2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY check oil
[x] Cancel search: check oilPage 108 of 2321

WHEEL ALIGNMENT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................3CURB HEIGHT MEASUREMENT............3
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CURB HEIGHT
MEASUREMENT
The wheel alignment is to be checked and all align-
ment adjustments made with the vehicle at its
required curb height specification.
Vehicle height is to be checked with the vehicle on
a flat, level surface, preferably a vehicle alignment
rack. The tires are to be inflated to the recommended
pressure. All tires are to be the same size as stan-
dard equipment. Vehicle height is checked with the
fuel tank full of fuel, and no passenger or luggage
compartment load.
Vehicle height is not adjustable. If the measure-
ment is not within specifications, inspect the vehiclefor bent or weak suspension components. Compare
the parts tag on the suspect coil spring(s) to the
parts book and the vehicle sales code, checking for a
match. Once removed from the vehicle, compare the
coil spring height to a correct new or known good coil
spring. The heights should vary if the suspect spring
is weak.
(1) Measure from the inboard edge of the wheel
opening fender lip directly above the wheel center
(spindle), to the floor or alignment rack surface.
(2) When measuring, the maximum left-to-right
differential is not to exceed 12.5 mm (0.5 in.).
(3) Compare the measurements to the specifica-
tions listed in the following Curb Height Specifica-
tions charts.
CURB HEIGHT SPECIFICATIONS - LONG WHEEL BASE VEHICLES WITH SDF SUSPENSION
TIRE SALES CODE/TIRE SIZE FRONT REAR
TMM / 215/65 R 16756mm 10mm
29.76 in. 0.39 in.772mm 10mm
30.39 in. 0.39 in.
CURB HEIGHT SPECIFICATIONS - LONG WHEEL BASE VEHICLES WITH SDF + SER
SUSPENSION
TIRE SALES CODE/TIRE SIZE FRONT REAR
TMM / 215/65 R 16756mm 10mm
29.76 in. 0.39 in.771mm 10mm
30.35 in. 0.39 in.
CURB HEIGHT SPECIFICATIONS - SHORT WHEEL BASE VEHICLES
TIRE SALES CODE/TIRE SIZE FRONT REAR
TMM / 215/65 R 16755mm 10mm
29.72 in. 0.39 in.770mm 10mm
30.31 in. 0.39 in.
RGWHEEL ALIGNMENT2a-3
ProCarManuals.com
Page 136 of 2321

adjustment, maintenance or fluid checks required
during the life of the unit.
The overrunning clutch allows the rear wheels to
overrun the front wheels during a rapid front wheel
lock braking maneuver. The overrunning action pre-
vents any feed-back of front wheel braking torque to
the rear wheels. It also allows the braking system to
control the braking behavior as a two wheel drive
(2WD) vehicle.
The overrunning clutch housing has a separate oil
sump and is filled independently from the differen-
tial. The fill plug is located on the side of the over-
running clutch case. When filling the overrunning
clutch with lubricant use MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission FluidÐType 9602) or equivalent.
The differential assembly contains a conventional
open differential with hypoid ring gear and pinion
gear set. The hypoid gears are lubricated by SAE
80W-90 gear lubricant.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR DRIVELINE
MODULE NOISE
Different sources can be the cause of noise that the
rear driveline module assembly is suspected of mak-
ing. Refer to the following causes for noise diagnosis.
DRIVELINE MODULE ASSEMBLY NOISE
The most important part of driveline module ser-
vice is properly identifying the cause of failures and
noise complaints. The cause of most driveline module
failures is relatively easy to identify. The cause of
driveline module noise is more difficult to identify.
If vehicle noise becomes intolerable, an effort
should be made to isolate the noise. Many noises that
are reported as coming from the driveline module
may actually originate at other sources. For example:
Fig. 1 AWD Driveline Module Assembly
1 - TORQUE ARM
2 - INPUT FLANGE
3 - FLANGE NUT
4 - WASHER
5 - SHIELD
6 - VENT
7 - O-RING
8 - WASHER
9 - BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH (BOC)
10 - VISCOUS COUPLER11 - SHIM (SELECT)
12 - O-RING
13 - DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
14 - PLUG-DIFFERENTIAL FILL
15 - PLUG-OVERRUNNING CLUTCH HOUSING DRAIN
16 - SNAP RING
17 - BEARING
18 - OVERRUNING CLUTCH HOUSING
19 - SEAL-INPUT FLANGE
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-27
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 191 of 2321

STANDARD PROCEDURE - BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL CHECKING
Check master cylinder reservoir fluid level a mini-
mum of twice annually.
Fluid reservoirs are marked with the words FULL
and ADD to indicate proper brake fluid fill level of
the master cylinder.
If necessary, add brake fluid to bring the level to
the bottom of the FULL mark on the side of the mas-
ter cylinder fluid reservoir.
Use only Mopartbrake fluid or equivalent from a
sealed container. Brake fluid must conform to DOT 3
specifications (DOT 4 or DOT 4+ are acceptable).
DO NOTuse brake fluid with a lower boiling
point, as brake failure could result during prolonged
hard braking.
Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container.
DO NOTuse petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage will result. Petroleum based fluids would be
items such as engine oil, transmission fluid, power
steering fluid etc.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications (DOT 4 and DOT 4+ are
acceptable) and SAE J1703 standards. No other type
of brake fluid is recommended or approved for usage
in the vehicle brake system. Use only MopartBrake
Fluid or equivalent from a tightly sealed container.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container of brake fluid will absorb moisture
from the air and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-based
fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of such
type fluids will result in seal damage of the vehicle
brake hydraulic system causing a failure of the
vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids would
be items such as engine oil, transmission fluid,
power steering fluid, etc.
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
A junction block is used on vehicles that are not
equipped with antilock brakes (ABS). The junction
block mounts in the same location as the integrated
control unit (ICU) does on vehicles equipped withABS. This allows for use of the same brake tube con-
figuration on all vehicles. The junction block is
located on the driver's side of the front suspension
cradle/crossmember below the master cylinder (Fig.
46).
It has six threaded ports to which the brake tubes
connect. Two are for the primary and secondary
brake tubes coming from the master cylinder. The
remaining four are for the chassis brake tubes going
to each brake assembly.
OPERATION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
The junction block distributes the brake fluid com-
ing from the master cylinder primary and secondary
ports to the four chassis brake tubes leading to the
brakes at each wheel. Since the junction block
mounts in the same location as the ABS integrated
control unit (ICU), it allows for the common use of
brake tubes going to the brakes whether the vehicle
is equipped with or without ABS.
NOTE: Although the brake tubes coming from the
master cylinder to the junction block or ABS ICU
may appear to be the same, they are not. They are
unique to each brake system application.
REMOVAL - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
(1) Using a brake pedal depressor, move and lock
the brake pedal to a position past its first 1 inch of
travel. This will prevent brake fluid from draining
out of the master cylinder when the brake tubes are
removed from the junction block.
(2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(3) If the vehicle is equipped with speed control,
perform the following:
(a) Disconnect the battery positive cable.
(b) Remove the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - REMOVAL).
(c) Disconnect the vacuum hose connector at the
tank built into the battery tray.
(d) Remove the screw securing the coolant filler
neck to the battery tray.
(e) Remove the battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - REMOVAL).
(f) Remove the fasteners and move the speed
control servo off to the side, out of the way.
CAUTION: Before removing the brake tubes from
the junction block, the junction block and the brake
tubes must be thoroughly cleaned. This is required
to prevent contamination from entering the brake
hydraulic system.
5 - 32 BRAKES - BASERS
FLUID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 238 of 2321

BRAKES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - BASE........................... 1BRAKES - ABS........................... 10
BRAKES - BASE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - BASE
DESCRIPTION............................1
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL
DESCRIPTION............................1
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................1
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL CHECKING...........1
MASTER CYLINDER - RHD
DESCRIPTION............................2
REMOVAL...............................2
INSTALLATION............................3
PEDAL TORQUE SHAFT
REMOVAL...............................3
INSTALLATION............................4POWER BRAKE BOOSTER - RHD
REMOVAL...............................4
INSTALLATION............................6
ROTORS
SPECIFICATIONS.........................8
PARKING BRAKE
DESCRIPTION............................8
CABLES - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL...............................8
INSTALLATION............................8
LEVER - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL...............................8
INSTALLATION............................9
BRAKES - BASE
DESCRIPTION - BASE BRAKES
Four-Wheel Disc Antilock Brakes are standard on
all models.
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL
DESCRIPTION - DISC BRAKES
All vehicles are equipped with Four-Wheel-Disc
brakes. Both 15º (BRE) and 16º (BR3) disc/disc brake
systems are available. The disc brakes are manufac-
tured by Continental Teves. The BR3 system is stan-
dard equipment on all-wheel drive and all right-hand
drive models. It is optional on other models.
The BR3 system features larger, externally vented
front brake rotors.
Although there are different disc/disc systems, they
are serviced using the same service procedures. Some
specifications differ.
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL CHECKING
Right hand drive vehicles feature a brake fluid res-
ervoir with the same markings as left hand drive res-
ervoirs.
Check master cylinder reservoir fluid level a mini-
mum of twice annually.
Fluid reservoirs are marked with the words FULL
and ADD to indicate proper brake fluid fill level of
the master cylinder.
If necessary, add brake fluid to bring the level to
the bottom of the FULL mark on the side of the mas-
ter cylinder fluid reservoir.
Use only Mopartbrake fluid or equivalent from a
sealed container. Brake fluid must conform to DOT 3
specifications (DOT 4 or DOT 4+ are acceptable).
DO NOTuse brake fluid with a lower boiling
point, as brake failure could result during prolonged
hard braking.
RGBRAKES5a-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 255 of 2321

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH SYSTEM
Clutch problem diagnosis will generally require a
road test to determine the type of fault. Component
inspection will then determine the problem after road
testing.
Drive the vehicle at normal speeds during road
test. Shift the transaxle through all gear ranges and
observe clutch action. If chatter, grab, slip, or
improper release is experienced, remove and inspect
the clutch components. If the problem is noise or
hard shifting, further diagnosis may be needed. The
transaxle or other driveline components may actually
be at fault.
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS - CLUTCH GRAB/CHATTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLUTCH DISC FACING
COVERED WITH OIL OR
GREASEOil leak at engine rear main or
transaxle input shaft seal.Correct leak and replace modular clutch
assembly (2.4L Gas) or clutch cover and
disc (2.5L TD).
Too much grease applied to splines
of disc and input shaft.Apply lighter coating of grease to splines.
NO FAULT FOUND WITH
CLUTCH
COMPONENTSProblem actually related to
suspension or driveline component.Further diagnosis required. Check
engine/transmission mounts, suspension
attaching parts and other driveline
components as needed.
Engine related problems. Check EFI and ignition systems.
PARTIAL ENGAGEMENT
OF CLUTCH DISCClutch cover, spring, or release
fingers bent, distorted (rough
handling, improper assembly).Replace modular clutch assembly (2.4L
Gas) or clutch cover and disc (2.5L TD).
Clutch disc damaged or distorted. Replace modular clutch assembly (2.4L
Gas) or clutch cover and disc (2.5L TD).
Clutch misalignment. Verify modular clutch pilot plate alignment
to crankshaft. Replace the modular clutch
assembly (2.4L Gas) or clutch cover and
disc (2.5L TD) if the pilot plate is loose or
bent.
Improper transaxle-to-engine
installation.Verify transaxle is properly installed to
engine.
Fig. 8 Release Bearing and Lever (RHD)
1 - RELEASE LEVER
2 - RELEASE BEARING
6a - 4 CLUTCHRG
CLUTCH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 258 of 2321
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRIVE PLATE
MISALIGNMENT
Common causes of misalignment are:
²Heat warping
²Mounting drive plate on a dirty crankshaft
flange
²Incorrect bolt tightening
²Improper seating on the crankshaft shoulder
²Loose crankshaft bolts
Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
drive plate. Dirt and grease on the flange surface
may misalign the flywheel, causing excessive runout.
Use new bolts when mounting drive plate to crank-
shaft. Tighten drive plate bolts to specified torque
only. Over-tightening can distort the drive plate hub
causing excessive runout.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH COVER
AND DISC RUNOUT
Check condition of the clutch cover before installa-
tion. A warped cover or diaphragm spring will cause
grab and/or incomplete release or engagement. Use
care when handling the clutch assembly. Impact can
distort the cover, diaphragm spring, and release fin-
gers.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH CHATTER
COMPLAINTS
For all clutch chatter complaints, perform the fol-
lowing:
(1) Check for loose, misaligned, or broken engine
and transmission mounts. If present, they should be
corrected at this time. Test vehicle for chatter. If
chatter is gone, there is no need to go any further.
(2) If chatter persists, check hydraulic clutch
release system is functioning properly.
(3) Check for loose connections in drivetrain. Cor-
rect any problems and determine if clutch chatter
complaints have been satisfied. If not:
(a) Remove transaxle.
(b) Check to see if the release bearing is sticky
or binding. Replace bearing, if needed.
(c) Check linkage for excessive wear on the pivot
stud and fork fingers. Replace all worn parts.
(d) Check clutch assembly for contamination
(dirt, oil). Replace clutch assembly, if required.
(e) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines
are damaged. Replace with new clutch assembly, if
necessary.
(f) Check input shaft splines for damage.
Replace, if necessary.
(g) Check for uneven wear on clutch fingers.
(h) Check for broken clutch cover diaphragm
spring fingers. Replace with new clutch assembly,
if necessary.
SPECIAL TOOLS
SPECIAL TOOLS - T850 TRANSAXLE
CLUTCH RELEASE CABLE -
LHD
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3)Diesel models:Remove underbody splash
shield.
(4) Remove clutch bellhousing cap.
(5) Some models will have a clutch cable retainer
clip at the transaxle to secure it to the case (Fig. 9).
If retainer clip is installed, dislodge clip from from
inside bellhousing using a suitable screwdriver (Fig.
10), pull outward on cable conduit, guiding cable core
wire through slot in bellhousing and disengaging
cable ªTº from clutch release lever (Fig. 11). If
retainer is not installed, disengage clutch cable from
transaxle by pulling outward on cable conduit, guid-
Disconnect Tool, 6638A
Remover/Installer, 6891
RGCLUTCH6a-7
CLUTCH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 268 of 2321

COOLING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLING
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................3
COOLING SYSTEM LEAK TEST.............3
COOLING SYSTEM FLOW CHECK..........3
COOLING SYSTEM AERATION.............3
COOLING SYSTEM DEAERATION...........3
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................4COOLING SYSTEM - DRAINING............4
COOLING SYSTEM - REFILLING............4
COOLANT - ADDING ADDITIONAL...........4
COOLANT LEVEL CHECK - ROUTINE........5
SPECIFICATIONS.........................6
SPECIAL TOOLS..........................6
ACCESSORY DRIVE.......................7
ENGINE................................13
TRANSMISSION.........................36
COOLING
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system components consist of a radia-
tor, electric fan motors, shroud, pressure cap, thermo-
stat, transmission oil cooler, water pump, hoses,
clamps, coolant, and a coolant reserve system to com-
plete the circuit.
DESCRIPTION - HOSE CLAMPS
The cooling system uses spring type hose clamps.
If a spring type clamp replacement is necessary,
replace with the original Mopartequipment spring
type clamp.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter (Fig. 1).
OPERATION - COOLING SYSTEM
The engine cooling systems primary purpose is to
maintain engine temperature in a range that will
provide satisfactory engine performance and emission
levels under all expected driving conditions. It also
provides hot water (coolant) for heater performance
and cooling for automatic transmission oil. It does
this by transferring heat from engine metal to cool-
ant, moving this heated coolant to the radiator, and
then transferring this heat to the ambient air.²When engine is cold: thermostat is closed, cool-
ing system has no flow through the radiator. The
coolant bypass flows through the engine only.
²When engine is warm: thermostat is open, cool-
ing system has bypass flow and coolant flow through
radiator.
Coolant flow circuits for the 2.4L and 3.3/3.8L
engines are shown in (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 Spring Clamp Size Location
1 - SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
RSCOOLING7-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 272 of 2321
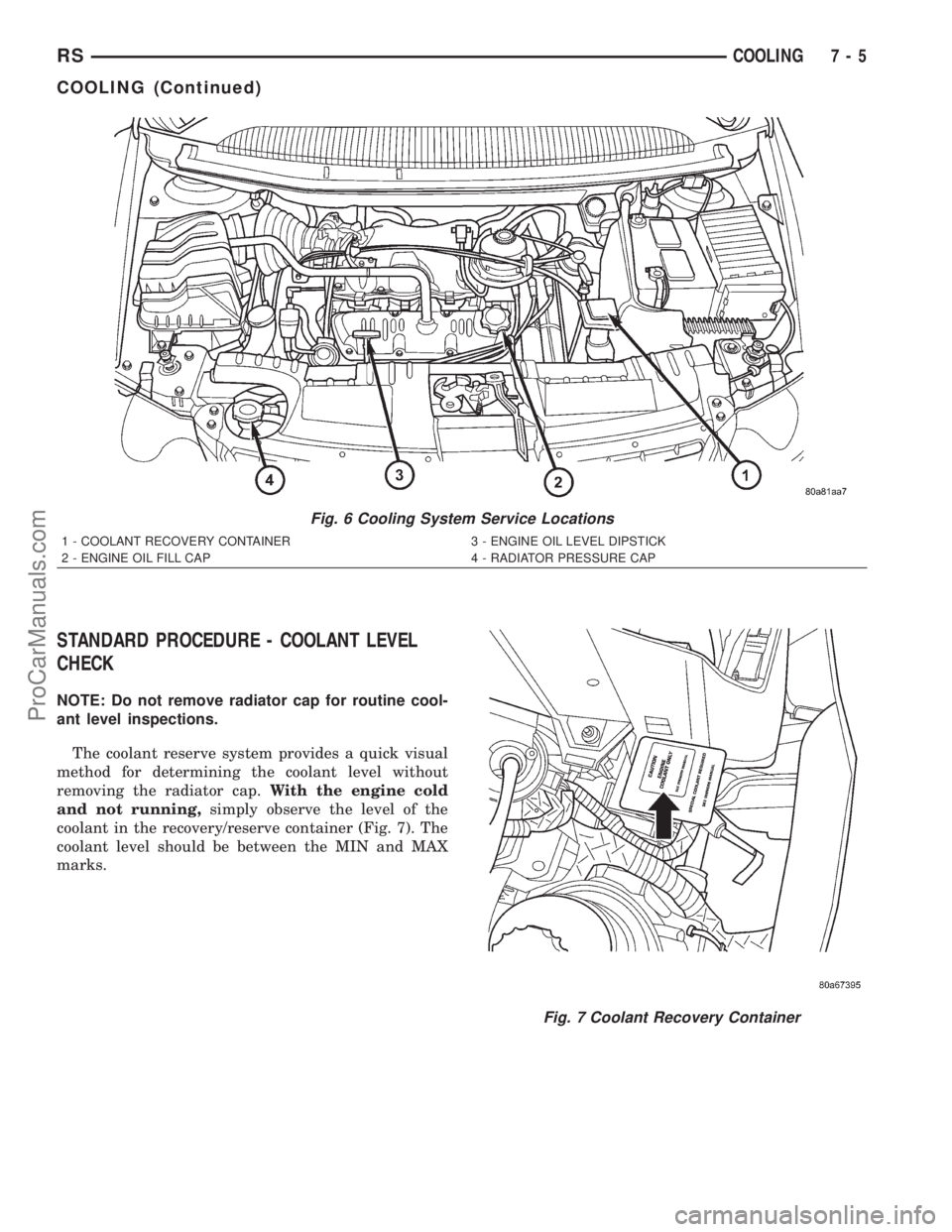
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT LEVEL
CHECK
NOTE: Do not remove radiator cap for routine cool-
ant level inspections.
The coolant reserve system provides a quick visual
method for determining the coolant level without
removing the radiator cap.With the engine cold
and not running,simply observe the level of the
coolant in the recovery/reserve container (Fig. 7). The
coolant level should be between the MIN and MAX
marks.
Fig. 6 Cooling System Service Locations
1 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER 3 - ENGINE OIL LEVEL DIPSTICK
2 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP 4 - RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
Fig. 7 Coolant Recovery Container
RSCOOLING7-5
COOLING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com