2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 2654 of 4284

(3) Apply MopartEngine RTV GEN II at the
camshaft cap corners and at the top edges of the 1/2
round seal (Fig. 32).
(4) Install cylinder head cover assembly to cylin-
der head. Install all bolts, ensuring the two (2) bolts
containing the sealing washer are located in the cen-
ter locations of cover. Tighten bolts in sequence
shown in (Fig. 33). Using a 3 step torque method as
follows:
(a) Tighten all bolts to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(b) Tighten all bolts to 9.0 N´m (80 in. lbs.).
(c) Tighten all bolts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(5) Install ignition coil and spark plug wires.
Tighten fasteners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(6) If the PCV valve was removed, apply Mopart
Thread Sealant with Teflon to threads and install
valve to cylinder head cover. Tighten PCV valve to 8
N´m (70 in. lbs.).
(7) Connect PCV and make-up air hoses to cylin-
der head cover.(8) Install upper intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel. They
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Viton
rubber valve stem seals are integral with the spring
seats. The valves have three-bead lock keepers to
retain springs and to promote valve rotation.
CLEANING
(1) Clean all valves thoroughly and discard
burned, warped and cracked valves.
VALVE SPRINGS
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1) Remove camshafts.
(2) Rotate crankshaft until piston is at TDC on
compression.
(3) With air hose attached to adapter tool installed
in spark plug hole, apply 90-120 psi air pressure.
(4) Using Special Tool MD-998772-A with adapter
6779 (Fig. 34), compress valve springs and remove
valve locks.
(5) Remove valve spring(s).
(6) Remove valve stem seal(s) by a using valve
stem seal tool (Fig. 36).
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) With cylinder head removed, compress valve
springs using a universal valve spring compressor.
(2) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(3) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
Fig. 32 Sealer Locations
1 ± SEALER LOCATION
Fig. 33 Cylinder Head Cover Tightening Sequence
(Typical Cover Shown)
9 - 30 ENGINE 2.4LRS
CYLINDER HEAD COVER (Continued)
Page 2655 of 4284

age to the valve guides.Identify valves to insure
installation in original location.
(4) Inspect the valves. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS - INSPECTION)
INSPECTION
(1) Whenever valves have been removed for inspec-
tion, reconditioning or replacement, valve springs
should be tested for correct tension. Discard the
springs that do not meet specifications. The following
specifications apply to both intake and exhaust
valves springs:
²Valve Closed Nominal TensionÐ76 lbs. @ 38.0
mm (1.50 in.)
²Valve Open Nominal TensionÐ136 lbs. @ 29.75
mm (1.17 in.)
(2) Inspect each valve spring for squareness with a
steel square and surface plate, test springs from both
ends. If the spring is more than 1.5 mm (1/16 inch)
out of square, install a new spring.
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1) Install valve seal/valve spring seat assembly
(Fig. 35). Push the assembly down to seat it onto the
valve guide.
(2) Install valve spring and retainer, use Special
Tool MD-998772-A with adapter 6779 to compress
valve springs only enough to install locks (Fig. 34).
Correct alignment of tool is necessary to avoid nick-
ing valve stems.
(3) Remove air hose and install spark plugs.
(4) Install camshafts and cylinder head cover .
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert in cylinder head.(2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves
using a valve stem seal tool (Fig. 36). The valve stem
seals should be pushed firmly and squarely over
valve guide.
CAUTION: When oversize valves are used, the cor-
responding oversize valve seal must also be used.
Excessive guide wear may result if oversize seals
are not used with oversize valves.
(3) Install valve springs and retainers. Compress
valve springs only enough to install locks, taking
care not to misalign the direction of compression.
Nicked valve stems may result from misalignment of
the valve spring compressor.
Fig. 34 Valve Spring - Removal/Installation
1 - VALVE SPRING COMPRESSOR MD 998772A
2 - AIR HOSEFig. 35 Valve Stem Seal/Valve Spring Seat
1 - VALVE RETAINING LOCKS
2 - VALVE SPRING
3 - VALVE SEAL AND VALVE SPRING SEAT ASSEMBLY
4 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER
Fig. 36 Valve Stem Oil Seal Tool
1 - VALVE SEAL TOOL
2 - VALVE STEM
RSENGINE 2.4L9-31
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 2656 of 4284

CAUTION: When depressing the valve spring retain-
ers with valve spring compressor the locks can
become dislocated. Ensure both locks are in the
correct location after removing tool.
(4) Check the valve spring installed height B after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 37). Make sure mea-
surements are taken from top of spring seat to the
bottom surface of spring retainer. If height is greater
than 38.75 mm (1.525 in.), install a 0.762 mm (0.030
in.) spacer under the valve spring seat to bring
spring height back within specification.
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LASH ADJUSTER
(TAPPET) NOISE
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) During this time, turn engine off and let set for
a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several
times after engine has reached normal operating
temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor (integral to the head gasket)
in the vertical oil passage to the cylinder head is
plugged with debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Faulty lash adjuster.
²Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head. Depress part of rocker
arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel very
firm. Spongy adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
²Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace as
necessary.
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure is for in-vehicle service with
camshafts installed.
(1) Remove cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove rocker arm. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove hydraulic lifter (Fig. 38).
(4) Repeat removal procedure for each hydraulic
lifter.
(5) If reusing, mark each hydraulic lifter for reas-
sembly in original position. Lifters are serviced as an
assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install hydraulic lifter (Fig. 38). Ensure the
lifters are at least partially full of engine oil. This is
indicated by little or no plunger travel when the
lifter is depressed.
(2) Install rocker arm. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - INSTALLATION)
(3) Repeat installation procedure for each hydrau-
lic lifter.
(4) Install cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 37 Checking Spring Installed Height and Valve
Tip Height Dimensions
1 - GARTER SPRING
2 - VALVE SPRING SEAT
3 - CYLINDER HEAD SURFACE
Fig. 38 Hydraulic Lifter
9 - 32 ENGINE 2.4LRS
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 2657 of 4284

ROCKER ARMS
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure is for in-vehicle service with
camshafts installed.
(1) Remove cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove fuel rail. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove spark plugs.
(4) Rotate engine until the camshaft lobe, on the
follower being removed, is position on its base circle
(heel). Also, the piston should be a minimum of 6.3
mm (0.25 in) below TDC position.
CAUTION: If cam follower assemblies are to be
reused, always mark position for reassembly in
their original positions.
(5) Using Special Tools 8215 and 8436 slowly
depress valve assembly until rocker arm can be
removed (Fig. 39).
NOTE: It may be necessary to remove additional
brackets or components to allow clearance for tool
handle movement.
(6) Repeat removal procedure for each rocker arm.
INSPECTION
Inspect the rocker arm for wear or damage (Fig.
40). Replace as necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate rocker arm with clean engine oil.
(2) Using Special Tools 8215 and 8436 slowly
depress valve assembly until rocker arm can be
installed on the hydraulic lifter and valve stem (Fig.
39).
(3) Repeat installation procedure for each rocker
arm.
(4) Install spark plugs.
(5) Install fuel rail. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - INSTALLATION)
(6) Install cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The cast iron cylinder block is a two-piece assem-
bly, consisting of the cylinder block and bedplate (Fig.
41). The bedplate incorporates the main bearing caps
and bolts to the cylinder block. This design offers a
much stronger lower end and increased cylinder
block rigidity. The rear oil seal retainer is integral
with the block. The bedplate and block are serviced
as an assembly.
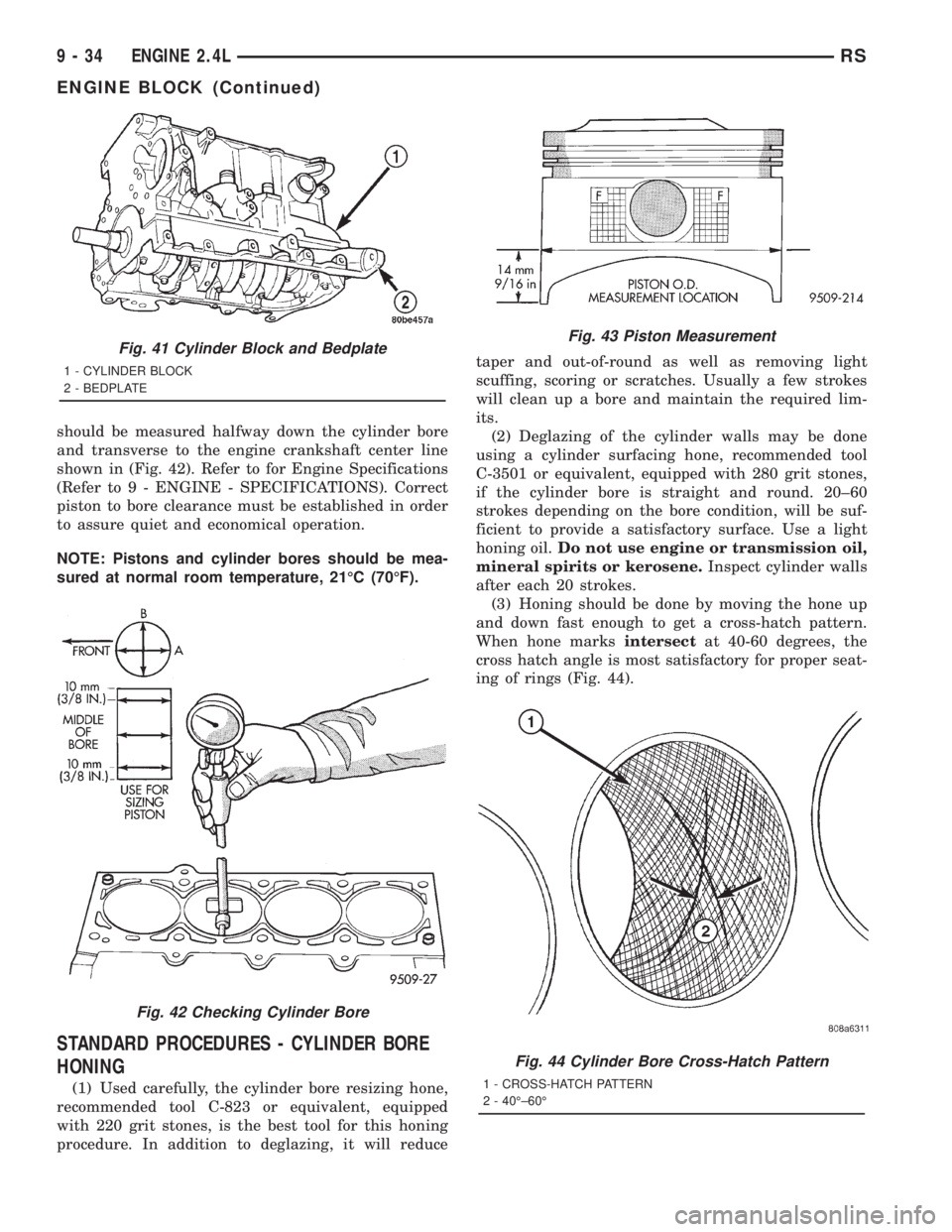
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON TO
CYLINDER BORE FITTING
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Piston diameter should be measured 90 degrees to
piston pin about 14 mm (9/16 inch.) from the bottom
of the skirt as shown in (Fig. 43). Cylinder bores
Fig. 39 Rocker Arm - Removal/Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8215
2 - ROCKER ARM
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 8436
Fig. 40 Rocker Arm
1 - TIP
2 - LASH ADJUSTER POCKET
3 - ROLLER
RSENGINE 2.4L9-33
Page 2658 of 4284
should be measured halfway down the cylinder bore
and transverse to the engine crankshaft center line
shown in (Fig. 42). Refer to for Engine Specifications
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). Correct
piston to bore clearance must be established in order
to assure quiet and economical operation.
NOTE: Pistons and cylinder bores should be mea-
sured at normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
STANDARD PROCEDURES - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
(1) Used carefully, the cylinder bore resizing hone,
recommended tool C-823 or equivalent, equipped
with 220 grit stones, is the best tool for this honing
procedure. In addition to deglazing, it will reducetaper and out-of-round as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring or scratches. Usually a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done
using a cylinder surfacing hone, recommended tool
C-3501 or equivalent, equipped with 280 grit stones,
if the cylinder bore is straight and round. 20±60
strokes depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Use a light
honing oil.Do not use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.Inspect cylinder walls
after each 20 strokes.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a cross-hatch pattern.
When hone marksintersectat 40-60 degrees, the
cross hatch angle is most satisfactory for proper seat-
ing of rings (Fig. 44).
Fig. 41 Cylinder Block and Bedplate
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - BEDPLATE
Fig. 42 Checking Cylinder Bore
Fig. 43 Piston Measurement
Fig. 44 Cylinder Bore Cross-Hatch Pattern
1 - CROSS-HATCH PATTERN
2 - 40ɱ60É
9 - 34 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)
Page 2659 of 4284

(4) A controlled hone motor speed between
200±300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40±60
degree angle. Faster up and down strokes increase
the cross-hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned again to remove all traces of abrasive.
CAUTION: Ensure all abrasives are removed from
engine parts after honing. It is recommended that a
solution of soap and hot water be used with a
brush and the parts then thoroughly dried. The bore
can be considered clean when it can be wiped
clean with a white cloth and cloth remains clean.
Oil the bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder block thoroughly using a suitable
cleaning solvent.
INSPECTION
ENGINE BLOCK
(1) Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all
core hole plugs for evidence of leaking.
(2) If new core plugs are to be installed, refer to
Engine Core Plugs for procedures (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Examine block and cylinder bores for cracks or
fractures.
(4) Check block deck surfaces for flatness. Deck
surface must be within service limit of 0.1 mm (0.004
in.).
CYLINDER BORE
NOTE: The cylinder bores should be measured at
normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C119 or equivalent (Fig.
45). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) If
the cylinder walls are badly scuffed or scored, the
cylinder block should be replaced, and new pistons
and rings fitted.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 45). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 in.) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 in.) up from bottom of bore.
Refer to Engine Specifications (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- SPECIFICATIONS).
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
CONNECTING RODÐFITTING
(1) For measuring connecting rod bearing clear-
ance procedure and use of Plastigage(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE). For bearing
clearance refer to Engine Specifications. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS)
NOTE: The rod bearing bolts should not be reused.
(2) Before installing theNEWbolts the threads
should be oiled with clean engine oil.
(3) Install each bolt finger tight than alternately
torque each bolt to assemble the cap properly.
(4) Tighten the bolts to 27 N´m PLUS 1/4 turn (20
ft. lbs. PLUS 1/4 turn)Do not use a torque
wrench for last step.
(5) Using a feeler gauge, check connecting rod side
clearance (Fig. 46). Refer to clearance specifications
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
Fig. 45 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
RSENGINE 2.4L9-35
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)
Page 2660 of 4284

CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft is made of nodular cast iron and
includes five main bearing journals and four connect-
ing rod journals (Fig. 47). The number three journal
is the location for the thrust bearing. The mains and
connecting rod journals have undercut fillet radiuses
that are rolled for added strength. To optimize bear-
ing loading, eight counterweights are used.
OPERATION
The crankshaft transfers force generated by com-
bustion within the cylinder to the flywheel or flex-
plate.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CRANKSHAFT END
PLAY
(1) Using Dial Indicator C-3339 and Mounting
Post L-4438, attach to front of engine, locating probe
perpendicular on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 48).
(2) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel.
(3) Zero the dial indicator.
(4) Move crankshaft all the way to the front and
read the dial indicator. Refer to Engine Specifica-
tions.
REMOVAL
NOTE: Crankshaft can not be removed when engine
is in vehicle.
(1) Remove engine assembly from vehicle. (Refer to
9 - ENGINE - REMOVAL)
(2) Separate engine from transaxle.
(3) Remove flex plate and crankshaft rear oil seal.
(4) Mount engine on a repair stand.
(5) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(6) Remove the oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL)
(7) Remove the timing belt covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(8) Remove the timing belt. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL)
(9) Remove the oil pump. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL)
Fig. 46 Connecting Rod Side Clearance
Fig. 47 CRANKSHAFT - TYPICAL
1 - MAIN BEARING JOURNALS
2 - COUNTER BALANCE WEIGHTS
Fig. 48 CHECKING CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
9 - 36 ENGINE 2.4LRS
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 2661 of 4284

(10) Remove balance shafts and housing assembly.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/BALANCE
SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(11) Remove all bedplate bolts from the engine
block (Fig. 49).
(12) Using a mallet gently tap the bedplate loose
from the engine block dowel pins.
CAUTION: Do not pry up on one side of the bed-
plate. Damage may occur to cylinder block to bed-
plate alignment and thrust bearing.
(13) Bedplate should be removed evenly from the
cylinder block dowel pins to prevent damage to the
dowel pins and thrust bearing.
(14) Lift out crankshaft from cylinder block. Do
not damage the main bearings or journals when
removing the crankshaft.
INSPECTION
The crankshaft journals should be checked for
excessive wear, taper and scoring (Fig. 50). Limits of
taper or out of round on any crankshaft journals
should within specitifications. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
SPECIFICATIONS) Journal grinding should not
exceed 0.305 mm (0.012 in.) under the standard jour-
nal diameter. DO NOT grind thrust faces of No. 3
main bearing. DO NOT nick crank pin or bearing fil-
lets. After grinding, remove rough edges from crank-
shaft oil holes and clean out all passages.
CAUTION: With the nodular cast iron crankshafts, it
is important that the final paper or cloth polish be
in the same direction as normal rotation in the
engine.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the main bearing shells with the lubri-
cation groove in the cylinder block (Fig. 51).(2) Make certain oil holes in block line up with oil
hole in bearings and bearing tabs seat in the block
tab slots.
CAUTION: Do not get oil on the bedplate mating
surface. It will affect the sealer ability to seal the
bedplate to cylinder block.
(3) Oil the bearings and journals. Install crank-
shaft.
CAUTION: Use only the specified anaerobic sealer
on the bedplate or damage may occur to the
engine.
Fig. 49 Bedplate Bolt Tightenening Sequence
Fig. 50 Crankshaft Journal Measurements
Fig. 51 Installing Main Bearing Upper Shell
1 - LUBRICATION GROOVES
2 - OIL HOLES
RSENGINE 2.4L9-37
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)