2001 DODGE RAM rear diff
[x] Cancel search: rear diffPage 2554 of 2889

(7) Apply MopartSilicone Sealer to mating surface
of PTO cover and to cover bolt shanks and underside
of bolt heads. Then install and tighten bolts to 27-34
N´m (20-25 ft. lbs.) torque.
INSTALLATION
(1) Align and seat transfer case on transmission.
Be sure transfer case input gear splines are aligned
with transmission output shaft. Align splines by
rotating transfer case rear output shaft yoke if nec-
essary. Do not install any transfer case attaching
nuts until the transfer case is completely seated
against the transmission.
(2) Install and tighten transfer case attaching
nuts. Tighten nuts to 30-41 N´m (20-30 ft.lbs.).
(3) Install rear crossmember.(4) Remove jack stand from under transmission.
(5) Align and connect propeller shafts. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(6) Connect vacuum harness and vent hose.
(7) Connect shift rod to transfer case lever or floor
shift arm. Use channel lock style pliers to press rod
back into lever grommet.
(8) Adjust shift linkage, if necessary.
(9) Fill transfer case with recommended transmis-
sion fluid and install fill plug.
(10) Install skid plate, if equipped. (Refer to 13 -
FRAMES & BUMPERS/FRAME/TRANSFER CASE
SKID PLATE - INSTALLATION)
(11) Lower vehicle
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Plug, Detent 16-24 12-18 -
Bolt, Diff. Case 17-27 15-24 -
Plug, Drain/Fill 40-45 30-40 -
Bolt, Extension Housing 35-46 26-34 -
Bolt, Front Brg. Retainer 16-27 12-24 -
Bolt, Case Half 35-46 26-34 -
Nut, Front Yoke 122-176 90-130 -
Screw, Oil Pump 1.2-1.8 - 12-15
Nut, Range Lever 27-34 20-25 -
Bolt, Rear Retainer 35-46 26-34 -
Nuts, Mounting 30-41 20-30 -
Bolts, U-Joint 19 17 -
Vacuum Switch 20-34 15-25 -
BR/BETRANSFER CASE - NV241HD 21 - 919
TRANSFER CASE - NV241HD (Continued)
Page 2556 of 2889
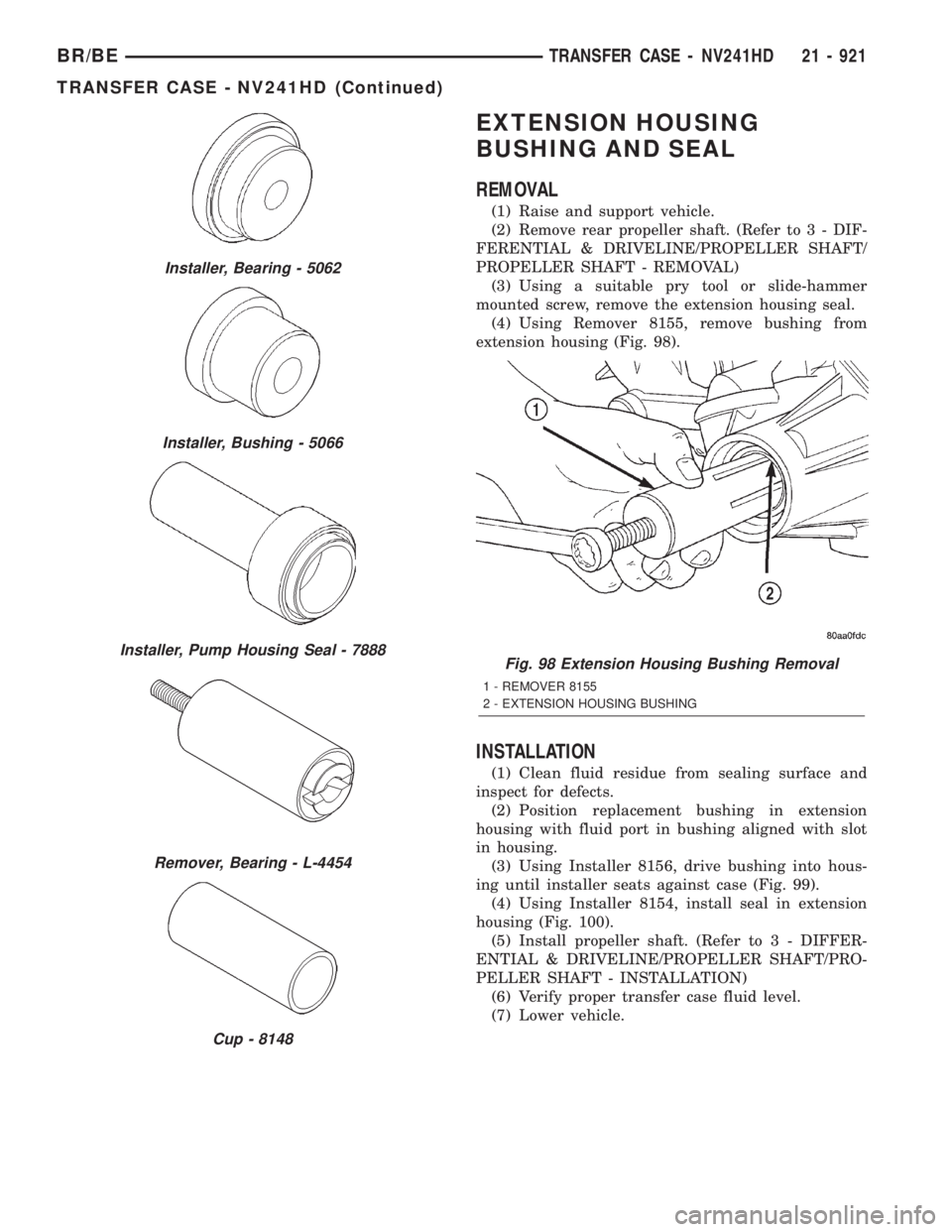
EXTENSION HOUSING
BUSHING AND SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove rear propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIF-
FERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/
PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(3) Using a suitable pry tool or slide-hammer
mounted screw, remove the extension housing seal.
(4) Using Remover 8155, remove bushing from
extension housing (Fig. 98).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean fluid residue from sealing surface and
inspect for defects.
(2) Position replacement bushing in extension
housing with fluid port in bushing aligned with slot
in housing.
(3) Using Installer 8156, drive bushing into hous-
ing until installer seats against case (Fig. 99).
(4) Using Installer 8154, install seal in extension
housing (Fig. 100).
(5) Install propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PRO-
PELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(6) Verify proper transfer case fluid level.
(7) Lower vehicle.
Installer, Bearing - 5062
Installer, Bushing - 5066
Installer, Pump Housing Seal - 7888
Remover, Bearing - L-4454
Cup - 8148
Fig. 98 Extension Housing Bushing Removal
1 - REMOVER 8155
2 - EXTENSION HOUSING BUSHING
BR/BETRANSFER CASE - NV241HD 21 - 921
TRANSFER CASE - NV241HD (Continued)
Page 2563 of 2889
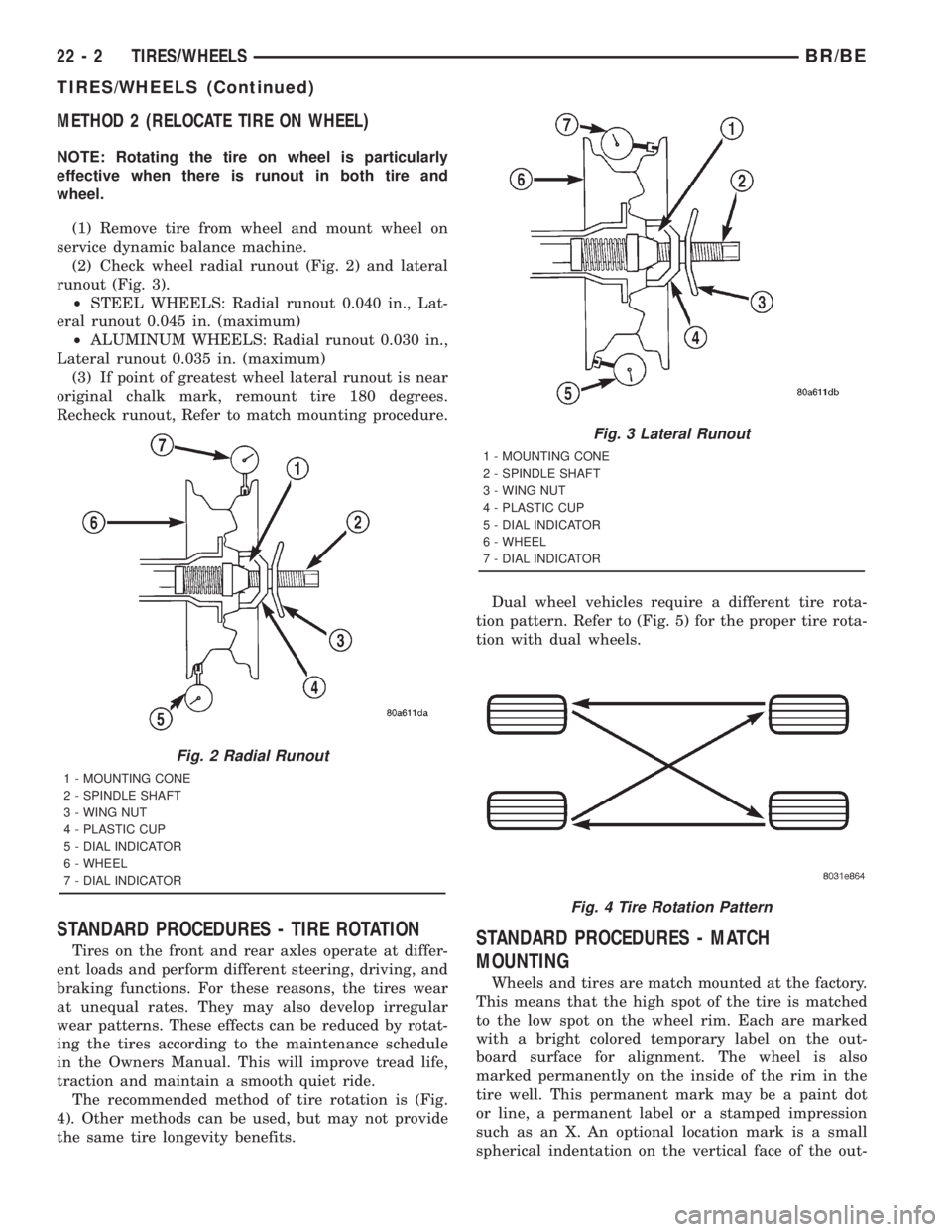
METHOD 2 (RELOCATE TIRE ON WHEEL)
NOTE: Rotating the tire on wheel is particularly
effective when there is runout in both tire and
wheel.
(1) Remove tire from wheel and mount wheel on
service dynamic balance machine.
(2) Check wheel radial runout (Fig. 2) and lateral
runout (Fig. 3).
²STEEL WHEELS: Radial runout 0.040 in., Lat-
eral runout 0.045 in. (maximum)
²ALUMINUM WHEELS: Radial runout 0.030 in.,
Lateral runout 0.035 in. (maximum)
(3) If point of greatest wheel lateral runout is near
original chalk mark, remount tire 180 degrees.
Recheck runout, Refer to match mounting procedure.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - TIRE ROTATION
Tires on the front and rear axles operate at differ-
ent loads and perform different steering, driving, and
braking functions. For these reasons, the tires wear
at unequal rates. They may also develop irregular
wear patterns. These effects can be reduced by rotat-
ing the tires according to the maintenance schedule
in the Owners Manual. This will improve tread life,
traction and maintain a smooth quiet ride.
The recommended method of tire rotation is (Fig.
4). Other methods can be used, but may not provide
the same tire longevity benefits.Dual wheel vehicles require a different tire rota-
tion pattern. Refer to (Fig. 5) for the proper tire rota-
tion with dual wheels.STANDARD PROCEDURES - MATCH
MOUNTING
Wheels and tires are match mounted at the factory.
This means that the high spot of the tire is matched
to the low spot on the wheel rim. Each are marked
with a bright colored temporary label on the out-
board surface for alignment. The wheel is also
marked permanently on the inside of the rim in the
tire well. This permanent mark may be a paint dot
or line, a permanent label or a stamped impression
such as an X. An optional location mark is a small
spherical indentation on the vertical face of the out-
Fig. 2 Radial Runout
1 - MOUNTING CONE
2 - SPINDLE SHAFT
3 - WING NUT
4 - PLASTIC CUP
5 - DIAL INDICATOR
6 - WHEEL
7 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 3 Lateral Runout
1 - MOUNTING CONE
2 - SPINDLE SHAFT
3 - WING NUT
4 - PLASTIC CUP
5 - DIAL INDICATOR
6 - WHEEL
7 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 4 Tire Rotation Pattern
22 - 2 TIRES/WHEELSBR/BE
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
Page 2567 of 2889

DESCRIPTION
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life and
ride quality, and decrease rolling resistance.
Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock
Brakes.
The use of tires from different manufactures on the
same vehicle is NOT recommended. The proper tire
pressure should be maintained on all four tires.
DESCRIPTION
Where speed limits allow the vehicle to be driven
at high speeds, correct tire inflation pressure is very
important. For speeds up to and including 120 km/h
(75 mph), tires must be inflated to the pressures
shown on the tire placard. For continuous speeds inexcess of 120 km/h (75 mph), tires must be inflated
to the maximum pressure specified on the tire side-
wall.
Vehicles loaded to the maximum capacity should
not be driven at continuous speeds above 75 mph
(120 km/h).
For emergency vehicles that are driven at speeds
over 90 mph (144 km/h), special high speed tires
must be used. Consult tire manufacturer for correct
inflation pressure recommendations.
DESCRIPTION
The original equipment tires provide a proper bal-
ance of many characteristics such as:
²Ride
²Noise
²Handling
²Durability
²Tread life
²Traction
²Rolling resistance
²Speed capability
It is recommended that tires equivalent to the orig-
inal equipment tires be used when replacement is
needed.
Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may
adversely affect the safety and handling of the vehi-
cle.
The use of oversize tires may cause interference
with vehicle components. Under extremes of suspen-
sion and steering travel, interference with vehicle
components may cause tire damage.
WARNING: FAILURE TO EQUIP THE VEHICLE WITH
TIRES HAVING ADEQUATE SPEED CAPABILITY
CAN RESULT IN SUDDEN TIRE FAILURE.
DESCRIPTION
Under inflation will cause rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and possible tire failure (Fig. 12) .
Over inflation will cause rapid center wear and
loss of the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 13) .
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
²Unsatisfactory ride
²Vehicle drift
For proper tire pressure specification refer to the
Tire Inflation Pressure Chart provided with the vehi-
cles Owners Manual. A Certification Label on the
drivers side door pillar provides the minimum tire
and rim size for the vehicle. The label also list the
cold inflation pressure for these tires at full load
operation
Fig. 11 Tire Identification
22 - 6 TIRES/WHEELSBR/BE
TIRES (Continued)
Page 2574 of 2889

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
DESCRIPTION............................1
WARNING...............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................2
WATER LEAKS..........................2
WIND NOISE...........................3
SPECIFICATIONS.........................4
DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE........62
DOOR - FRONT..........................67DOOR - CARGO.........................77
EXTERIOR..............................86
HOOD.................................99
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM.............104
INTERIOR.............................118
PAINT................................129
SEATS................................131
STATIONARY GLASS.....................145
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS..................152
BODY
DESCRIPTION ± PUSH-IN FASTENERS
DaimlerChrysler Corporation uses many different
types of push-in fasteners to secure the interior and
exterior trim to the body. Most of these fasteners can
be reused to assemble the trim during various repair
procedures. At times, a push-in fastener cannot be
removed without damaging the fastener or the com-
ponent it is holding. If it is not possible to remove a
fastener without damaging a component or body, cut
or break the fastener and use a new one when
installing the component. Never pry or pound on a
plastic or pressed-board trim component. Using a
suitable fork-type prying device, pry the fastener
from the retaining hole behind the component being
removed. When installing, verify fastener alignment
with the retaining hole by hand. Push directly on or
over the fastener until it seats. Apply a low-force pull
to the panel to verify that it is secure.
When it is necessary to remove components to ser-
vice another, it should not be necessary to apply
excessive force or bend a component to remove it.
Before damaging a trim component, verify hidden
fasteners or captured edges holding the component in
place.
DESCRIPTION ± LOCK CYLINDERS
Ignition, door, deck lid, and rear hatch lock cylin-
ders are all codable to the key. Lock barrels, tum-
blers, and tumbler springs are available to allow the
technician to change replacement locks cylinders to
match the customer's original key set. See the appro-
priate section in this manual for lock cylinder
removal. See the Moparž catalogue for part numbers
and lock coding procedures.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: USE A OSHA APPROVED BREATHING
FILTER WHEN SPRAYING PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN
A CONFINED AREA. PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH PETRO-
LEUM OR ALCOHOL ± BASED CLEANING SOL-
VENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
DO NOT STAND UNDER A HOISTED VEHICLE THAT
IS NOT PROPERLY SUPPORTED ON SAFETY
STANDS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: When holes must be drilled or punched
in an inner body panel, verify depth of space to the
outer body panel, electrical wiring, or other compo-
nents. Damage to vehicle can result.
Do not weld exterior panels unless combustible
material on the interior of vehicle is removed from
the repair area. Fire or hazardous conditions, can
result.
Always have a fire extinguisher ready for use when
welding.
Disconnect the negative (-) cable clamp from the
battery when servicing electrical components that
are live when the ignition is OFF. Damage to electri-
cal system can result.
Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds on
painted surfaces. Damage to finish can result.
Do not use harsh alkaline based cleaning solvents
on painted or upholstered surfaces. Damage to fin-
ish or color can result.
Do not hammer or pound on plastic trim panel
when servicing interior trim. Plastic panels can
break.
BR/BEBODY 23 - 1
Page 2718 of 2889

STATIONARY GLASS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STATIONARY GLASS
DESCRIPTION..........................145
OPERATION............................145
BACKLITE
REMOVAL.............................145
INSTALLATION..........................145
BACKLITE LATCH AND KEEPER
REMOVAL.............................146
INSTALLATION..........................146
BACKLITE VENT GLASS
REMOVAL.............................147INSTALLATION..........................147
WINDSHIELD
DESCRIPTION..........................148
REMOVAL.............................148
INSTALLATION..........................148
QUARTER WINDOW
REMOVAL.............................151
INSTALLATION..........................151
STATIONARY GLASS
DESCRIPTION
Windshields are made of two pieces of glass with a
plastic inner layer. Windshields and selected station-
ary glass are structural members of the vehicle. The
windshield glass is bonded to the windshield frame
with urethane adhesive.
OPERATION
Windshields and other stationary glass protect the
occupants from the effects of the elements. Wind-
shields are also used to retain some airbags in posi-
tion during deployment. Urethane bonded glass is
difficult to salvage during removal. The urethane
bonding is difficult to cut or clean from any surface.
Before removing the glass, check the availability of
replacement components.
BACKLITE
REMOVAL
It is difficult to salvage the backlite during the
removal operation. The backlite is part of the struc-
tural support for the roof. The urethane bonding
used to secure the glass to the fence is difficult to cut
or clean from any surface. Since the molding is set in
urethane, it is unlikely it would be salvaged. Before
removing the backlite, check the availability from the
parts supplier.
The backlite is attached to the window frame with
urethane adhesive. The urethane adhesive is applied
cold and seals the surface area between the window
opening and the glass. The primer adheres the ure-
thane adhesive to the backlite.(1) Roll down door glass.
(2) Remove headliner. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INTE-
RIOR/HEADLINER - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove rear closer panel trim. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/REAR CLOSURE PANEL TRIM -
REMOVAL).
(4) Bend backlite retaining tabs (Fig. 1) inward
against glass.
(5) Using a suitable pneumatic knife from inside
the vehicle, cut urethane holding backlite frame to
opening fence.
(6) Separate glass from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean urethane adhesive from around backlite
opening fence.
Fig. 1 Backlite Tabs
1 - BACKLITE
2-TAB
BR/BESTATIONARY GLASS 23 - 145
Page 2721 of 2889

WINDSHIELD
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE THE VEHICLE
WITHIN 24 HOURS OF WINDSHIELD INSTALLATION.
IT TAKES AT LEAST 24 HOURS FOR URETHANE
ADHESIVE TO CURE. IF IT IS NOT CURED, THE
WINDSHIELD MAY NOT PERFORM PROPERLY IN
AN ACCIDENT.
URETHANE ADHESIVES ARE APPLIED AS A SYS-
TEM. USE GLASS CLEANER, GLASS PREP SOL-
VENT, GLASS PRIMER, PVC (VINYL) PRIMER AND
PINCH WELD (FENCE) PRIMER PROVIDED BY THE
ADHESIVE MANUFACTURER. IF NOT, STRUCTURAL
INTEGRITY COULD BE COMPROMISED.
DAIMLERCHRYSLER DOES NOT RECOMMEND
GLASS ADHESIVE BY BRAND. TECHNICIANS
SHOULD REVIEW PRODUCT LABELS AND TECHNI-
CAL DATA SHEETS, AND USE ONLY ADHESIVES
THAT THEIR MANUFACTURES WARRANT WILL
RESTORE A VEHICLE TO THE REQUIREMENTS OF
FMVSS 212. TECHNICIANS SHOULD ALSO INSURE
THAT PRIMERS AND CLEANERS ARE COMPATIBLE
WITH THE PARTICULAR ADHESIVE USED.
BE SURE TO REFER TO THE URETHANE MANU-
FACTURER'S DIRECTIONS FOR CURING TIME
SPECIFICATIONS, AND DO NOT USE ADHESIVE
AFTER ITS EXPIRATION DATE.
VAPORS THAT ARE EMITTED FROM THE URE-
THANE ADHESIVE OR PRIMER COULD CAUSE
PERSONAL INJURY. USE THEM IN A WELL-VENTI-
LATED AREA.
SKIN CONTACT WITH URETHANE ADHESIVE
SHOULD BE AVOIDED. PERSONAL INJURY MAY
RESULT.
ALWAYS WEAR EYE AND HAND PROTECTION
WHEN WORKING WITH GLASS.
CAUTION: Protect all painted and trimmed surfaces
from coming in contact with urethane or primers.
Be careful not to damage painted surfaces when
removing moldings or cutting urethane around
windshield.
OPERATION
The windshield is attached to the window frame
with urethane adhesive. The urethane adhesive is
applied cold and seals the surface area between the
window opening and the glass. The primer adheres
the urethane adhesive to the windshield.
It is difficult to salvage a windshield during the
removal operation. The windshield is part of the
structural support for the roof. The urethane bonding
used to secure the windshield to the fence is difficultto cut or clean from any surface. If the moldings are
set in urethane, it would also be unlikely they could
be salvaged. Before removing the windshield, check
the availability of the windshield and moldings from
the parts supplier.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove inside rear view mirror. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/REAR VIEW MIRROR - REMOV-
AL).
(2) Remove cowl grill. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTE-
RIOR/COWL GRILLE - REMOVAL).
(3) With doors open, remove windshield molding
(Fig. 7). Pull outward on molding beginning at the
bottom of A-pillars using pliers.
(4) Cut urethane bonding from around windshield
using a suitable sharp cold knife (C-4849). A pneu-
matic cutting device can be used but is not recom-
mended (Fig. 8).
(5) Separate windshield from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: Allow the urethane at least 24 hours to
cure before returning the vehicle to use.
CAUTION: Roll down the left and right front door
glass and open the rear glass slider (if available)
before installing windshield to avoid pressurizing
the passenger compartment if a door is slammed
before urethane is cured. Water leaks can result.
The windshield fence should be cleaned of most of
its old urethane bonding material. A small amount of
old urethane, approximately 1-2 mm in height,
Fig. 7 Windshield Moldings
1 - WINDSHIELD
2 - WINDSHIELD MOLDING
23 - 148 STATIONARY GLASSBR/BE
Page 2775 of 2889

STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM CHARGE
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
After the refrigerant system has been tested for
leaks and evacuated, a refrigerant charge can be
injected into the system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - SPECIFICA-
TIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY)
A R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging
station that meets SAE Standard J2210 must be
used to charge the refrigerant system with R-134a
refrigerant. Refer to the operating instructions sup-
plied by the equipment manufacturer for proper care
and use of this equipment.
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
The R-134a refrigerant system charge capacity for
this vehicle is: 0.907 kilograms (32 ounces).
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION - A/C COMPRESSOR
The air conditioning system uses a Sanden
SD7H15 seven cylinder, reciprocating wobble plate-
type compressor on all models. This compressor has a
fixed displacement of 150 cubic centimeters (9.375
cubic inches), and has both the suction and discharge
ports located on the cylinder head. A label identifying
the use of R-134a refrigerant is located on the com-
pressor.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
A high pressure relief valve is located on the com-
pressor cylinder head, which is at the rear of the
compressor. This mechanical valve is designed to
vent refrigerant from the system to protect against
damage to the compressor and other system compo-
nents, caused by condenser air flow restriction or an
overcharge of refrigerant.
OPERATION - A/C COMPRESSOR
The compressor is driven by the engine through an
electric clutch, drive pulley and belt arrangement.
The compressor is lubricated by refrigerant oil that iscirculated throughout the refrigerant system with the
refrigerant.
The compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant
vapor from the evaporator through its suction port. It
then compresses the refrigerant into a high-pressure,
high-temperature refrigerant vapor, which is then
pumped to the condenser through the compressor dis-
charge port.
The compressor cannot be repaired. If faulty or
damaged, the entire compressor assembly must be
replaced. The compressor clutch, pulley and clutch
coil are available for service.
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
The high pressure relief valve vents the system
when a discharge pressure of 3445 to 4135 kPa (500
to 600 psi) or above is reached. The valve closes with
a minimum discharge pressure of 2756 kPa (400 psi)
is reached.
The high pressure relief valve vents only enough
refrigerant to reduce the system pressure, and then
re-seats itself. The majority of the refrigerant is con-
served in the system. If the valve vents refrigerant, it
does not mean the valve is faulty.
The high pressure relief valve is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The valve cannot be adjusted or
repaired, and must not be removed or otherwise dis-
turbed. The valve is only serviced as a part of the
compressor assembly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
When investigating an air conditioning related
noise, you must first know the conditions under
which the noise occurs. These conditions include:
weather, vehicle speed, transmission in gear or neu-
tral, engine speed, engine temperature, and any
other special conditions. Noises that develop during
air conditioning operation can often be misleading.
For example: What sounds like a failed front bearing
or connecting rod, may be caused by loose bolts, nuts,
mounting brackets, or a loose compressor clutch
assembly.
Drive belts are speed sensitive. At different engine
speeds and depending upon belt tension, belts can
develop noises that are mistaken for a compressor
noise. Improper belt tension can cause a misleading
noise when the compressor clutch is engaged, which
may not occur when the compressor clutch is disen-
gaged. Check the serpentine drive belt condition and
tension as described in Cooling before beginning this
procedure.
(1) Select a quiet area for testing. Duplicate the
complaint conditions as much as possible. Switch the
compressor on and off several times to clearly iden-
tify the compressor noise. Listen to the compressor
while the clutch is engaged and disengaged. Probe
24 - 46 PLUMBINGBR/BE
PLUMBING (Continued)