2000 SUZUKI SWIFT ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 322 of 698
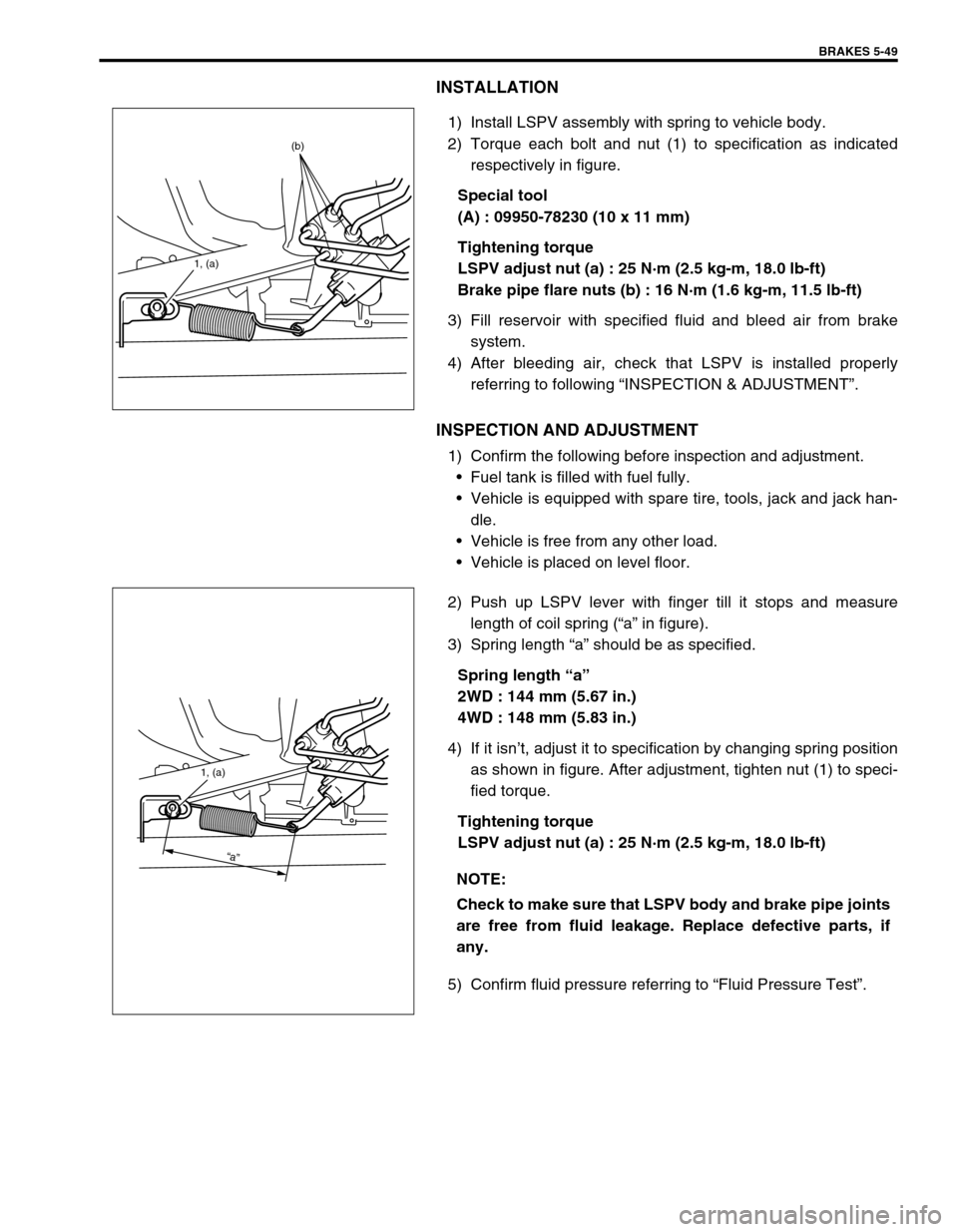
BRAKES 5-49
INSTALLATION
1) Install LSPV assembly with spring to vehicle body.
2) Torque each bolt and nut (1) to specification as indicated
respectively in figure.
Special tool
(A) : 09950-78230 (10 x 11 mm)
Tightening torque
LSPV adjust nut (a) : 25 N·m (2.5 kg-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
Brake pipe flare nuts (b) : 16 N·m (1.6 kg-m, 11.5 lb-ft)
3) Fill reservoir with specified fluid and bleed air from brake
system.
4) After bleeding air, check that LSPV is installed properly
referring to following “INSPECTION & ADJUSTMENT”.
INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT
1) Confirm the following before inspection and adjustment.
Fuel tank is filled with fuel fully.
Vehicle is equipped with spare tire, tools, jack and jack han-
dle.
Vehicle is free from any other load.
Vehicle is placed on level floor.
2) Push up LSPV lever with finger till it stops and measure
length of coil spring (“a” in figure).
3) Spring length “a” should be as specified.
Spring length “a”
2WD : 144 mm (5.67 in.)
4WD : 148 mm (5.83 in.)
4) If it isn’t, adjust it to specification by changing spring position
as shown in figure. After adjustment, tighten nut (1) to speci-
fied torque.
Tightening torque
LSPV adjust nut (a) : 25 N·m (2.5 kg-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
5) Confirm fluid pressure referring to “Fluid Pressure Test”.
1, (a)
(b)
NOTE:
Check to make sure that LSPV body and brake pipe joints
are free from fluid leakage. Replace defective parts, if
any.
1, (a)
“a”
Page 350 of 698

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E-25
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1 1) Disconnect applicable ABS wheel speed sensor coupler
with ignition switch OFF.
2) Measure resistance between terminals of ABS wheel
speed sensor. Refer to “FRONT WHEEL SPEED SEN-
SOR” and/or “REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR” in this
section.
Is measured resistance value as specified?Go to Step 2. Replace ABS wheel
speed sensor
assembly.
2 1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit/control module connec-
tor.
3) Check for proper connection to ABS control module at
each sensor terminal.
4) If OK, then turn ignition switch ON and measure voltage
between sensor terminal of module connector and body
ground.
Is it 0V?Go to Step 3. ABS wheel speed
sensor circuit
shorted to power.
3 1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Connect ABS wheel speed sensor coupler.
3) Measure resistance between the following points.
Both ABS hydraulic unit/control module connector termi-
nals of the corresponding sensor.
This check result should be the same as above Step 1.
Either terminal of wheel speed sensor coupler and body
ground.
This check result should be no continuity.
Are both check results OK?Go to Step 4. Circuit open or
shorted to ground.
4 1) Remove applicable ABS wheel speed sensor.
2) Check sensor for damage or foreign material attached.
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 5. Clean, repair or
replace.
5 Check front and/or rear sensor ring for the following
(remove rear drum as necessary) :
Rotor serration (teeth) neither missing nor damaged.
No foreign material being attached.
Rotor not being eccentric.
Wheel bearing free from excessive play.
Are they in good condition?Go to Step 6. Clean, repair or
replace.
6 1) Install ABS wheel speed sensor to knuckle.
2) Tighten sensor bolt to specified torque and check that
there is no clearance between sensor and knuckle.
Is it OK?Go to Step 7. Replace ABS wheel
speed sensor.
7 Referring to “Reference” of “FRONT WHEEL SPEED SEN-
SOR” and/or “Reference” of “REAR WHEEL SPEED SEN-
SOR” in this section, check output voltage or waveform.
Is specified voltage and/or waveform obtained?Substitute a known-
good ABS hydrau-
lic unit/control mod-
ule assembly and
recheck.Replace sensor and
recheck.
Page 371 of 698

6-2 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS ......................................... 6-6
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ............................. 6-6
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
(VEHICLE WITH IMMOBILIZER INDICATOR
LAMP) ............................................................. 6-7
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
(VEHICLE WITHOUT IMMOBILIZER
INDICATOR LAMP) ...................................... 6-10
PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING
TROUBLE ..................................................... 6-11
ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE ......... 6-12
CUSTOMER PROBLEM INSPECTION
FORM (EXAMPLE) ................................... 6-14
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL)
CHECK...................................................... 6-15
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC)
CHECK...................................................... 6-15
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC)
CLEARANCE ............................................ 6-16
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC)
TABLE ....................................................... 6-17
FAIL-SAFE TABLE.................................... 6-20
VISUAL INSPECTION .............................. 6-22
ENGINE BASIC INSPECTION.................. 6-23
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS TABLE ................... 6-26
SCAN TOOL DATA....................................... 6-31
INSPECTION OF ECM AND ITS
CIRCUITS ..................................................... 6-36
ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE............. 6-37
TERMINAL RESISTANCE TABLE............ 6-43
COMPONENT LOCATION ........................... 6-45
TABLE A-1 MALFUNCTION INDICATOR
LAMP CIRCUIT CHECK - LAMP DOES NOT
COME “ON” AT IGNITION SWITCH ON
(BUT ENGINE AT STOP) ............................. 6-46
TABLE A-2 MALFUNCTION INDICATOR
LAMP CIRCUIT CHECK - LAMP REMAINS
“ON” AFTER ENGINE STARTS ................... 6-47
TABLE A-3 MIL CHECK - MIL FLASHES
AT IGNITION SWITCH ON (VEHICLE
WITHOUT IMMOBILIZER INDICATOR
LAMP) ........................................................... 6-48
TABLE A-4 MIL CHECK - MIL DOES NOT
FLASH OR JUST REMAINS ON EVEN
WITH GROUNDING DIAGNOSIS SWITCH
TERMINAL (VEHICLE WITHOUT
IMMOBILIZER INDICATOR LAMP) .............. 6-48
TABLE A-5 ECM POWER AND GROUND
CIRCUIT CHECK - MIL DOESN’T LIGHT
AT IGNITION SWITCH ON AND ENGINE
DOESN’T START THOUGH IT IS
CRANKED UP .............................................. 6-49
DTC P0105 (DTC NO.11) MANIFOLD
ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION ............................................ 6-52
DTC P0110 (DTC NO.18) INTAKE AIR
TEMP. (IAT) CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION ....... 6-55
DTC P0115 (DTC NO.19) ENGINE
COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION ............................................ 6-57DTC P0120 (DTC NO.13) THROTTLE
POSITION CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION ........... 6-60
DTC P0121 THROTTLE POSITION CIRCUIT
RANGE/PERFORMANCE PROBLEM .......... 6-63
DTC P0130 (DTC NO.14) HEATED OXYGEN
SENSOR (HO2S) CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
(SENSOR-1) .................................................. 6-66
DTC P0133 HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(HO2S) CIRCUIT SLOW RESPONSE
(SENSOR-1) .................................................. 6-68
DTC P0134 HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(HO2S) CIRCUIT NO ACTIVITY DETECTED
(SENSOR-1) .................................................. 6-69
DTC P0135 (DTC NO.14) HEATED OXYGEN
SENSOR (HO2S) HEATER CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION (SENSOR-1) ....................... 6-70
DTC P0136 HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(HO2S) CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
(SENSOR-2) .................................................. 6-72
DTC P0141 HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(HO2S) HEATER CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
(SENSOR-2) .................................................. 6-74
DTC P0171 FUEL SYSTEM TOO LEAN ....... 6-76
DTC P0172 FUEL SYSTEM TOO RICH ....... 6-76
DTC P0300 RANDOM MISFIRE DETECTED
(MISFIRE DETECTED AT 2 OR MORE
CYLINDERS) ................................................. 6-81
DTC P0301 CYLINDER 1 MISFIRE
DETECTED ................................................... 6-81
DTC P0302 CYLINDER 2 MISFIRE
DETECTED ................................................... 6-81
DTC P0303 CYLINDER 3 MISFIRE
DETECTED ................................................... 6-81
DTC P0304 CYLINDER 4 MISFIRE
DETECTED ................................................... 6-81
DTC P0325 (DTC NO.17) KNOCK SENSOR
CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION ............................. 6-86
DTC P0335 (DTC NO.23) CRANKSHAFT
POSITION (CKP) SENSOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION ............................................. 6-88
DTC P0340 (DTC NO.15) CAMSHAFT
POSITION (CMP) SENSOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION ............................................. 6-91
DTC P0400 EXHAUST GAS
RECIRCULATION FLOW MALFUNCTION ... 6-94
DTC P0420 CATALYST SYSTEM
EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD ............ 6-97
DTC P0443 PURGE CONTROL VALVE
CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION ........................... 6-100
DTC P0480 RADIATOR COOLING FAN
CONTROL SYSTEM MALFUNCTION ........ 6-101
DTC P0500 (DTC NO.16) VEHICLE SPEED
SENSOR (VSS) MALFUNCTION ................ 6-103
DTC P0505 (DTC NO.26) IDLE CONTROL
SYSTEM MALFUNCTION ........................... 6-105
DTC P1450 BAROMETRIC PRESSURE
SENSOR LOW/HIGH INPUT....................... 6-108
DTC P1451 BAROMETRIC PRESSURE
SENSOR PERFORMANCE PROBLEM ...... 6-108
Page 380 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-11
DATA LINK CONNECTOR (DLC)
ELC (1) is in compliance with SAEJ1962 in its installation posi-
tion, the shape of connector and pin assignment.
Serial data line (K line of ISO 9141) is used for SUZUKI scan tool
(Tech-1) to communicate with ECM, TCM, ABS control module
and Air bag SDM.
SUZUKI serial data line is used for SUZUKI scan tool (Tech -1) to
communicate with immobilizer control module.
PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLE
Do not disconnect couplers from ECM, battery cable from battery, ECM ground wire harness from engine or
main fuse before confirming diagnostic information (DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in ECM memory.
Such disconnection will erase memorized information in ECM memory.
Diagnostic information stored in ECM memory can be cleared as well as checked by using SUZUKI scan
tool (Tech-1) or generic scan tool (Vehicle with immobilizer indicator lamp). Before using scan tool, read its
Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to have good understanding as to what functions are available and
how to use it.
Priorities for diagnosing troubles (Vehicle with immobilizer indicator lamp).
If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the flow table of the DTC which has detected earliest in the order
(it can be identified by referring to freeze frame data) and follow the instruction in that table.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot diagnostic trouble codes according to the following priorities.
–Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) other than DTC P0171/P0172 (Fuel system too lean/too rich), DTC
P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304 (Misfire detected) and DTC P0400 (EGR flow malfunction)
–DTC P0171/P0172 (Fuel system too lean/too rich) and DTC P0400 (EGR flow malfunction)
–DTC P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304 (Misfire detected)
Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service” in Section 0A before inspection and observe what
is written there.
ECM Replacement
When substituting a known-good ECM, check for following conditions. Neglecting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
–Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as specified respectively.
–MAP sensor and TP sensor are in good condition and none of power circuits of these sensors is shorted
to ground.AMBIENT
TEMPERATURETIME TO CUT POWER TO ECM
Over 0°C (32°F) 60 sec. or longer
Under 0°C (32°F) Not specifiable. Select a place with
temperature higher than 0°C (32°F).
2. B+
3. Serial data line (K line of ISO 9141)
4. ECM ground
5. Body ground
6. SUZUKI serial data line
2
3456
1
Page 386 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-17
Without Using Scan Tool
1) Turn the ignition switch OFF position.
2) Disconnect battery negative cable for specified time below to
erase diagnostic trouble code stored in ECM memory and
reconnect it.
Time required to erase DTC :
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) TABLE
Ambient
temperatureTime to cut power to ECM
Over 0°C (32°F) 30 sec. or longer
Under 0°C
(32°F)Not specifiable.
Select a place with higher than 0°C
(32°F) temperature.
DTC
NO.DETECTING ITEM DETECTING CONDITION
(DTC will set when detecting :)MIL
(vehicle
with immo-
bilizer indi-
cator lamp)MIL
(vehicle
without
immobi-
lizer indica-
tor lamp)
P0105
(No.11)Manifold absolute pressure
circuit malfunctionLow pressure-high vacuum-low voltage
(or MAP sensor circuit shorted to ground)
High pressure-low vacuum-high voltage
(or MAP sensor circuit open)1 driving
cycle1 driving
cycle
P0110
(No.18)Intake air temp. circuit mal-
functionIntake air temp. circuit low input
Intake air temp. circuit high input1 driving
cycle1 driving
cycle
P0115
(No.19)Engine coolant temp. cir-
cuit malfunctionEngine coolant temp. circuit low input
Engine coolant temp. circuit high input1 driving
cycle1 driving
cycle
P0120
(No.13)Throttle position circuit mal-
functionThrottle position circuit low input
Throttle position circuit high input1 driving
cycle1 driving
cycle
P0121 Throttle position circuit per-
formance problemPoor performance of TP sensor 2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0130
(No.14)HO2S circuit malfunction
(Sensor-1)Min. output voltage of HO2S-higher than
specification
Max. output voltage of HO2S-lower than
specification2 driving
cycle1 driving
cycle
P0133 HO2S circuit slow response
(Sensor-1)Response time of HO2S-1 output voltage
between rich and lean is longer than spec-
ification.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0134 HO2S circuit no activity
detected (Sensor-1)Output voltage of HO2S-1 fails to go above
specification (or HO2S-1 circuit shorted to
ground).2 driving
cycles1 driving
cycle
P0135
(No.14)HO2S heater circuit mal-
function (Sensor-1)Terminal voltage is lower than specifica-
tion at heater OFF or it is higher at heater
ON.2 driving
cycles1 driving
cycle
P0136 HO2S circuit malfunction
(Sensor-2)Max. voltage of HO2S-2 is lower than
specification or its min. voltage is higher
than specification2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
Page 397 of 698
6-28 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Poor gasoline mile-
age Leaks or loose connection of high-tension
cordHigh-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Faulty spark plug (improper gap, heavy
deposits and burned electrodes, etc.)Spark plugs in Section 6F1.
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E1.
High idle speed Refer to item “Improper engine idle
speed” previously outlined.
Poor performance of TP sensor, ECT sensor
or MAP sensorTP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP sensor
in Section 6E1.
Faulty EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E1.
Faulty fuel injector(s) Diagnostic Flow Table B-1.
Faulty ECM
Poor valve seating Valves inspection in Section 6A1.
Dragging brakes Trouble diagnosis in Section 5.
Slipping clutch Trouble diagnosis in Section 7C.
Thermostat out of order Thermostat in Section 6B.
Improper tire pressure Refer to Section 3F.
Low Compression Previously outlined
Excessive engine
oil consumption Blown cylinder head gasket Cylinder head in Section 6A1.
Leaky camshaft oil seals Camshaft in Section 6A1.
Sticky piston ring Piston cleaning in Section 6A1.
Worn piston and cylinder Pistons and cylinders inspection in Sec-
tion 6A1.
Worn piston ring groove and ring Pistons inspection in Section 6A1.
Improper location of piston ring gap Pistons assembly in Section 6A1.
Worn or damaged valve stem seal Valves removal and installation in Sec-
tion 6A1.
Worn valve stem Valves inspection in Section 6A1.
Engine hesitates
(Momentary lack of
response as accel-
erator is depressed.
Can occur at all
vehicle speeds.
Usually most severe
when first trying to
make vehicle move,
as from a stop sign.)Spark plug faulty or plug gap out of adjust-
mentSpark plugs in Section 6F1.
Leaky high-tension cord High-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3.
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in section 6E1.
Poor performance of TP sensor, ECT sensor
or MAP sensorTP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP sensor
in Section 6E1.
Faulty fuel injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1.
Faulty ECM
Engine overheating Refer to “Overheating” section.
Low compression Previously outlined.
Surge
(Engine power vari-
ation under steady
throttle or cruise.
Feels like vehicle
speeds up and
down with no
change in accelera-
tor pedal.)Leaky or loosely connected high-tension cord High-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Faulty spark plug (excess carbon deposits,
improper gap, and burned electrodes, etc.)Spark plugs in Section 6F1.
Variable fuel pressure Diagnostic Flow Table B-3.
Kinky or damaged fuel hose and lines
Faulty fuel pump (clogged fuel filter)
Malfunctioning EGR valve EGR system in Section 6E1.
Poor performance of MAP sensor MAP sensor in Section 6E1.
Faulty fuel injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1.
Faulty ECM Condition Possible Cause Correction
Page 437 of 698

6-68 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P0133 HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S) CIRCUIT SLOW RESPONSE
(SENSOR-1)
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0130 section.
Fig. 1
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
Refer to DTC P0130 section.
INSPECTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
When running at specified idle speed after engine warmed up and
running at specified vehicle speed, response time (time to change
from lean to rich or from rich to lean) of HO2S-1 output voltage is
about 1 sec. at minimum or average time of 1 cycle is 5 sec. at
minimum. See. Fig. 1
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, Monitoring once/1 driving.Heated oxygen sensor-1 malfunction
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Is there DTC(s) other than HO2S-1 (DTC
P0133)?Go to applicable DTC
Diag. Flow Table.Replace HO2S-1.
Page 458 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-89
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check CKP Sensor and Connector for proper
installation.
Is CKP sensor installed properly and connector
connected securely?Go to Step 3. Correct.
3 Check Wire Harness and Connection.
1) Disconnect connector from CKP sensor.
2) Check for proper connection to CKP sensor at
each terminal.
3) If OK, turn ignition switch ON and check for
voltage at each terminal of sensor connector
disconnected. See Fig. 1.
Terminal “B+” : 10 – 14 V
Terminal “Vout” : 4 – 5 V
Terminal “GND” : – 0 V
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 5. Go to Step 4.
4 Was terminal “Vout” voltage out of specification in
Step 3 check?“YEL/BLK” wire open,
short or poor connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.“BLK/RED” or “BLK/
ORN” wire open, short
or poor connection.
5 Check Ground Circuit for open.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Check for continuity between “GND” terminal
of CKP sensor connector and engine ground.
Is continuity indicated?Go to Step 6.“BLK/ORN” wire open
or poor ground con-
nection.
6 Check CKP Sensor for operation.
1) Remove CKP sensor from sensor case.
2) Remove metal particles on end face of CKP
sensor, if any.
3) Connect each connector to ECM and CKP
sensor.
4) Turn ignition switch ON.
5) Check for voltage at terminal C42-23 of con-
nector connected to ECM by passing magnetic
substance (iron) while keeping approximately
1 mm (0.03 in.) gap with respect to end face of
CKP sensor. See Fig. 2 and 3.
Does voltage vary from low (0 –1 V) to high (4 – 5
V) or from high to low?Go to Step 7. Replace CKP sensor.
7 Check Signal Rotor for the following. See Fig. 4.
Damage
No foreign material attached
Is it in good condition?Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.Clean rotor teeth or
replace CMP sensor.