Page 153 of 698
3B1-12 ELECTRICAL POWER STEERING (P/S) SYSTEM
DTC (displayed
on SUZUKI scan
tool)“EPS” light flashing pattern
DTC (indicated
by “EPS” light
flashing pattern)Model DIAGNOSTIC ITEM DIAGNOSIS
NO DTC 12 NormalThis code appears
when none of the other
codes are identified.
C1111 11
Torque sensor
Diagnose trouble
according to “DIAG-
NOSTIC FLOW
TABLE” corresponding
to each code No. C1113 13
C1114 14
C1115 15
C1116 16
C1121 21
VSS signal C1123 23
C1124 24
C1122 22Engine speed sig-
nal
C1141 41
Motor C1142 42
C1143 43
C1144 44
C1145 45
C1151 51 Clutch
C1152 52
P/S control module C1154 54
C1155 55
C1153 53P/S control module
power supply
Page 179 of 698
3C-6 STEERING WHEEL AND COLUMN
STEERING WHEEL
REMOVAL
1) Remove driver air bag (inflator) module from steering wheel.
Refer to “DRIVER AIR BAG (INFLATOR) MODULE”.
2) Remove steering shaft nut.
3) Make alignment marks (1) on steering wheel and shaft for a
guide during reinstallation.
4) Remove steering wheel (1) with special tool.
Special tool
(A) : 09944-36011 CAUTION:
Removal of the steering wheel allows the contact coil to
turn freely but do not turn the contact coil (on the combi-
nation switch) more than allowable number of turns
(about two and a half turns from the center position
clockwise or counterclockwise respectively), or coil will
break.
CAUTION:
Do not hammer the end of the shaft. Hammering it will
loosen the plastic shear pins which maintain the column
length and impair the collapsible design of the column.
Page 181 of 698
3C-8 STEERING WHEEL AND COLUMN
4) From the position where contact coil became unable to turn
any further (it stopped), turn it back clockwise about two and
a half rotations and align center mark (1) with alignment
mark.
CONTACT COIL AND COMBINATION SWITCH
ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
1) Remove steering wheel from steering column referring to
“STEERING WHEEL” in this section.
2) Remove steering column hole cover (1).
3) Remove steering column cover screws (1).
4) Separate upper cover (2) and lower cover (3), then remove
them.
CAUTION:
Do not turn contact coil (on combination switch) more
than allowable number of turns (about two and a half
turns from the center position clockwise or counter-
clockwise respectively), or coil will break.
1
Page 251 of 698
3F-6 WHEELS AND TIRES
INFLATION OF TIRES
The pressure recommended for any model is carefully calculated to give a satisfactory ride, stability, steering,
tread wear, tire life and resistance to bruises.
Tire pressure, with tires cold, (after vehicle has set for 3 hours or more, or driven less than one mile) should be
checked monthly or before any extended trip. Set to the specifications on the “Tire Placard” located on the left
door (right door for right-hand side steering vehicle) lock pillar.
It is normal for tire pressure to increase when the tires become hot during driving.
Do not bleed or reduce tire pressure after driving. Bleeding reduces the “Cold Inflation Pressure”.
Higher than recommended pressure can cause :
Hard ride
Tire bruising or carcass damage
Rapid tread wear at center of tire
Unequal pressure on same axle can cause :
Uneven braking
Steering lead
Reduced handling
Swerve on acceleration
Lower than recommended pressure can cause :
Tire squeal on turns
Hard Steering
Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread
Tire rim bruises and rupture
Tire cord breakage
High tire temperature
Reduced handling
High fuel consumption
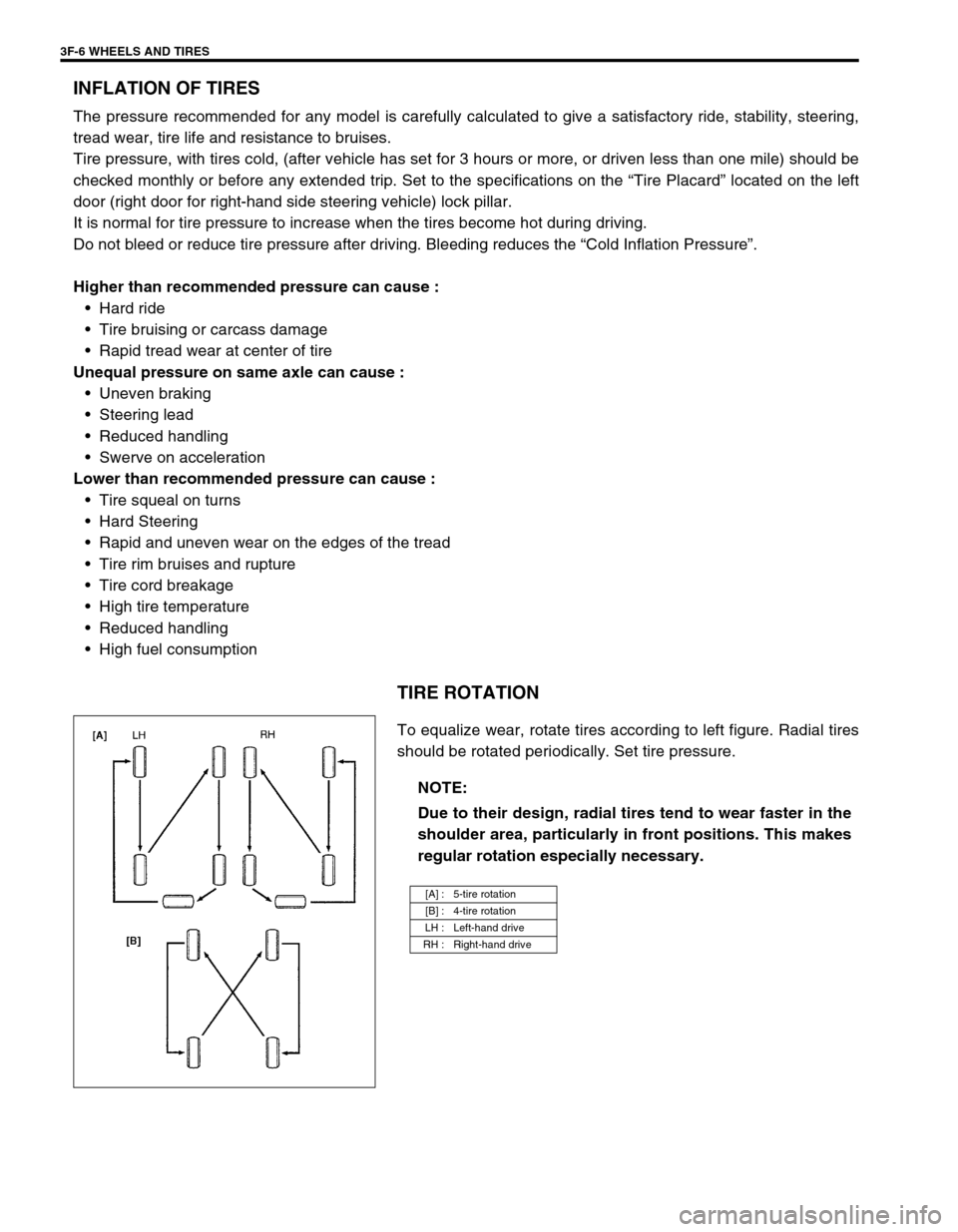
TIRE ROTATION
To equalize wear, rotate tires according to left figure. Radial tires
should be rotated periodically. Set tire pressure.
NOTE:
Due to their design, radial tires tend to wear faster in the
shoulder area, particularly in front positions. This makes
regular rotation especially necessary.
[A] : 5-tire rotation
[B] : 4-tire rotation
LH : Left-hand drive
RH : Right-hand drive
Page 261 of 698
4A-8 FRONT DRIVE SHAFT
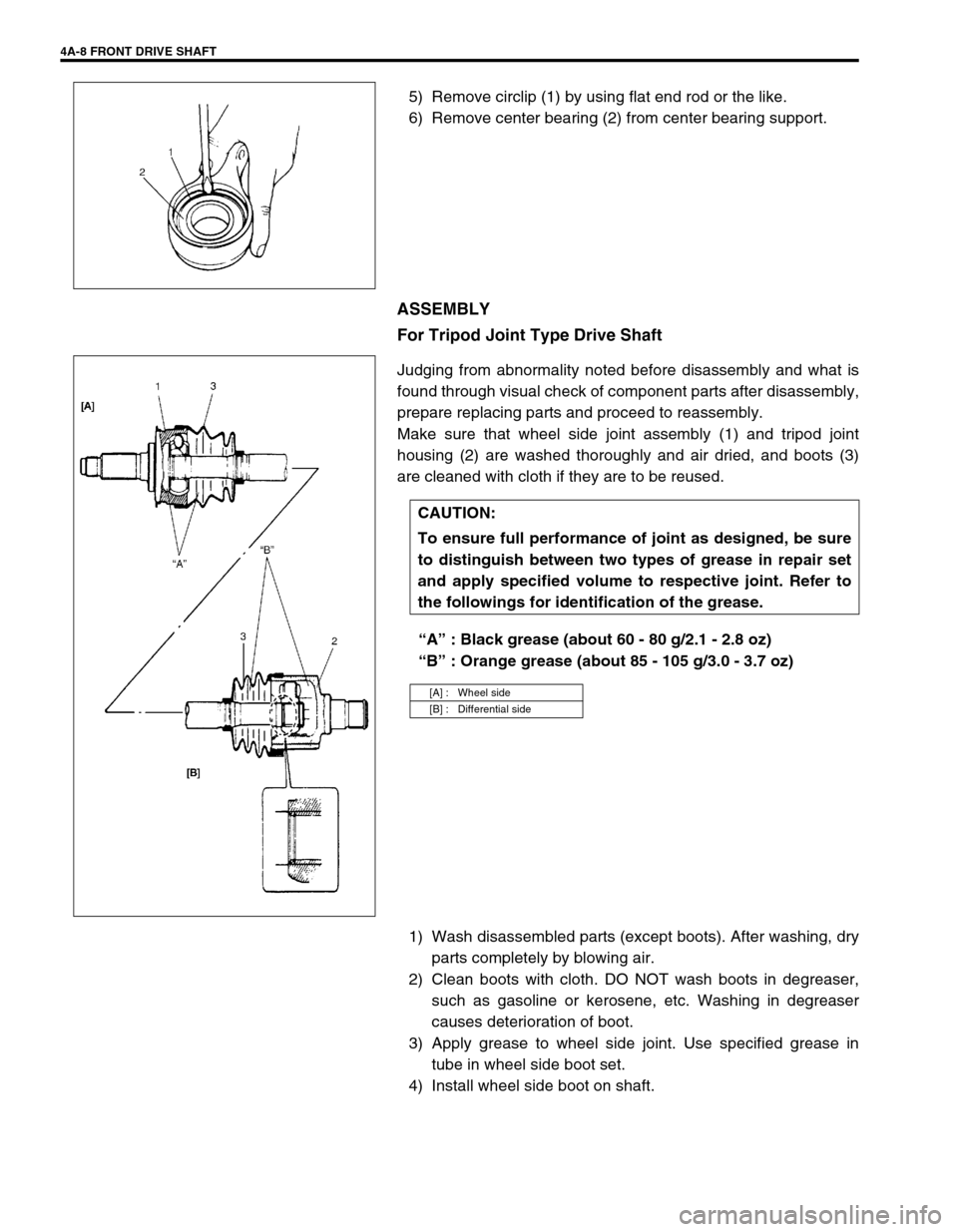
5) Remove circlip (1) by using flat end rod or the like.
6) Remove center bearing (2) from center bearing support.
ASSEMBLY
For Tripod Joint Type Drive Shaft
Judging from abnormality noted before disassembly and what is
found through visual check of component parts after disassembly,
prepare replacing parts and proceed to reassembly.
Make sure that wheel side joint assembly (1) and tripod joint
housing (2) are washed thoroughly and air dried, and boots (3)
are cleaned with cloth if they are to be reused.
“A” : Black grease (about 60 - 80 g/2.1 - 2.8 oz)
“B” : Orange grease (about 85 - 105 g/3.0 - 3.7 oz)
1) Wash disassembled parts (except boots). After washing, dry
parts completely by blowing air.
2) Clean boots with cloth. DO NOT wash boots in degreaser,
such as gasoline or kerosene, etc. Washing in degreaser
causes deterioration of boot.
3) Apply grease to wheel side joint. Use specified grease in
tube in wheel side boot set.
4) Install wheel side boot on shaft.
CAUTION:
To ensure full performance of joint as designed, be sure
to distinguish between two types of grease in repair set
and apply specified volume to respective joint. Refer to
the followings for identification of the grease.
[A] : Wheel side
[B] : Differential side
Page 264 of 698
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT 4A-11
For DOJ Type Drive Shaft
Judging from abnormality noted before disassembly and what is
found though visual check of component parts after disassembly,
prepare replacing parts and proceed to reassembly.
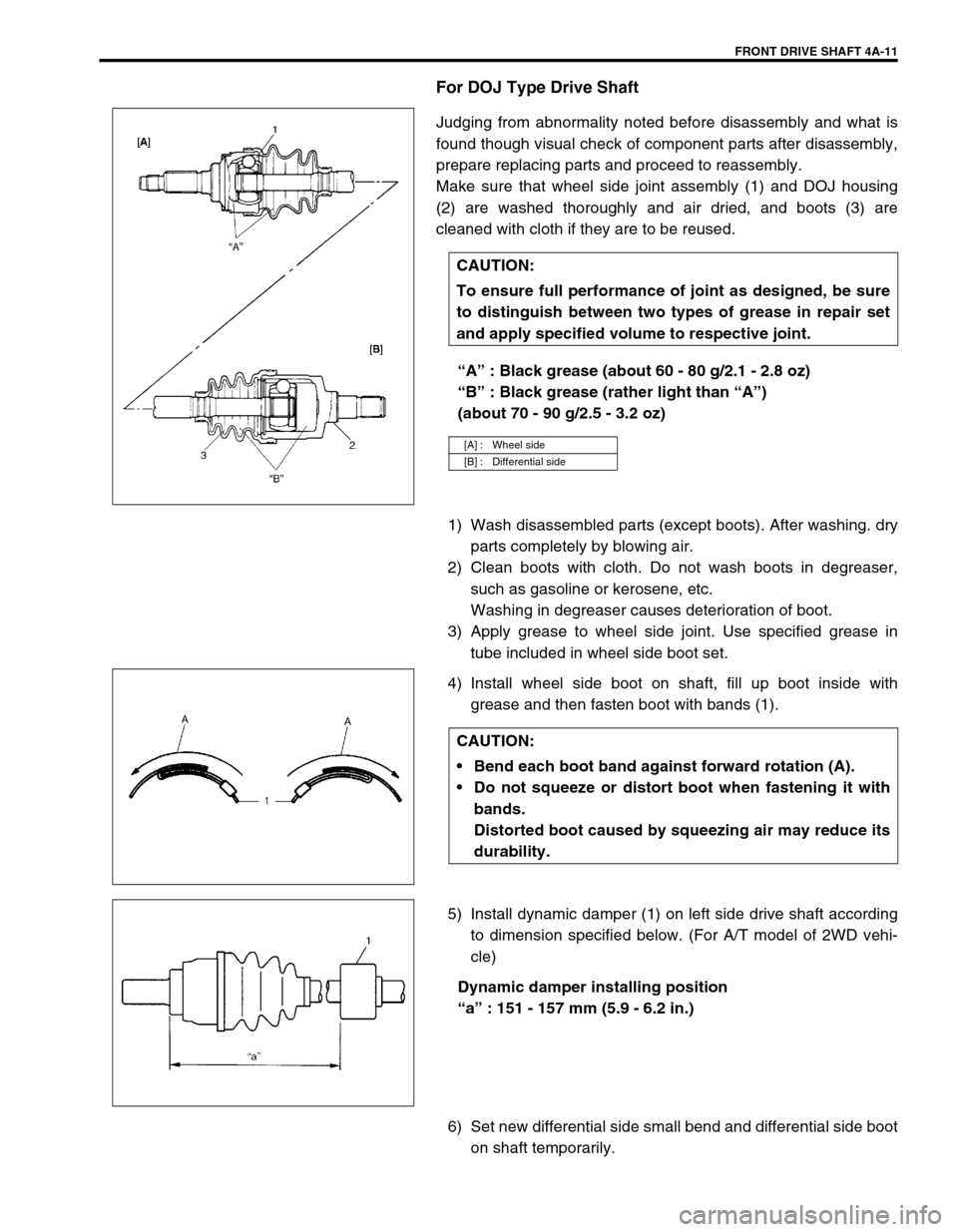
Make sure that wheel side joint assembly (1) and DOJ housing
(2) are washed thoroughly and air dried, and boots (3) are
cleaned with cloth if they are to be reused.
“A” : Black grease (about 60 - 80 g/2.1 - 2.8 oz)
“B” : Black grease (rather light than “A”)
(about 70 - 90 g/2.5 - 3.2 oz)
1) Wash disassembled parts (except boots). After washing. dry
parts completely by blowing air.
2) Clean boots with cloth. Do not wash boots in degreaser,
such as gasoline or kerosene, etc.
Washing in degreaser causes deterioration of boot.
3) Apply grease to wheel side joint. Use specified grease in
tube included in wheel side boot set.
4) Install wheel side boot on shaft, fill up boot inside with
grease and then fasten boot with bands (1).
5) Install dynamic damper (1) on left side drive shaft according
to dimension specified below. (For A/T model of 2WD vehi-
cle)
Dynamic damper installing position
“a” : 151 - 157 mm (5.9 - 6.2 in.)
6) Set new differential side small bend and differential side boot
on shaft temporarily. CAUTION:
To ensure full performance of joint as designed, be sure
to distinguish between two types of grease in repair set
and apply specified volume to respective joint.
[A] : Wheel side
[B] : Differential side
CAUTION:
Bend each boot band against forward rotation (A).
Do not squeeze or distort boot when fastening it with
bands.
Distorted boot caused by squeezing air may reduce its
durability.
Page 283 of 698

5-10 BRAKES
PARKING BRAKE INSPECTION AND
ADJUSTMENT
INSPECTION
Hold center of parking brake lever grip and pull it up with 200 N
(20 kg, 44 lbs) force.
With parking brake lever pulled up as shown, count ratchet
notches. There should be 4 to 9 notches.
Also, check if both right and left rear wheels are locked firmly.
To count number of notches easily, listen to click sounds that
ratchet makes while pulling parking brake lever without pressing
its button.
One click sound corresponds to one notch.
If number of notches is out of specification, adjust cable referring
to adjustment procedure so as to obtain specified parking brake
store.
ADJUSTMENT
After confirming that above conditions are all satisfied, adjust
parking brake lever stoke by loosening or tightening adjust nut
(1).NOTE:
Check tooth tip of each notch for damage or wear.
If any damage or wear is found, replace parking brake
lever.
NOTE:
Make sure for the following conditions before cable
adjustment.
No air is trapped in brake system.
Brake pedal travel is proper.
Brake pedal has been depressed a few times with
about 100 N (10 kg, 22 lbs) load.
Parking brake lever is pulled up a few times with about
500 N (50 kg, 110 lbs) load.
Rear brake shoes are not worn beyond limit, and self
adjusting mechanism operates properly.
If parking brake lever stroke is less than specification,
loosen adjusting nut (1) as far as end of bolt. Then
depress brake pedal repeatedly with about 300 N (30
kg, 66 lbs) load until adjuster actuator clicking sound
can not be heard from drum brake.
NOTE:
Check brake drum for dragging after adjustment.
Page 286 of 698
BRAKES 5-13
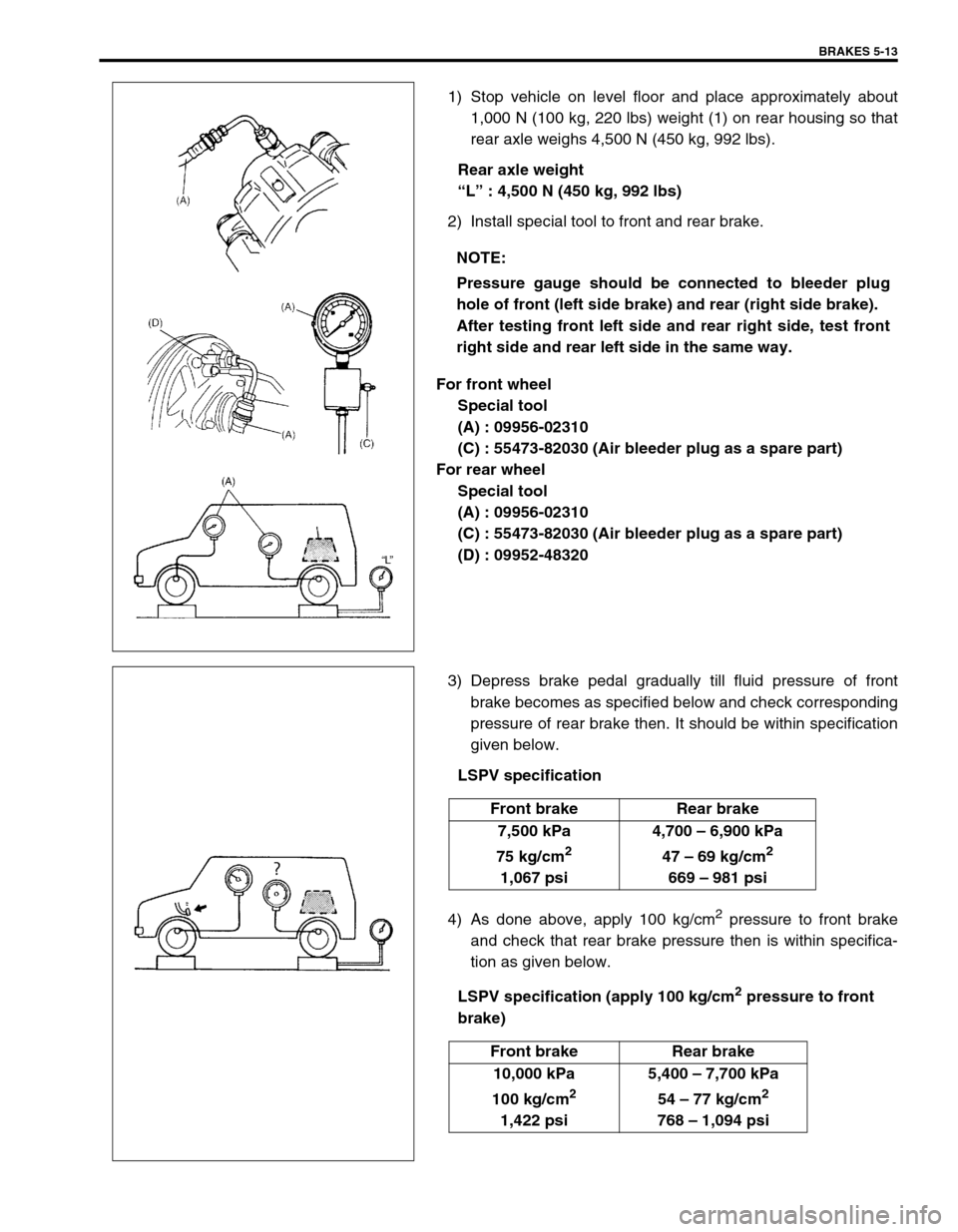
1) Stop vehicle on level floor and place approximately about
1,000 N (100 kg, 220 lbs) weight (1) on rear housing so that
rear axle weighs 4,500 N (450 kg, 992 lbs).
Rear axle weight
“L” : 4,500 N (450 kg, 992 lbs)
2) Install special tool to front and rear brake.
For front wheel
Special tool
(A) : 09956-02310
(C) : 55473-82030 (Air bleeder plug as a spare part)
For rear wheel
Special tool
(A) : 09956-02310
(C) : 55473-82030 (Air bleeder plug as a spare part)
(D) : 09952-48320
3) Depress brake pedal gradually till fluid pressure of front
brake becomes as specified below and check corresponding
pressure of rear brake then. It should be within specification
given below.
LSPV specification
4) As done above, apply 100 kg/cm
2 pressure to front brake
and check that rear brake pressure then is within specifica-
tion as given below.
LSPV specification (apply 100 kg/cm
2 pressure to front
brake) NOTE:
Pressure gauge should be connected to bleeder plug
hole of front (left side brake) and rear (right side brake).
After testing front left side and rear right side, test front
right side and rear left side in the same way.
Front brake Rear brake
7,500 kPa
75 kg/cm
2
1,067 psi4,700 – 6,900 kPa
47 – 69 kg/cm
2
669 – 981 psi
Front brake Rear brake
10,000 kPa
100 kg/cm
2
1,422 psi5,400 – 7,700 kPa
54 – 77 kg/cm
2
768 – 1,094 psi