2001 DODGE RAM ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 1510 of 2889
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
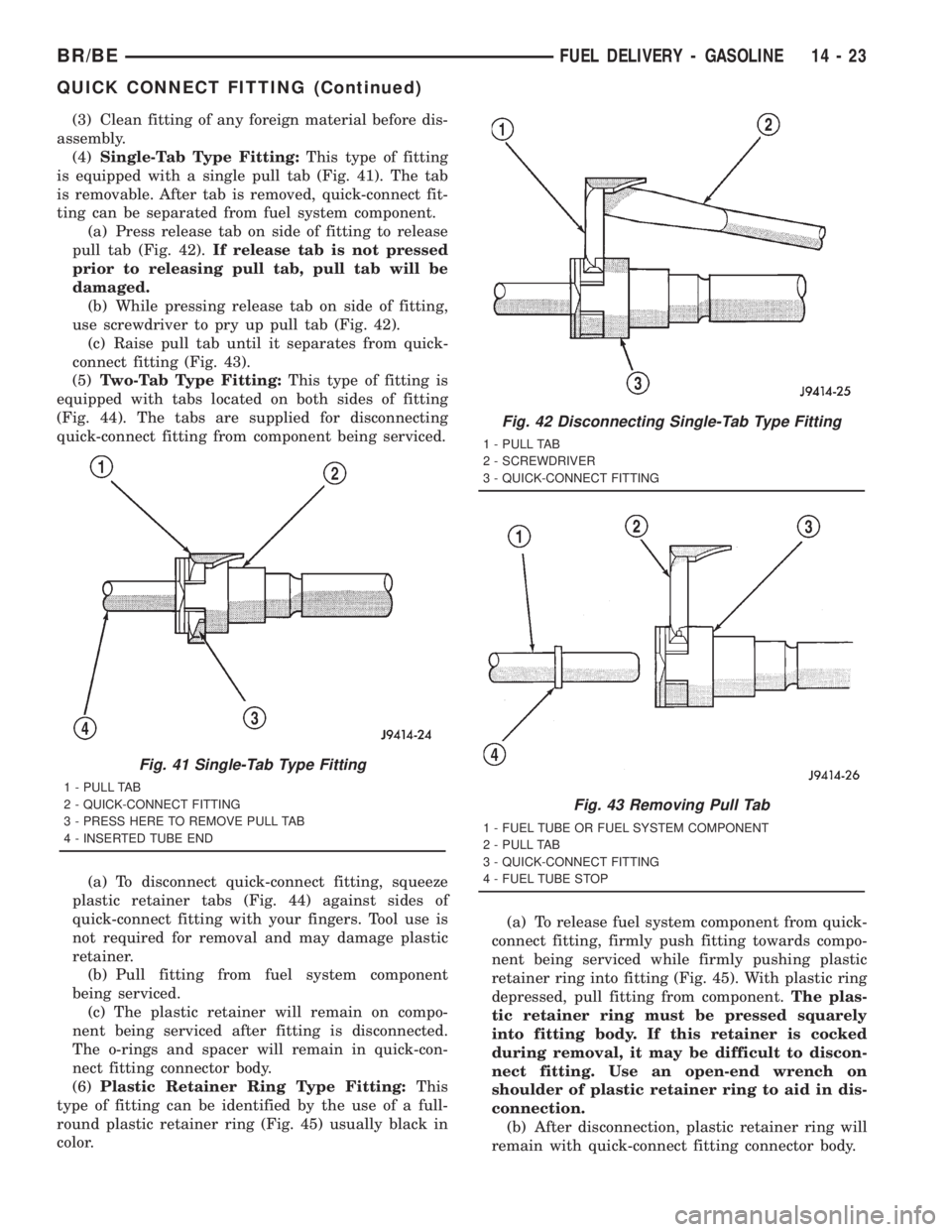
(4)Single-Tab Type Fitting:This type of fitting
is equipped with a single pull tab (Fig. 41). The tab
is removable. After tab is removed, quick-connect fit-
ting can be separated from fuel system component.
(a) Press release tab on side of fitting to release
pull tab (Fig. 42).If release tab is not pressed
prior to releasing pull tab, pull tab will be
damaged.
(b) While pressing release tab on side of fitting,
use screwdriver to pry up pull tab (Fig. 42).
(c) Raise pull tab until it separates from quick-
connect fitting (Fig. 43).
(5)Two-Tab Type Fitting:This type of fitting is
equipped with tabs located on both sides of fitting
(Fig. 44). The tabs are supplied for disconnecting
quick-connect fitting from component being serviced.
(a) To disconnect quick-connect fitting, squeeze
plastic retainer tabs (Fig. 44) against sides of
quick-connect fitting with your fingers. Tool use is
not required for removal and may damage plastic
retainer.
(b) Pull fitting from fuel system component
being serviced.
(c) The plastic retainer will remain on compo-
nent being serviced after fitting is disconnected.
The o-rings and spacer will remain in quick-con-
nect fitting connector body.
(6)Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting:This
type of fitting can be identified by the use of a full-
round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 45) usually black in
color.(a) To release fuel system component from quick-
connect fitting, firmly push fitting towards compo-
nent being serviced while firmly pushing plastic
retainer ring into fitting (Fig. 45). With plastic ring
depressed, pull fitting from component.The plas-
tic retainer ring must be pressed squarely
into fitting body. If this retainer is cocked
during removal, it may be difficult to discon-
nect fitting. Use an open-end wrench on
shoulder of plastic retainer ring to aid in dis-
connection.
(b) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
Fig. 41 Single-Tab Type Fitting
1 - PULL TAB
2 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
3 - PRESS HERE TO REMOVE PULL TAB
4 - INSERTED TUBE END
Fig. 42 Disconnecting Single-Tab Type Fitting
1 - PULL TAB
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
Fig. 43 Removing Pull Tab
1 - FUEL TUBE OR FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT
2 - PULL TAB
3 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
4 - FUEL TUBE STOP
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 23
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)
Page 1515 of 2889

FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................28
VISUAL INSPECTION - 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
ENGINES.............................28
VISUAL INSPECTION - 8.0L ENGINE........32
SPECIFICATIONS........................35
SPECIAL TOOLS.........................36
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
REMOVAL..............................37
INSTALLATION...........................37
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................38
OPERATION.............................38
REMOVAL..............................39
INSTALLATION...........................40
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION...........................41
OPERATION.............................41
REMOVAL..............................41
INSTALLATION...........................41
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION...........................41
OPERATION.............................41
REMOVAL..............................42
INSTALLATION...........................42
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................43
OPERATION.............................43
REMOVAL..............................43
INSTALLATION...........................43
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................44OPERATION.............................44
REMOVAL..............................45
INSTALLATION...........................45
O2 SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................46
OPERATION.............................46
REMOVAL..............................47
INSTALLATION...........................48
PTO SWITCH
DESCRIPTION...........................48
OPERATION.............................48
THROTTLE BODY
DESCRIPTION...........................48
OPERATION.............................48
REMOVAL..............................48
INSTALLATION...........................49
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL..............................50
INSTALLATION...........................50
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................51
OPERATION.............................51
REMOVAL..............................51
INSTALLATION...........................52
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION...........................53
OPERATION.............................53
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................53
FUEL INJECTOR TEST...................53
REMOVAL..............................53
INSTALLATION...........................53
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
ENGINES
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected or incor-
rectly routed wires and hoses should be made. This
should be done before attempting to diagnose or ser-
vice the fuel injection system. A visual check will
help spot these faults and save unnecessary test and
diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:
(1) Verify that the three 32±way electrical connec-
tors are fully inserted into the connector of the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) (Fig. 1).(2) Inspect the battery cable connections. Be sure
that they are clean and tight.
(3) Inspect fuel pump relay and air conditioning
compressor clutch relay (if equipped). Inspect the
ASD relay connections. Inspect starter motor relay
connections. Inspect relays for signs of physical dam-
age and corrosion. The relays are located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 2). Refer to
label on PDC cover for relay location.
(4) Inspect ignition coil connections. Verify that
coil secondary cable is firmly connected to coil (Fig.
3).
14 - 28 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
Page 1517 of 2889

(11) Inspect accelerator cable, transmission throt-
tle cable (if equipped) and cruise control cable con-
nections (if equipped). Check their connections to the
throttle arm of throttle body for any binding or
restrictions.
(12) If equipped with vacuum brake booster, verify
that vacuum booster hose is firmly connected to fit-
ting on intake manifold. Also check connection to
brake vacuum booster.
(13) Inspect the air cleaner inlet and air cleaner
element for dirt or restrictions.
(14) Inspect radiator grille area, radiator fins and
air conditioning condenser for restrictions.
(15) Verify that the intake manifold air tempera-
ture sensor wire connector is firmly connected to har-
ness connector (Fig. 5).
(16) Verify that MAP sensor electrical connector is
firmly connected to MAP sensor (Fig. 6). Also verify
that rubber L-shaped fitting from MAP sensor to the
throttle body is firmly connected (Fig. 7).
(17) Verify that fuel injector wire harness connec-
tors are firmly connected to injectors in the correct
order. Each harness connector is numerically tagged
with the injector number (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.) of its
corresponding fuel injector and cylinder number.
(18) Verify harness connectors are firmly con-
nected to idle air control (IAC) motor, throttle posi-
tion sensor (TPS) and manifold absolute pressure
(MAP) sensor (Fig. 6).
(19) Verify that wire harness connector is firmly
connected to the engine coolant temperature sensor
(Fig. 8).
(20) Raise and support the vehicle.(21) Verify oxygen sensor wire connectors are
firmly connected to the sensors. Inspect sensors and
connectors for damage (Fig. 9), (Fig. 10) or (Fig. 11).
(22) Inspect for pinched or leaking fuel tubes.
Inspect for pinched, cracked or leaking fuel hoses.
Fig. 5 Air Temperature
1 - INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
Fig. 6 Sensor and IAC Motor LocationÐTypical (V-8
Shown)
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
3 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 7 Rubber L-Shaped FittingÐMAP Sensor-to-
Throttle BodyÐ3.9L/5.2L/5.9L Engines
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - RUBBER FITTING
3 - IDLE AIR PASSAGE
14 - 30 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1524 of 2889
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage or kink the
cable core wire (within the cable sheathing) while
servicing accelerator pedal or cables.
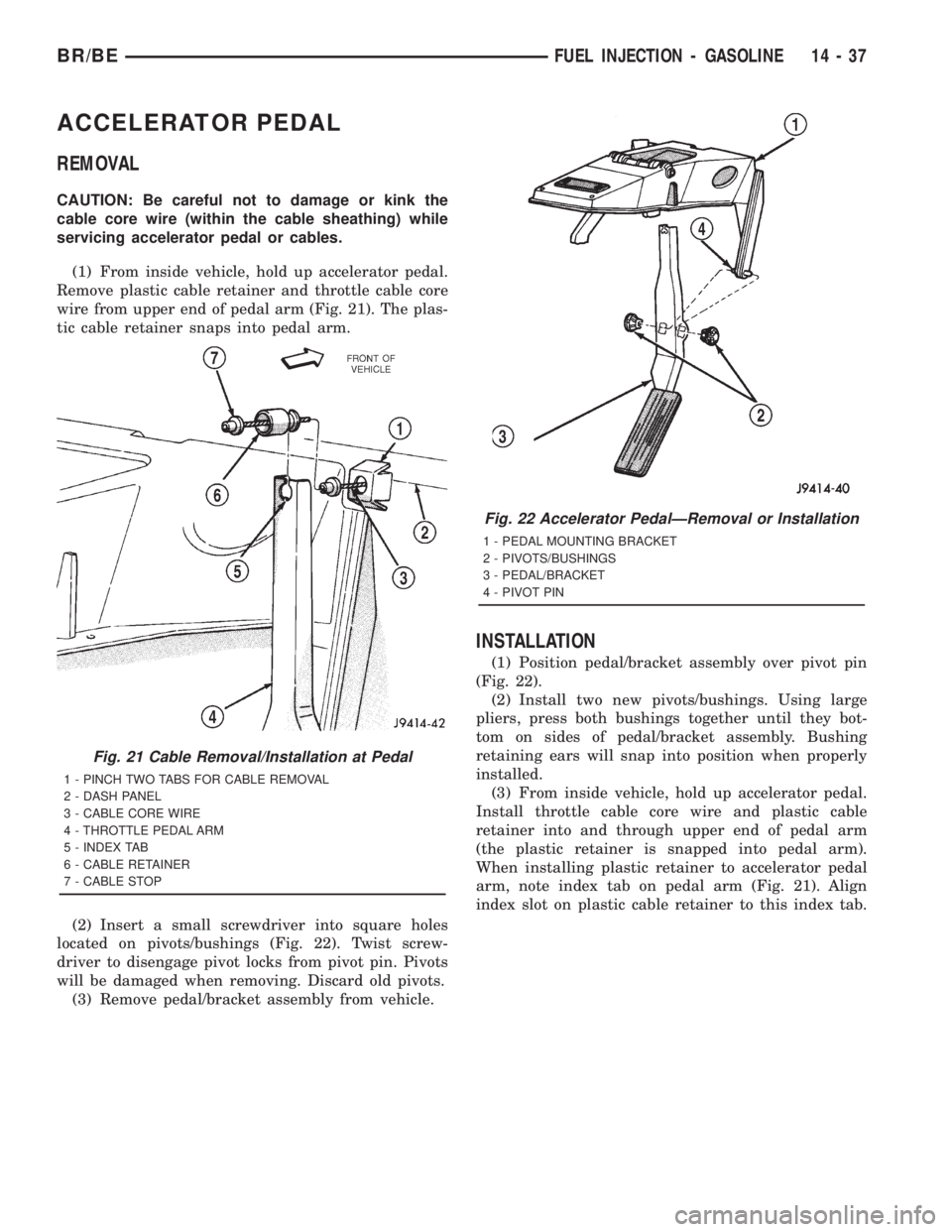
(1) From inside vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Remove plastic cable retainer and throttle cable core
wire from upper end of pedal arm (Fig. 21). The plas-
tic cable retainer snaps into pedal arm.
(2) Insert a small screwdriver into square holes
located on pivots/bushings (Fig. 22). Twist screw-
driver to disengage pivot locks from pivot pin. Pivots
will be damaged when removing. Discard old pivots.
(3) Remove pedal/bracket assembly from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position pedal/bracket assembly over pivot pin
(Fig. 22).
(2) Install two new pivots/bushings. Using large
pliers, press both bushings together until they bot-
tom on sides of pedal/bracket assembly. Bushing
retaining ears will snap into position when properly
installed.
(3) From inside vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Install throttle cable core wire and plastic cable
retainer into and through upper end of pedal arm
(the plastic retainer is snapped into pedal arm).
When installing plastic retainer to accelerator pedal
arm, note index tab on pedal arm (Fig. 21). Align
index slot on plastic cable retainer to this index tab.
Fig. 21 Cable Removal/Installation at Pedal
1 - PINCH TWO TABS FOR CABLE REMOVAL
2 - DASH PANEL
3 - CABLE CORE WIRE
4 - THROTTLE PEDAL ARM
5 - INDEX TAB
6 - CABLE RETAINER
7 - CABLE STOP
Fig. 22 Accelerator PedalÐRemoval or Installation
1 - PEDAL MOUNTING BRACKET
2 - PIVOTS/BUSHINGS
3 - PEDAL/BRACKET
4 - PIVOT PIN
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 37
Page 1531 of 2889

(1) Install sensor to intake manifold. Tighten to
12±15 N´m (110±130 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install electrical connector.
(3) Install air cleaner.
INSTALLATION - 8.0L
The intake manifold air temperature sensor is
located in the side of the intake manifold near the
front of throttle body (Fig. 35).
(1) Install sensor to intake manifold. Tighten to
12±15 N´m (110±130 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install electrical connector.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION - 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L/8.0L
On 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L engines, the MAP sensor is
mounted on the side of the engine throttle body. The
sensor is connected to the throttle body with a rubber
L-shaped fitting.
On the 8.0L 10±cylinder engine, the MAP sensor is
mounted into the right side of the intake manifold.
OPERATION - 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L/8.0L
The MAP sensor is used as an input to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). It contains a silicon
based sensing unit to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When manifold absolute pressure (MAP) equals
Barometric pressure, the pulse width will be at max-
imum.
A 5 volt reference is supplied from the PCM and
returns a voltage signal to the PCM that reflects
manifold pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V
and full scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of 0±15
psi, the voltage changes 4.0V. To operate the sensor,
it is supplied a regulated 4.8 to 5.1 volts. Ground is
provided through the low-noise, sensor return circuit
at the PCM.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to fuel injector pulse width. The most important
function of the MAP sensor is to determine baromet-
ric pressure. The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is
at sea level or at a higher altitude, because the air
density changes with altitude. It will also help to cor-
rect for varying barometric pressure. Barometric
pressure and altitude have a direct inverse correla-
tion; as altitude goes up, barometric goes down. At
key-on, the PCM powers up and looks at MAP volt-
age, and based upon the voltage it sees, it knows the
current barometric pressure (relative to altitude).
Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at the voltageagain, continuously every 12 milliseconds, and com-
pares the current voltage to what it was at key-on.
The difference between current voltage and what it
was at key-on, is manifold vacuum.
During key-on (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring a known good sensor.
As the altitude increases, the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to a
very different altitude than where it was at key-on,
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open Throttle (WOT), based
upon Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) angle and RPM,
it will update barometric pressure in the MAP mem-
ory cell. With periodic updates, the PCM can make
its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor input to aid in cal-
culating the following:
²Manifold pressure
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (certain automatic trans-
missions only)
²Idle speed
²Decel fuel shutoff
The MAP sensor signal is provided from a single
piezoresistive element located in the center of a dia-
phragm. The element and diaphragm are both made
of silicone. As manifold pressure changes, the dia-
phragm moves causing the element to deflect, which
stresses the silicone. When silicone is exposed to
stress, its resistance changes. As manifold vacuum
increases, the MAP sensor input voltage decreases
proportionally. The sensor also contains electronics
that condition the signal and provide temperature
compensation.
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; meaning as
pressure changes, voltage changes proportionately.
The range of voltage output from the sensor is usu-
ally between 4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3
volts at 26 in. of Hg. Barometric pressure is the pres-
sure exerted by the atmosphere upon an object. At
sea level on a standard day, no storm, barometric
pressure is approximately 29.92 in Hg. For every 100
feet of altitude, barometric pressure drops .10 in. Hg.
If a storm goes through it can change barometric
pressure from what should be present for that alti-
tude. You should know what the average pressure
and corresponding barometric pressure is for your
area.
14 - 44 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1532 of 2889

REMOVAL - 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
throttle body (Fig. 36). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
37).The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
throttle body (Fig. 36). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
37).
(1) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(2) Remove two MAP sensor mounting bolts
(screws) (Fig. 36).
(3) While removing MAP sensor, slide the vacuum
rubber L-shaped fitting (Fig. 37) from the throttle
body.
(4) Remove rubber L-shaped fitting from MAP sen-
sor.
REMOVAL - 8.0L
The MAP sensor is mounted into the right upper
side of the intake manifold (Fig. 38). A rubber gasket
is used to seal the sensor to the intake manifold. The
rubber gasket is part of the sensor and is not ser-
viced separately.
(1) Remove the electrical connector at the sensor.
(2) Clean the area around the sensor before
removal.
(3) Remove the two sensor mounting bolts.
(4) Remove the sensor from the intake manifold.
INSTALLATION - 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
throttle body (Fig. 36). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
37).
(1) Install rubber L-shaped fitting to MAP sensor.
(2) Position sensor to throttle body while guiding
rubber fitting over throttle body vacuum nipple.
Fig. 36 MAP Sensor LocationÐ3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
Engines
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS (2)
Fig. 37 MAP Sensor L-Shaped Rubber FittingÐ3.9L/
5.2L/5.9L Engines
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - RUBBER FITTING
3 - IDLE AIR PASSAGE
Fig. 38 MAP Sensor LocationÐ8.0L V-10 EngineÐ
Typical
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - THROTTLE BODY
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 45
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1533 of 2889

(3) Install MAP sensor mounting bolts (screws).
Tighten screws to 3 N´m (25 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install air cleaner.
INSTALLATION - 8.0L
The MAP sensor is mounted into the right upper
side of the intake manifold (Fig. 38). A rubber gasket
is used to seal the sensor to the intake manifold. The
rubber gasket is part of the sensor and is not ser-
viced separately.
(1) Check the condition of the sensor seal. Clean
the sensor and lubricate the rubber gasket with clean
engine oil.
(2) Clean the sensor opening in the intake mani-
fold.
(3) Install the sensor into the intake manifold.
(4) Install sensor mounting bolts. Tighten bolts to
2 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install the electrical connector to sensor.
O2 SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Oxygen Sensors (O2S) are attached to, and
protrude into the vehicle exhaust system. Depending
on the emission package, the vehicle may use a total
of either 2 or 4 sensors.
3.9L/5.2L/Light Duty 5.9L Engine:Four sensors
are used: 2 upstream (referred to as 1/1 and 2/1) and
2 downstream (referred to as 1/2 and 2/2). With this
emission package, the right upstream sensor (2/1) is
located in the right exhaust downpipe just before the
mini-catalytic convertor. The left upstream sensor
(1/1) is located in the left exhaust downpipe just
before the mini-catalytic convertor. The right down-
stream sensor (2/2) is located in the right exhaust
downpipe just after the mini-catalytic convertor, and
before the main catalytic convertor. The left down-
stream sensor (1/2) is located in the left exhaust
downpipe just after the mini-catalytic convertor, and
before the main catalytic convertor.
Medium and Heavy Duty 8.0L V-10 Engine:
Four sensors are used (2 upstream, 1 pre-catalyst
and 1 post-catalyst). With this emission package, the
1/1 upstream sensor (left side) is located in the left
exhaust downpipe before both the pre-catalyst sensor
(1/2), and the main catalytic convertor. The 2/1
upstream sensor (right side) is located in the right
exhaust downpipe before both the pre-catalyst sensor
(1/2), and the main catalytic convertor. The pre-cata-
lyst sensor (1/2) is located after the 1/1 and 2/1 sen-
sors, and just before the main catalytic convertor.
The post-catalyst sensor (1/3) is located just after the
main catalytic convertor.Heavy Duty 5.9L Engine:Two sensors are used.
They arebothreferred to as upstream sensors (left
side is referred to as 1/1 and right side is referred to
as 2/1). With this emission package, a sensor is
located in each of the exhaust downpipes before the
main catalytic convertor.
OPERATION
An O2 sensor is a galvanic battery that provides
the PCM with a voltage signal (0-1 volt) inversely
proportional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
In other words, if the oxygen content is low, the volt-
age output is high; if the oxygen content is high the
output voltage is low. The PCM uses this information
to adjust injector pulse-width to achieve the
14.7±to±1 air/fuel ratio necessary for proper engine
operation and to control emissions.
The O2 sensor must have a source of oxygen from
outside of the exhaust stream for comparison. Cur-
rent O2 sensors receive their fresh oxygen (outside
air) supply through the wire harness. This is why it
is important to never solder an O2 sensor connector,
or pack the connector with grease.
Four wires (circuits) are used on each O2 sensor: a
12±volt feed circuit for the sensor heating element; a
ground circuit for the heater element; a low-noise
sensor return circuit to the PCM, and an input cir-
cuit from the sensor back to the PCM to detect sen-
sor operation.
Oxygen Sensor Heaters/Heater Relays:
Depending on the emissions package, the heating ele-
ments within the sensors will be supplied voltage
from either the ASD relay, or 2 separate oxygen sen-
sor relays. Refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams to determine
which relays are used.
The O2 sensor uses a Positive Thermal Co-efficient
(PTC) heater element. As temperature increases,
resistance increases. At ambient temperatures
around 70ÉF, the resistance of the heating element is
approximately 4.5 ohms. As the sensor's temperature
increases, resistance in the heater element increases.
This allows the heater to maintain the optimum
operating temperature of approximately 930É-1100ÉF
(500É-600É C). Although the sensors operate the
same, there are physical differences, due to the envi-
ronment that they operate in, that keep them from
being interchangeable.
Maintaining correct sensor temperature at all times
allows the system to enter into closed loop operation
sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain in closed
loop operation during periods of extended idle.
In Closed Loop operation, the PCM monitors cer-
tain O2 sensor input(s) along with other inputs, and
adjusts the injector pulse width accordingly. During
Open Loop operation, the PCM ignores the O2 sensor
input. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width based
14 - 46 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1537 of 2889
(5) Install control cables.
(6) Install electrical connectors.
(7) Install air cleaner housing to throttle body.
(8) Install 4 air cleaner housing mounting nuts.
Tighten nuts to 11 N´m (96 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install air cleaner housing cover.
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage or kink the
cable core wire (within the cable sheathing) while
servicing accelerator pedal or cables.
(1) From inside the vehicle, hold up the accelerator
pedal. Remove the plastic cable retainer and throttle
cable core wire from upper end of pedal arm (Fig.
21). The plastic cable retainer snaps into pedal the
arm.
(2) Remove the cable core wire at the pedal arm.
(3) Remove the air cleaner housing.
(4) From inside the vehicle, pinch both sides of the
plastic cable housing retainer tabs at the dash panel
(Fig. 21).
(5) Remove cable housing from dash panel and
pull the cable into the engine compartment.
(6)3.9L/5.2L/5.9L Engines:Disconnect the cable
from the routing/holddown clip at the radiator fan
shroud.
(7)8.0L V-10 Engine:Remove the throttle cable
socket at throttle lever ball. (Fig. 45) (snaps off).
(8)3.9L/5.2L/5.9L Engines:Slip the cable end
rearward from pin on throttle body (Fig. 44).
(9) Remove cable housing at throttle body mount-
ing bracket by pressing on release tab with a small
screwdriver (Fig. 46) or (Fig. 45).To prevent cable
housing breakage, press on the tab only enough
to release the cable from the bracket.Lift the
cable housing straight up from bracket while press-
ing on release tab. Remove throttle cable from vehi-
cle.
INSTALLATION
(1)3.9L/5.2L/5.9L Engines:
(a) Rotate and hold the throttle cam in the full
wide open position. Snap the cable end onto lever
pin (Fig. 44).
(b) Connect cable to throttle body mounting
bracket (push down and lock).
(c) Connect cable to fan shroud routing clip.
(2)8.0L V-10 Engine:
(a) Connect cable end socket to throttle body
lever ball (snaps on) (Fig. 45).
(b) Connect cable to throttle body mounting
bracket (push down and lock).
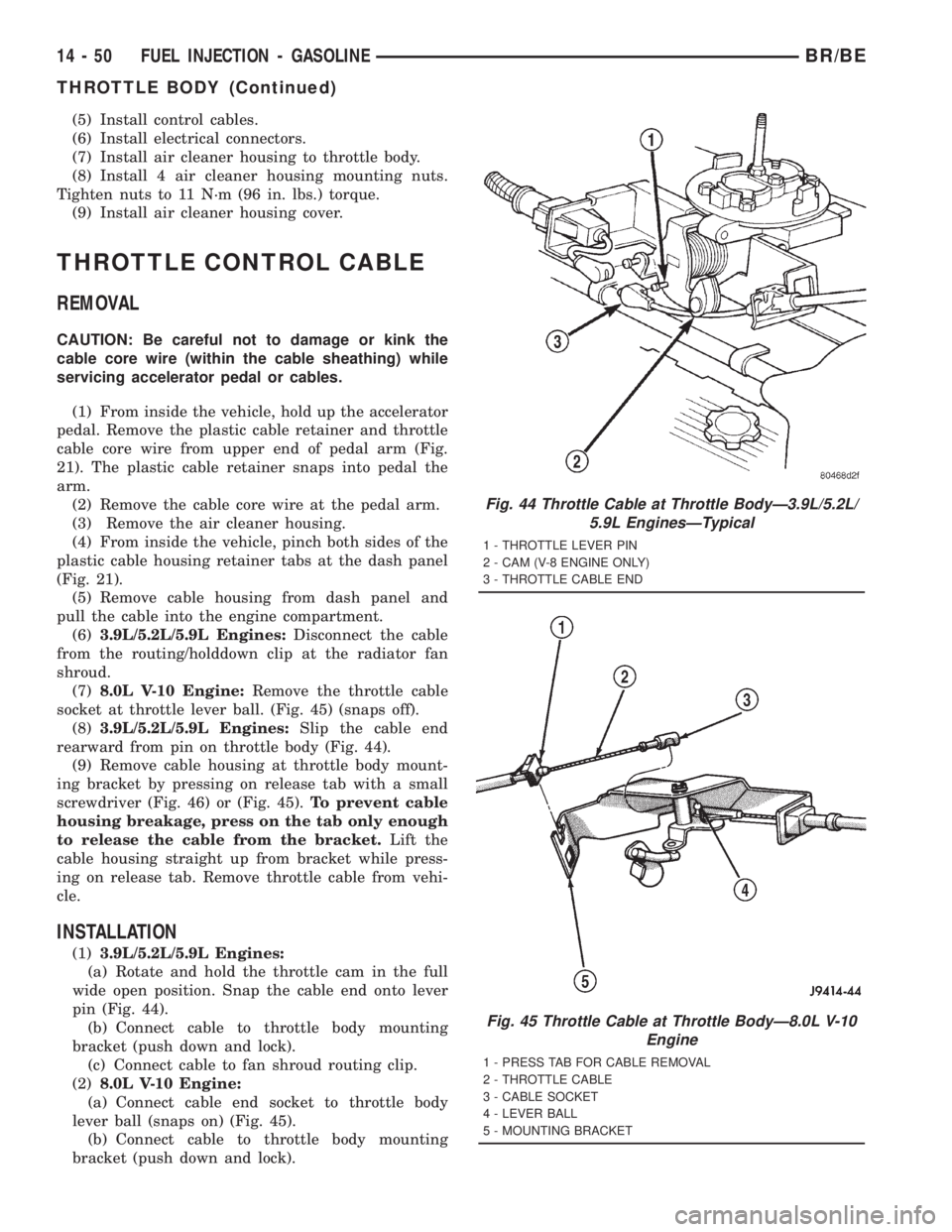
Fig. 44 Throttle Cable at Throttle BodyÐ3.9L/5.2L/
5.9L EnginesÐTypical
1 - THROTTLE LEVER PIN
2 - CAM (V-8 ENGINE ONLY)
3 - THROTTLE CABLE END
Fig. 45 Throttle Cable at Throttle BodyÐ8.0L V-10
Engine
1 - PRESS TAB FOR CABLE REMOVAL
2 - THROTTLE CABLE
3 - CABLE SOCKET
4 - LEVER BALL
5 - MOUNTING BRACKET
14 - 50 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
THROTTLE BODY (Continued)