2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 1238 of 2321

CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM (beyond
the recommended speed), can damage the sealing
surfaces. The mild (white, 120 grit) bristle disc is
recommended. If necessary, the medium (yellow, 80
grit) bristle disc may be used on cast iron surfaces
with care.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., connecting
rods, pistons, valves, etc.)(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from re-occurring.
CAUTION: Squirt approximately one teaspoon of oil
into the cylinders, rotate engine to lubricate the cyl-
inder walls to prevent damage on restart.
(8) Install new spark plugs.
(9) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(10) Install a new oil filter.
(11) Fill engine with specified amount of approved
oil.
(12) Connect negative battery cable.
(13) Start engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (excluding spark plug
and camshaft bearing cap attaching threads) can be
repaired. Essentially, this repair consists of drilling
out worn or damaged threads, tapping the hole with
a special Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing
an insert into the tapped hole. This brings the hole
back to its original thread size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
Fig. 4 PROPER TOOL USAGE FOR SURFACE
PREPARATION
1 - ABRASIVE PAD
2 - 3M ROLOCYBRISTLE DISC
3 - PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-81
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1257 of 2321
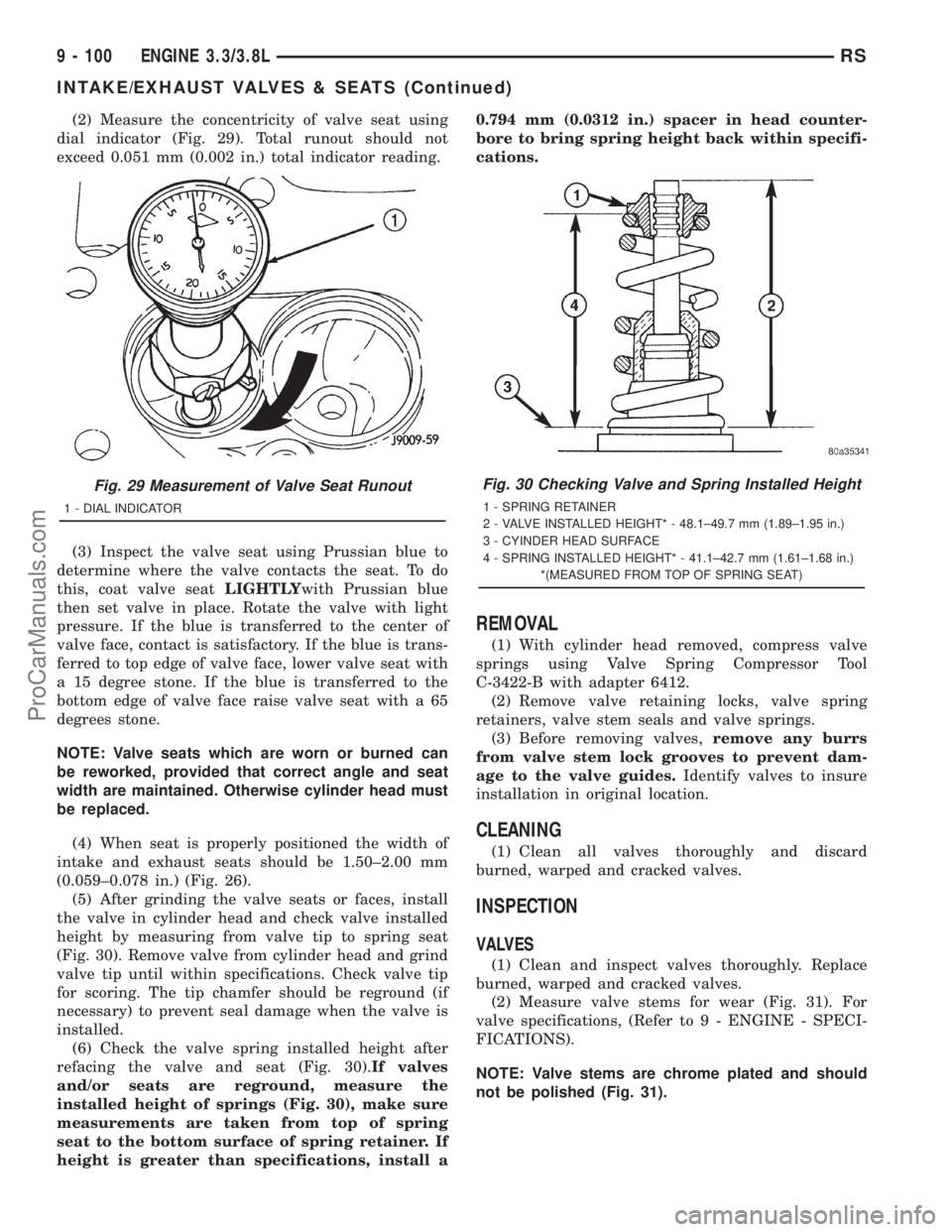
(2) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using
dial indicator (Fig. 29). Total runout should not
exceed 0.051 mm (0.002 in.) total indicator reading.
(3) Inspect the valve seat using Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seatLIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to top edge of valve face, lower valve seat with
a 15 degree stone. If the blue is transferred to the
bottom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 65
degrees stone.
NOTE: Valve seats which are worn or burned can
be reworked, provided that correct angle and seat
width are maintained. Otherwise cylinder head must
be replaced.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake and exhaust seats should be 1.50±2.00 mm
(0.059±0.078 in.) (Fig. 26).
(5) After grinding the valve seats or faces, install
the valve in cylinder head and check valve installed
height by measuring from valve tip to spring seat
(Fig. 30). Remove valve from cylinder head and grind
valve tip until within specifications. Check valve tip
for scoring. The tip chamfer should be reground (if
necessary) to prevent seal damage when the valve is
installed.
(6) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 30).If valves
and/or seats are reground, measure the
installed height of springs (Fig. 30), make sure
measurements are taken from top of spring
seat to the bottom surface of spring retainer. If
height is greater than specifications, install a0.794 mm (0.0312 in.) spacer in head counter-
bore to bring spring height back within specifi-
cations.
REMOVAL
(1) With cylinder head removed, compress valve
springs using Valve Spring Compressor Tool
C-3422-B with adapter 6412.
(2) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(3) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
age to the valve guides.Identify valves to insure
installation in original location.
CLEANING
(1) Clean all valves thoroughly and discard
burned, warped and cracked valves.
INSPECTION
VALVES
(1) Clean and inspect valves thoroughly. Replace
burned, warped and cracked valves.
(2) Measure valve stems for wear (Fig. 31). For
valve specifications, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECI-
FICATIONS).
NOTE: Valve stems are chrome plated and should
not be polished (Fig. 31).
Fig. 29 Measurement of Valve Seat Runout
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 30 Checking Valve and Spring Installed Height
1 - SPRING RETAINER
2 - VALVE INSTALLED HEIGHT* - 48.1±49.7 mm (1.89±1.95 in.)
3 - CYINDER HEAD SURFACE
4 - SPRING INSTALLED HEIGHT* - 41.1±42.7 mm (1.61±1.68 in.)
*(MEASURED FROM TOP OF SPRING SEAT)
9 - 100 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1262 of 2321

DISASSEMBLY - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
CAUTION: Do not attempt to drive the bolt from the
rocker shaft. This can damage the retainer and bolt
assembly.
(1) Remove the rocker arm retainer and bolt by
performing the following procedure:
(a) Using adjustable pliers, grip the edges of the
retainer (Fig. 39).
(b) Apply an upward force with a slight rocking
motion until the retainer disengages from shaft
(Fig. 39).
(2) Remove rocker arms (Fig. 40). Identify the
component locations for reassembly in original loca-
tions.
ASSEMBLY - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
(1) Install rocker arms on the shaft (Fig. 40).
Install in the orginal positions if re-used.Ensurethe
rocker shaft, all the retainers and washers are prop-
erly positioned and installed in the correct locations
(Fig. 40).(2) Install rocker arms and shaft to the cylinder
head. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/
ROCKER ARMS - INSTALLATION)
INSTALLATION - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
CAUTION: Ensure the longer shaft retaining bolt is
installed in the proper location on the rocker shaft.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER
ARMS - ASSEMBLY)
(1) Position the rocker arm and shaft assemblies
on the pedestal mounts.
CAUTION: Ensure all pushrods are properly located
on the lifter and the rocker arm socket.
(2) Align each rocker arm socket with each push-
rod end.
CAUTION: The rocker arm shaft should be tight-
ened down slowly, starting with the center bolts.
Allow 20 minutes lifter bleed down time after instal-
lation of the rocker shafts before engine operation.
Fig. 40 ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
1 - BOLT (ROCKER SHAFT OIL FEED - LONGER LENGTH) 5 - ROCKER ARM - EXHAUST
2 - SHAFT RETAINER/SPACER - 21.5 mm (0.84 in.) 6 - WASHER
3 -SHAFT RETAINER/SPACER - 37.5 mm (1.47 in.) 7 - ROCKER ARM - INTAKE (LARGER OFFSET)
4 - SHAFT RETAINER/SPACER - 40.9 mm (1.61 in.) 8 - ROCKER ARMS LUBRICATION FEED HOLE (POSITION
UPWARD & TOWARD VALVE SPRING_
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 105
ROCKER ARMS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1263 of 2321

(3) Slowly tighten rocker shaft bolts evenly until
shaft is seated. Tighten bolts to 23 N´m (200 in. lbs.)
(Fig. 41).
(4) Install the cylinder head cover(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
VALVE STEM SEALS
DESCRIPTION
The valve stem seals are made of Viton rubber. The
seals are positioned over the valve stem and seated
on the valve guide (Fig. 42).
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the valve springs. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS -
REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the valve stem seal (Fig. 42).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the valve stem seal squarely over the
valve guide, using the valve stem as a guide (Fig.
42). Do not force the seal against top of the valve
guide.
(2) Install the valve spring. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS - INSTALLA-
TION)
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder block is made of cast iron and is a
deep skirt design.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
(1)Used carefully, the cylinder bore resizing hone,
recommended tool C-823 or equivalent, equipped with
220 grit stones, is the best tool for this honing proce-
dure. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce taper and
out-of-round as well as removing light scuffing, scor-
ing or scratches. Usually a few strokes will clean up a
bore and maintain the required limits.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done
using a cylinder surfacing hone, recommended tool
C-3501 or equivalent, equipped with 280 grit stones,
if the cylinder bore is straight and round. 20±60
strokes depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Use a light
honing oil.Do not use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.Inspect cylinder walls
after each 20 strokes.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a cross-hatch pattern.
When hone marksintersectat 40-60 degrees, the
cross hatch angle is most satisfactory for proper seat-
ing of rings (Fig. 43).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between
200±300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40±60
degree angle. Faster up and down strokes increase
the cross-hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned again to remove all traces of abrasive.
CAUTION: Ensure all abrasives are removed from
engine parts after honing. It is recommended that a
solution of soap and hot water be used with a
brush and the parts then thoroughly dried. The bore
can be considered clean when it can be wiped
clean with a white cloth and cloth remains clean.
Oil the bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
Fig. 41 ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
1 - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT ASSEMBLY
2 - ROCKER SHAFT BOLTS
Fig. 42 Valve Stem Seal
9 - 106 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ROCKER ARMS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1276 of 2321

OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the MAX mark on dipstick, it is
possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil
while engine is running and create foaming. Foam in
oil pan would be fed to the hydraulic lifters by the oil
pump causing them to become soft and allow valves
to seat noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which
when fed to the lifters it causes them to become soft
and allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake
side of pump, through which air can be drawn, will
create the same lifter noise. Check the lubrication
system from the intake strainer to the oil pump
cover, including the relief valve retainer cap. When
lifter noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent
or constant, and usually more than one lifter will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
the engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all
of the air inside of the lifters to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
To determine source of valve train noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and
listen for source of the noise.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy lifters. If such is the
case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
Valve lifter noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger which will
necessitate replacing the lifter, or by the plunger par-
tially sticking in the lifter body cylinder. A heavy
click is caused either by a lifter check valve not seat-
ing, or by foreign particles becoming wedged between
the plunger and the lifter body causing the plunger
to stick in the down position. This heavy click will be
accompanied by excessive clearance between the
valve stem and rocker arm as valve closes. In either
case, lifter assembly should be removed for inspec-
tion.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the yoke retainer and aligning yokes
(Fig. 71).
(3) Remove the hydraulic lifters. If necessary use
Special Tool C-4129, or equivalent to remove liftersfrom bores. If lifters are to be reused, identify each
lifter to ensure installation in original location.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the lifters with engine oil.
NOTE: Position the lifter in bore with the lubrication
hole facing upward (Fig. 70).
(2) Install the hydraulic lifters with the lubrication
hole facing upward towards middle of block (Fig. 70).
Install lifters in original positions, if reused.
(3) Install lifter aligning yokes (Fig. 71).
(4) Install yoke retainer and torque screws to 12
N´m (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 71).
(5) Install the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION)
(6) Start and operate engine. Warm up to normal
operating temperature.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to valve mechanism,
engine must not be run above fast idle until all
hydraulic lifters have filled with oil and have
become quiet.
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons are made of cast aluminum alloy and
are a strutless, short skirt design. The piston rings
consist of two compression rings and a three piece oil
ring. Piston pins connect the piston to the forged
steel connecting rods. The piston pins are a press fit
into the connecting rod.
Fig. 70 LIFTER LUBRICATION HOLE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 119
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN BLOCK) (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1294 of 2321
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Fill crankcase with oil to proper level.
OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove oil pan.
(2) Drill a 3.175 mm (1/8 in.) hole in the center of
the retainer cap (Fig. 109). Insert a self-threading
sheet metal screw into the cap.
(3) Using suitable pliers, remove cap and discard.
(4) Remove spring and relief valve (Fig. 109).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean relief valve, spring and bore.
NOTE: Lubricate relief valve with clean engine oil
before installing.
(2) Install relief valve and spring into housing.
(3) Install new retainer cap until flush with seal-
ing surface.
(4) Install oil pan.
(5) Fill crankcase with proper oil to correct level.
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The engine oil pressure switch is located on the
lower left front side of the engine. It screws into the
oil filter adapter. The normally closed switch provides
an input through a single wire to the low pressure
indicator light on the instrument cluster.
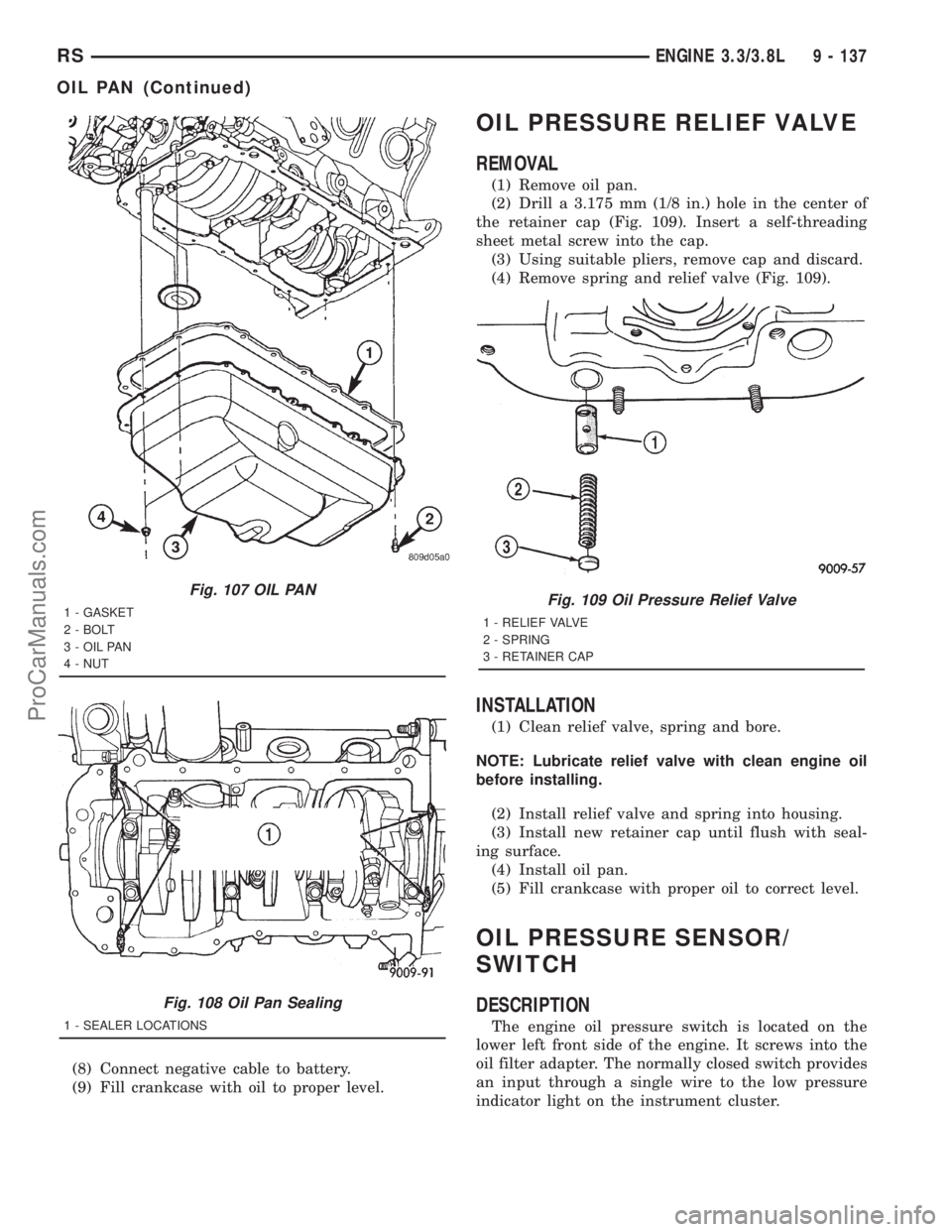
Fig. 107 OIL PAN
1 - GASKET
2 - BOLT
3 - OIL PAN
4 - NUT
Fig. 108 Oil Pan Sealing
1 - SEALER LOCATIONS
Fig. 109 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
1 - RELIEF VALVE
2 - SPRING
3 - RETAINER CAP
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 137
OIL PAN (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1295 of 2321

OPERATION
The oil pressure switch provides a ground for the
instrument cluster low oil pressure indicator light.
The switch receives oil pressure input from the
engine main oil gallery. When engine oil pressure is
greater than 27.5 Kpa (4 psi), the switch contacts
open, providing a open circuit to the low pressure
indicator light. For wiring circuits and diagnostic
information, (Refer to Appropriate Wiring/Diagnostic
Information).
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from switch.
(3) Remove oil pressure switch (Fig. 110).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install oil pressure switch (Fig. 110).
(2) Connect electrical connector to switch.
(3) Lower the vehicle.
(4) Start engine and check for leaks.
(5) Check engine oil level. Adjust as necessary.
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump is located in the timing chain cover.
It is driven by the crankshaft.
REMOVAL
The oil pump is contained within the timing chain
cover housing (Fig. 111).
(1) Remove oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the timing chain cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(3) Disassemble oil pump from timing chain cover.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP -
DISASSEMBLY)
(4) Clean and Inspect oil pump components. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - CLEAN-
ING) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL
PUMP - INSPECTION)
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove oil pump cover screws, and lift off
cover (Fig. 111).
(2) Remove oil pump rotors (Fig. 111).
(3) Clean and inspect oil pump components. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - CLEAN-
ING) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL
PUMP - INSPECTION)
CLEANING
(1) Clean all parts thoroughly in a suitable sol-
vent.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect mating surface of the chain case cover.
Surface should be smooth. Replace cover if scratched
or grooved.
(2) Lay a straightedge across the pump cover sur-
face (Fig. 112). If a 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) feeler gauge
can be inserted between cover and straight edge,
cover should be replaced.
(3) Measure thickness and diameter of outer rotor.
If outer rotor thickness measures 7.64 mm (0.301 in.)
or less (Fig. 113), or if the diameter is 79.95 mm
(3.148 in.) or less, replace outer rotor.
(4) If inner rotor thickness measures 7.64 mm
(0.301 in.) or less, replace inner rotor (Fig. 114).
(5) Install outer rotor into chain case cover. Press
rotor to one side with fingers and measure clearance
between rotor and chain case cover (Fig. 115). If mea-
surement is 0.39 mm (0.015 in.) or more, replace
chain case cover, only if outer rotor is in specification.
Fig. 110 OIL FILTER ADAPTER
1 - SEAL
2 - OIL FILTER ADAPTER
3 - OIL FILTER
4 - BOLT
5 - OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
6 - BOLT
9 - 138 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1301 of 2321

CLEANING
(1) Discard gasket(s).
(2) Clean all sealing surfaces.
INSPECTION
Check manifold for:
²Damage and cracks.
²Mounting surface distortion by using a straight-
edge and thickness gauge.
INSTALLATION - 3.3L
(1) If the following components were removed from
manifold, install and tighten to specifications:
CAUTION: The special screws used for the compos-
ite manifold attached components must be installed
slowly using hand tools only. This requirement is to
prevent the melting of material that causes stripped
threads. If threads become stripped, an oversize
repair screw is available. For more information and
procedure (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/IN-
TAKE MANIFOLD - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
²MAP sensor - 1.7 N´m (15 in. lbs.)
²Throttle cable bracket - 5.6 N´m (50 in. lbs.)
(2) Remove covering on lower intake manifold and
clean surfaces.
(3) Inspect manifold gasket condition. Gaskets can
be re-used, if not damaged. To replace, remove gasket
from upper manifold (Fig. 127). Position new gasket
in seal channel and press lightly in-place. Repeat
procedure for each gasket position.
Fig. 124 PCV & HOSE
1 - HOSE - PCV
2 - P C V VA LV E
Fig. 125 POWER STEERING FLUID RESERVOIR
1 - POWER STEERING RESERVOIR
2 - BOLT - RESERVOIR TO MANIFOLD
3 - NUT - RESERVOIR TO COIL BRACKET
Fig. 126 BRAKE BOOSTER & LDP VACUUM HOSES
1 - LDP & SPEED CONTROL VACUUM HOSE
2 - BRAKE BOOSTER VACUUM HOSE
3 - MAP SENSOR
9 - 144 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER 3.3L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com