2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER mirror
[x] Cancel search: mirrorPage 1163 of 4284

4.3 WARNINGS
4.3.1 VEHICLE DAMAGE WARNINGS
Before disconnecting any control module, make
sure the ignition is ``off ''. Failure to do so could
damage the module.
When testing voltage or continuity at any control
module, use the terminal side (not the wire end) of
the connector. Do not probe a wire through the
insulation, this will damage it and eventually cause
it to fail because of corrosion.
Be careful when performing electrical tests so as
to prevent accidental shorting of terminals. Such
mistakes can damage fuses or components. Also, a
second code could be set, making diagnosis of the
original problem more difficult.
4.3.2 ROAD TESTING A COMPLAINT
VEHICLE
Some complaints will require a test drive as part
of the repair verification procedure. The purpose of
the test drive is to try to duplicate the diagnostic
code or symptom condition.
WARNING: BEFORE ROAD TESTING A
VEHICLE, BE SURE THAT ALL
COMPONENTS ARE REASSEMBLED.
DURING THE TEST DRIVE, DO NOT TRY TO
READ THE DRB SCREEN WHILE IN MOTION.
DO NOT HANG THE DRBIIITFROM THE
REAR VIEW MIRROR OR OPERATE IT
YOURSELF. HAVE AN ASSISTANT
AVAILABLE TO OPERATE THE DRBIIIT.
4.4 DIAGNOSIS
1. Your diagnostic test procedure must begin with a
thorough visual inspection of the ABS system for
damaged components or disconnected connec-
tors. The brake lamps must be operational, and
if they are not, repair them prior to continuing.
2. Connect the DRBIIItto the data link connector,
which is located under the dash to the left of the
steering column. If the DRBIIItdoes not power
up, check the power and ground supplies to the
connector.
3. Turn the ignition on. Select ªAntilock Brakesº. If
the DRBIIItdisplays ªNo Responseº condition
you must diagnose that first.
4. Read and record all ABS diagnostic trouble
codes. If the ªCAB Power Feed Circuitº diagnos-
tic trouble code is present, it must be repaired
prior to addressing any other DTC's. If any
additional DTC's are present, proceed to theappropriate test by locating the matching test in
the Table of Contents and begin to diagnose the
symptom.
5. If there are no diagnostic trouble codes present,
identify the customer complaint. Select ªInputs/
Outputsº and read the brake switch input as you
press and release the brake pedal. If the display
does not match the state of the pedal, perform
the proper test by locating the matching test in
the Table of Contents and begin to diagnose the
symptom. If a problem exists with the yellow
ªABSº warning indicator or the red ªBrakeº
indicator exists, refer to the proper tests by
locating the matching test in the Table of Con-
tents and begin to diagnose the symptom. Read
the traction control switch input as you press
and release the switch. If the display does not
match the state of the indicator perform the
proper test by locating the matching test in the
Table of Contents and begin to diagnose the
symptom.
6. If no other problems are found, it will be neces-
sary to road test the vehicle. Perform several
antilock stops from above 50 Km/h (30 mph) and
then repeat step 4. If any diagnostic trouble
codes are present, proceed to the appropriate test.
7. The following conditions should be considered
ªNORMALº operation, and no repairs should be
attempted to correct them.
± Brake pedal feedback during an ABS stop
(clicking, vibrating).
± Clicking, groaning or buzzing at 25 Km/h (15
mph) or 40 Km/h (24 mph) (drive off self test).
± Groaning noise during an ABS stop.
± Slight brake pedal drop and pop noise when
ignition is initially turned on.
± Brake pedal ratcheting down at the end of an
ABS stop.
8. If the complaint is ABS ªcyclingº at the end of a
stop at low speeds, it may be caused by a
marginal wheel speed sensor signal. The sensor
air gap, tone wheel condition, and/or brakes
hanging up are possible causes of this condition.
9. After a road test in which no problems were
found, refer to any Technical Service Bulletins
that may apply.
5.0 REQUIRED TOOLS AND
EQUIPMENT
DRBIIIt(diagnostic read-out box)
jumper wires
ohmmeter
voltmeter
test light
6
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 1205 of 4284

DIAGNOSTIC JUNCTION PORT - BLACK 16 WAYCAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (PCM/SKIM)
2 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (HVAC)
3 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (RADIO)
4 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (ORC)
5 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (CLUSTER)
6 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (BCM)
7 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (DLC)
8 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (OVERHEAD CONSOLE)
9 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (IPM)
10 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (LSIACM)
11 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (MEMORY SEAT/MIRROR)
12 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (PWR DOOR/ LT, RT LIFTGATE)
13 D25 20WT/VT PCI BUS (RSIACM)
14 - -
15 - -
16 - -
INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE C4 - GRAY 10 WAYCAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 Z127 12BK/DG GROUND
2 T750 12YL/GY ENGINE STARTER MOTOR RELAY OUTPUT
3 K342 16BR/WT AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY OUTPUT
4 F500 18DG/PK (ANTILOCK
BRAKES)FUSED IGNITION SWITCH RELAY OUTPUT (RUN)
5- -
6 D25 16WT/VT (ANTILOCK
BRAKES)PCI BUS
7 A107 12TN/RD (ANTILOCK
BRAKES)FUSED B(+)
8 A111 12DG/RD (ANTILOCK
BRAKES)FUSED B(+)
9 A701 14BR/RD FUSED B(+)
10 - -
LEFT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR - BLACK 2 WAYCAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 B9 18DG/LG LEFT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL
2 B8 18DG/TN LEFT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR 12 VOLT SUPPLY
C
O
N
N
E
C
T
O
R
P
I
N
O
U
T
S
48
CONNECTOR PINOUTS
Page 1227 of 4284

4.3 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
4.3.1 ROAD TEST WARNINGS
Some complaints will require a test drive as part
of the repair verification procedure. The purpose of
the test drive is to try to duplicate the diagnostic
code or symptom condition.
CAUTION: BEFORE ROAD TESTING A
VEHICLE, BE SURE THAT ALL
COMPONENTS ARE REASSEMBLED. DUR-
ING THE TEST DRIVE, DO NOT HANG THE
DRBIIITFROM THE REAR VIEW MIRROR. DO
NOT ATTEMPT TO READ THE DRBIIITWHILE
DRIVING. HAVE AN ASSISTANT AVAILABLE
TO OPERATE THE DRBIIIT.
4.3.2 VEHICLE DAMAGE CAUTIONS
Before disconnecting any control module, make
sure the ignition is off. Failure to do so could
damage the module. When testing voltage or circuit
integrity at any control module, use the terminal
side (not the wire end) of the harness connector. Do
not probe through the insulation; this will damage
it and eventually cause it to fail because of corro-
sion.
Be careful when performing electrical test so as to
prevent accidental shorting of terminals. Such a
mistake can damage fuses or components. Also, a
second code could be set, making diagnosis of the
original problem more difficult.
5.0 REQUIRED TOOLS AND
EQUIPMENT
DRBIIIt(diagnostic read-out box) scan tool
vacuum gauge
ammeter
ohmmeter
jumper wires and probes
oscilloscope
6.0 GLOSSARY OF TERMS
A/Cair conditioning
APPaccelerator pedal position (sensor)
backfire,
popbackfuel ignites in either the intake or
the exhaust system
BCMbody control module
BPboost pressure (sensor)CKPcrankshaft position (sensor)
CMPcamshaft position (sensor)
cuts out,
missesa steady pulsation or the inability of
the engine to maintain a consistent
rpm
DLCdata link connector
detona-
tion,
spark
knocka mild to severe ping, especially un-
der loaded engine conditions
ECMengine control module
ECTengine coolant temperature (sensor)
EGRexhaust gas recirculation
(solenoid/valve)
hard
startthe engine takes longer than usual
to start, even though it is able to
crank at normal speed.
IATintake air temperature (sensor)
IPMintelligent power module
lack of
power,
sluggishthe engine power output has been
reduced
MAFmass air flow (sensor)
MILmalfunction indicator lamp
msmillisecond(s)
PDCpower distribution center
poor fuel
economythere is significantly less fuel mile-
age than other vehicles of the same
design and configuration
runs
rough/
unstable
idlethe engine runs unevenly at idle
causing the engine to shake if it is
severe enough
S/Cspeed control
SKIMsentry key immobilizer module
SKISsentry key immobilizer system
start and
stallThe engine starts but immediately
dies (stalls)
surgeengine rpm fluctuation without cor-
responding change in accelerator
pedal position
SRCsignal range check
WIFwater in fuel (sensor)
VSSvehicle speed sensor
8
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 1825 of 4284

ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................1
PCM/SKIM PROGRAMMING................1
BODY CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION............................2
OPERATION.............................3
REMOVAL...............................3
INSTALLATION............................3
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE
DESCRIPTION............................3
OPERATION.............................3
REMOVAL...............................4
INSTALLATION............................4
DATA LINK CONNECTOR
DESCRIPTION............................5
OPERATION.............................5
FRONT CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION............................5
OPERATION.............................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................6
FRONT CONTROL MODULE...............6
REMOVAL...............................6
INSTALLATION............................6
MEMORY HEATED SEAT/MIRROR MODULE
REMOVAL...............................7
INSTALLATION............................7
POWER LIFTGATE MODULE
DESCRIPTION............................7
OPERATION.............................7REMOVAL...............................7
INSTALLATION............................8
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION............................8
OPERATION.............................19
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................21
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES...............................21
REMOVAL..............................22
INSTALLATION...........................22
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE
DESCRIPTION...........................22
OPERATION.............................23
REMOVAL..............................23
INSTALLATION...........................23
SLIDING DOOR CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION...........................23
OPERATION.............................24
REMOVAL..............................24
INSTALLATION...........................24
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION...........................24
OPERATION.............................24
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................27
PINION FACTOR PROCEDURE............27
QUICK LEARN PROCEDURE..............27
TCC BREAK-IN VIEW/RESET PROCEDURE. . . 28
REMOVAL..............................28
INSTALLATION...........................29
ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PCM/SKIM
PROGRAMMING
NOTE: Before replacing the PCM for a failed driver,
control circuit or ground circuit, be sure to check
the related component/circuit integrity for failures
not detected due to a double fault in the circuit.
Most PCM driver/control circuit failures are caused
by internal component failures (i.e. relay and sole-
noids) and shorted circuits (i.e. pull-ups, drivers
and switched circuits). These failures are difficult to
detect when a double fault has occurred and only
one DTC has set.When a PCM (SBEC) and the SKIM are replaced
at the same time perform the following steps in
order:
(1) Program the new PCM (SBEC)
(2) Program the new SKIM
(3) Replace all ignition keys and program them to
the new SKIM.
PROGRAMMING THE PCM (SBEC)
The SKIS Secret Key is an ID code that is unique
to each SKIM. This code is programmed and stored
in the SKIM, PCM and transponder chip (ignition
keys). When replacing the PCM it is necessary to
program the secret key into the new PCM using the
DRB III. Perform the following steps to program the
secret key into the PCM.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-1
Page 1831 of 4284
MEMORY HEATED SEAT/
MIRROR MODULE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Move seat to full forward position.
(3) Working under the seat, disconnect the module
wire harness connectors.
(4) Remove the module retaining screws.
(5) Remove the module from under the seat.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the module under the seat.
(2) Install the module retaining screws.
(3) Working under the seat, connect the module
wire harness connectors.
(4) Connect and isolate the negative battery cable.
POWER LIFTGATE MODULE
DESCRIPTION
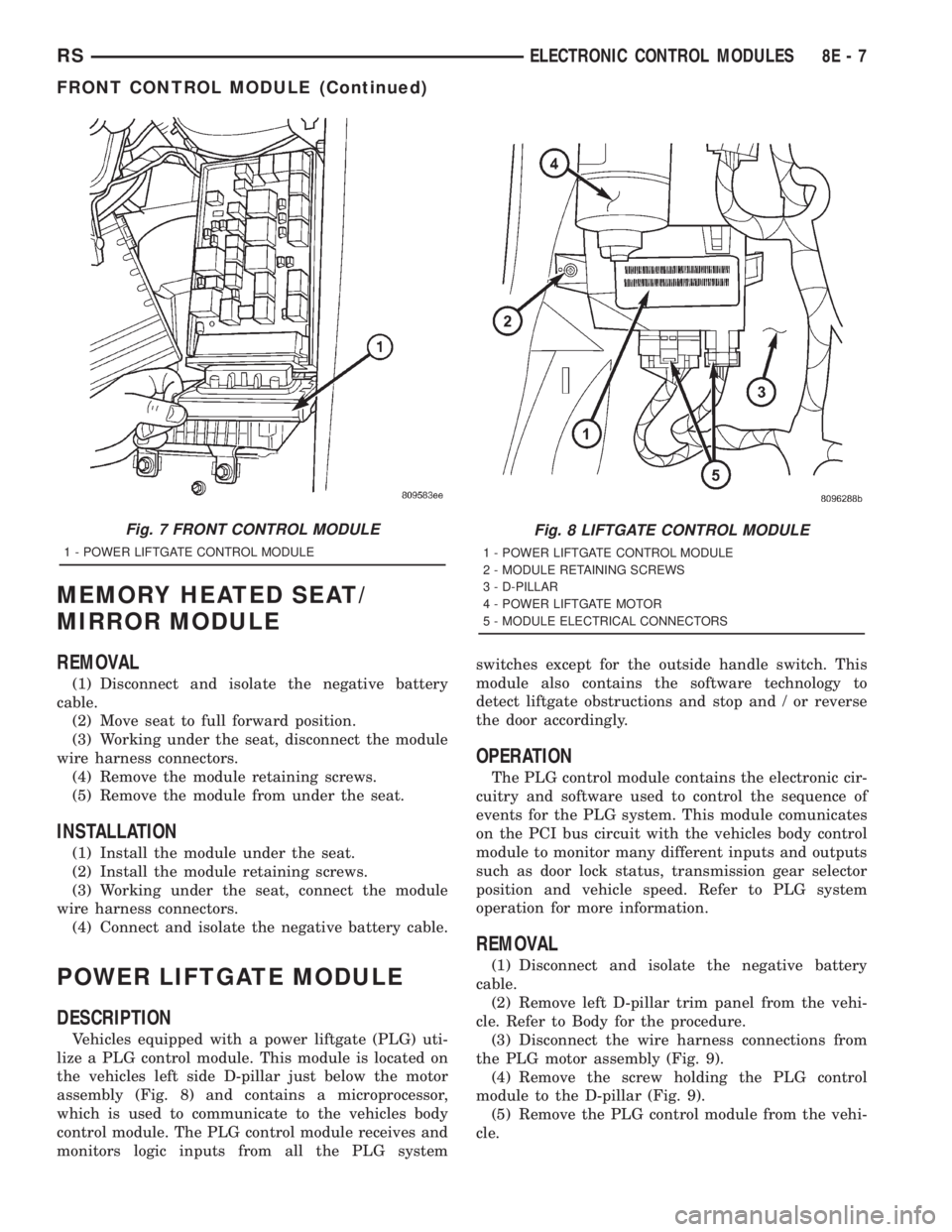
Vehicles equipped with a power liftgate (PLG) uti-
lize a PLG control module. This module is located on
the vehicles left side D-pillar just below the motor
assembly (Fig. 8) and contains a microprocessor,
which is used to communicate to the vehicles body
control module. The PLG control module receives and
monitors logic inputs from all the PLG systemswitches except for the outside handle switch. This
module also contains the software technology to
detect liftgate obstructions and stop and / or reverse
the door accordingly.
OPERATION
The PLG control module contains the electronic cir-
cuitry and software used to control the sequence of
events for the PLG system. This module comunicates
on the PCI bus circuit with the vehicles body control
module to monitor many different inputs and outputs
such as door lock status, transmission gear selector
position and vehicle speed. Refer to PLG system
operation for more information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove left D-pillar trim panel from the vehi-
cle. Refer to Body for the procedure.
(3) Disconnect the wire harness connections from
the PLG motor assembly (Fig. 9).
(4) Remove the screw holding the PLG control
module to the D-pillar (Fig. 9).
(5) Remove the PLG control module from the vehi-
cle.
Fig. 7 FRONT CONTROL MODULE
1 - POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
Fig. 8 LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
1 - POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
2 - MODULE RETAINING SCREWS
3 - D-PILLAR
4 - POWER LIFTGATE MOTOR
5 - MODULE ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-7
FRONT CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1897 of 4284

HEATED SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED GLASS........................... 1
HEATED MIRRORS......................... 5HEATED SEAT SYSTEM..................... 7
HEATED GLASS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED GLASS
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................2
DEFOGGER RELAY
DESCRIPTION............................2
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER GRID
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................2
GRID LINE REPAIR-REAR.................2REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER SWITCH
DESCRIPTION............................2
OPERATION.............................2
WINDSHIELD GRID
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................3
SYSTEM TEST..........................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................3
GRID LINE AND TERMINAL REPAIR.........3
HEATED GLASS
DESCRIPTION
The electrically heated Rear Window Defogger (Fig.
1), Heated Power Side View Mirrors, and HeatedWindshield Wiper De-icer (Fig. 2) is available on
select models.
Fig. 1 REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER (TYPICAL)
1 - REAR DEFOGGER GRID
2 - REAR WINDOW
Fig. 2 (TYPICAL) Heated Windshield Wiper De-icer
1 - DEFROSTER OUTLET
2 - VIN #
3 - HEATED WINDSHIELD GRID
RSHEATED SYSTEMS8G-1
Page 1898 of 4284

OPERATION
The Rear Window Defogger (Fig. 1) system consists
of two vertical bus bars linked by a series of grid
lines on the inside surface of the rear window. The
electrical circuit consists of the rear defogger switch
in the HVAC control assembly and a relay with timer
switch to turn OFF the system after ten minutes.
The main feed circuit is protected by fuse 13 (40
amp) in the Power Distribution Center (PDC) which
is integrated as a unit call Integrated Power Module
(IPM). The rear defogger switch and relay also acti-
vates the heated power side view mirrors and heated
windshield wiper de-icer. The heated windshield
wiper de-icer is powered by the RUN/ACC relay in
the IPM and feed thru fuse #11 (20 amp) in the PDC.
The heated mirror circuit is protected by a non-servi-
cable Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) located
inside the PDC. The heated windshield wiper de-icer
circuit is protected by fuse 11 (20 amp) in the PDC.
The Heated Windshield Wiper Deicer is also acti-
vated when the DEFROST mode is selected on the
HVAC. In the DEFROST mode the rear defogger
relay/timer is bypassed, the heated windshield wiper
de-icer will stay ON until the another mode is
selected. For circuit information and component loca-
tion refer to appropriate section for Wiring Diagrams.
CAUTION:
Since grid lines can be damaged or scraped off
with sharp instruments, care should be taken in
cleaning the glass or removing foreign materials,
decals or stickers. Normal glass cleaning solvents
or hot water used with rags or toweling is recom-
mended.
DEFOGGER RELAY
DESCRIPTION
There is no heated glass relay it is integrated into
the (E.B.L) relay that is located in the IPM in the
engine compartment.
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
GRID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - GRID LINE
REPAIR-REAR
For Grid repair procedure for the rear window
defogger (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HEATED
GLASS/WINDSHIELD GRID - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The rear window defogger switch is integrated into
the HVAC control panel assembly (Fig. 3)
OPERATION
A LED indicator will illuminate when the switch is
activated. The switch energizes the HVAC control
assembly when it requests the Front Control Module
(FCM) to activate the rear window defogger relay.
The relay controls the current to flow to the grids of
the rear window defogger, heated power side view
mirrors and the heated windshield wiper de-icer. The
defogger relay will be on for approximately 10 min-
utes or until the control switch or ignition is turned
off.
Fig. 3 HVAC CONTROL PANEL
1 - Trim Bezel
2 - ACT Sensor
3 - A/C Request Switch
4 - Rear Window Defogger/Heated Mirrors Switch Combo
5 - Front Window Defroster Mode Selector
8G - 2 HEATED GLASSRS
HEATED GLASS (Continued)
Page 1901 of 4284

HEATED MIRRORS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION............................5
OPERATION.............................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................5
HEATED MIRROR TEST...................5
MIRROR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION............................5OPERATION.............................5
HEATED MIRROR GRID
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................6
HEATED MIRROR.......................6
RELAY
DESCRIPTION............................6
HEATED MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION
Heated mirrors are available on models with
Power Mirrors and Rear Window Defogger only.
OPERATION
The heated mirror is controlled by the rear window
defogger switch. The heated mirror is ON when the
rear window defogger is ON (Fig. 1)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESING - HEATED MIRROR
TEST
Heated mirrors are available on models with
Power Mirrors and Rear Window Defogger only. The
heated mirror is controlled by the rear window defog-
ger switch. The heated mirror is ON when the rear
window defogger is ON.
(1) The mirror glass should be warm to the touch.
(2) If not, check the 20 amp fuse (11) in the Power
Distribution Center (PDC) part of the Integrated
Power Module (IPM) in the engine compartment.
(3) Test voltage at rear window defogger switch.
²If no voltage repair wire.
²Remove mirror glass and test the wires for con-
tinuity. If no continuity repair wires.
²If wires are OK, replace mirror glass.
²To test defogger switch refer to the appropriate
section in Electrical.
MIRROR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The heated mirror switch is integrated into the
rear window defogger switch located in the HVAC
control panel (Fig. 1)
OPERATION
A LED indicator will illuminate when the switch is
activated. The switch energizes the HVAC control
assembly when it requests the Front Control Module
(FCM) to activate the rear window defogger relay.
The relay controls the current to flow to the grids of
the rear window defogger, heated power side view
mirrors and the heated windshield wiper de-icer. The
defogger relay will be on for approximately 10 min-
utes or until the control switch or ignition is turned
off.
Fig. 1 HVAC CONTROL PANEL
1 - Trim Bezel
2 - ACT Sensor
3 - A/C Request Switch
4 - Rear Window Defogger/Heated Mirrors Switch Combo
5 - Front Window Defroster Mode Selector
RSHEATED MIRRORS8G-5