2001 DODGE RAM differential
[x] Cancel search: differentialPage 149 of 2889
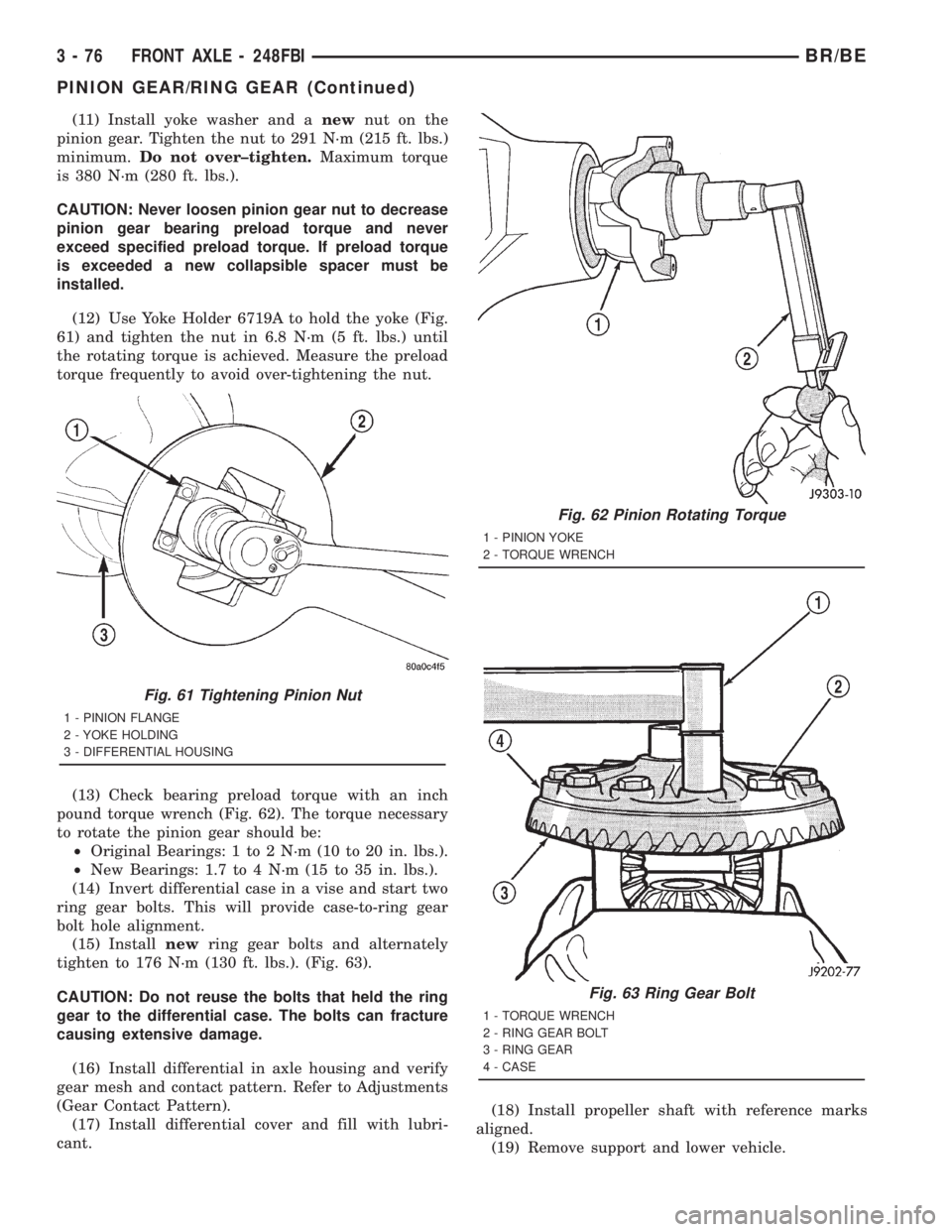
(11) Install yoke washer and anewnut on the
pinion gear. Tighten the nut to 291 N´m (215 ft. lbs.)
minimum.Do not over±tighten.Maximum torque
is 380 N´m (280 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Never loosen pinion gear nut to decrease
pinion gear bearing preload torque and never
exceed specified preload torque. If preload torque
is exceeded a new collapsible spacer must be
installed.
(12) Use Yoke Holder 6719A to hold the yoke (Fig.
61) and tighten the nut in 6.8 N´m (5 ft. lbs.) until
the rotating torque is achieved. Measure the preload
torque frequently to avoid over-tightening the nut.
(13) Check bearing preload torque with an inch
pound torque wrench (Fig. 62). The torque necessary
to rotate the pinion gear should be:
²Original Bearings: 1 to 2 N´m (10 to 20 in. lbs.).
²New Bearings: 1.7 to 4 N´m (15 to 35 in. lbs.).
(14) Invert differential case in a vise and start two
ring gear bolts. This will provide case-to-ring gear
bolt hole alignment.
(15) Installnewring gear bolts and alternately
tighten to 176 N´m (130 ft. lbs.). (Fig. 63).
CAUTION: Do not reuse the bolts that held the ring
gear to the differential case. The bolts can fracture
causing extensive damage.
(16) Install differential in axle housing and verify
gear mesh and contact pattern. Refer to Adjustments
(Gear Contact Pattern).
(17) Install differential cover and fill with lubri-
cant.(18) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(19) Remove support and lower vehicle.
Fig. 61 Tightening Pinion Nut
1 - PINION FLANGE
2 - YOKE HOLDING
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
Fig. 62 Pinion Rotating Torque
1 - PINION YOKE
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 63 Ring Gear Bolt
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - RING GEAR BOLT
3 - RING GEAR
4 - CASE
3 - 76 FRONT AXLE - 248FBIBR/BE
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR (Continued)
Page 150 of 2889

REAR AXLE-91/4
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR AXLE-91/4
DESCRIPTION...........................77
OPERATION.............................77
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................80
AXLE................................80
REMOVAL..............................83
INSTALLATION...........................84
ADJUSTMENTS..........................84
SPECIFICATIONS........................90
SPECIAL TOOLS.........................90
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL..............................93
INSTALLATION...........................93
AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL..............................94
INSTALLATION...........................94
AXLE BEARINGS
REMOVAL..............................94
INSTALLATION...........................95PINION SEAL
REMOVAL..............................95
INSTALLATION...........................95
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL..............................96
DISASSEMBLY...........................97
ASSEMBLY.............................98
INSTALLATION...........................98
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................98
TRAC-LOK............................98
DISASSEMBLY...........................99
ASSEMBLY............................101
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................103
INSTALLATION..........................103
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR/TONE RING
REMOVAL.............................103
INSTALLATION..........................105
REAR AXLE-91/4
DESCRIPTION
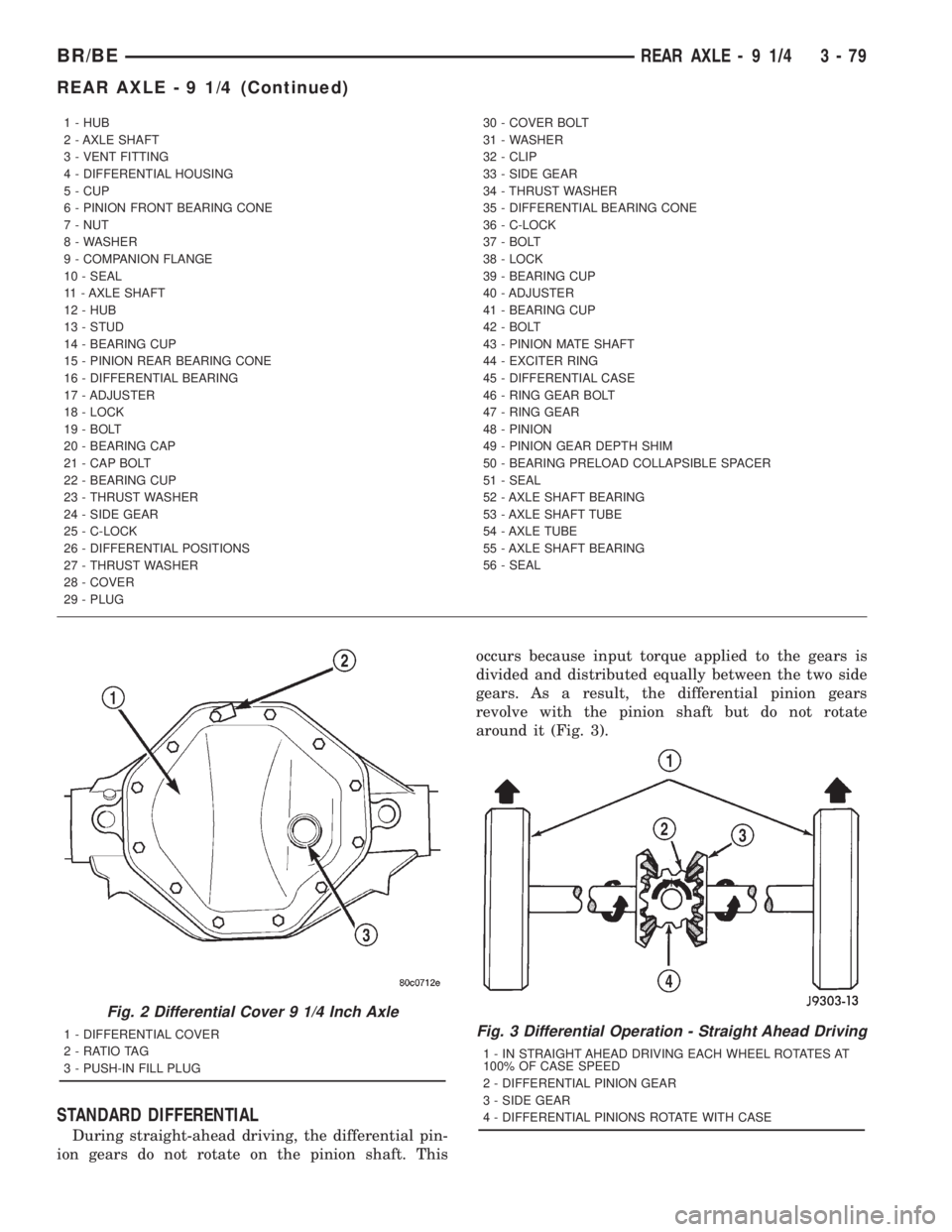
The 9 1/4 Inch axle housings consist of a cast iron
center section with axle tubes extending from either
side. The tubes are pressed into and welded to the
differential housing to form a one-piece axle housing
(Fig. 1).
The axles have a vent hose to relieve internal pres-
sure caused by lubricant vaporization and internal
expansion.
The axles are equipped with semi-floating axle
shafts, meaning vehicle loads are supported by the
axle shaft and bearings. The axle shafts are retained
by C-locks in the differential side gears.
The removable, stamped steel cover provides a
means for inspection and service without removing
the complete axle from the vehicle.
The axle has a date tag and a gear ratio tag. The
tags are attached to the differential housing by a
cover bolt.
The rear wheel anti-lock (RWAL) brake speed sen-
sor is attached to the top, forward exterior of the dif-
ferential housing. A seal is located between the
sensor and the wire harness connector. The seal must
be in place when the wire connector is connected to
the sensor. The RWAL brake exciter ring is press-fit-ted onto the differential case against the ring gear
flange.
The differential case is a one-piece design. The dif-
ferential pinion shaft is retained with a screw. Differ-
ential bearing preload and ring gear backlash are set
and maintained by threaded adjusters at the outside
of the differential housing. Pinion bearing preload is
set and maintained by the use of a collapsible spacer.
Axles equipped with a Trac-Lokydifferential are
optional. A differential has a one-piece differential
case, and the same internal components as a stan-
dard differential, plus two clutch disc packs.
AXLE IDENTIFICATION
The axle differential cover can be used for identifi-
cation of the axle (Fig. 2). A ratio tag is attached to
the top of the differential cover.
OPERATION
The axle receives power from the transmission/
transfer case through the rear propeller shaft. The
rear propeller shaft is connected to the drive pinion
which rotates the differential through the gear mesh
with the ring gear bolted to the differential case. The
engine power is transmitted to the axle shafts
through the differential pinions and side gears. The
side gears are splined to the axle shafts.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 9 1/4 3 - 77
Page 152 of 2889
STANDARD DIFFERENTIAL
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pin-
ion gears do not rotate on the pinion shaft. Thisoccurs because input torque applied to the gears is
divided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the differential pinion gears
revolve with the pinion shaft but do not rotate
around it (Fig. 3).
1 - HUB
2 - AXLE SHAFT
3 - VENT FITTING
4 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
5 - CUP
6 - PINION FRONT BEARING CONE
7 - NUT
8 - WASHER
9 - COMPANION FLANGE
10 - SEAL
11 - AXLE SHAFT
12 - HUB
13 - STUD
14 - BEARING CUP
15 - PINION REAR BEARING CONE
16 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING
17 - ADJUSTER
18 - LOCK
19 - BOLT
20 - BEARING CAP
21 - CAP BOLT
22 - BEARING CUP
23 - THRUST WASHER
24 - SIDE GEAR
25 - C-LOCK
26 - DIFFERENTIAL POSITIONS
27 - THRUST WASHER
28 - COVER
29 - PLUG30 - COVER BOLT
31 - WASHER
32 - CLIP
33 - SIDE GEAR
34 - THRUST WASHER
35 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING CONE
36 - C-LOCK
37 - BOLT
38 - LOCK
39 - BEARING CUP
40 - ADJUSTER
41 - BEARING CUP
42 - BOLT
43 - PINION MATE SHAFT
44 - EXCITER RING
45 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
46 - RING GEAR BOLT
47 - RING GEAR
48 - PINION
49 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM
50 - BEARING PRELOAD COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
51 - SEAL
52 - AXLE SHAFT BEARING
53 - AXLE SHAFT TUBE
54 - AXLE TUBE
55 - AXLE SHAFT BEARING
56 - SEAL
Fig. 2 Differential Cover 9 1/4 Inch Axle
1 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER
2 - RATIO TAG
3 - PUSH-IN FILL PLUGFig. 3 Differential Operation - Straight Ahead Driving
1 - IN STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING EACH WHEEL ROTATES AT
100% OF CASE SPEED
2 - DIFFERENTIAL PINION GEAR
3 - SIDE GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL PINIONS ROTATE WITH CASE
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 9 1/4 3 - 79
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)
Page 153 of 2889
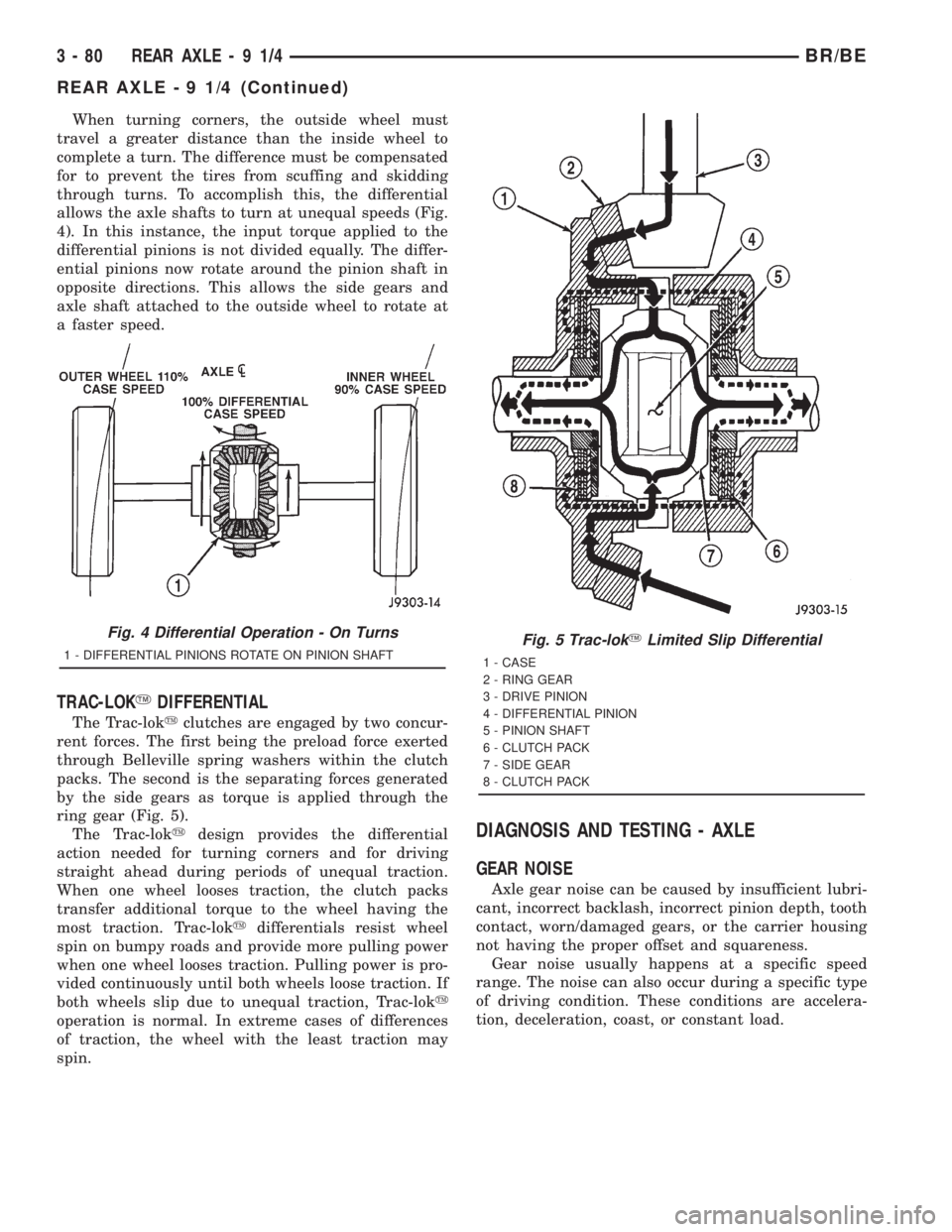
When turning corners, the outside wheel must
travel a greater distance than the inside wheel to
complete a turn. The difference must be compensated
for to prevent the tires from scuffing and skidding
through turns. To accomplish this, the differential
allows the axle shafts to turn at unequal speeds (Fig.
4). In this instance, the input torque applied to the
differential pinions is not divided equally. The differ-
ential pinions now rotate around the pinion shaft in
opposite directions. This allows the side gears and
axle shaft attached to the outside wheel to rotate at
a faster speed.
TRAC-LOKYDIFFERENTIAL
The Trac-lokyclutches are engaged by two concur-
rent forces. The first being the preload force exerted
through Belleville spring washers within the clutch
packs. The second is the separating forces generated
by the side gears as torque is applied through the
ring gear (Fig. 5).
The Trac-lokydesign provides the differential
action needed for turning corners and for driving
straight ahead during periods of unequal traction.
When one wheel looses traction, the clutch packs
transfer additional torque to the wheel having the
most traction. Trac-lokydifferentials resist wheel
spin on bumpy roads and provide more pulling power
when one wheel looses traction. Pulling power is pro-
vided continuously until both wheels loose traction. If
both wheels slip due to unequal traction, Trac-loky
operation is normal. In extreme cases of differences
of traction, the wheel with the least traction may
spin.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AXLE
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, incorrect pinion depth, tooth
contact, worn/damaged gears, or the carrier housing
not having the proper offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.
Fig. 4 Differential Operation - On Turns
1 - DIFFERENTIAL PINIONS ROTATE ON PINION SHAFTFig. 5 Trac-lokYLimited Slip Differential
1 - CASE
2 - RING GEAR
3 - DRIVE PINION
4 - DIFFERENTIAL PINION
5 - PINION SHAFT
6 - CLUTCH PACK
7 - SIDE GEAR
8 - CLUTCH PACK
3 - 80 REAR AXLE-91/4BR/BE
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)
Page 154 of 2889

When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion shaft can also cause a snap-
ping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 9 1/4 3 - 81
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)
Page 155 of 2889
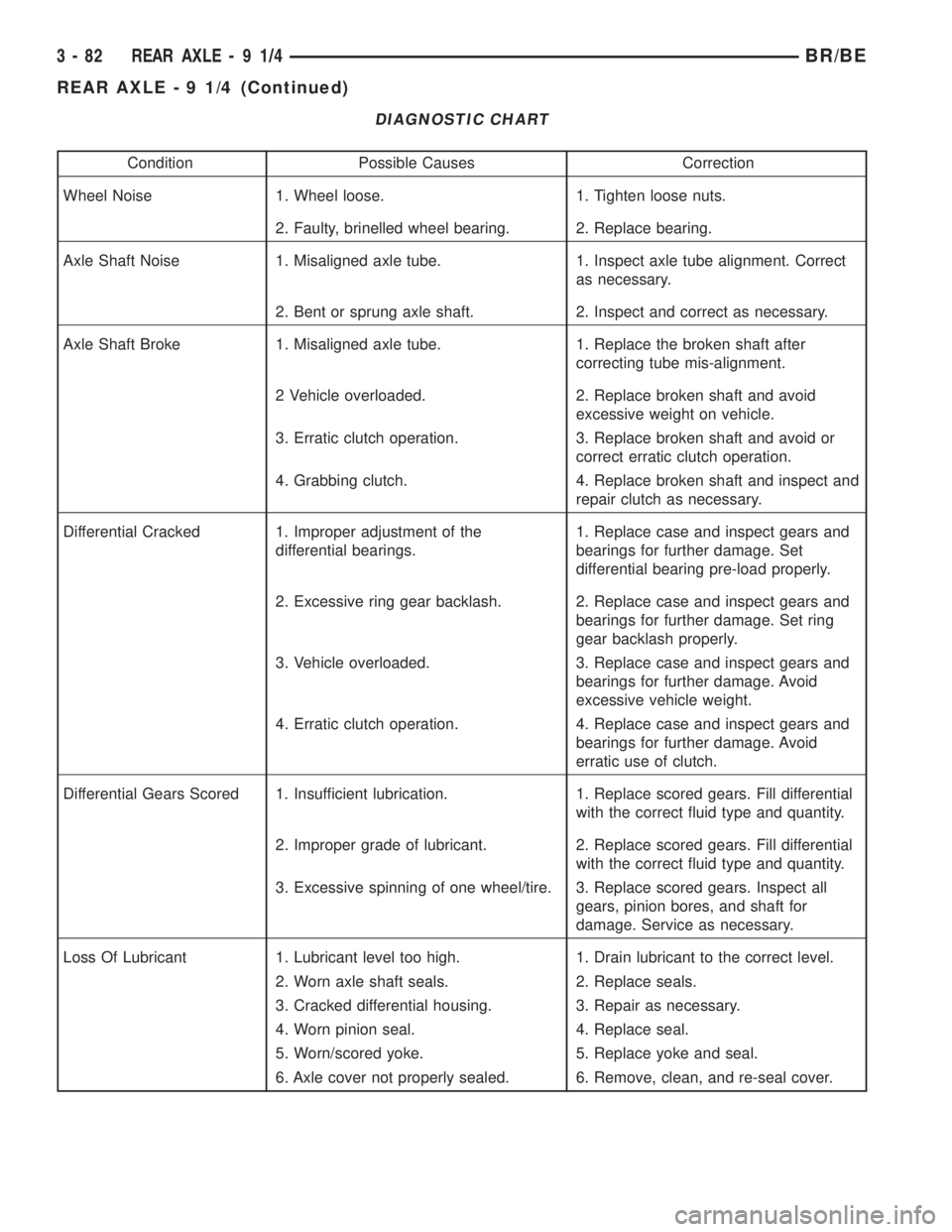
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment. Correct
as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid or
correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect and
repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Set
differential bearing pre-load properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Set ring
gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Avoid
excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Avoid
erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill differential
with the correct fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill differential
with the correct fluid type and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one wheel/tire. 3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal cover.
3 - 82 REAR AXLE-91/4BR/BE
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)
Page 156 of 2889

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other gears
and bearings for possible damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure ring
gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion contact
pattern. Adjust backlash or pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched ring
gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out. Replace
components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap bolts. 8. Inspect differential components and
replace as necessary. Ensure that the
bearing caps are torqued tot he proper
specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a suitable lifting device under the
axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove the wheels and tires.
(5) Secure brake drums to the axle shaft.
(6) Remove the RWAL sensor from the differential
housing, if necessary. Refer to 5 Brakes for proce-
dures.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block. Do not disconnect the brake hydraulic lines at
the wheel cylinders. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.(8) Disconnect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(9) Disconnect the vent hose from the axle shaft
tube.
(10) Mark the propeller shaft and companion
flange for installation alignment reference.
(11) Remove propeller shaft.
(12) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle.
(13) Remove the spring clamps and spring brack-
ets. Refer to 2 Suspension for procedures.
(14) Separate the axle from the vehicle.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 9 1/4 3 - 83
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)
Page 157 of 2889

INSTALLATION
(1) Raise the axle with lifting device and align to
the leaf spring centering bolts.
(2) Install the spring clamps and spring brackets.
Refer to 2 Suspension for procedures.
(3) Install shock absorbers and tighten nuts to 82
N´m (60 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install the RWAL sensor to the differential
housing, if necessary. Refer to 5 Brakes for proce-
dures.
(5) Connect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(6) Install the brake drums. Refer to 5 Brakes for
procedures.
(7) Connect the brake hose to the axle junction
block. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.
(8) Install axle vent hose.
(9) Align propeller shaft and pinion companion
flange reference marks. Install the companion flange
bolts. Tighten to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(10) Install the wheels and tires.
(11) Add gear lubricant, if necessary. Refer to
Specifications for lubricant requirements.
(12) Remove lifting device from axle and lower the
vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring gear and pinion are supplied as matched sets
only. The identifying numbers for the ring gear and
pinion are painted onto the pinion gear head (Fig. 6)
and the side of the ring gear. A plus (+) number,
minus (±) number or zero (0) along with the gear set
sequence number (01 to 99) is on each gear. This first
number is the amount (in thousandths of an inch)
the depth varies from the standard depth setting of a
pinion marked with a (0). The next two numbers are
the sequence number of the gear set. The standard
depth provides the best teeth contact pattern. Refer
to Backlash and Contact Pattern for additional infor-
mation.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with select shims. The shims are placed
behind the rear pinion bearing. (Fig. 7).
If a new gear set is being installed, note the depth
variance painted onto both the original and replace-
ment pinion. Add or subtract the thickness of the
original depth shims to compensate for the difference
in the depth variances. Refer to the Depth Variance
chart.
Note where Old and New Pinion Marking columns
intersect. Intersecting figure represents plus or
minus the amount needed.Note the painted number on the shaft of the drive
pinion (±1, ±2, 0, +1, +2, etc.). The numbers repre-
sent thousands of an inch deviation from the stan-
dard. If the number is negative, add that value to the
required thickness of the depth shims. If the number
is positive, subtract that value from the thickness of
the depth shim. If the number is 0 no change is nec-
essary.
Fig. 6 Pinion ID Number
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBER
2 - PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
Fig. 7 Adjustment Shim Locations
1 - AXLE HOUSING
2 - COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
3 - PINION BEARING
4 - PINION DEPTH SHIM
5 - DRIVE PINION GEAR
6 - BEARING CUP
3 - 84 REAR AXLE-91/4BR/BE
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)