Page 452 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-83
2 Is there DTC other than Fuel system (DTC P0171/
P0172) and misfire (DTC P0300-P0304)?Go to applicable DTC
Diag. Flow Table.Go to Step 3.
3 Check Ignition System.
1) Remove spark plugs and check them for;
Air gap : 1.0 – 1.1 mm (0.040 – 0.043 in.) See Fig. 1.
Carbon deposits/Insulator damage/Plug type
If abnormality is found, adjust, clean or replace.
2) Disconnect all injector connectors.
3) Connect spark plugs to high tension cords and then
ground spark plugs.
4) Crank engine and check that each spark plug sparks.
Are above check results satisfactory?Go to Step 4. Check ignition sys-
tem parts (Refer to
Section 6F1)
4 Check Fuel Pressure (Refer to Section 6E1 for details).
1) Release fuel pressure from fuel feed line.
2) Install fuel pressure gauge. See Fig. 2.
3) Check fuel pressure.
With fuel pump operating and engine at stop : 270 –
310 kPa, 2.7 – 3.1 kg/cm
2, 38.4 – 44.0 psi.
At specified idle speed : 270 – 310 kPa, 2.7 – 3.1 kg/
cm
2, 38.4 – 44.0 psi.
Is measured value as specified?Go to Step 5. Go to Diag. Flow
Table B-3 fuel
pressure check.
5 Check Fuel Injectors and Circuit.
1) Using sound scope (1) or such, check operating
sound of each injector (2) when engine is running.
Cycle of operating sound should very according to
engine speed. See Fig 3.
If no sound or an unusual sound is heard, check
injector circuit (wire or connector) or injector.
2) Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect a fuel injec-
tor connector.
3) Check for proper connection to fuel injector at each
terminal. See Fig. 4.
4) If OK, then check injector resistance.
Injector Resistance : 11.3 – 13.8 ohm at 20°C (68°F)
5) Carry out steps 1) and 3) on each injector.
6) Check each injector for injected fuel volume referring
to Section 6E1. See Fig. 5.
Injected Fuel Volume : 43 – 47 cc/15 sec (1.45/1.51 –
1.58/1.65 US/Imp. oz/15 sec)
7) Check each injector for fuel leakage after injector
closed.
Fuel Leakage : Less than 1 drop/min.
Is check result in step 1) and 3) to 7) satisfactory?Go to Step 6. Check injector cir-
cuit or replace fuel
injector(s).
6 Check PCV Valve for clogging (See Section 6E1).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 7. Replace PCV
valve. Step Action Yes No
Page 468 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-99
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check Short Term Fuel Trim.
Did short term fuel trim vary within – 20% –
+20% range in step 3) of DTC confirmation
test?Go to Step 3. Check fuel system.
Go to DTC P0171/P0172
Diag. Flow Table.
3 Check HO2S-2 for Output Voltage.
Perform steps 1) through 9) of DTC confirma-
tion procedure for DTC P0136 (HO2S-2 mal-
function) and check output voltage of HO2S-2
then.
Is over 0.6 V and below 0.3 V indicated?Replace three way cata-
lytic converter.Check “BRN” and “YEL”
wires for open and short,
and connections for poor
connection.
If wires and connections
are OK, replace HO2S-2.
Page 506 of 698
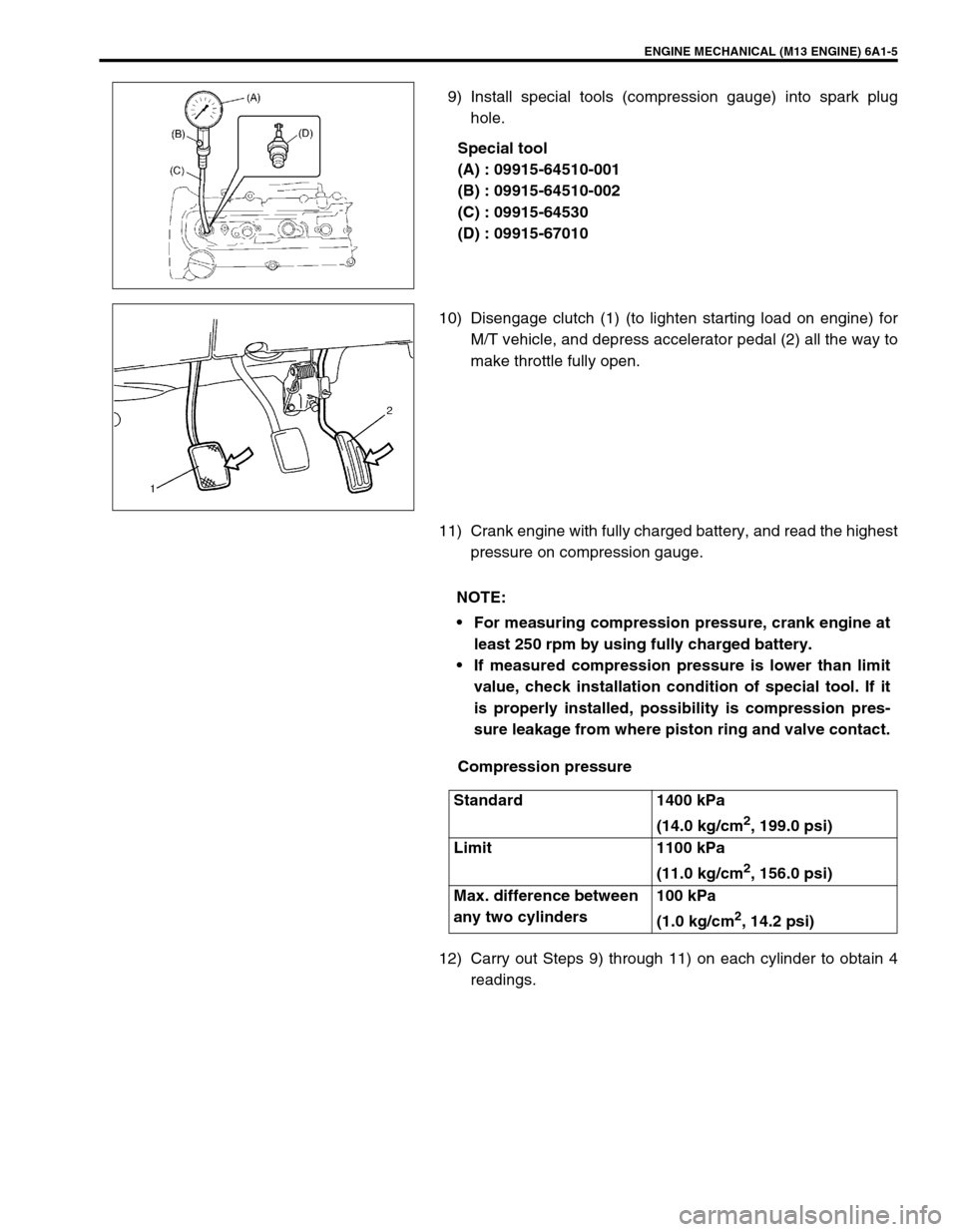
ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE) 6A1-5
9) Install special tools (compression gauge) into spark plug
hole.
Special tool
(A) : 09915-64510-001
(B) : 09915-64510-002
(C) : 09915-64530
(D) : 09915-67010
10) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for
M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator pedal (2) all the way to
make throttle fully open.
11) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest
pressure on compression gauge.
Compression pressure
12) Carry out Steps 9) through 11) on each cylinder to obtain 4
readings.
NOTE:
For measuring compression pressure, crank engine at
least 250 rpm by using fully charged battery.
If measured compression pressure is lower than limit
value, check installation condition of special tool. If it
is properly installed, possibility is compression pres-
sure leakage from where piston ring and valve contact.
Standard 1400 kPa
(14.0 kg/cm
2, 199.0 psi)
Limit 1100 kPa
(11.0 kg/cm
2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between
any two cylinders100 kPa
(1.0 kg/cm
2, 14.2 psi)
Page 548 of 698
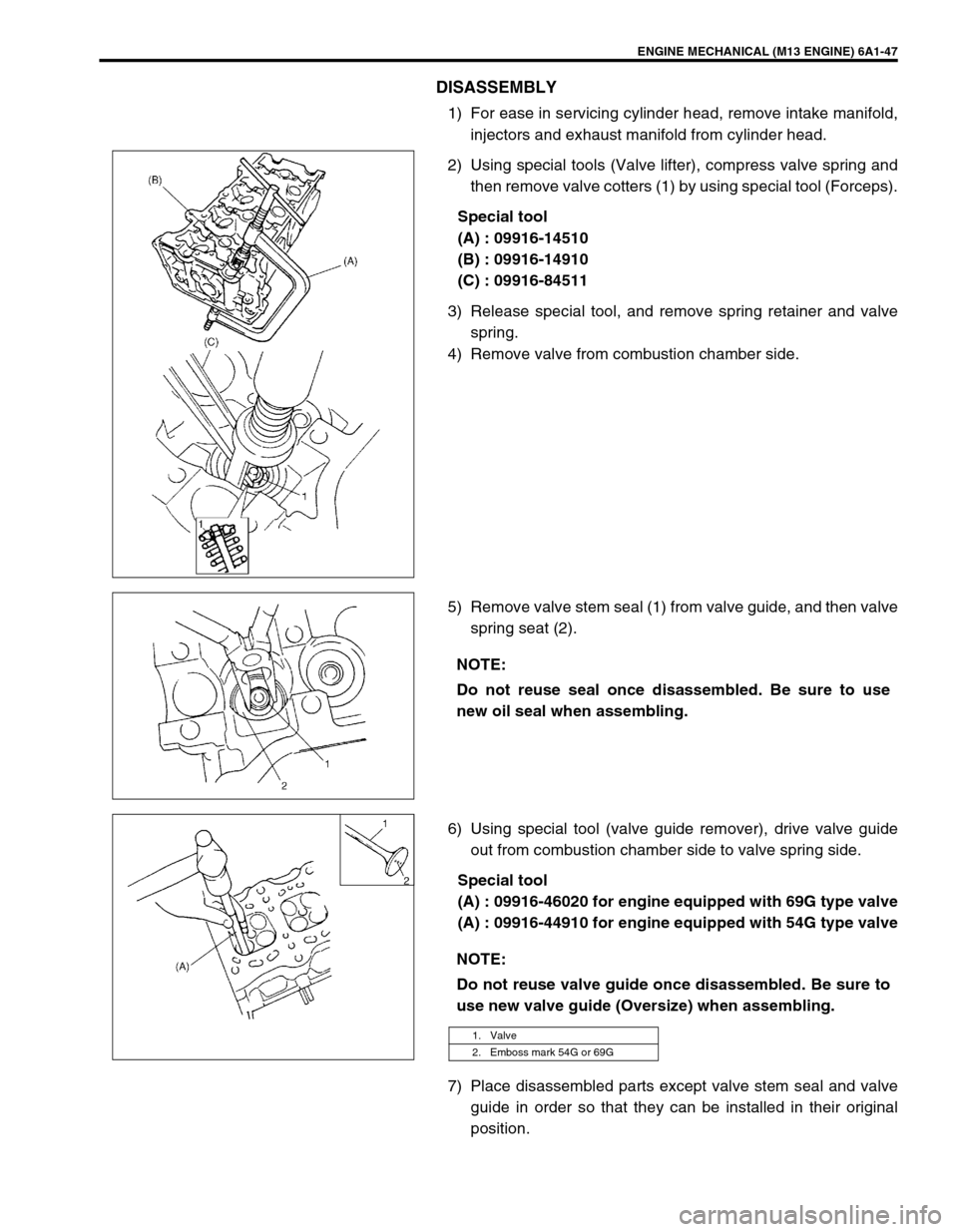
ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE) 6A1-47
DISASSEMBLY
1) For ease in servicing cylinder head, remove intake manifold,
injectors and exhaust manifold from cylinder head.
2) Using special tools (Valve lifter), compress valve spring and
then remove valve cotters (1) by using special tool (Forceps).
Special tool
(A) : 09916-14510
(B) : 09916-14910
(C) : 09916-84511
3) Release special tool, and remove spring retainer and valve
spring.
4) Remove valve from combustion chamber side.
5) Remove valve stem seal (1) from valve guide, and then valve
spring seat (2).
6) Using special tool (valve guide remover), drive valve guide
out from combustion chamber side to valve spring side.
Special tool
(A) : 09916-46020 for engine equipped with 69G type valve
(A) : 09916-44910 for engine equipped with 54G type valve
7) Place disassembled parts except valve stem seal and valve
guide in order so that they can be installed in their original
position.
NOTE:
Do not reuse seal once disassembled. Be sure to use
new oil seal when assembling.
NOTE:
Do not reuse valve guide once disassembled. Be sure to
use new valve guide (Oversize) when assembling.
1. Valve
2. Emboss mark 54G or 69G
Page 551 of 698
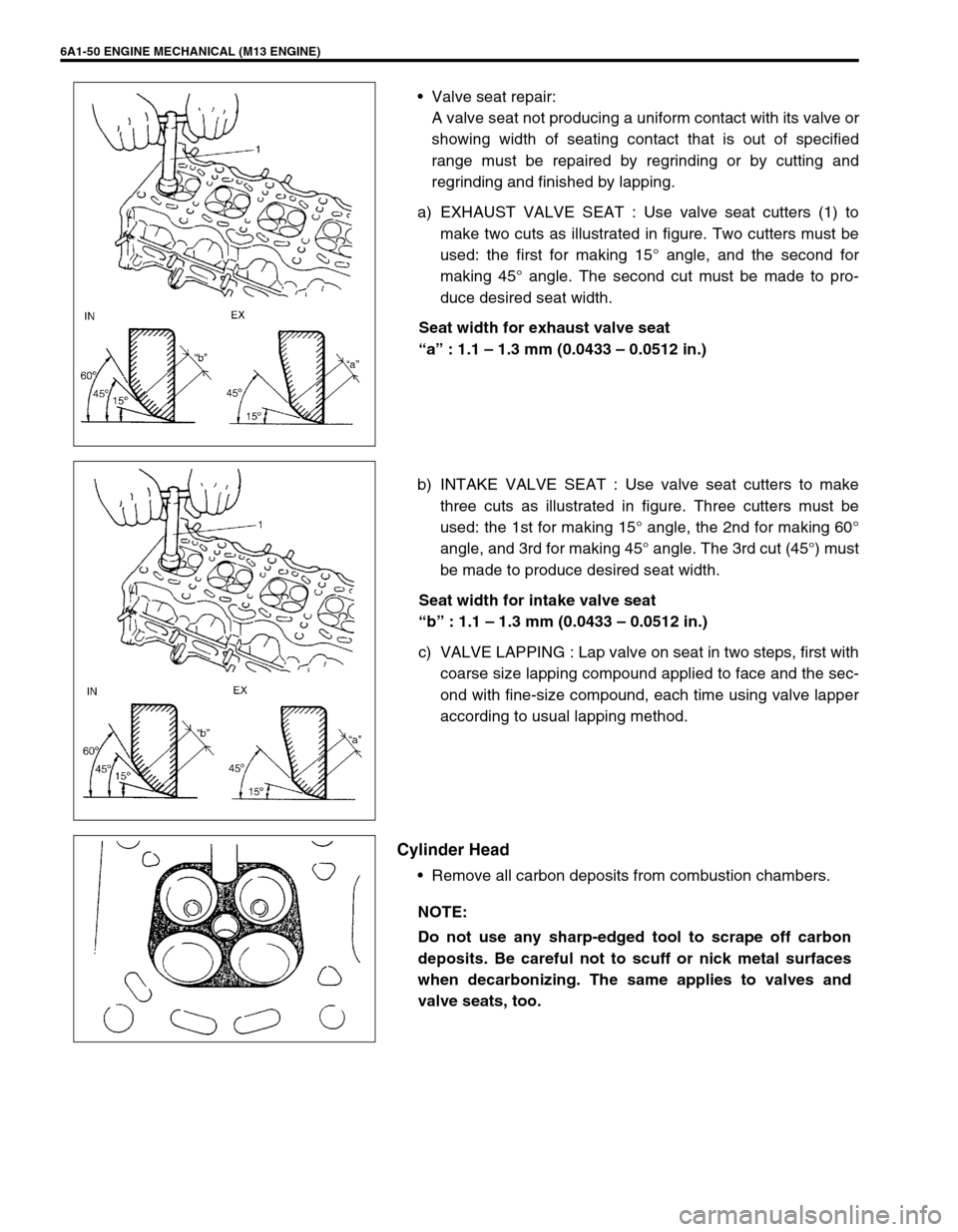
6A1-50 ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE)
Valve seat repair:
A valve seat not producing a uniform contact with its valve or
showing width of seating contact that is out of specified
range must be repaired by regrinding or by cutting and
regrinding and finished by lapping.
a) EXHAUST VALVE SEAT : Use valve seat cutters (1) to
make two cuts as illustrated in figure. Two cutters must be
used: the first for making 15° angle, and the second for
making 45° angle. The second cut must be made to pro-
duce desired seat width.
Seat width for exhaust valve seat
“a” : 1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0433 – 0.0512 in.)
b) INTAKE VALVE SEAT : Use valve seat cutters to make
three cuts as illustrated in figure. Three cutters must be
used: the 1st for making 15° angle, the 2nd for making 60°
angle, and 3rd for making 45° angle. The 3rd cut (45°) must
be made to produce desired seat width.
Seat width for intake valve seat
“b” : 1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0433 – 0.0512 in.)
c) VALVE LAPPING : Lap valve on seat in two steps, first with
coarse size lapping compound applied to face and the sec-
ond with fine-size compound, each time using valve lapper
according to usual lapping method.
Cylinder Head
Remove all carbon deposits from combustion chambers.
NOTE:
Do not use any sharp-edged tool to scrape off carbon
deposits. Be careful not to scuff or nick metal surfaces
when decarbonizing. The same applies to valves and
valve seats, too.
Page 589 of 698
6A1-88 ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE)
09916-37810 09916-38210 09916-44910 09916-46020
Reamer (6 mm) Reamer (11 mm) Valve guide remover Valve guide remover
09916-56011 09916-57350 09916-58210 09916-67020
Valve guide installer
attachmentValve guide installer han-
dleValve guide installer han-
dleTappet holder
09916-77310 09916-84511 09917-98221 09917-88240
Piston ring compressor Forceps Camshaft lock holder Valve guide installer
09917-88250 09917-98221 09924-17810
Valve guide installer Valve stem seal installer Flywheel holder
Page 597 of 698

6B-8 ENGINE COOLING
3) Stop engine and drain coolant.
4) Close drain plug. Add water until system is filled and run
engine until upper radiator hose is hot again.
5) Repeat Steps 3) and 4) several times until drained liquid is
nearly colorless.
6) Drain system and then close radiator drain plug (1) tightly.
7) Remove reservoir tank (1) and remove cap (2) from reservoir
tank (1) and pour out any fluid, scrub and clean inside of
tank with soap and water.
Flush it well with clean water and drain. Reinstall tank.
8) Add coolant that is a mixture of good quality ethylene glycol
antifreeze and water to radiator and reservoir tank. For cool-
ant concentration referring to “COOLANT”.
Fill radiator to the bottom of filler neck and reservoir tank to
FULL level mark (3).
9) Reinstall reservoir tank cap and align match marks (4) on
reservoir tank and its tank cap.
10) Run engine with radiator cap removed, until radiator inlet
hose is hot.
11) With engine idling, add coolant to radiator until level reaches
the bottom of filler neck. Install radiator cap, making sure
that the ear of cap lines is parallel to radiator.
1
LOW FULL
4 1
1 3
2
2 1
Page 627 of 698

6E1-6 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
The fuel system consists of fuel tank (1), fuel pump (2) (with built-in fuel filter (3) and fuel pressure regulator (4)),
delivery pipe (5), injectors (6) and fuel feed line (7).
The fuel (8) in the fuel tank (1) is pumped up by the fuel pump (2), sent into delivery pipe (5) and injected by the
injectors (6).
As the fuel pump assembly is equipped with built-in fuel filter (3) and fuel pressure regulator (4), the fuel (8) is fil-
tered and its pressure is regulated before being sent to the delivery pipe (5).
The excess fuel from fuel pressure regulation process is returned back (9) into the fuel tank.
Also, fuel vapor generated in fuel tank is led through the fuel vapor line (10) into the EVAP canister (12).
FUEL PUMP
An in-tank type electric pump has been adopted for the fuel pump
(1). Incorporated in the pump assembly are;
Tank pressure control valve (2) which keeps the pressure in
the fuel tank constant, and prevents the fuel from spouting
and tank itself from being deformed.
Relief valve (3) which prevents the pressure in tank from ris-
ing excessively.
Fuel cut valve (4) which closes as the float rises so that the
fuel will not enter the canister when the fuel level in the tank
rises high depending on the fuel level in the tank and the
vehicle tilt angle.
Also, a fuel filter (5) and a fuel pressure regulator (6) are included
and a fuel level gauge (7) is attached.
Addition of the fuel pressure regulator (6) to the fuel pump makes
it possible to maintain the fuel pressure at constant level and
ECM controls compensation for variation in the intake manifold
pressure.
11. Intake manifold