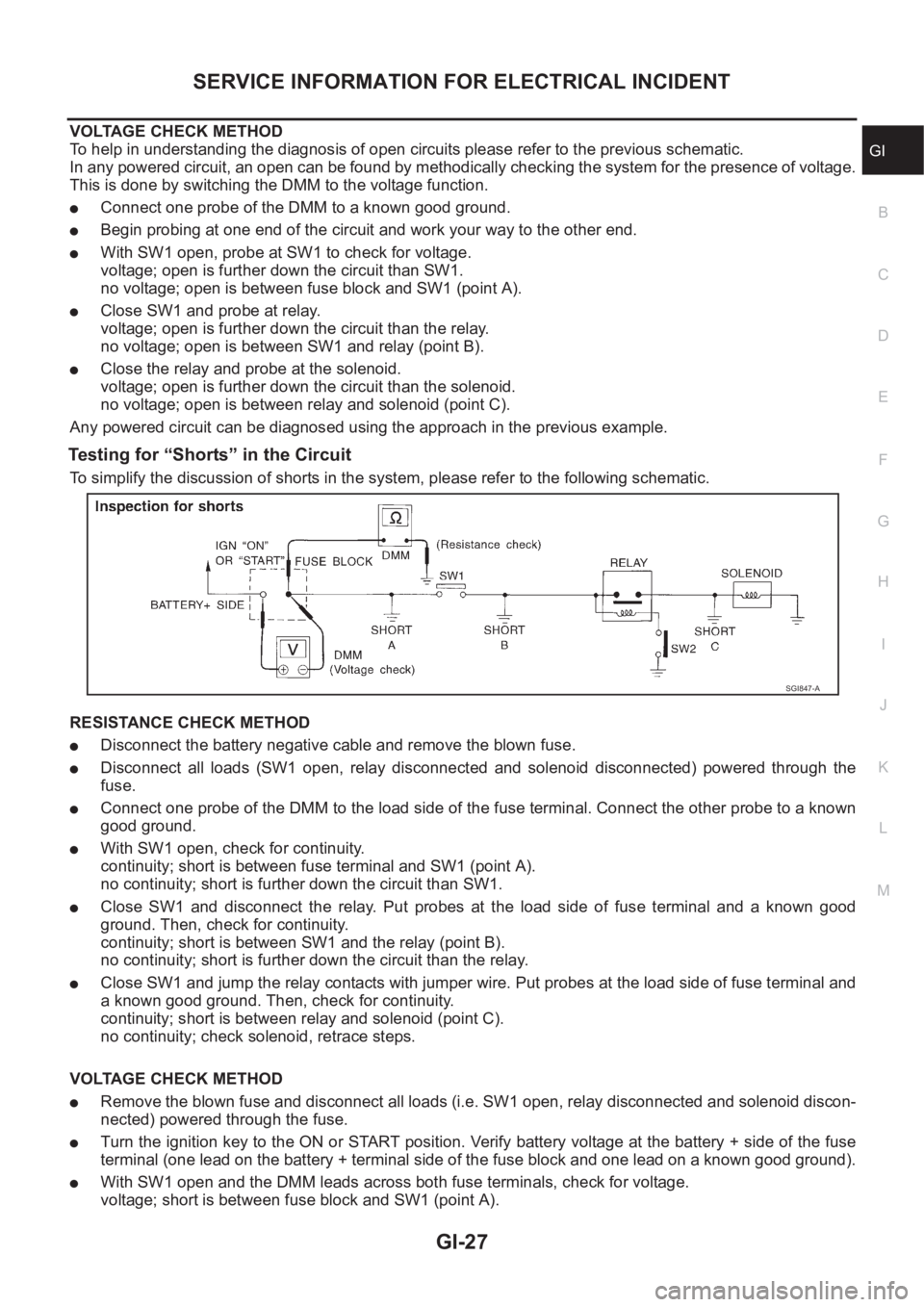
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits please refer to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodically checking the system for the presence of voltage.
This is done by switching the DMM to the voltage function.
●Connect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
●Begin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end.
●With SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
●Close SW1 and probe at relay.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
●Close the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
Testing for “Shorts” in the Circuit
To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system, please refer to the following schematic.
RESISTANCE CHECK METHOD
●Disconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
●Disconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the
fuse.
●Connect one probe of the DMM to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a known
good ground.
●With SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
●Close SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good
ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
●Close SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and
a known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
●Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
●Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify battery voltage at the battery + side of the fuse
terminal (one lead on the battery + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
●With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
SGI847-A
Page 30 of 3833

GI-28
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
●With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check
for voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
●With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
●Remove the ground bolt or screw.
●Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
●Clean as required to assure good contact.
●Reinstall bolt or screw securely.
●Inspect for “add-on” accessories which may be interfering with the ground circuit.
●If several wires are crimped into one ground eyelet terminal, check for proper crimps. Make sure all of the
wires are clean, securely fastened and providing a good ground path. If multiple wires are cased in one
eyelet make sure no ground wires have excess wire insulation.
For detailed ground distribution information, refer to “Ground Distribution” in PG section.
Voltage Drop Tests
Voltage drop tests are often used to find components or circuits which have excessive resistance. A voltage
drop in a circuit is caused by a resistance when the circuit is in operation.
Check the wire in the illustration. When measuring resistance with DMM, contact by a single strand of wire will
give reading of 0 ohms. This would indicate a good circuit. When the circuit operates, this single strand of wire
is not able to carry the current. The single strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will be picked
up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
●Undersized wiring (single strand example)
●Corrosion on switch contacts
●Loose wire connections or splices.
SGI853
Page 354 of 3833

EC-4
.271
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................271
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................271
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................272
Wiring Diagram .....................................................273
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................274
Component Inspection ..........................................275
Removal and Installation ......................................275
DTC P1121 ELECTRIC THROTTLE CONTROL
ACTUATOR .............................................................276
Description ............................................................276
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................276
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................276
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................277
DTC P1122 ELECTRIC THROTTLE CONTROL
FUNCTION ..............................................................278
Description ............................................................278
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.278
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................278
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................279
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................279
Wiring Diagram .....................................................280
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................281
Remove and Installation .......................................284
DTC P1124, P1126 THROTTLE CONTROL MOTOR
RELAY .....................................................................285
Component Description ........................................285
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.285
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................285
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................285
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................285
Wiring Diagram .....................................................287
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................288
Component Inspection ..........................................289
DTC P1128 THROTTLE CONTROL MOTOR .........290
Component Description ........................................290
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................290
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................290
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................290
Wiring Diagram .....................................................292
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................293
Component Inspection ..........................................294
Remove and Installation .......................................294
DTC P1143 HO2S1 .................................................295
Component Description ........................................295
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.295
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................295
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................296
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................296
Overall Function Check ........................................297
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................297
Component Inspection ..........................................299
Removal and Installation ......................................300
DTC P1144 HO2S1 .................................................301
Component Description ........................................301
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode .301
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................301
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................302
DTC Confirmation Procedure ................................302
Overall Function Check .........................................303
Diagnostic Procedure ............................................303
Component Inspection ..........................................305
Removal and Installation .......................................306
DTC P1146 HO2S2 ..................................................307
Component Description ........................................307
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.307
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................307
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................307
DTC Confirmation Procedure ................................308
Overall Function Check .........................................308
Wiring Diagram .....................................................310
Diagnostic Procedure ............................................311
Component Inspection ..........................................312
Removal and Installation .......................................314
DTC P1147 HO2S2 ..................................................315
Component Description ........................................315
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.315
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................315
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................315
DTC Confirmation Procedure ................................316
Overall Function Check .........................................316
Wiring Diagram .....................................................318
Diagnostic Procedure ............................................319
Component Inspection ..........................................320
Removal and Installation .......................................322
DTC P1217 ENGINE OVER TEMPERATURE ........323
System Description ...............................................323
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.323
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................324
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................324
Overall Function Check .........................................325
Wiring Diagram .....................................................327
Diagnostic Procedure ............................................328
Main 12 Causes of Overheating ...........................335
Component Inspection ..........................................336
DTC P1225 TP SENSOR ........................................337
Component Description ........................................337
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................337
DTC Confirmation Procedure ................................337
Diagnostic Procedure ............................................338
Remove and Installation .......................................338
DTC P1226 TP SENSOR ........................................339
Component Description ........................................339
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................339
DTC Confirmation Procedure ................................339
Diagnostic Procedure ............................................340
Remove and Installation .......................................340
DTC P1229 SENSOR POWER SUPPLY ................341
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................341
DTC Confirmation Procedure ................................341
Page 357 of 3833

EC-7
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
ECA On Board Diagnosis Logic ................................... 528
DTC Confirmation Procedure ............................... 528
Wiring Diagram .................................................... 530
Diagnostic Procedure ........................................... 531
Component Inspection ......................................... 533
Remove and Installation ....................................... 533
DTC P0134 HO2S1 ................................................. 534
Component Description ........................................ 534
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
. 534
ECM Terminals and Reference Value .................. 534
On Board Diagnosis Logic ................................... 535
DTC Confirmation Procedure ............................... 535
Wiring Diagram .................................................... 536
Diagnostic Procedure ........................................... 537
Component Inspection ......................................... 538
Removal and Installation ...................................... 539
DTC P0222, P0223 TP SENSOR ........................... 540
Component Description ........................................ 540
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
. 540
ECM Terminals and Reference Value .................. 540
On Board Diagnosis Logic ................................... 541
DTC Confirmation Procedure ............................... 541
Wiring Diagram .................................................... 543
Diagnostic Procedure ........................................... 544
Component Inspection ......................................... 545
Remove and Installation ....................................... 545
DTC P0327, P0328 KS ........................................... 546
Component Description ........................................ 546
ECM Terminals and Reference Value .................. 546
On Board Diagnosis Logic ................................... 546
DTC Confirmation Procedure ............................... 546
Wiring Diagram .................................................... 548
Diagnostic Procedure ........................................... 549
Component Inspection ......................................... 550
Removal and Installation ...................................... 550
DTC P0335 CKP SENSOR (POS) .......................... 551
Component Description ........................................ 551
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
. 551
ECM Terminals and Reference Value .................. 551
On Board Diagnosis Logic ................................... 552
DTC Confirmation Procedure ............................... 552
Wiring Diagram .................................................... 553
Diagnostic Procedure ........................................... 554
Component Inspection ......................................... 556
Removal and Installation ...................................... 556
DTC P0340 CMP SENSOR (PHASE) ..................... 557
Component Description .......................................
. 557
ECM Terminals and Reference Value .................. 557
On Board Diagnosis Logic ................................... 557
DTC Confirmation Procedure ............................... 558
Wiring Diagram .................................................... 559
Diagnostic Procedure ........................................... 560
Component Inspection ......................................... 562
Removal and Installation ...................................... 562
DTC P0500 VSS ..................................................... 563
Component Description ........................................ 563ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................563
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................563
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................563
Overall Function Check ........................................564
Wiring Diagram .....................................................565
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................567
DTC P0550 PSP SENSOR .....................................568
Component Description ........................................568
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.568
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................568
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................568
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................568
Wiring Diagram .....................................................570
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................571
Component Inspection ..........................................572
DTC P0605 ECM .....................................................573
Component Description ........................................573
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................573
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................573
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................575
DTC P0650 MI .........................................................576
Component Description ........................................576
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................576
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................576
Overall Function Check ........................................576
Wiring Diagram .....................................................577
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................578
DTC P1065 ECM POWER SUPPLY .......................580
Component Description ........................................580
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................580
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................580
Wiring Diagram .....................................................581
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................582
DTC P1121 ELECTRIC THROTTLE CONTROL
ACTUATOR .............................................................584
Description ............................................................584
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................584
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................584
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................585
DTC P1122 ELECTRIC THROTTLE CONTROL
FUNCTION ..............................................................586
Description ............................................................586
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.586
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................586
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................587
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................587
Wiring Diagram .....................................................588
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................589
Remove and Installation .......................................592
DTC P1124, P1126 THROTTLE CONTROL MOTOR
RELAY .....................................................................593
Component Description ........................................593
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.593
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................593
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................593
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................593
Page 362 of 3833

EC-12
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................954
Component Inspection ..........................................955
Removal and Installation ......................................955
DTC P0335 CKP SENSOR (POS) ..........................956
Component Description ........................................956
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.956
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................956
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................957
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................957
Wiring Diagram .....................................................958
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................959
Component Inspection ..........................................961
Removal and Installation ......................................961
DTC P0340 CMP SENSOR (PHASE) .....................962
Component Description ........................................962
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................962
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................962
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................963
Wiring Diagram .....................................................964
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................965
Component Inspection ..........................................967
Removal and Installation ......................................967
DTC P0420 THREE WAY CATALYST FUNCTION . 968
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................968
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................968
Overall Function Check ........................................969
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................970
DTC P0444, P0445 EVAP CANISTER PURGE VOL-
UME CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE ......................972
Description ............................................................972
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.972
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................972
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................973
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................973
Wiring Diagram .....................................................974
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................975
Component Inspection ..........................................976
Removal and Installation ......................................977
DTC P0500 VSS ......................................................978
Component Description ........................................978
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................978
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................978
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................978
Overall Function Check ........................................979
Wiring Diagram .....................................................980
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................982
DTC P0550 PSP SENSOR ......................................983
Component Description ........................................983
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.983
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................983
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................983
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................983
Wiring Diagram .....................................................985
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................986
Component Inspection ..........................................987DTC P0605 ECM .....................................................988
Component Description ........................................988
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................988
DTC Confirmation Procedure ................................988
Diagnostic Procedure ............................................989
DTC P0650 MI .........................................................991
Component Description ........................................991
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................991
DTC Confirmation Procedure ................................991
Wiring Diagram .....................................................992
Diagnostic Procedure ............................................993
DTC P1065 ECM POWER SUPPLY ........................995
Component Description ........................................995
On Board Diagnosis Logic ....................................995
DTC Confirmation Procedure ................................995
Wiring Diagram .....................................................996
Diagnostic Procedure ............................................997
DTC P1102 MAF SENSOR .....................................999
Component Description ........................................999
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
.999
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ...................999
On Board Diagnosis Logic ...................................1000
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................1000
Wiring Diagram ....................................................1001
Diagnostic Procedure ........................................... 1002
Component Inspection .........................................1003
Removal and Installation ......................................1004
DTC P1111 IVT CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE ....1005
Component Description .......................................1005
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
1005
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ..................1005
On Board Diagnosis Logic ...................................1005
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................1006
Wiring Diagram ....................................................1007
Diagnostic Procedure ........................................... 1008
Component Inspection .........................................1009
Removal and Installation ......................................1009
DTC P1121 ELECTRIC THROTTLE CONTROL
ACTUATOR ............................................................1010
Description ...........................................................1010
On Board Diagnosis Logic ...................................1010
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................1010
Diagnostic Procedure ........................................... 1011
DTC P1122 ELECTRIC THROTTLE CONTROL
FUNCTION .............................................................1012
Description ...........................................................1012
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ..................1012
On Board Diagnosis Logic ...................................1012
DTC Confirmation Procedure ...............................1013
Wiring Diagram ....................................................1014
Diagnostic Procedure ........................................... 1015
Component Inspection .........................................1017
DTC P1123 THROTTLE CONTROL MOTOR RELAY 1018
Component Description .......................................1018
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor Mode
1018
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ..................